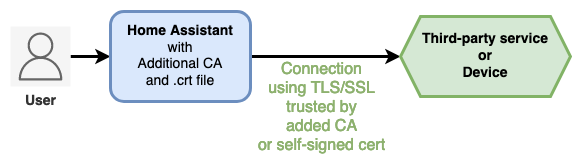
Additional CA integration for Home Assistant loads automatically private Certificate Authority or self-signed certificate into Home Assistant in order to access 3rd-party service with TLS/SSL, even after Home Assistant OS or Home Assistant with Docker is upgraded.
-
In case you manage your own CA, or you trust a CA, it gives you a kind of
ca.crtfile (or equivalent), that could be named shortly a personal / own / private / custom CA. -
In case you generate a self-signed TLS/SSL certificate, it gives you a
.crtfile (or equivalent), that could be an equivalent of a personal / own / private / custom trusted CA.
📒 This documentation uses 'private CA' or 'self-signed cert' alternatively for the same purpose.
You want to import Certificate file into Home Assistant OS / Docker container trust store, in order to access 3rd-party service with TLS/SSL:
- Some of your installed integrations in Home Assistant need to access devices or third-party services with TLS/SSL (HTTPS, etc), and you got a ca.crt (or equivalent) from the service provider, you can load it with Additional CA integration.
- You generated a self-signed TLS/SSL certificate for your own service (personal HTTPS Web server, SMTP, LDAP, etc) that you want to be trusted by Home Assistant, you can load it with Additional CA integration.
- Install HACS
- Install Additional CA integration via HACS or manually without HACS, full docs here-under
- Copy private CA to config folder:
mkdir -p config/additional_ca
cp my_ca.crt config/additional_ca/# configuration.yaml
---
default_config:
additional_ca:
my_private_ca: my_ca.crt
# ...- Export environment variable if running Home Assistant with Docker (no need in case of Home Assistant OS):
# compose.yml
version: '3'
services:
homeassistant:
# ...
environment:
- REQUESTS_CA_BUNDLE=/etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt- Restart Home Assistant
- Done!
Table of contents
- Additional CA for Home Assistant
- 📘 What to understand meaning private Certificate Authority (CA) ?
- 📘 What are the use-cases with this integration ?
- 📘 Quick Setup (TL;DR)
- 1. INSTALL WITH HACS
- 2. INSTALL WITHOUT HACS
- 3. CONFIGURATION
- 4. UPGRADE
- 5. HOW DOES Additional CA WORK UNDER THE HOOD ?
- 6. SET
REQUESTS_CA_BUNDLEENVIRONMENT VARIABLE - 7. HOW TO TEST YOUR CA WITH HTTPS
- 8. HOW TO REMOVE A PRIVATE CA ?
- 9. UNINSTALL
- 10. TROUBLESHOOTING
- 11. KNOWN ISSUES
- Install HACS if not already done.
- Then, go to your Home Assistant,
- -> HACS
- -> Search for "Additional CA"
- -> Click the three-dots menu in line with Additional CA, then click Download
If you're running Home Assistant with Docker:
- Download and install using
git:
# move to your Home Assistant directory containing the 'config' folder
cd /path/to/home-assistant
# git clone Addition CA integration
git clone https://github.com/Athozs/hass-additional-ca.git
# copy additional_ca integration to Home Assistant custom components
mkdir -p config/custom_components
cp -r hass-additional-ca/custom_components/additional_ca config/custom_components/
# Installation done, now see Configuration section (README.md)- Download and install using
wget:
# move to your Home Assistant directory containing the 'config' folder
cd /path/to/home-assistant
# download Addition CA integration archive
wget https://github.com/Athozs/hass-additional-ca/releases/latest/download/additional_ca.zip
# unzip archive
unzip additional_ca.zip
# copy additional_ca integration to Home Assistant custom components
mkdir -p config/custom_components
cp -r additional_ca config/custom_components/
# Installation done, now see Configuration section (README.md)-
Download and install manually
If you're running Home Assistant from HAOS:
- Go to the Add-on store
- Install one of the SSH add-ons (you need to enable advanced mode in your user profile to see them)
- Configure the SSH add-on you chose by following the documentation for it
- Start the SSH add-on
- Connect to the SSH add-on
- Download the latest release of Additional CA from Github (.zip):
wget https://github.com/Athozs/hass-additional-ca/releases/latest/download/additional_ca.zip- Unzip archive:
unzip additional_ca.zip- Move or copy folder
additional_caintoconfig/custom_components/directory:
mkdir -p config/custom_components
cp -r additional_ca config/custom_components/If you're running Home Assistant core (Python package) directly on host, you don't need Additional CA integration. You should update your CAs from your host OS.
For now, Additional CA won't be visible in Home Assistant integrations dashboard, there is no UI component for Additional CA integration. This may be possible in future release.
- CA files must be in PEM format (often
.crtor.pemextension). Check content with a text editor. Content example (following is a fake):
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
ACeuur4QnujqmguSrHU3mhf+cJodzTQNqo4tde+PD1/eFdYAELu8xF+0At7xJiPY
i5RKwilyP56v+3iY2T9lw7S8TJ041VLhaIKp14MzSUzRyeoOAsJ7QADMClHKUDlH
UU2pNuo88Y6igovT3bsnwJNiEQNqymSSYhktw0taduoqjqXn06gsVioWTVDXysd5
qEx4t6sIgIcMm26YH1vJpCQEhKpc2y07gRkklBZRtMjThv4cXyyMX7uTcdT7AJBP
ueifCoV25JxXuo8d5139gwP1BAe7IBVPx2u7KN/UyOXdZmwMf/TmFGwDdCfsyHf/
ZsB2wLHozTYoAVmQ9FoU1JLgcVivqJ+vNlBhHXhlxMdN0j80R9Nz6EIglQjeK3O8
I/cFGm/B8+42hOlCId9ZdtndJcRJVji0wD0qwevCafA9jJlHv/jsE+I9Uz6cpCyh
sw+lrFdxUgqU58axqeK89FR+No4q0IIO+Ji1rJKr9nkSB0BqXozVnE1YB/KLvdIs
uYZJuqb2pKku+zzT6gUwHUTZvBiNOtXL4Nxwc/KT7WzOSd2wP10QI8DKg4vfiNDs
HWmB1c4Kji6gOgA5uSUzaGmq/v4VncK5Ur+n9LbfnfLc28J5ft/GotinMyDk3iar
F10YlqcOmeX1uFmKbdi/XorGlkCoMF3TDx8rmp9DBiB/
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
- Create directory
config/additional_caand copy your private CAs into it:
mkdir -p config/additional_ca
cp my_ca.crt config/additional_ca/Optionally, you could group CAs into folders.
Directories structure example:
.
├── compose.yml
├── config/
│ ├── additional_ca/
│ │ ├── my_ca.crt
│ │ ├── selfcert.crt
│ │ └── my_folder/
│ │ └── selfcert_2.pem
│ │ └── some_folder/
| | ├── ca2.pem
│ │ └── ca3.crt
│ ├── blueprints/
│ │ └── ...
│ ├── configuration.yaml
│ ├── custom_components/
│ │ └── additional_ca/
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── const.py
│ │ └── manifest.json
│ ├── ...
...
- Enable Additional CA integration in
configuration.yamland set private CAs.
Additional CA searches into config/additional_ca/ to find your CA, with config/additional_ca/my_ca.crt your configuration.yaml looks like this:
# configuration.yaml
---
default_config:
additional_ca:
some_ca: my_ca.crt
# ...Model:
# configuration.yaml
---
default_config:
additional_ca:
<string>: <Certificate filename or Certificate relative path as string>
<string>: <Certificate filename or Certificate relative path as string>
# ...: ...An other example:
# configuration.yaml
---
default_config:
additional_ca:
some_ca: my_ca.crt # a cert file
ca_foo: some_folder/ca2.pem # relative path + a cert file
ca_bar: some_folder/ca3.crt # relative path + a cert file
my_self_signed_cert: selfcert.crt # a self-signed certificate
self_signed_crt: my_folder/selfcert_2.pem # relative path + a self-signed certificate
# ...- Optionally, if you're running Home Assistant with Docker, set environment variable
REQUESTS_CA_BUNDLE=/etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt:
Example with Docker Compose:
# compose.yml
version: '3'
services:
homeassistant:
container_name: homeassistant
hostname: home-assistant
image: homeassistant/home-assistant:2023.5.2
volumes:
- ./config:/config
environment:
- TZ=Europe/Paris
- REQUESTS_CA_BUNDLE=/etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt
restart: unless-stopped
network_mode: host- Restart Home Assistant.
After upgrading Home Assistant to a new version, you need to reboot Home Assistant to load again your certificates.
- Check the logs, look for pattern
additional_cain traces (there is not UI for Additional CA).
If you upgrade to a new version of Home Assistant, you need to reboot Home Assistant to load again your certificates with Additional CA.
If you upgrade to a new version of Additional CA, you need to reboot Home Assistant to load again your certificates.
If you're running Home Assistant with Docker:
When enabled, Additional CA integration looks for private Certificates Authorities files (CAs) and self-signed certs in config/additional_ca directory.
Additional CA loads private CAs and self-signed certs only at Home Assistant startup.
It copies private CAs and self-signed certs to /usr/local/share/ca-certificates/ directory inside container and uses update-ca-certificates command line to update TLS/SSL trust store.
HAOS is actually a Linux OS running a homeassistant Docker container inside.
If you're running Home Assistant from HAOS or Supervised installation, Additional CA integration works the same way as with Docker, but you can't export environment variable permanently in HAOS, so there is a workaround: Additional CA integration will also add private CA in Certifi CA bundle /usr/local/lib/python3.xx/site-packages/certifi/cacert.pem inside homeassistant container if not yet present (thanks to @nabbi for the contribution).
Thus, for HAOS, your private CA or self-signed cert will appear in container CA trust store and in Certifi CA bundle (both inside homeassistant container).
After upgrading Home Assistant to a new version, you need to reboot Home Assistant to load again your certificates.
Home Assistant implements an SSL context based on the environment variable REQUESTS_CA_BUNDLE.
Only for Docker installation type and Core installation type, you may need to set environment variable REQUESTS_CA_BUNDLE=/etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt
This is optional, it depends on your installed integrations.
Anyway, setting environment variable REQUESTS_CA_BUNDLE=/etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt should not break your Home Assistant server.
📝 Note: At time of writing, I could not find on the internet a reliable way to set permanently an environment variable in Home Assistant OS. As a workaround, Additional CA integration adds your private CA into Certifi CA bundle if not yet present.
After adding your CA, you could create a test action/service to verify https connection is working.
- Here is an example of
configuration.yamlto create an actionRESTful Command: additional_ca_test:
# configuration.yaml
logger:
default: info
additional_ca:
my_ca: ca.crt
rest_command:
additional_ca_test:
url: "https://your-server.com/" # <- use your own url here
method: get
verify_ssl: true
timeout: 30
-
Then perform action
RESTful Command: additional_ca_testfrom Developer tools panel. Starting from Home Assistant version 2024.2.x, you should seestatus: 200in response to confirm success. -
If TLS/SSL does not work, you will see error details in Home Assistant logs:
[homeassistant.components.rest_command] Client error. Url: https://your-server.com/. Error: Cannot connect to host your-server.com ssl:True [SSLCertVerificationError: (1, '[SSL: CERTIFICATE_VERIFY_FAILED] certificate verify failed: unable to get local issuer certificate (_ssl.c:1006)')]
If you're running Home Assistant with Docker, then from your shell prompt, run:
docker exec CONTAINER_NAME curl -v -I https://your-server.comYou should see an HTTP code 200 to confirm success.
If you're running Home Assistant from HAOS:
- Turn off Protection mode on SSH add-on in order to enable
dockerCLI (Settings > Add-ons > SSH > turn off Protection mode). - Connect to HAOS with SSH, then from command line, run:
docker exec homeassistant curl -v -I https://your-server.comYou should see an HTTP code 200 to confirm success.
Remove or comment CA entry under additional_ca domain key in configuration.yaml:
# configuration.yaml
---
default_config:
additional_ca:
# some_ca: my_ca.crt
# ...Note: additional_ca domain key need to be enabled in configuration.yaml to remove CA files on next restart of Home Assistant.
Optionally remove your private CA file from config/additional_ca/ directory.
Then, restart Home Assistant.
- Delete Additional CA from custom components:
Uninstall from HACS, go to your Home Assistant,
- -> HACS
- -> Locate Additional CA
- -> Click the three-dots menu in line with Additional CA, then click Remove
Or uninstall manually:
rm -r config/custom_components/additional_ca- Remove
additional_cadomain key fromconfiguration.yaml:
# configuration.yaml
---
default_config:
# additional_ca:
# some_ca: my_ca.crt
# ...- Optionally remove additional_ca folder containing your private CA:
rm -r config/additional_ca- Restart Home Assistant.
If using Docker Compose, recreate container:
docker compose up -d --force-recreateSome tips to clean your CA trust store inside Home Assistant in case of failure.
- Enable INFO logs level in Home Assistant (see Tips below)
- Check error logs in Home Assistant Settings > System > Logs
To reset CA trust store in Home Assistant with Docker:
- Stop and remove HA container, it will remove all changes made inside container, then start again Home Assistant with Docker.
Otherwise you could do the following:
- Manually remove private CA files from
/usr/local/share/ca-certificates/directory inside HA container. - Then update manually CA trust store by running command
update-ca-certificatesinside HA container.
To reset CA trust store in Home Assistant from HAOS or Supervised installation, you could reset Certifi CA bundle:
- Turn off Protection mode on SSH add-on in order to enable
dockerCLI (Settings > Add-ons > SSH > turn off Protection mode) - Connect to HAOS with SSH, then from command line, run the following to stop and remove
homeassistantDocker container inside HAOS and reboot HAOS:
docker stop homeassistant
docker rm homeassistant
rebootOtherwise you could do the following:
- Download original bundle from https://raw.githubusercontent.com/certifi/python-certifi/master/certifi/cacert.pem
- Replace it at Certifi bundle path
- To get Certifi bundle path: Connect to HAOS with SSH, then from command line, run
docker exec -ti homeassistant python -m certifi.
- To get Certifi bundle path: Connect to HAOS with SSH, then from command line, run
- To enable INFO logs level, add the following to your
configuration.yaml:
# configuration.yaml
logger:
default: info- To check your certificate validity, if using x509 certs, run:
openssl x509 -in config/additional_ca/my_ca.crt -text -nooutn/a