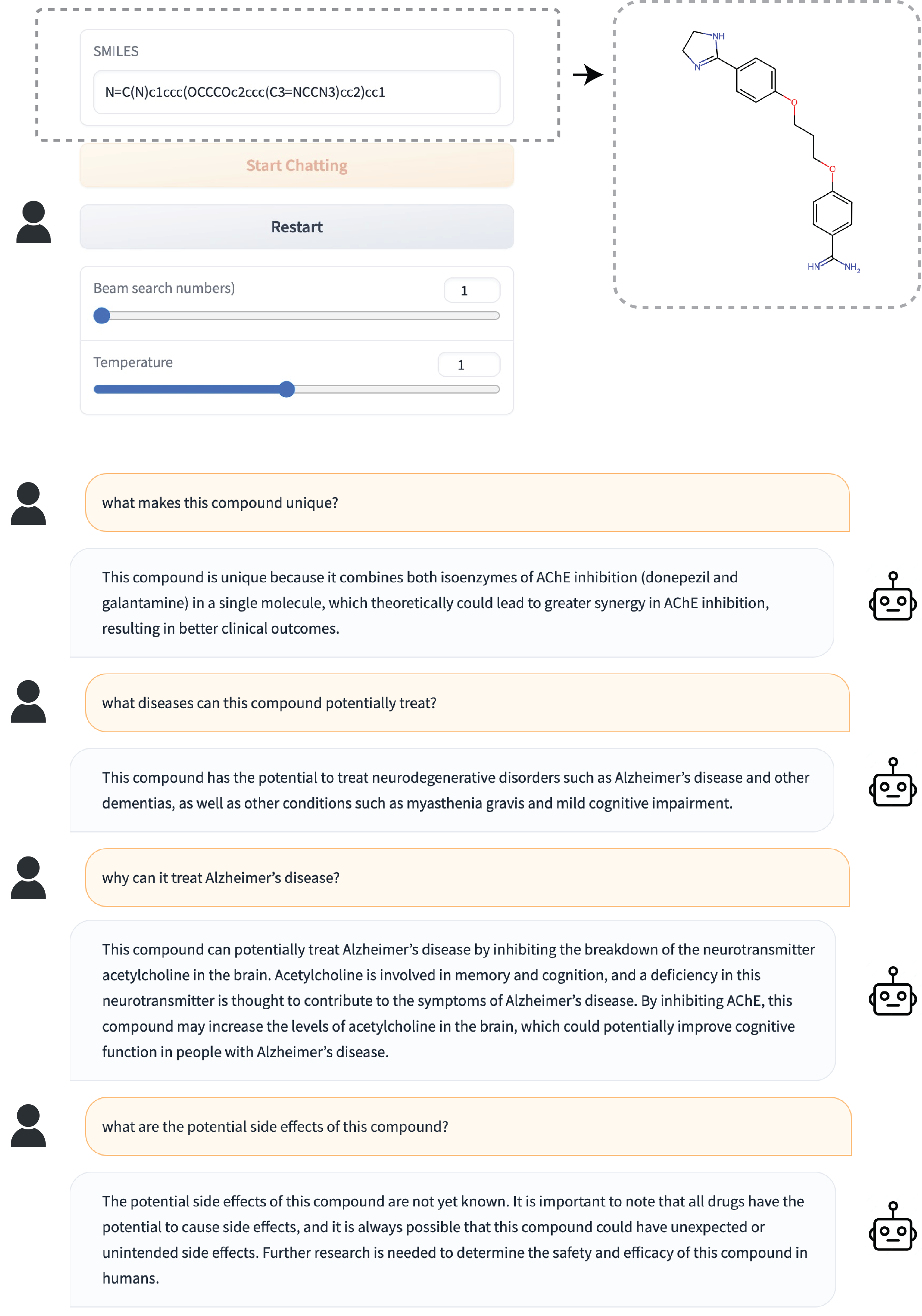
This repository holds the code and data of DrugChat: Towards Enabling ChatGPT-Like Capabilities on Drug Molecule Graphs.
Technical report is available here
- In this work, we make an initial attempt towards enabling ChatGPT-like capabilities on drug molecule graphs, by developing a prototype system DrugChat.
- DrugChat works in a similar way as ChatGPT. Users upload a compound molecule graph and ask various questions about this compound. DrugChat will answer these questions in a multi-turn, interactive manner.
- The DrugChat system consists of a graph neural network (GNN), a large language model (LLM), and an adaptor. The GNN takes a compound molecule graph as input and learns a representation for this graph. The adaptor transforms the graph representation produced by the GNN into another representation that is acceptable to the LLM. The LLM takes the compound representation transformed by the adaptor and users' questions about this compound as inputs and generates answers. All these components are trained end-to-end.
- To train DrugChat, we collected instruction tuning datasets which contain 10,834 drug compounds and 143,517 question-answer pairs.
The file data/ChEMBL_QA.json and data/PubChem_QA.json contains data for the ChEMBL Drug Instruction Tuning Dataset and the PubChem Drug Instruction Tuning Dataset. The data structure is as follows.
{SMILES String: [ [Question1 , Answer1], [Question2 , Answer2]... ] }
These instructions largely follow those in MiniGPT-4.
1. Prepare the code and the environment
Git clone our repository, creating a python environment and ativate it via the following command
git clone https://github.com/UCSD-AI4H/drugchat
cd drugchat
conda env create -f environment.yml
conda activate drugchatVerify the installation of torch and torchvision is successful by running python -c "import torchvision; print(torchvision.__version__)". If it outputs the version number without any warnings or errors, then you can go to the next step (installing PyTorch Geometric). If it outputs any warnings or errors, try to uninstall torch by conda uninstall pytorch torchvision torchaudio cudatoolkit and then reinstall them following here. You need to find the correct command according to the CUDA version your GPU driver supports (check nvidia-smi). For example, I found my GPU driver supported CUDA 11.6, so I run conda install pytorch==1.12.1 torchvision==0.13.1 torchaudio==0.12.1 cudatoolkit=11.6 -c pytorch -c conda-forge.
Run conda install pyg=2.3.0 pytorch-scatter=2.1.0 -c pyg to install PyTorch Geometric. If some error related to PyTorch Geometric or pytorch-scatter show up later when running the code, try to follow here to reinstall them.
2. Prepare the pretrained Vicuna weights
The current version of DrugChat is built on the v0 versoin of Vicuna-13B. Please refer to our instruction here to prepare the Vicuna weights. The final weights would be in a single folder in a structure similar to the following:
vicuna_weights
├── config.json
├── generation_config.json
├── pytorch_model.bin.index.json
├── pytorch_model-00001-of-00003.bin
...
Then, set the path to the vicuna weight in the model config file here at Line 16.
You need roughly 40 GB GPU memory for the training.
The training configuration file is train_configs/drugchat_stage2_finetune.yaml. You may want to change the number of epochs and other hyper-parameters there, such as max_epoch, init_lr, min_lr,warmup_steps, batch_size_train. You need to adjust iters_per_epoch so that iters_per_epoch * batch_size_train = your training set size.
Start training the projection layer that connects the GNN output and the LLaMA model by running bash finetune_gnn.sh.
To get the inference to work properly, you need to create another environment (rdkit) and launch a backend process which converts SMILES strings to Torch Geometric graphs.
It takes around 24 GB GPU memory for the demo.
To create the rdkit environment and run the process, run
conda create -c conda-forge -n rdkit rdkit
conda activate rdkit
pip install numpy
python dataset/smiles2graph_demo.py
Then, the smiles2graph_demo.py will be running in the backend to serve the demo.py.
Find the checkpoint you save in the training process above, which is located under the folder pipeline/output/pipeline_stage2_finetune/ by default. Copy it to the folder ckpt by running cp pipeline/output/pipeline_stage2_finetune/the_remaining_path ckpt/with_gnn_node_feat.pth.
Now we launch the demo.py in our original environment. Make sure you have run conda activate drugchat. Then, start the demo demo.sh on your local machine by running bash demo.sh. Then, open the URL created by the demo and try it out!
- MiniGPT-4 This repo is based on MiniGPT-4, an awesome repo for vision-language chatbot!
- Lavis
- Vicuna
This repository is under BSD 3-Clause License. Many codes are based on MiniGPT-4 with BSD 3-Clause License here, which is based on Lavis with BSD 3-Clause License here.
This is a prototype system that has not been systematically and comprehensively validated by pharmaceutical experts yet. Please use with caution.
Trained models and demo websites will be released after we thoroughly validate the system with pharmaceutical experts.
If you're using DrugChat in your research or applications, please cite using this BibTeX:
@article{liang2023drugchat,
title={DrugChat: Towards Enabling ChatGPT-Like Capabilities on Drug Molecule Graphs},
author={Liang, Youwei and Zhang, Ruiyi and Zhang, li and Xie, Pengtao},
journal={TechRxiv},
year={2023}
}