smbclient-ng, a fast and user friendly way to interact with SMB shares.




-
bat: Pretty prints the contents of a file. Syntax:bat <file> -
cat: Get the contents of a file. Syntax:cat <file> -
cd: Change the current working directory. Syntax:cd <directory> -
close: Closes the SMB connection to the remote machine. Syntax:close -
connect: Connect to the remote machine (useful if connection timed out). Syntax:connect -
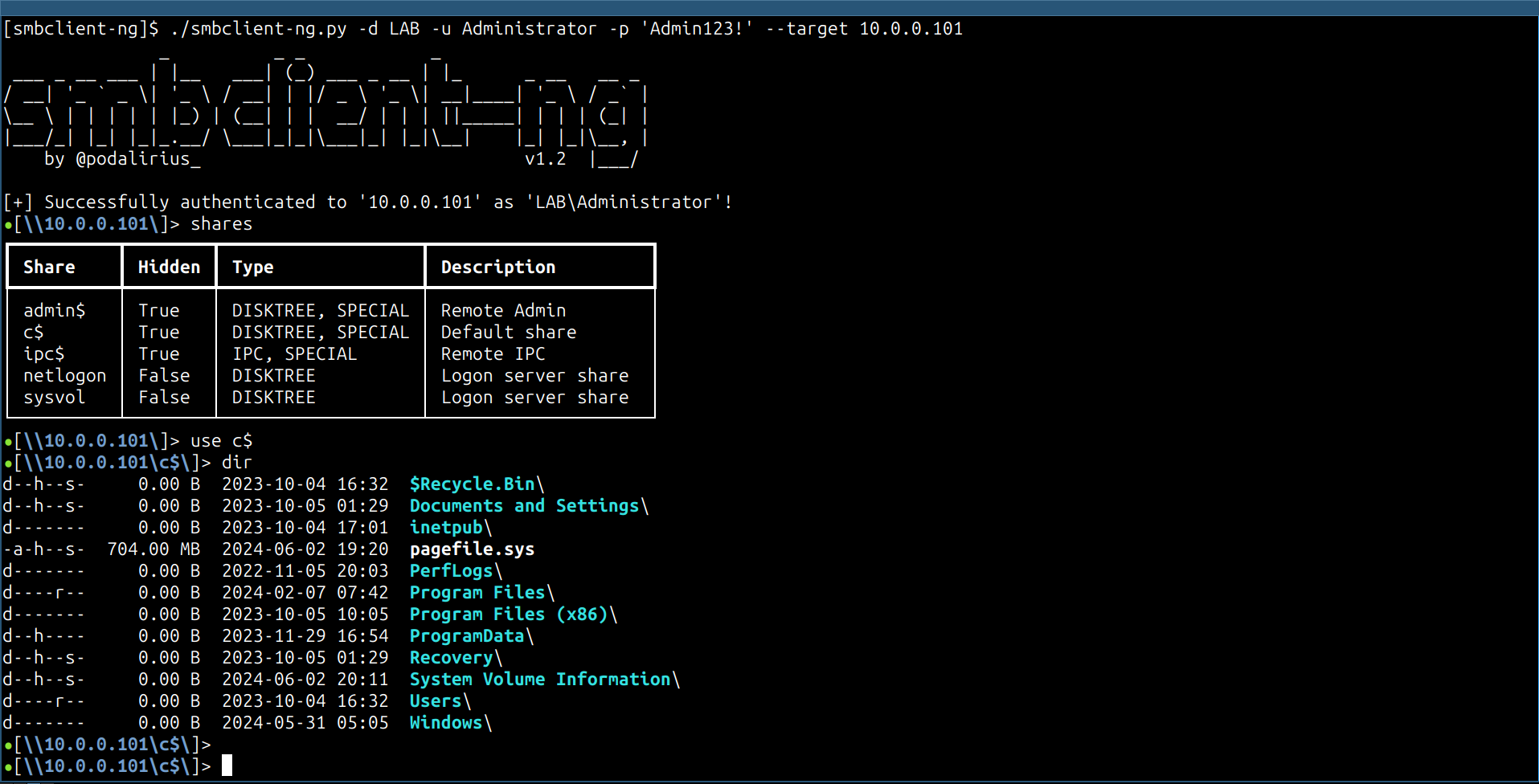
dir: List the contents of the current working directory. Syntax:dir -
exit: Exits the smbclient-ng script. Syntax:exit -
get: Get a remote file. Syntax:get [-r] <directory or file> -
help: Displays this help message. Syntax:help -
info: Get information about the server and or the share. Syntax:info [server|share] -
lcd: Changes the current local directory. Syntax:lcd <directory> -
lls: Lists the contents of the current local directory. Syntax:lls -
lmkdir: Creates a new local directory. Syntax:lmkdir <directory> -
lpwd: Shows the current local directory. Syntax:lpwd -
lrm: Removes a local file. Syntax:lrm <file> -
lrmdir: Removes a local directory. Syntax:lrmdir <directory> -
ls: List the contents of the current remote working directory. Syntax:ls -
ltree: Displays a tree view of the local directories. Syntax:ltree [directory] -
mkdir: Creates a new remote directory. Syntax:mkdir <directory> -
module: Loads a specific module for additional functionalities. Syntax:module <name> -
put: Put a local file or directory in a remote directory. Syntax:put [-r] <directory or file> -
reconnect: Reconnect to the remote machine (useful if connection timed out). Syntax:reconnect -
reset: Reset the TTY output, useful if it was broken after printing a binary file on stdout. Syntax:reset -
rmdir: Removes a remote directory. Syntax:rmdir <directory> -
rm: Removes a remote file. Syntax:rm <file> -
shares: Lists the SMB shares served by the remote machine. Syntax:shares -
use: Use a SMB share. Syntax:use <sharename> -
tree: Displays a tree view of the remote directories. Syntax:tree [directory]
To install smbclient-ng, you can use pip. Run the following command in your terminal:
python3 -m pip install smbclientng
$ smbclientng -h
_ _ _ _
___ _ __ ___ | |__ ___| (_) ___ _ __ | |_ _ __ __ _
/ __| '_ ` _ \| '_ \ / __| | |/ _ \ '_ \| __|____| '_ \ / _` |
\__ \ | | | | | |_) | (__| | | __/ | | | ||_____| | | | (_| |
|___/_| |_| |_|_.__/ \___|_|_|\___|_| |_|\__| |_| |_|\__, |
by @podalirius_ v1.3.1 |___/
usage: smbclientng [-h] [--debug] --target ip address [--kdcHost FQDN KDC] [-d DOMAIN] [-u USER]
[--no-pass | -p PASSWORD | -H [LMHASH:]NTHASH | --aes-key hex key] [-k]
smbclient-ng, a fast and user friendly way to interact with SMB shares.
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--debug Debug mode
--target ip address IP Address of the SMB Server to connect to.
Authentication & connection:
--kdcHost FQDN KDC FQDN of KDC for Kerberos.
-d DOMAIN, --domain DOMAIN
(FQDN) domain to authenticate to
-u USER, --user USER user to authenticate with
--no-pass Don't ask for password (useful for -k)
-p PASSWORD, --password PASSWORD
password to authenticate with
-H [LMHASH:]NTHASH, --hashes [LMHASH:]NTHASH
NT/LM hashes, format is LMhash:NThash
--aes-key hex key AES key to use for Kerberos Authentication (128 or 256 bits)
-k, --kerberos Use Kerberos authentication. Grabs credentials from .ccache file (KRB5CCNAME) based on target parameters. If valid credentials
cannot be found, it will use the ones specified in the command line
- Connect to a remote SMB server:
./smbclient-ng.py -u "Administrator" -d LAB -p 'Admin123!' --target "10.0.0.201"
Pull requests are welcome. Feel free to open an issue if you want to add other features.