CAT - Conversational Agents for Database Transactions
Databases for OLTP are often the backbone for applications such as hotel room or cinema ticket booking applications. However, developing a conversational agent (i.e., a chatbot-like interface) to allow end-users to interact with an application using natural language requires both immense amounts of training data and NLP expertise.
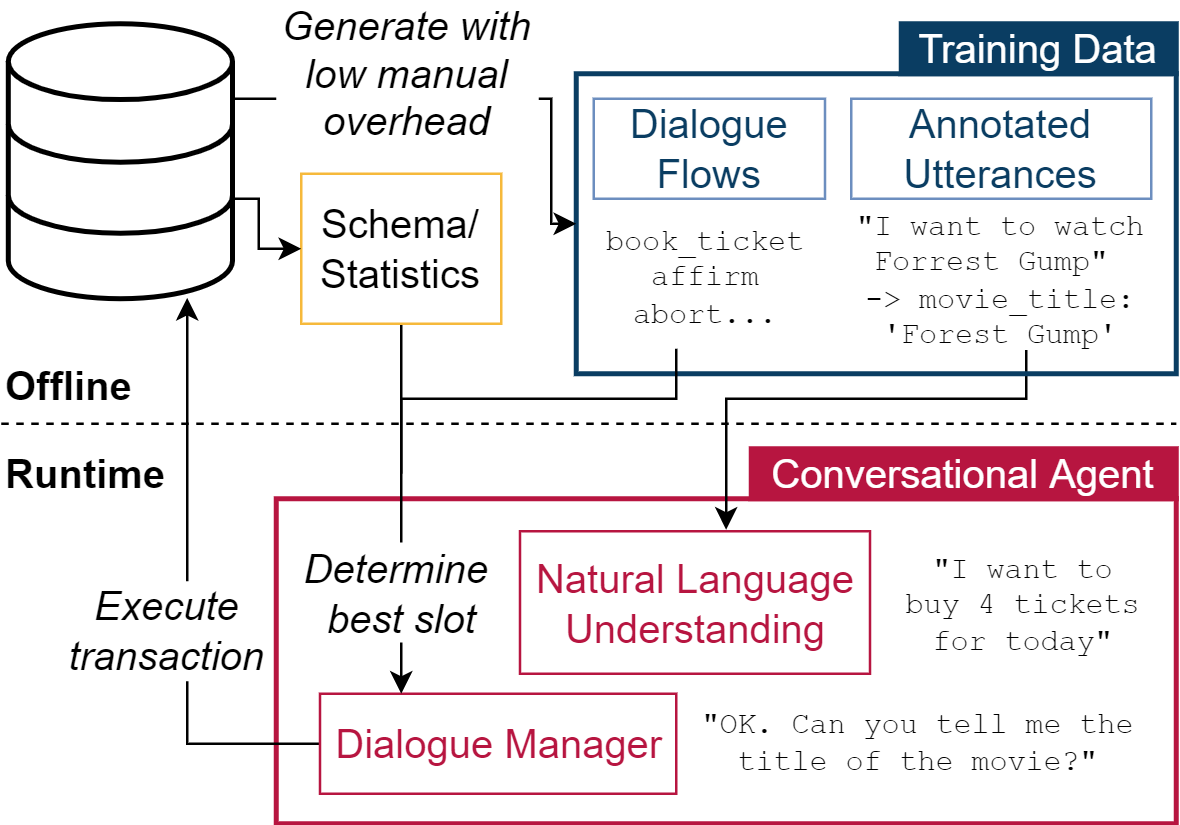
This motivates CAT, which can be used to easily create conversational agents for transactional databases. The main idea is that, for a given OLTP database, CAT uses weak supervision to synthesize the required training data to train a state-of-the-art conversational agent, allowing users to interact with the OLTP database. Furthermore, CAT provides an out-of-the-box integration of the resulting agent with the database.
As a major difference to existing conversational agents, agents synthesized by CAT are data-aware. This means that the agent decides which information should be requested from the user based on the current data distributions in the database, which typically results in markedly more efficient dialogues compared with non-data-aware agents.
We publish the code for CAT as open source here.
CAT was presented at VLDB'22. Learn more in our paper or watch our demo video.
If you use CAT, please cite it as follows:
Marius Gassen, Benjamin Hättasch, Benjamin Hilprecht, Nadja Geisler, Alexander Fraser, and Carsten Binnig. Demonstrating CAT: Synthesizing Data-Aware Conversational Agents for Transactional Databases. PVLDB, 15(12): 3586 - 3589, 2022. doi:10.14778/3554821.355485
Setup
System requirements
- Python -- tested with Pyton 3.7
- Node.js
- Requirements specified in requirements.txt
- To run the configuration UI server refer to the UI README
Environment setup
To install pip3, virtualenv, the Python packages npm modules run ./setup.sh or proceed manually.
Add user defined functions in entropy.sql to your database.
Usage
Configuration backend
The configuration backend allows connecting to arbitrary (currently PostgreSQL) databases and extract the schema's tables and procedures with their datatypes and foreign key relations. The backend's API is required to run CAT's configuration frontend for easy schema annotation, task configuration and response and intent template creation.
The server.py backend script located in cat/common/ can be run with the following arguments:
| Argument | Default | Usage |
|---|---|---|
-i/--interface |
127.0.0.1 |
The interface to listen on |
-p/--port |
5001 |
The port the API can be reached on |
-vv/--debug |
False |
Whether to enable debug mode |
-j/--jwt_on |
False |
Whether to enable JWT authentication (use in production) |
-s/--jwt_secret |
secret |
Secret to be used for JWT authentication |
-a/--jwt_passphrase |
passphrase |
Passphrase to be used for JWT authentication |
-c/--cors_allowed_origins |
* |
Allowed origins |
By default the API can be reached on http://127.0.0.1:5001/api/v1
Currently there are 3 endpoints
auth: Authentication endpoint if JWT is enabledlogin: Expects the login data (passphrase) and returns an access tokenrefresh: Refreshs an access token
database: Connect to and retrieve database schema information, JWT protected if enabledconnect: Try to establish a connection to a given databasetables: retrieve tablestables/{table}: Retrieve information about a given tabletables/{table}/columns: Retrieve columns of a given tabletables/{table}/columns/{column}: Retrieve information about a table's columntables/{table}/columns/{column}/values: Retrieve distinct values of a table's columnprocedures: Retrieve information about stored procedures with their parameters and return values
nl: Natural language specific operationssynonyms/{word}: Retrieves a list of synonyms for a given word from NLTKs SynSet
Configuration frontend
The configuration frontend is used to generate tasks. See cat-ui\README.md for installation and running instructions.
In short:
- Install dependencies
- serve via
npx ng serve - Use the webfrontend (by default available at http://localhost:4200) to create a conversational agent.
Running a conversational agent
- Make sure the virtual environment is activated and all requirements are installed
- Go to the bots directory and run
rasa trainwith the domain, config, templates and stories.- This will start the core training process for stories in
data/stories.md - This will then start NLU training for training examples in
data/nlu.json - The used configuration and domain are taken from
config.ymlanddomain.ymlrespectively
- This will start the core training process for stories in
- Once the models are trained we can run our bot server
- Run an action server will your custom actions:
python -m rasa_sdk.endpoint --actions actions -vv, this will be used for running actions that the rasa server predicts based on the user input - Start the Rasa server
rasa runand send messages to the bot over the (REST) API or any other channel - Or combine the CLI with the server startup
rasa shell- NOTE: Depending on the time the execution of a task takes, go to
rasa.core.channels.consoleand change theDEFAULT_STREAM_READING_TIMEOUT_IN_SECONDSto a bigger value then 10s, otherwise the client will timeout if the action server takes to long
- NOTE: Depending on the time the execution of a task takes, go to
- Run an action server will your custom actions: