Simple ECS addon for godot v4.0
This addon fully written in GDScript, so don't count on high performance. Main target is usability and customizable.
❗ code snippets like some_class.function(param:int=0) doesn't fit GDScript syntax and represents only for methods signature demonstration
Looking ECS addon for godot v3? It's right here
- any
Objectcan be a component - readonly components
- handy entity filtering outside
Systemclass - nodes binding with entity
- discrete mode to process systems step by step
Entity- a class of components containerEntitySignature- a static class allowing you matching entities with specified components setEntityFilter- class which gets filtered entities from ECSECS- autoload which binds all togetherSystem- system implementation asNode
To create component just assign COMPONENT_TYPE property to any instance. ECS detects components exacly by its existence. There is no point is it Object or AnimationPlayer, so you can control any scene with ease how you do it without using ECS. Example:
extends Node2D
class_name C_JustNode2D
const COMPONENT_TYPE = "C_JustNode2D" # this line makes C_JustNode2D a componentReadonly status sets by ECS.set_component_readonly(component:Object) autoload (see 'ECS autoload' section)
Godot implements Object type feature, so you can specify flag-components without creating an instance:
class FlagComponent:
extends RefCounted
const COMPONENT_TYPE = "FlagComponent"
...
entity.add_component(FlagComponent)Keep in mind that if you will specify readonly as true, FlagComponent will be setted as readonly everywhere, including other entities to which it was passed as non-readonly.
Autoload keeping all filters and entites existing now.
You can register an entity filter for giving it a matching entities:
ECS.register_filter(filter:EntityFilter)Unregister it for stop monitoring entities for it:
ECS.unregister_filter(filter:EntityFilter)Register entity for passing it into filters it matches:
ECS.register_entity(entity:Entity)Unregister it for remove from all registered filters and stop passing it into them:
ECS.unregister_entity(entity:Entity)But usually you shouldn't register and unregister entity manually, Entity do it for you, what wrong for entity filters.
Also you can call ECS.revise_entity(entity:Entity) for adding and removing it from filters. It useful when entity got or lost component and should be added or removed from filter because of changing it components set. But like registration you shouldn't call this method, it will be automatically called in Entity class in methods changing entity components set.
You can call ECS.clear_entities() for freeing all registered entities.
And finally, ECS singleton provides you methods for checking if object is component, set and check component readonly status:
ECS.is_instance_component(object:Object)
ECS.is_component_readonly(object:Object)
ECS.set_component_readonly(object:Object)You can enter discrete mode using method below:
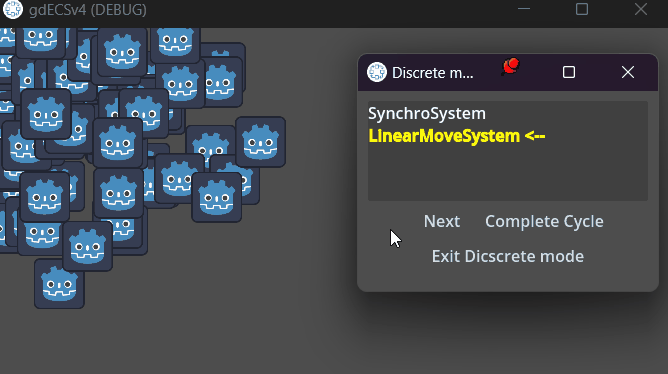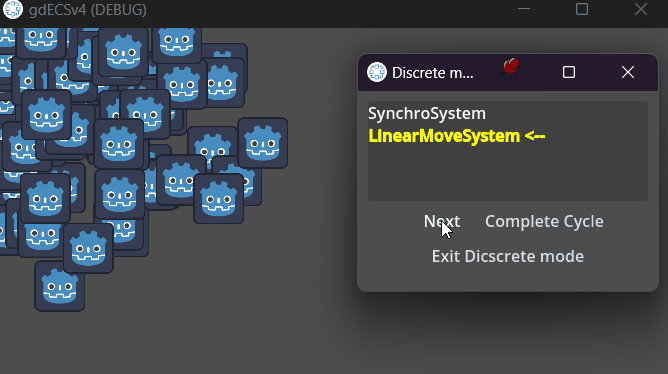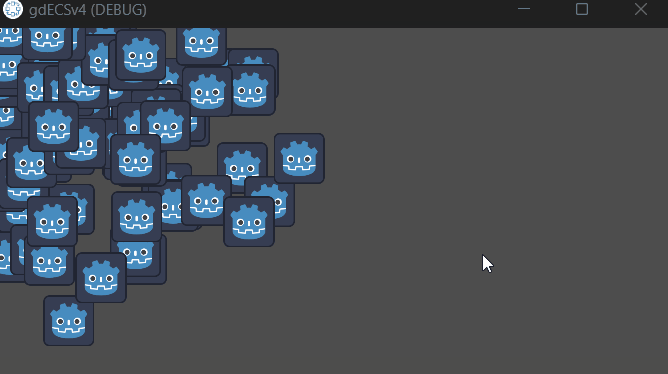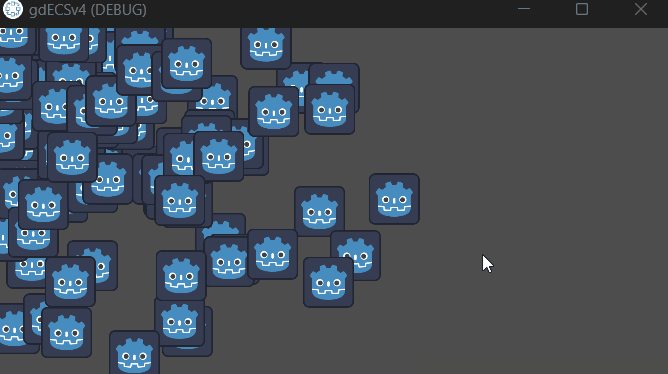
ECS.enter_discrete_mode()When discrete mode active you can see control panel.
Here are shown three (if has so) systems:
- Last processed
- Current to be processed
- Next system
Yellow system is the first system to be proceed in regular frame. System, on which pointers arrow, is the system to be processed next.
There are three buttons on the panel:
- next - processes system, on which pointers arrow
- Exit discrete mode - diactivates discrete mode. If you didn't complete systems' cycle, an warning will be shown.
- Complete systems cycle - processes systems before a system which is processed first in one frame in queue
Closing window is the same as button Exit discrete mode.
You can create entities by Entity class. Its constructor takes two optional arguments:
var entity : Entity = Entity.new(components:Array=[], # list of components instances
autoregister:bool=true) # will it be automatically registered in ECS (see 'ECS autoload' section)It has the signals below:
signal enter_ecs # emittied when entity registered in ECS
signal exit_ecs # emmited when entity unregistered in ECS
Control entity components with the methods below:
entity.add_component(comp_instance:Object, # component instance
readonly:bool=false, # readonly components cannot be removed or overwritten (component's data still can be modified)
overwrite:bool=false) # allows or not overwriting existing component with the same name as comp_instance has if has it
# removes component with specified typename if it isn't readonly
# prints message if has no component with specified typename or it was set as readonly
entity.remove_component(comp_type:String)
entity.has_component(comp_type:String) # returns whether entity has component with specified typename
# returns component instance with specified typename
# otherwise just returns null
entity.get_component(comp_type:String)
entity.get_all_components() # returns an array with all components instances
entity.get_all_components_names() # returns an array with all components typenamesAlso you can specify nodes which will be freed at the same time entity will be freed:
entity.bind_node(node:Node) # entity will call `node.queue_free()` when deleted
# you can bind only one node (scene)You can safely free entity like any other object:
entity.free() # it will automatically do needed thingsEntitySignature is a static class for checking entity for having and not specified components. Just create dictionary as in example below:
var signature : Dictionary = {
EntitySignature.NECESSARY_STRING : ["C_MyComponent"],
EntitySignature.BANNED_STRING : ["C_NotThat"]
}or
var signature : Dictionary = EntitySignature.create_signature(["C_MyComponent"], ["C_NotThat"])Where EntitySignature.NECESSARY_STRING and EntitySignature.BANNED_STRING by default is "NECESSARY_COMPONENTS" and "BANNED_COMPONENTS" accordingly.
Then check does entity match specified component set:
EntitySignature.match_entity(signature:Dictionary, entity:Entity)If the signature has no necessary and banned, it will return true. Empty Entity (without components) will fit any filter.
The reason why dictionaries were used is the possibility to write them into a const expression:
const SIGNATURE = {
EntitySignature.NECESSARY_STRING : [
"C_NecessaryComponent1"
],
EntitySignature.BANNED_STRING : [
"C_BannedComponent1"
]
}Class, instance of which can be registered in ECS autoload (see 'ECS autoload' section) and get valid entities from it. Just specify signature when instancing:
var entity_filter : EntityFilter = EntityFilter.new(signature:Dictionary) # specify valid components setAnd you should register it for able it getting entities:
ECS.register_filter(filter:EntityFilter)After it valid entities will automatically be added to valid_entites array:
entity_filter.valid_entites # keeps all valid entitiesAlso you can unregister filter, after it its valid_entities will be cleaned and wouldn't be touched by ECS until re-registration:
ECS.unregister_filter(filter:EntityFilter)It has signals:
signal entity_added(entity) # emmited when valid entity added to valid_entitites array
signal entity_removed(entity) # emmited when entity leaves valid_entities because of any reason
signal was_registered # emitted after filter got valid entities
signal pre_unregister # emitted before valid entities cleanedAnd you can monitor EntityFilter registration status by:
entity_filter.registeredAddon provides you system implementation with System class. Just override this three methods:
# here system logic
on_entity_process(entity:Entity, # entity to process
delta:float) # the same as delta in `_process`
# returns an array of necessary components
get_necessary_components()
# returns an array of banned components
get_banned_components()Activate and deactivate it with related export variable.
This implementation Suitable with discrete mode.