An abortable async function library with React Hooks
JavaScript promises are not abortable/cancelable. However, DOM provides AbortController which can be used for aborting promises in general.
This is an experimental library to provide an easy way to handle async function with React Hooks API.
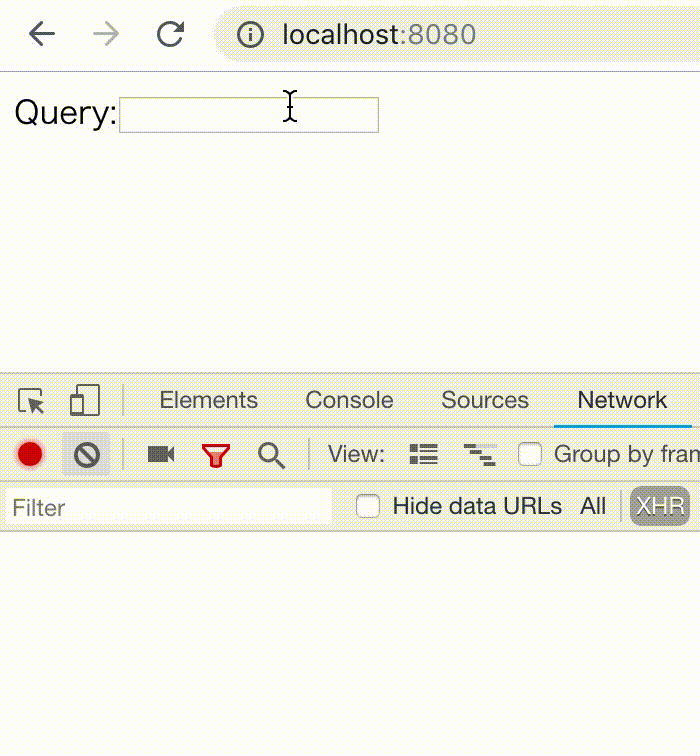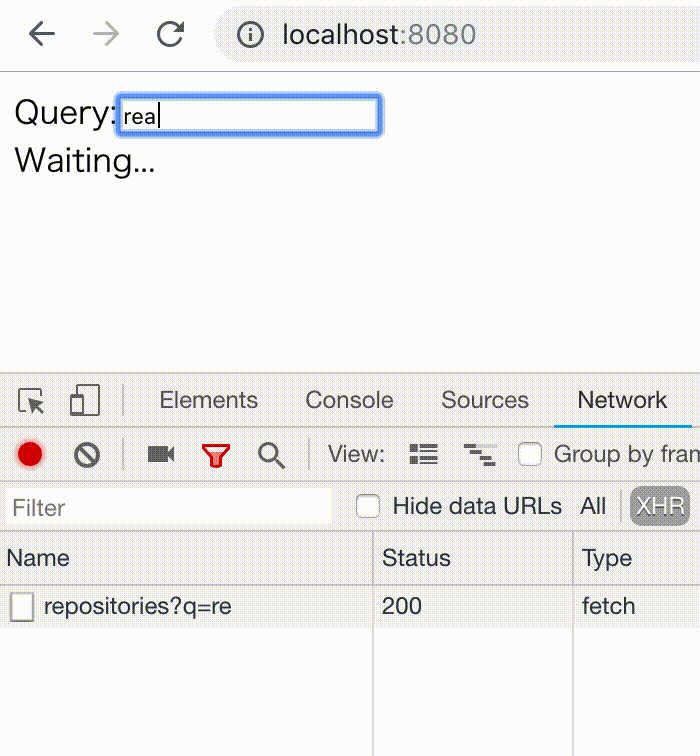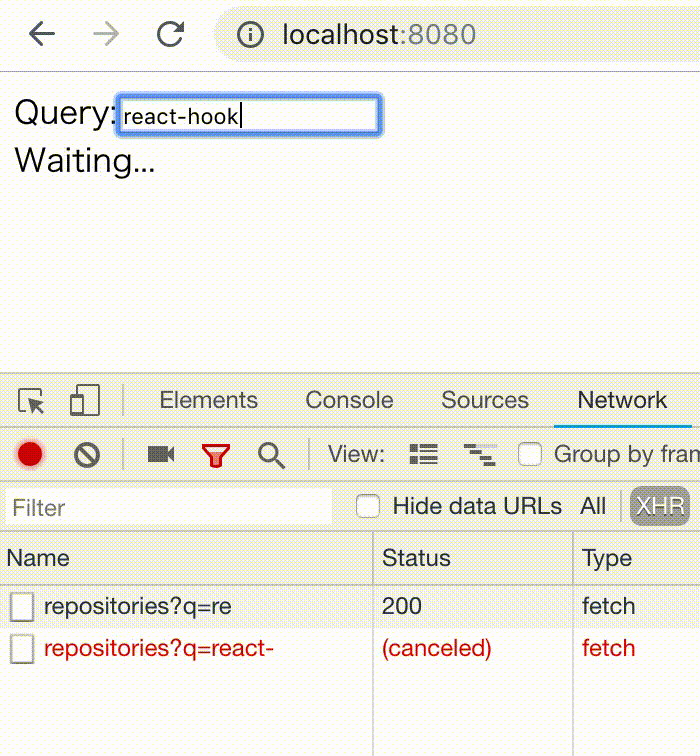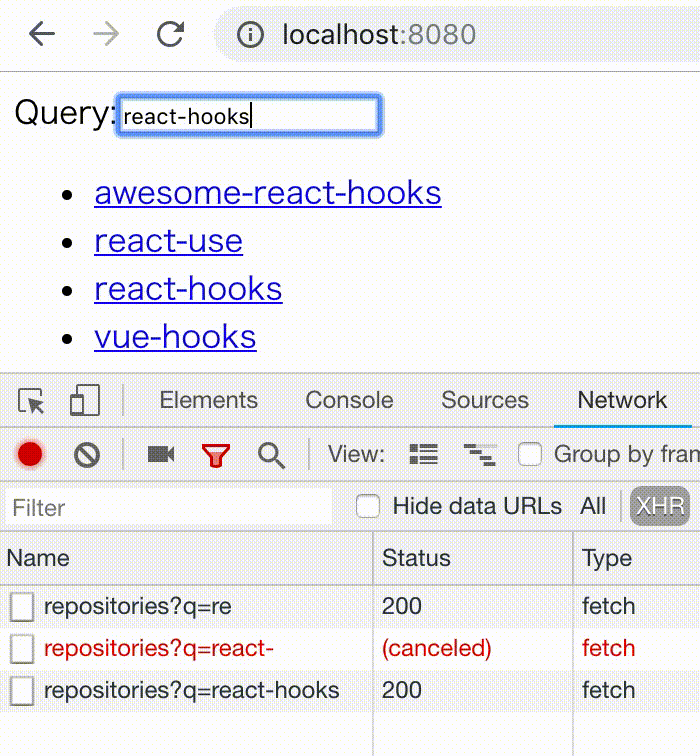
npm install react-hooks-asyncA typeahead search example.
import React, { useCallback, useState } from 'react';
import {
useAsyncCombineSeq,
useAsyncRun,
useAsyncTaskFetch,
useAsyncTaskDelay,
} from 'react-hooks-async';
const GitHubSearch = ({ query }) => {
const url = `https://api.github.com/search/repositories?q=${query}`;
const delayTask = useAsyncTaskDelay(500, [query]);
const fetchTask = useAsyncTaskFetch(url);
const combinedTask = useAsyncCombineSeq(delayTask, fetchTask);
useAsyncRun(combinedTask);
if (delayTask.pending) return <div>Waiting...</div>;
if (fetchTask.error) return <Err error={fetchTask.error} />;
if (fetchTask.pending) return <Loading abort={fetchTask.abort} />;
if (!fetchTask.result) return <div>No result</div>;
return (
<ul>
{fetchTask.result.items.map(({ id, name, html_url }) => (
<li key={id}><a target="_blank" href={html_url}>{name}</a></li>
))}
</ul>
);
};
const App = () => {
const [query, setQuery] = useState('');
return (
<div>
Query:
<input value={query} onChange={e => setQuery(e.target.value)} />
{query && <GitHubSearch query={query} />}
</div>
);
};The examples folder contains working examples. You can run one of them with
PORT=8080 npm run examples:minimaland open http://localhost:8080 in your web browser.
You can also try them in codesandbox.io: 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08
const task = useAsyncTask(func, inputs);This function is to create a new async task.
The first argument func is a function with an argument
which is AbortController. This function returns a promise,
but the function is responsible to cancel the promise by AbortController.
The second argument inputs is an array of inputs just like
the second argument of useEffect.
This controls when to create an async task.
The return value task is an object that contains information about
the state of the task and some internal information.
The state of the task can be destructured like the following:
const { pending, error, result } = task;useAsyncRun(task);This function is to run an async task. When the task is updated, this function aborts the previous running task and start the new one.
The first argument task is an object returned by useAsyncTask
and its variants. This can be a falsy value and in that case
it won't run any tasks. Hence, it's possible to control the timing by:
useAsyncRun(ready && task);The return value of this function is void.
You need to keep using task to get the state of the task.
const combinedTask = useAsyncCombineSeq(task1, task2, ...);This function combines multiple tasks in a sequential manner.
The arguments task1, task2, ... are tasks created by useAsyncTask.
They shouldn't be started running.
The return value combinedTask is a newly created combined task which
holds an array of each task results in the result property.
const combinedTask = useAsyncCombineAll(task1, task2, ...);This function combines multiple tasks in a parallel manner.
The arguments and return value are the same as useAsyncCombineSeq.
const combinedTask = useAsyncCombineRace(task1, task2, ...);This function combines multiple tasks in a "race" manner.
The arguments and return value are the same as useAsyncCombineSeq.
These hooks are just wrappers of useAsyncTask.
const task = useAsyncTaskTimeout(func, delay);This function returns an async task that runs func after delay ms.
Note the identity of func is important, and if func is changed,
a new async task is created. Hence, typically it is
wrapped by useCallback.
const task = useAsyncTaskDelay(milliSeconds, inputs);This function returns an async task that finishes after milliSeconds.
This is a simpler variant of useAsyncTaskTimeout.
The second argument inputs is the same as usual.
const task = useAsyncTaskFetch(input, init, bodyReader);This function returns an async task that runs
fetch.
The first argument input and the second argument init
are simply fed into fetch. The third argument bodyReader
is to read the response body, which defaults to JSON parser.
const task = useAsyncTaskAxios(config);This is similar to useAsyncTaskFetch but using
axios.
Note again the identity of config matters and
best to use with useMemo.
Due to the nature of React Hooks API, creating async tasks dynamically is not possible. For example, we cannot create arbitrary numbers of async tasks at runtime. For such a complex use case, we would use other solutions including upcoming react-cache and Suspense.