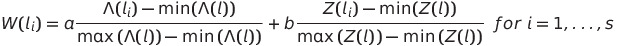OptimalPathApp
Summary
This application allows to interactively see network data, calculate the shortest or optimal path between two locations, and plot heatmaps of the edge attributes. The optimal path is calculated by the app using the following linear combination formula:
where W(li) is the global weight related to edge li, Z(li) is a variable related to the same edge i, a+b = 1, and max(λ(l)) and min(λ(l)) (say) is the maximum and the minimum value of all λ(li), which is the intensity counting measure defined for the linear segment li, i = 1, ..., s. Note that this expression is not affected by the relative scale of each criterion. Then 0 <= W(li) <= 1, for any i = 1, ..., s. The linear combination of both factors permits to have a better control between weight types, by changing the values of the a and b paramenters. For instance, if we take a = 0.8 and b = 0.2, our path selection is mainly based on the first covariate, although variable Z of the network is also taken into account.
Starting the App
First, download this repository and uncompress the files if compressed. Then, in the 'app/' folder, run the following R instruction to start the application:
shiny::runApp()Or the following if in the main folder ('OptimalPathApp/'):
shiny::runApp('app/')Input
It requires three datasets in .csv format containing information about the nodes, the edges, and the events occurring in the network.
-
Nodes: At least 3 columns with the node IDs, the x coordinates, and the y coordinates. All the other columns will be treated as attributes of the nodes.
-
Edges: Minimum of 4 columns containing the two endpoints of each edge (the nodes which form the edges) and two attributes that are used as covariates to calculate its linear combination. All extra columns are treated as edge attributes and are also selectable to be the covariates.
-
Events: Only two columns containing the coordinates x and y of the events occurring in the network.
The app gives options to load properly the data by selecting if the .csv data contain a header or not and the data separator (semicolon, comma, or tab). It also allows to preview the loaded files, by default only the header but all the data can be shown as well by selecting the option All under the Display section.
Interactive Plot
Loading the network
Once the input data is loaded, the app requires to select which edge attributes are the covariates that will be used to calculate its linear combination. The lowest weight on the resulting value from the linear combination determines the optimal paths, therefore, this value is directly related to the weight of the covariates. If the higher values of a covariate represent the best paths, the app offers the option invert which tells the linear combination formula to treat its higher values as lowest and the lowest as higher following the formula:
Z(li) = max(T(l)) - T(li)
where T(li) is the covariate weight of the network edge i.
The proportions a, b of the linear combination are selectable using the slider under the Weight proportion section. The number (blue part) represents the proportion a, the rest b (b = 100 - a). Notice that the proportion is in %, in the linear combination formula will automatically divide the proportions by 100 (% / 100).
Finally, the button Load Network will calculate the linear combination and load the interactive network in the below panel.
Interacive network UI
On the left, the app gives the option to select which node and edge attributes display directly on the plot. The area under these selectables, will display the information about the selected nodes and edges. On the right panel the network will be displayed which list of interactions are the following:
-
Zoom: With the mouse wheel, the network can be zoomed in or out focusing on the area where the mouse pointer is located.
-
Navigation: By clicking in an empty area and maintaining the click button pressed, we can navigate throughout the network by moving the mouse.
-
Selection: We can select the nodes and edges by clicking on them. For multiple selections, we need to press and maintain the keyboard control key (Ctrl) meanwhile selecting the nodes and edges.
-
Manipulation: We can change the form of the network by clicking and dragging any node or set of selected nodes.
Optimal Path
After loading the network, in this tab, we can find the options to calculate the minimal path between the locations Origin and Destination depending on the given Weight. Such weight must be present in the edge attributes (therefore, loaded with the edge data in the input window). Notice that 3 more fields will appear. Such fields are T(covariant1), T(covariant2) and W(l_i). The 'T()' fields represent each covariate part of the linear combination formula and the field 'W(l_i)' is the result of the formula.
Heatmap Plots
In this section, we can select any edge attribute to plot its heatmap. We can also show the events occurring in the network (which will appear as orange squares) and determine their transparency of them with the Event transparency slider. Notice that no plot is shown until the network is loaded in the Interactive Plot tab.