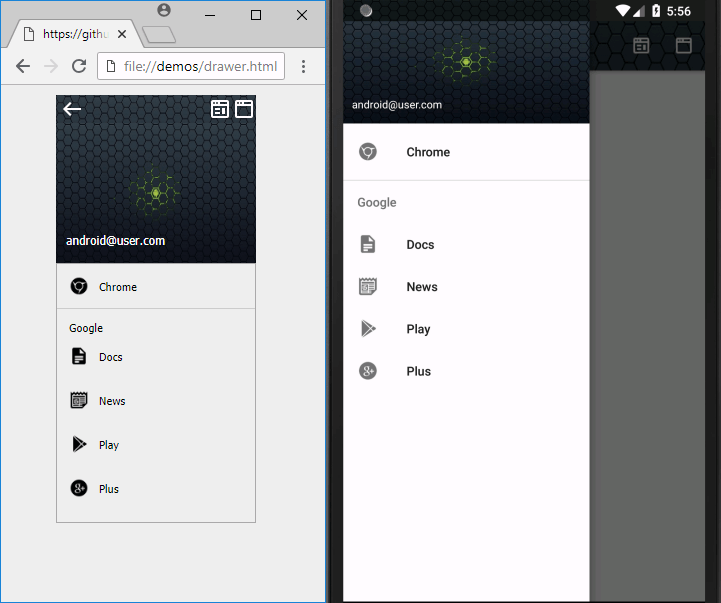
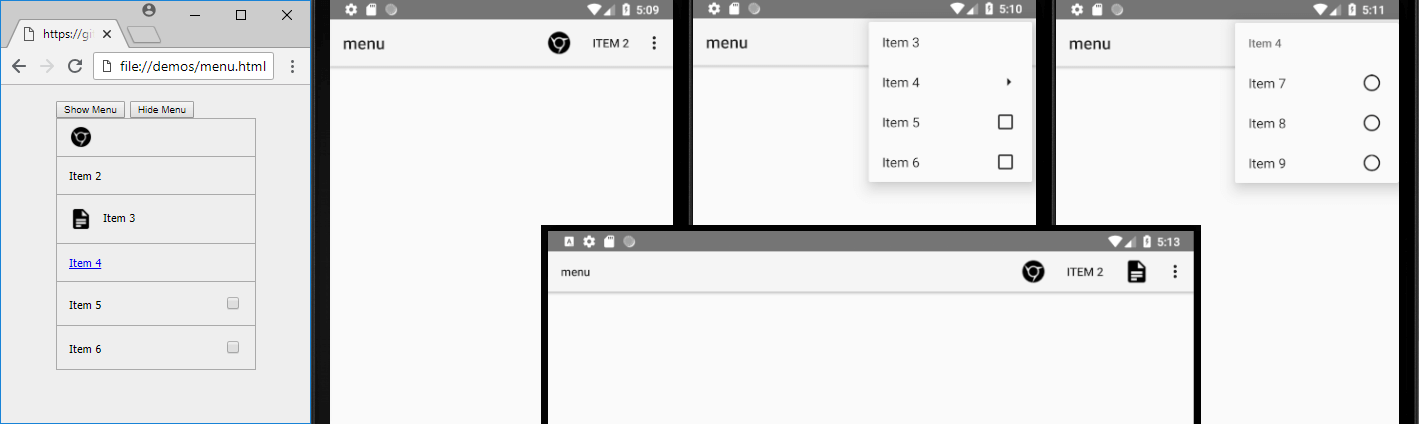
This program can convert moderately complex HTML pages into the standard XML layouts for Android. HTML is the most popular and versatile way to design user interfaces and can be used to generate the UI for any platform.
The ratio is about 1 line of HTML for every 10 lines of Android XML when using squared to generate the UI for your mobile application. It will also auto-generate the XML resources for the entire project. Using HTML best practices and techniques will output the fastest possible layout structure which is close to 95% efficient and better than most hand-written code.
There is also nearly full SVG support including transformations and CSS/SMIL animations.
Express server through Node.js is available with a provided default configuration. It is sufficient to load this program locally and can also be used for development. Using Express is highly recommended as you can create a ZIP archive of the generated resources from inside your browser which can be conveniently extracted into your project folder. Installing these dependencies are only required if you plan on using Express as your local web server.
- Install Node.js: http://www.nodejs.org
- Install squared: (choose one)
NPM
> npm install squared
> cd node_modules/squared
> node app.js
GitHub
> git clone https://github.com/anpham6/squared
> cd squared
> npm install
> npm run prod
> node app.js
- Open Browser: http://localhost:3000/demos/index.html
<script src="/dist/squared.min.js"></script>
<script src="/dist/squared.base.min.js"></script>
<script src="/dist/squared.svg.min.js"></script> /* optional */
<script src="/dist/android.framework.min.js"></script>
<script>
// optional
squared.settings.targetAPI = 26;
squared.settings.resolutionDPI = 160;
// without Express: use either console.log() or element.innerHTML to display using "system.write" commands
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', function() {
// required
squared.setFramework(android);
// required: zero or more DOM elements
squared.parseDocument(/* document.getElementById('mainview') */, /* 'subview' */, /* etc... */);
squared.close();
squared.saveAllToDisk(); /* Express required */
// optional: start new "parseDocument" session
squared.reset();
});
</script>The primary function "parseDocument" can be called on multiple elements and multiple times per session. The application will continuously and progressively build into a single entity with combined shared resources.
Library files are in the /dist folder. A minimum of three files are required to run squared.
- squared
- squared-base
- squared-svg - optional
- framework (e.g. android)
- extensions (e.g. android.widget) - optional
Usable combinations: 1-2-4 + 1-2-4-5 + 1-2-3-4-5 + 1-3
There are ES5 minified versions (*.min.js) and ES6 non-minified versions. ES5 is more compatible with older browsers. ES6 performs better in newer browsers and recommended for internal development.
NOTE: Calling "save" or "write" methods before the images have completely loaded can sometimes cause them to be excluded from the generated layout. In these cases you should use the "parseDocument" promise method "then" to set a callback for your commands.
<script>
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', function() {
squared.setFramework(android);
squared.parseDocument(/* 'mainview' */, /* 'subview' */).then(function() {
squared.close();
squared.saveAllToDisk();
});
});
</script>*** External CSS files cannot be parsed when loading HTML pages using the file:// protocol (hard drive) with Chrome 64 or higher. Loading the HTML page from a web server (http://localhost) or embedding the CSS files into a <style> tag can get you past this security restriction. You can also use your preferred browser Safari/Edge/Firefox. The latest version of Chrome is ideally what you should use to generate the production version of your program. ***
These settings are available in the global variable "squared" to customize your desired output structure. Each framework shares a common set of settings and also a subset of their own settings.
squared.settings = {
builtInExtensions: [
'android.delegate.fixed',
'android.delegate.max-width-height',
'android.delegate.percent',
'android.delegate.radiogroup',
'android.delegate.scrollbar',
'squared.external',
'squared.substitute',
'squared.sprite',
'squared.css-grid',
'squared.flexbox',
'squared.table',
'squared.list',
'squared.grid',
'squared.relative',
'squared.verticalalign',
'squared.whitespace',
'squared.accessibility',
'android.constraint.guideline',
'android.resource.includes',
'android.resource.background',
'android.resource.svg',
'android.resource.strings',
'android.resource.fonts',
'android.resource.dimens',
'android.resource.styles'
],
targetAPI: 26,
resolutionDPI: 160,
supportRTL: true,
preloadImages: true,
ellipsisOnTextOverflow: true,
supportNegativeLeftTop: true,
floatOverlapDisabled: false,
collapseUnattributedElements: true,
customizationsOverwritePrivilege: true,
showAttributes: true,
insertSpaces: 4, // tabs: 0
convertPixels: 'dp',
handleExtensionsAsync: true,
autoCloseOnWrite: true,
outputDirectory: 'app/src/main',
outputMainFileName: 'activity_main.xml',
outputArchiveFileType: 'zip', // zip | tar
outputMaxProcessingTime: 30
};There is no official documentation as this project is still in early development. The entire source code is available on GitHub if you need further clarification.
.settings // see user preferences section
setFramework(module: {}, cached?: boolean) // install application converter
parseDocument() // see installation section
ready() // boolean indicating if parseDocument can be called
close() // close current session preceding write to disk or local output
reset() // clear cached layouts and reopen new session
saveAllToDisk() // download entire project as zip archive - requires Node.js and Express
toString() // main layout file contents
include(extension: squared.base.Extension) // see extension configuration section | same: apply(extension: {})
retrieve(name: string) // retrieve an extension by namespace or control | same: apply(name: string)
configure(name: string, options: {}) // see extension configuration section | same: apply(name: string, options: {})
exclude(name: string) // remove an extension by namespace or controlMost attributes can be excluded from the generated XML using the dataset feature in HTML. One or more can be applied to any tag using the OR "|" operator. These may cause warnings when you compile your project and should only be used in cases when an extension has their custom attributes overwritten.
<div data-exclude-section="DOM_TRAVERSE | EXTENSION | RENDER | ALL"
data-exclude-procedure="LAYOUT | ALIGNMENT | AUTOFIT | OPTIMIZATION | CUSTOMIZATION | ACCESSIBILITY | LOCALIZATION | ALL"
data-exclude-resource="BOX_STYLE | BOX_SPACING | FONT_STYLE | VALUE_STRING | IMAGE_SOURCE | ASSET | ALL">
</div>
<div>
<span data-exclude-resource="FONT_STYLE">content</span>
<input id="cb1" type="checkbox" data-exclude-procedure="ACCESSIBILITY"><label for="cb1">checkbox text</label>
</div>System or extension generated attributes can be overridden with dataset. They will only be visible on the declared framework.
<div
data-android-attr-android="layout_width::match_parent;layout_height::match_parent"
data-android-attr-app="layout_scrollFlags::scroll|exitUntilCollapsed">
</div>It is sometimes necessary to append elements into other containers when trying to design a UI which will look identical on the Android device. Redirection will fail if the target "location" is not a block/container element.
<div>
<span>Item 1</span>
<span data-target="location">Item 2</span>
<div>
<ul id="location">
<li>Item 3</li>
<!-- span -->
</ul><LinearLayout>
<TextView>Item 1</TextView>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout>
<TextView>Item 3</TextView>
<TextView>Item 2</TextView>
</LinearLayout>Using "target" into a ConstraintLayout or RelativeLayout container will not include automatic positioning.
You can use the "system.customize" method to change the default settings for the specific controls which are applied when a view is rendered.
system.customize(build: number, widget: string, options: {}) // global attributes applied to specific views
system.addXmlNs(name: string, uri: string) // add global namespaces for third-party controls
system.writeLayoutAllXml(saveToDisk: boolean) // output generated xml
system.writeResourceAllXml(saveToDisk: boolean)
system.writeResourceAnimXml(saveToDisk: boolean)
system.writeResourceArrayXml(saveToDisk: boolean)
system.writeResourceColorXml(saveToDisk: boolean)
system.writeResourceDimenXml(saveToDisk: boolean)
system.writeResourceDrawableXml(saveToDisk: boolean)
system.writeResourceDrawableImageXml(saveToDisk: boolean)
system.writeResourceFontXml(saveToDisk: boolean)
system.writeResourceStringXml(saveToDisk: boolean)
system.writeResourceStyleXml(saveToDisk: boolean)<script>
// targetAPI: 0 - ALL, 26 - OREO
squared.system.customize(squared.settings.targetAPI, 'Button', {
android: {
minWidth: '35px',
minHeight: '25px'
}
});
</script>Most of the Android support library extensions can be configured using the same attribute name in the Android documentation. See /demo/*.html for usage instructions.
- android.widget.coordinator
- android.widget.floatingactionbutton
- android.widget.menu
- android.widget.bottomnavigation
- android.widget.toolbar
- android.widget.drawer
Layout rendering can also be customized using extensions as the program was built to be nearly completely modular. Some of the common layouts already have built-in extensions which you can load or unload based on your preference.
CSS Grid and Flexbox layouts are mostly supported. There is also support for SVG and most of the common floating techniques.
<script src="/dist/extensions/android.widget.coordinator.min.js"></script>
<script src="/dist/extensions/android.widget.menu.min.js"></script>
<script src="/dist/extensions/android.widget.toolbar.min.js"></script>
<script>
// required when handleExtensionsAsync = false
squared.include(android.widget.coordinator);
squared.include(android.widget.menu);
squared.include(android.widget.toolbar);
// configure an extension
squared.configure('android.widget.toolbar', { // optional: default configuration is usually provided
'elementId': { // HTML DOM
appBar: {
android: {
theme: '@style/ThemeOverlay.AppCompat.Dark.ActionBar'
}
}
}
});
// third-party: create an extension
class Sample extends squared.base.Extension {
constructor(name, framework = 0, tagNames = [], options = {}) {
// framework: universal = 0; android = 2;
super(name, framework, tagNames, options);
}
}
// third-party: install an extension
var sample = new Sample('your.namespace.sample', ['DIV'], { /* same as configure */ });
squared.include(sample);
</script>Some applications can benefit from using includes or merge tags to share common templates. Nested includes are also supported.
<div>
<div>Item 1</div>
<div data-android-include="filename1" data-android-include-merge="true">Item 2</div>
<div>Item 3</div>
<div data-android-include-end="true">Item 4</div>
<div data-android-include="filename2" data-android-include-end="true">Item 5</div>
</div><LinearLayout>
<TextView>Item 1</TextView>
<include layout="@layout/filename1" />
<include layout="@layout/filename2" />
</LinearLayout>
<!-- res/layout/activity_main.xml -->
<merge>
<TextView>Item 2</TextView>
<TextView>Item 3</TextView>
<TextView>Item 4</TextView>
</merge>
<!-- res/layout/filename1.xml -->
<TextView>Item 5</TextView>
<!-- res/layout/filename2.xml -->The attributes "android-include" and "android-include-end" can only be applied to elements which share the same parent container. See /demos/gradient.html for usage instructions.
Only the XML based layout and resource files are generated with squared which can be viewed on the Android device/emulator without any Java/Kotlin backend code. To play animations you also have to "start" the animation in MainActivity.java.
android.widget.ImageView imageView1 = findViewById(R.id.imageview_1);
if (imageView1 != null) {
android.graphics.drawable.Animatable animatable = imageView1.getDrawable();
animatable.start();
}Using excessive DIV tags are not required for mobile devices which can cause additional FrameLayouts or LinearLayouts to be generated. Block level elements are almost always rendered to preserve any CSS styles which are applied to the tag.
If you plan on using this library it adheres to strict HTML validation rules regarding "block-level" and "inline" elements. You can basically code the HTML any way you want although using reasonable techniques for mobile devices will lead you to a more accurate layout.