Code of our paper "Fixed Template Network and Dynamic Template Network: novel network designs for decoding steady-state visual evoked potentials".
This study proposed a novel network design motivated by the works of decomposition methods. Fixed Template Network (FTN) and Dynamic Template Network (DTN) are two novel networks combining the advantages of fixed templates and subject-specific templates. This study compared the intra-subject classification performance of DTN and FTN with that of state-of-the-art decomposition methods on three public SSVEP datasets.
Nakanishi2015, Yijun2016 and BETA were tested in this study.
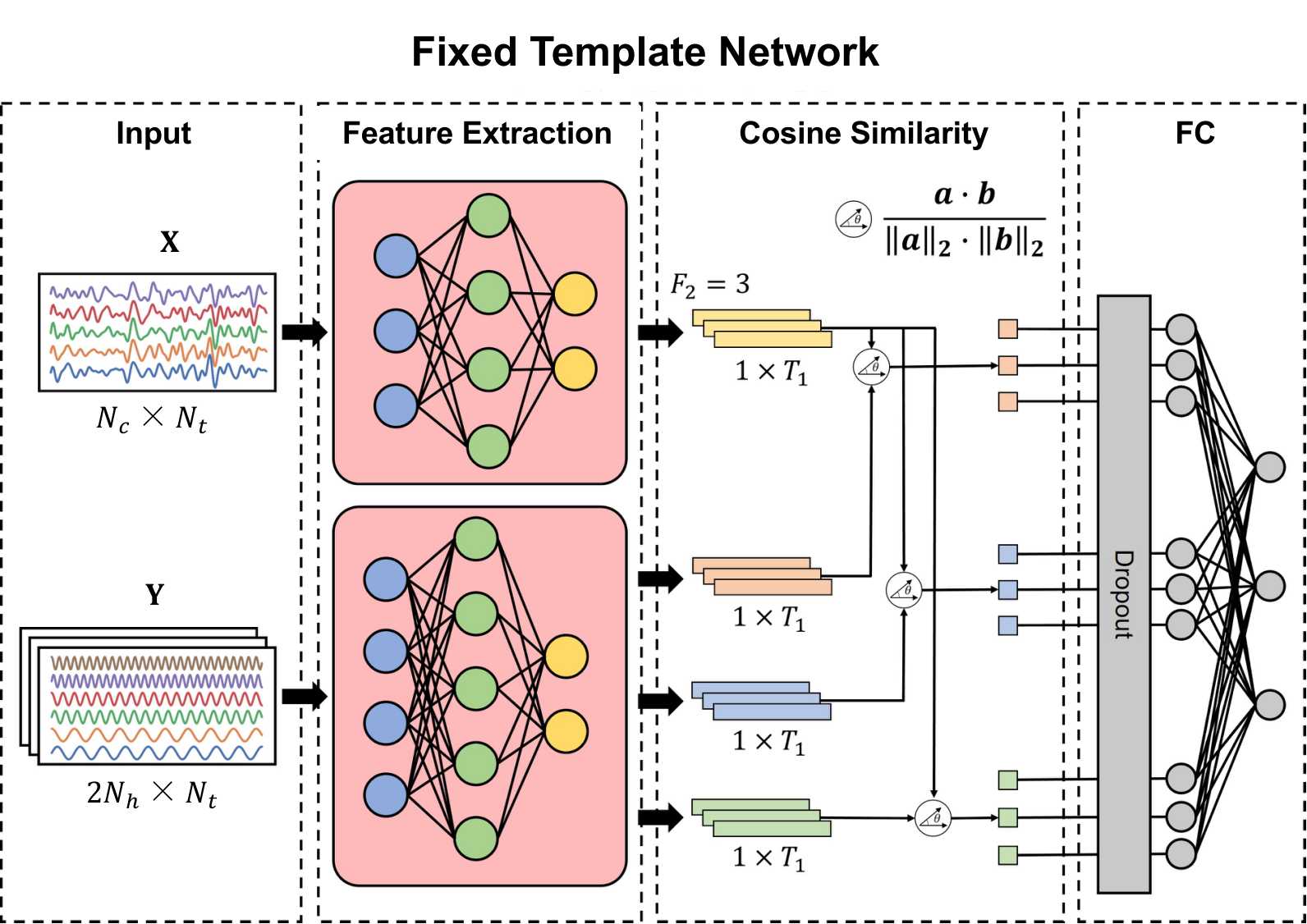
The fixed template network (FTN) was motivated by the design of eCCA that compares the data with pre-defined templates. The above figure illustrates the architecture of the FTN, considering the 3-class classification problem as an example. Three fixed templates and an input were provided to the FTN. The shape of the input was
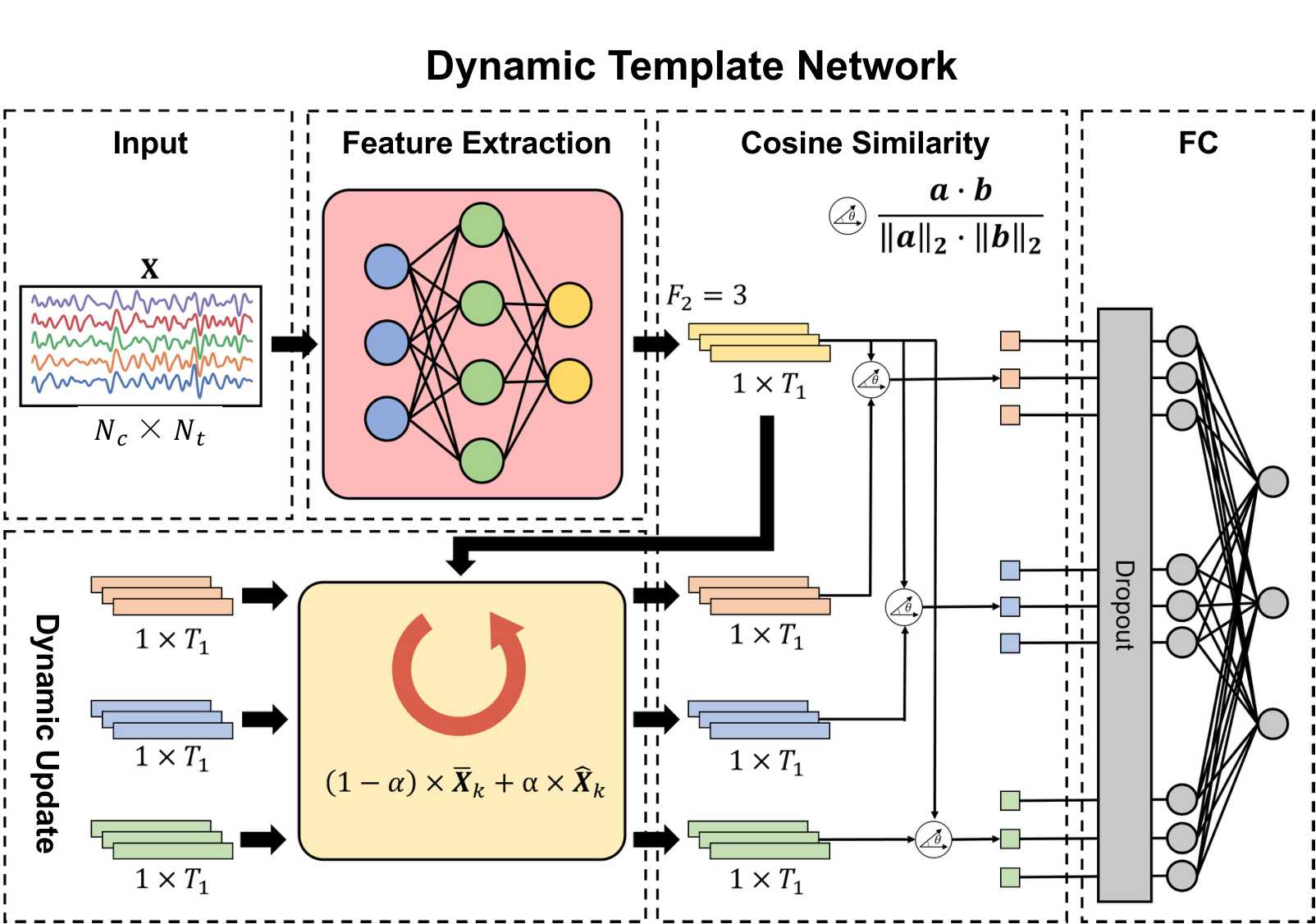
The dynamic template network (DTN) was motivated by the design of TRCA and DSP that compares the data with subject-specific templates. The above figure illustrates the architecture of the DTN, considering the 3-class classification problem as an example. In the DTN, all templates and input were applied with the feature extraction module instead of their separate feature extraction modules in the FTN. The rest of operations were the same as those in the FTN.
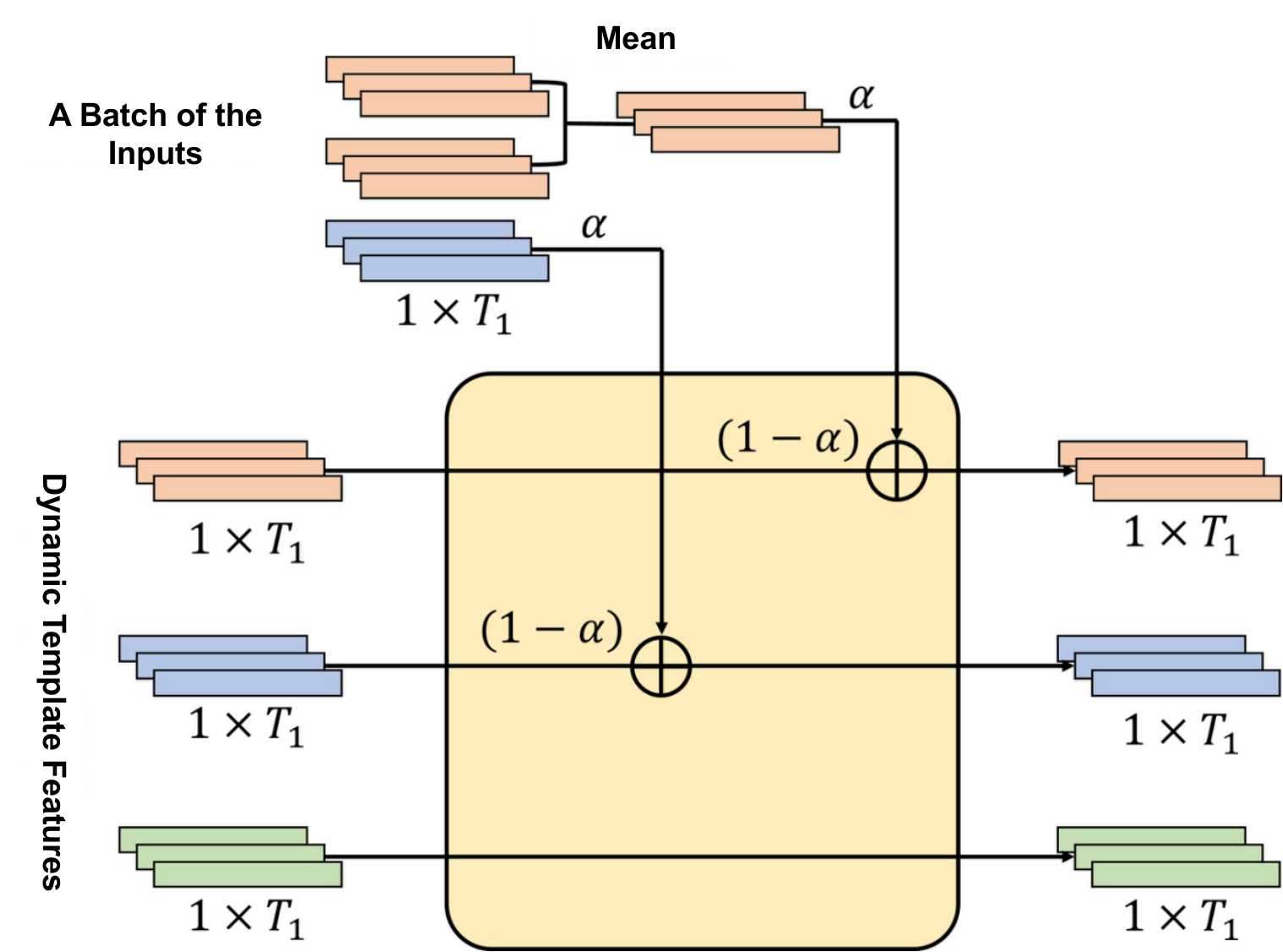
The most important part of the DTN is how to dynamically update templates based on each batch of the inputs in the training process. The below figure illustrates the template update process of the DTN, considering the 3-class classification problem as an example. The initial dynamic templates were set to zero. A batch of the inputs (two inputs colored in orange and one input colored in blue) was provided to the DTN. First, their batch templates were calculated by averaging the corresponding samples in the batch. Then, dynamic templates were updated with the exponential moving average.
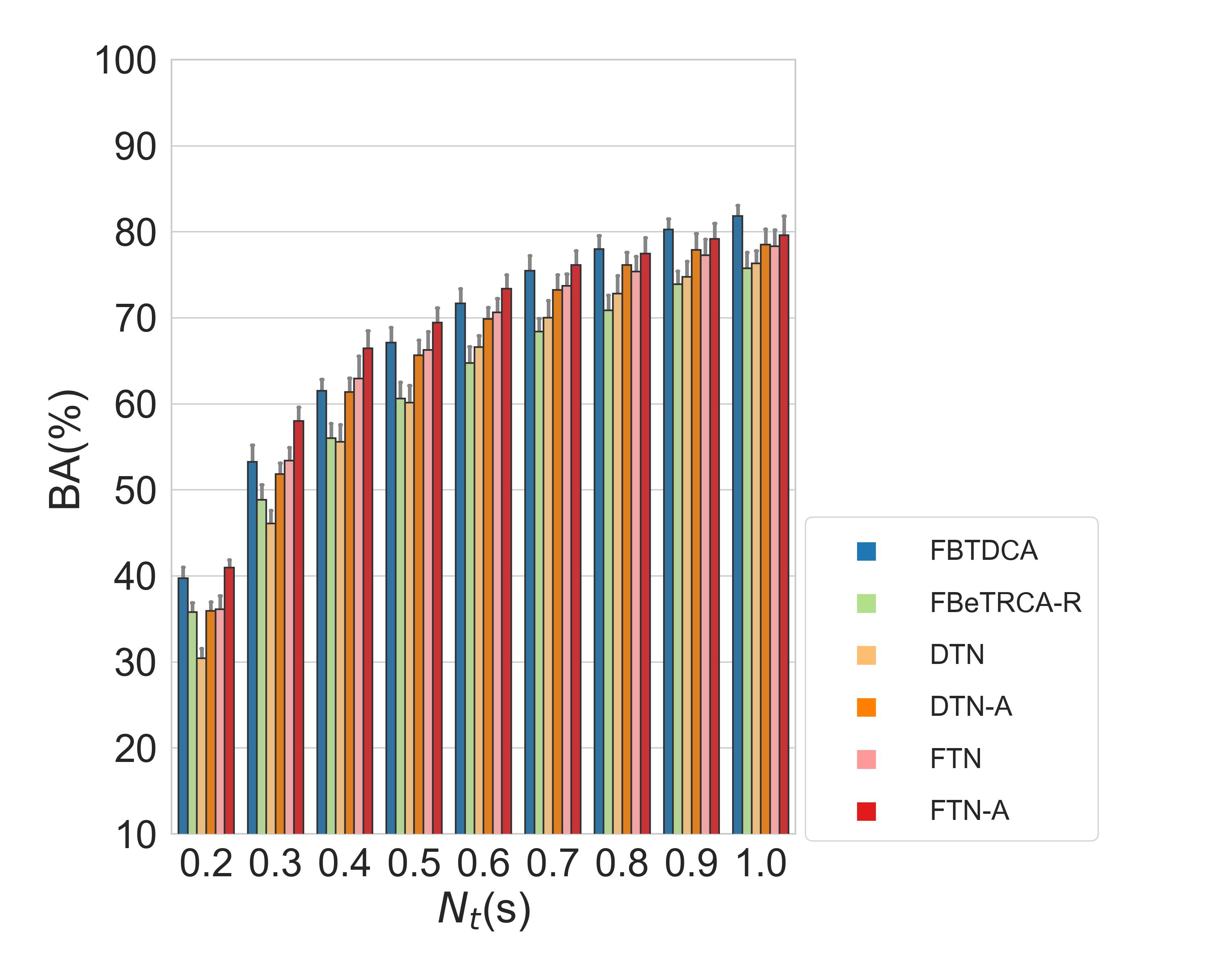
The above figure is the results of dataset BETA. Here FTN-A and DTN-A means that the networks were trained with the exactly same data used in those decomposition methods.
For dataset BETA, DTN and DTN-A has the balanced accuracy as 60.1% and 65.6% respectively with
The code relies on my toolbox to import SSVEP datasets and other matrix decomposition methods. See brainda for install instructions.
FTN and DTN implementation can be found in model.
Run notebook indices to generate train, validate and test indices for each dataset.
Run notebook matrix to generate accuracies for matrix decomposition methods (It requires a lot of time to regenerate the results. You can skip this notebook since the results have been uploaded).
Run notebook network to generate accuracies for FTN and DTN.(You can skip this notebook, too)
Run notebook results to collect figures for this paper.
If you find the code useful, please cite this paper:
@article{Xiao_2022, doi = {10.1088/1741-2552/ac9861}, url = {https://dx.doi.org/10.1088/1741-2552/ac9861}, year = {2022}, month = {nov}, publisher = {IOP Publishing}, volume = {19}, number = {5}, pages = {056049}, author = {Xiaolin Xiao and Lichao Xu and Jin Yue and Baizhou Pan and Minpeng Xu and Dong Ming}, title = {Fixed template network and dynamic template network: novel network designs for decoding steady-state visual evoked potentials}, journal = {Journal of Neural Engineering} }
If you have any questions, please feel free to contact me.
My Email: swolfforever@gmail.com