Slackmin allows you to easily integrate slack slash (/) commands, interactive components, message formatting & custom modals in your Node.js application. You can build and setup custom tailored tools for your daily ops like different analytics reports, content management interfaces, customer support modules and much more. Also send alerts and notifications over Slack for your team to take actions on critical events in your application.
- Use Slack’s Web, Desktop and Mobile apps to manage your Content, Orders, Reports, Customers and much more.
- Focus on your Product instead of building custom solutions for your admin needs. Use Slack to manage everything and save valuable time.
- Spend Less $ on Admin Tools. Use the tool you already have, use Slack!
- Use public and private channels in Slack to manage access to certain types of data and features. Additionally, you can whitelist slack users for specific functionalities.
- Leverage the robust Search features in Slack so your team has easy access to historical data.
- Users can setup their own push notifications in Slack to get alerts about the data they need most.
- Logs for actions taken by your admins like updated product details, Customer queries, Payment notifications and much more are easily searchable and accessible.
- Slackmin is open source. Developers can use (as it is) or modify Slackmin for their custom needs, for free!
- Slack has built a secure platform. Slackmin uses this secure infrastructure instead of you building your own security layers.
- Slackmin provides Message and Modal wrappers that help in easy formatting & sending messages, sending system alerts and creating modals. No need to create complex data structures for message and modal layout.
- Slackmin's multiple slack app support helps in overcoming the 25 slash commands limitation per slack app. You can also create multiple applications for better access control.
- The block actions payload and view submission payload are validated and parsed into a key-value pair of parameters.
Additionally, Slackmin provides following built-in security features as middlewares:
- Sanitize unwanted HTML tags from parameters obtained in the request body, query and headers. HTML sanitization is recommended by Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP)
- Signature / signed secret verification is provided as a middleware ready to be plugged in and used for all the requests coming from slack. This guide gives a detailed description of signature verification.
- Slack app id is validated against whitelisted app ids.
- Slack channel validation is done to only allow requests from whitelisted slack channels.
- User authentication helps in validating whether the slack user has the correct privileges or not.
- Slack app’s workspace domain validation is also exposed as a middleware.
As a demo of Slackmin, let's take an example use case: Customer Support Team receives a complaint on broken product. They want to check on the user’s order history and issue refund.
The customer support executive gets the order details using a slash command. Then the executive clicks on the "User Order History" button to get a sheet URL, which has all the past orders from that user. After checking the order history, executive clicks on the "Issue Refund" button to open the issue refund modal, provides the required information and clicks "Submit". Voila! Refund issued along with a log message in the channel, which brings in transparency.
order.refund_1.mp4
First things first, setup a slack app as mentioned in this guide. Following are the major steps involved:
- Create a slack app. Visit https://api.slack.com/apps.
- Configure request URL for interactive components. Click here for details.
- Configure slash commands. For more details click here.
- Add scopes chat:write and chat:write:public to the bot token scopes. Know more about Slack Scopes.
- Then install the app to your workspace.
Keep a note of your App ID and Signing Secret from the "Basic Information" section of your app. Also note the Bot User OAuth Token from the "OAuth & Permissions" section of your app. These details will be required later.
npm install @truesparrow/slackmin --saveWhile using the package, create a singleton object of Slackmin and then use it across the application. Example snippet for the Slackmin singleton object is given below.
const Slackmin = require('@truesparrow/slackmin');
const appConfigs = [
{
id: '<slack_app_id>',
secret: '<slack_signing_secret>',
slack_bot_user_oauth_token: '<slack_bot_user_oauth_token>',
slack_domain: '<your_slack_domain>'
}
];
const whiteListedChannels = ['<slack_channel_id>', '<slack_channel_id>', '<slack_channel_id>'];
const whitelistedUsers = ['<slack_member_id>', '<slack_member_id>', '<slack_member_id>'];
const slackmin = new Slackmin(
appConfigs,
whiteListedChannels,
whitelistedUsers
);
module.exports = slackmin;1. appConfigs is an array of app config objects allowing Slackmin to support multiple apps. Each app config consists of id, secret, token and domain.
- id: This is your slack app id.
- secret: Your app's signing secret. It is required for signature verification.
- slack_bot_user_oauth_token: This is the Bot User OAuth Token.
- slack_domain: This is your slack app's workspace domain. Apps can reside on different slack domains.
2. whiteListedChannels is an array of whitelisted channel ids. Only whitelisted users are allowed to execute slash commands in the whitelisted channels. Pass whiteListedChannels as an empty array to skip this validation.
3. whitelistedUsers is an array of whitelisted slack member ids. Only whitelisted users are allowed to execute slash commands in the whitelisted channels. Pass whitelistedUsers as an empty array to skip this validation.
Slackmin middlewares are used with slash commands as well as with interactive routes. These middlewares format and preprocess the Slack payload and sanitize unwanted HTML tags from parameters obtained in the request body, query and headers. Slackmin has a built-in security layer for request verification, app id validation, channel id validation and slack member id validation.
const express = require('express');
const slackmin = require('path-to-your-slackmin-singletone-provider');
const router = express.Router();
// common middlewares
// This set of middlewares can be used with slash commands as well as with interactive routes.
router.use(
slackmin.commonMiddlewares
);
// interactive-endpoint middlewares
// This set of middlewares can be used with interactive routes.
router.use(
slackmin.interactiveEndpointMiddlewares
);
// Example interactive endpoint
router.post(
'/interactive-endpoint',
async function(req, res, next) {
// your business logic
// req.decodedParams contains sanitized parameters and must be used to read data for further business logic.
console.log(req.decodedParams); }
);const express = require('express');
const slackmin = require('path-to-your-slackmin-singletone-provider');
const router = express.Router();
// common middlewares
// This set of middlewares can be used with slash commands as well as with interactive routes.
router.use(
slackmin.commonMiddlewares
);
// slash ('/') command middlewares
// This set of middlewares can be used with Slash commands.
router.use(
slackmin.slashCommandMiddlewares
);
// Write all routes specific to slash commands below.
// Example slash command endpoint
router.post(
'/slash-command',
async function(req, res, next) {
// your business logic
// req.decodedParams contains sanitized parameters and must be used to read data for further business logic.
console.log(req.decodedParams);
}
);Important Note: req.decodedParams contains sanitized parameters and must be used to read data for further business logic.
Validators are functions which expose the middleware functionality which can be used in non express Node js frameworks like Koa, Fastify, etc.
Methods
common- function accessed asslackmin.validators.common- Parameters: requestBody, requestQuery, requestHeaders, requestMethod
- Description: This method can be used for implementing common middleware for slash command and interactive-endpoint routes.
interactive- function accessed asslackmin.validators.interactive- Parameters: requestParams, requestBody, requestHeaders, decodedParams, internalDecodedParams
- Description: This method can be used for implementing interactive endpoint middleware for interactive-endpoint route.
slashCommands- function accessed asslackmin.validators.slashCommands- Parameters: requestBody, requestRawBody, requestHeaders, decodedParams
- Description: This method can be used for implementing slash command middleware for slash command route.
Refer validators methods usage examples here
Slack provides a range of visual components (Block Kit) used to layout complex information. These blocks are represented as JSON objects. You can include up to 50 blocks in a message and 100 blocks in a modal. You can find the Block Kit reference here.
Slackmin Message wrapper provides simple methods to create and format complex message layouts thus simplifying the creation of block elements.
Methods
addSectionaddSectionWithTextFieldsaddButtonaddButtonElements- Parameters: buttonDetails (array of objects with keys - buttonText, value, confirmText)
- Description: Adds an action block with multiple button elements.
Each button element comes with a confirmation popup.
buttonTextis the button label text,valueis the button value andconfirmTextis the confirmation pop up message. If you don't want to have a confirmation pop up, don't passconfirmText.
addDivider- Parameters: null
- Description: Adds divider block.
addCustomHeadersendUsingResponseUrl- Parameters: responseUrl (string), isTemporary (boolean)
- Description: Method for sending message using response url.
responseUrlis the response URL.isTemporaryis true for [ephemeral message] (https://api.slack.com/messaging/managing#ephemeral), otherwise false.
sendMessageToChannel- Parameters: postMessageParams (object with keys - channel, text), slackDomain (string)
- Description: Utilizes slack's Web API method
chat.postMessageto send message to channel.channelis the channel id or your slack channel name.textis the message title text.slackDomainis you slack app's workspace domain.slackDomainis optional parameter if not passed, then the first app's domain is taken.
When responding to a slash command or any other interaction, we have 2 choices - synchronous response and asynchronous response. If the generation of the message body is simple, then the response can be sent synchronously. Following is an example of the same.
const text = 'TITLE TEXT';
const slackMessageParams = {};
slackMessageParams.text = text;
slackMessageParams.channel = 'CHANNEL ID OR CHANNEL NAME HERE';
const message = new slackmin.interactiveElements.Message();
message.addDivider();
message.addSection(`*${text}*`);
message.addSection('Another section.');
message.sendMessageToChannel(slackMessageParams);Output of above code is shown in the screenshot below.
The following example explains how to send an asynchronous response using the response URL, obtained from the initial slack interaction. These response URLs expire after 30 minutes.
const responseUrl = 'Response URL HERE';
const message = new slackmin.interactiveElements.Message();
message.addCustomHeader('Message *title* `text` here.');
const texts = [
'2 Column Support.',
'`mrkdwn` is supported too.',
'Row 2, Column 1.',
'Row 2, Column 2.'
];
message.addSectionWithTextFields(texts);
const actionButtons = [];
// as a convention, we have value as a JSON string with keys action and hiddenParams.
// action specifies the next method call to be performed for interactive endpoint i.e call to testModal1Open opens the test modal 1
// hiddenParams in value are internal params that need to be forwarded
const testButton1 = {
buttonText: 'Test Button 1',
confirmText: 'Do you want to really click the test button 1?',
value:
"{\"action\":\"testModal1Open\",\"hiddenParams\":{\"user_id\":\"123\"}}"
};
actionButtons.push(testButton1);
const testButton2 = {
buttonText: 'Test Button 2',
confirmText: 'Do you want to really click the test button 2?',
value:
"{\"action\":\"testModal2Open\",\"hiddenParams\":{\"user_id\":\"123\"}}"
};
actionButtons.push(testButton2);
message.addButtonElements(actionButtons);
message.sendUsingResponseUrl(responseUrl);Output of above code is shown in the screenshot below. On clicking of the buttons a confirmation popup comes, as configured.
Slackmin Modal Wrapper simplifies the block elements by providing easy to use methods to create and format complex modal layouts.
Methods
addSubmitAndCancel- Parameters: submitText (string), cancelText (string)
- Description: Add submit and cancel button to the modal.
submitTextis the submit button label text.cancelTextis the cancel button label text.
addPlainTextSection- Parameters: text (string)
- Description: Adds a section block with the provided text.
addMarkdownTextContextaddDivider- Parameters: null
- Description: Adds divider block.
addTextbox- Parameters: labelText (string), multiline (boolean), isOptional (boolean), initialText (string), placeHolderText (string)
- Description: Adds an input block with an element type plain-text.
labelTextis the input block label text.multilineindicates whether the input will be a single line (false) or a larger textarea (true), defaults set to true.isOptionalis a boolean that indicates whether the input element may be empty when a user submits the modal, defaults to false.initialTextis the initial value, defaults to empty.placeHolderTextis the placeholder or help text, defaults to 'Write Something'.
addCheckBoxes- Parameters: labelText (string), options (Array of objects, each object with keys text, value), initialOptions (Array of objects, each object with keys text, value)
- Description: Adds an input block with an element type checkboxes.
labelTextis the input block label text.textis the individual checkbox option label text.valueis a unique string that specifies the value of the checkbox option.
addRadioButtons- Parameters: labelText (string), optionsArray (Array of objects, each object with keys text, value), initialOption (object with keys text and value)
- Description: Adds an input block with an element type radio buttons.
labelTextis the input block label text.textis the radio button label text.valueis a unique string value that will be passed to your app when any option is chosen. You can setinitial_optionin the element for selecting the radio button option by default.
addParamsMeta- Parameters: paramsMeta (array of strings)
- Description: To specify parameter names for the subsequent input block elements such as plain-text,
checkboxes and radio buttons.
paramsMetais sent in private_metadata in modal submissions.
addHiddenParamsMeta- Parameters: hiddenParamsMeta (object)
- Description: To pass on internal parameters on modal submit.
hiddenParamsMetacontains hidden parameters which have to be passed to the next modal action.hiddenParamsMetais sent in private_metadata in modal submissions.
addAction- Parameters: actionName (string)
- Description: You can provide the next action method/route to be executed on modal submit. As all the interactive component interactions are sent to a single request URL, this
actionNamehelps in deciding what needs to be done.actionNameis sent in private_metadata in modal submissions.
open- Parameters: triggerId (string)
- Description: Opens modal using the trigger id, which expires in 3 seconds.
triggerIdis obtained from interaction payload.
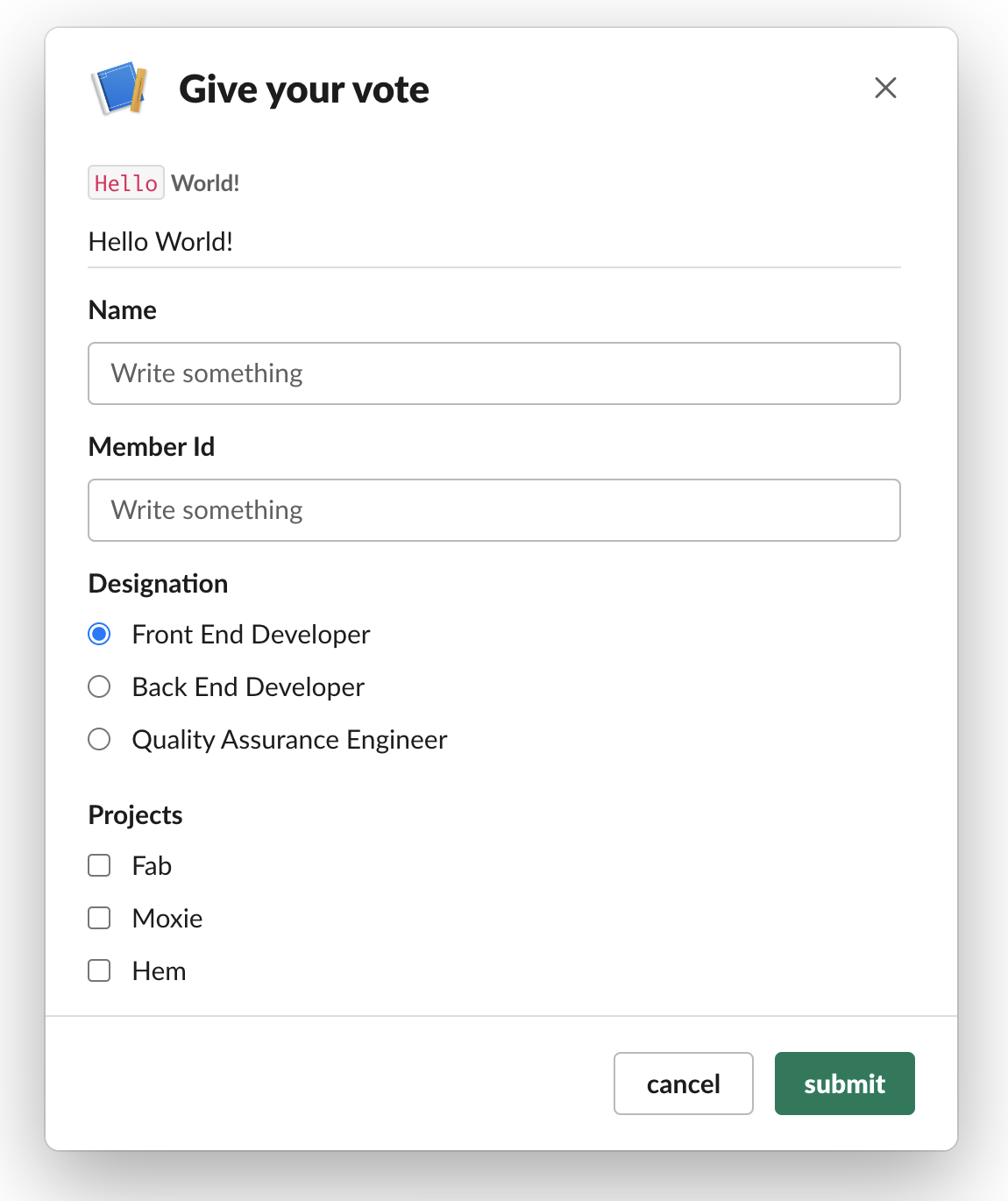
const triggerId = req.decodedParams.trigger_id; // Our middleware layer sets the trigger_id in req.decodedParams
const apiAppId = '<slack_app_id>'; // slack app id
const modal = new slackmin.interactiveElements.Modal(apiAppId, 'Give your vote');
// These are the parameter names for the subsequent textboxes.
const paramsMeta = ['name', 'member_id', 'designation', 'projects'];
modal.addParamsMeta(paramsMeta);
const hiddenParamsMeta = {param1: "value1"};
modal.addHiddenParamsMeta(hiddenParamsMeta);
modal.addAction('submitForm');
modal.addMarkdownTextContext('`Hello` *World!*');
modal.addPlainTextSection('Hello World!');
modal.addDivider();
modal.addTextbox('Name', false);
modal.addTextbox('Member Id', false);
modal.addRadioButtons(
'Designation',
[
{ text: 'Front End Developer', value: 'FE' },
{ text: 'Back End Developer', value: 'BE' },
{ text: 'Quality Assurance Engineer', value: 'QA' }
],
{ text: 'Front End Developer', value: 'FE' }
);
modal.addCheckBoxes('Projects', [
{ text: 'Fab', value: '1' },
{ text: 'Moxie', value: '2'},
{ text: 'Hem', value: '3' }
]);
modal.addSubmitAndCancel();
modal.open(triggerId);Output of above code is shown in the screenshot below.
Journey of Hidden Parameters
In this section, we will go through an example of our convention if handling hidden parameters. Hidden parameters have the contextual information needed for the CRUD operations like entity id, etc.
Following are the different parts of our example:
A slash command which sends a message with interactive buttons in it (refer Message Wrapper documentation to create message UI). The hidden parameters (user_id in our example) must be present in the value of the button element as shown in the following snippet.
// hiddenParams in value are internal params that need to be forwarded
const testButton1 = {
buttonText: 'Test Button 1',
confirmText: 'Do you want to really click the test button 1?',
value:
"{\"action\":\"testModal1Open\",\"hiddenParams\":{\"user_id\":\"123\"}}"
};
// Refer to the snippet given in section "Example 1 - Async Message" for the complete idea.
actionButtons.push(testButton1);When the button in the message is clicked, a confirmation popup is shown. On confirmation, a POST API call comes from slack to the interactive request URL (which was setup in the "Slack app setup" section above).
The block submission payload which comes from slack is converted to api parameters and assigned to req.decodedParams by our Interactive Component Middlewares.
A modal UI is created and opened using our Modal wrapper. Hidden parameters are forwarded to the modal view using addHiddenParamsMeta method of the Modal wrapper (refer documentation above).
On submission of the modal, the hidden parameters are obtained in the view submission payload, which is parsed and parameters are assigned to req.decodedParams by our Interactive Component Middlewares.
We have added code snippets for all demo slackmin commands available on https://truesparrow.com/slackmin
1. Refer Express code snippets to integrate Slackmin with Express
2. Refer Fastify code snippets to integrate Slackmin with Fastify
3. Refer Koa code snippets to integrate Slackmin with Koa
We welcome more helping hands to make Slackmin better. Feel free to report issues, raise PRs for fixes & enhancements.
Built with ❤️ by True Sparrow