漫谈 egg-bin
SunShinewyf opened this issue · 1 comments
前言:egg-bin是一个本地开发者工具,集成到
egg中,里面涵盖了很多功能,比如调试,单元测试和代码覆盖率等这些功能,可以说是比较强大了。
下面就egg-bin源码分析一些东西(针对的是 4.3.0 的版本)
egg-bin如何工作的
在本地运行egg项目的时候,我们往往会根据不同的场景(调试,测试等)来选择不同的命令(egg-bin dev、egg-bin debug)启动项目,从而达到我们需要的效果,但是egg-bin是如何让命令运作起来的呢?
比如在命令行中回车下面的命令:
$ egg-bin dev --port 7001开始进入node_modules/egg-bin/bin/egg-bin.js文件,文件代码比较简单:
#!/usr/bin/env node
'use strict';
const Command = require('..');
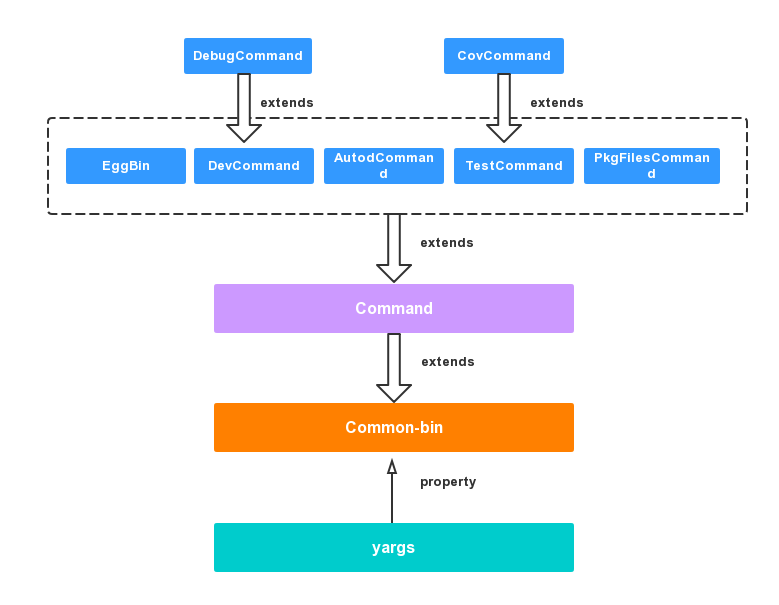
new Command().start();其中,Command对应的是node_modules/egg-bin/bin/egg-bin.js中的EggBin这个对象。首先理清一下egg-bin中对应的几个对象之间的关系,如下图:
其中最后导出的EggBin对象以及DevCommand、AutodCommand、TestCommand、PkgFilesCommand继承于egg-bin/lib/command.js里面导出的Command对象,而egg-bin/lib/command.js里面导出的Command又是继承于第三方库(其实也是egg核心contributors开发的)common-bin,而common-bin中导出的CommonBin对象又有一个yargs属性,该属性是目前比较流行的命令行工具yargs。DebugCommand和CovCommand则分别继承自DevCommand和TestCommand。
进入index.js文件源代码,该文件只是定义了EggBin这个对象,并且将一些sub command挂载到EggBin这个导出对象中,有如下几个子命令:
- Command --- 继承自
common-bin的基础命令对象 - CovCommand --- 代码覆盖率命令对象
- DevCommand --- 本地开发命令对象
- TestCommand --- 测试命令对象
- DebugCommand --- 调试命令对象
- PkgfilesCommand --- 包文件对象
接着就是执行new Command().start()这一行,首先会先去执行EggBin构造函数中的内容:
class EggBin extends Command {
constructor(rawArgv) {
// 获取用户输入的option
super(rawArgv);
this.usage = 'Usage: egg-bin [command] [options]';
// load对应目录下面的command文件
this.load(path.join(__dirname, 'lib/cmd'));
}
}获取命令参数
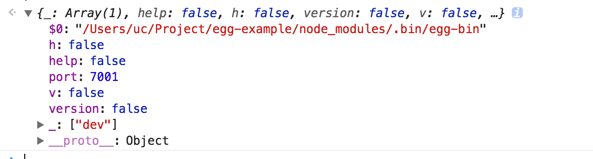
由于上面的继承关系,第一行就会直接执行到Common-bin/command.js中的构造函数中的参数获取:
this.rawArgv = rawArgv || process.argv.slice(2);此时this.rawArgv的值如下:
0:"dev"
1:"--port"
2:"7001"load配置文件
获取到这个参数之后就会直接将该参数传给yargs并将yargs对象赋给自己的一个yargs属性
然后就开始load命令行文件了,通过追踪,也可以发现最后执行的也是common-bin中的load成员函数,该函数要求参数是所需要获取的命令文件的绝对路径,其中common-bin/command.js中的load源码如下:
load(fullPath) {
// 省略对参数的校验
// load entire directory
const files = fs.readdirSync(fullPath);
const names = [];
for (const file of files) {
if (path.extname(file) === '.js') {
const name = path.basename(file).replace(/\.js$/, '');
names.push(name);
this.add(name, path.join(fullPath, file));
}
}
// 省略
}其中files文件的值为:
0:"autod.js"
1:"cov.js"
2:"debug.js"
3:"dev.js"
4:"pkgfiles.js"
5:"test.js"然后将files进行遍历,执行下面的addCommand的操作:
add(name, target) {
assert(name, `${name} is required`);
if (!(target.prototype instanceof CommonBin)) {
assert(fs.existsSync(target) && fs.statSync(target).isFile(), `${target} is not a file.`);
debug('[%s] add command `%s` from `%s`', this.constructor.name, name, target);
target = require(target);
assert(target.prototype instanceof CommonBin,
'command class should be sub class of common-bin');
}
this[COMMANDS].set(name, target);
}其中要求参数target也是某个子命令对应的文件的绝对路径。在进行条件判断之后直接使用set将该命令挂载在this[COMMANDS]变量中。遍历完成后this[COMMANDS]的值如下所示:
执行start()
最重要的start操作,追根溯源也是执行的common-bin里面的start(),start()里面主要是使用co包了一个generator函数,并且在generator函数中执行了this[DISPATCH],然后,重头戏来了,this[DISPATCH]的源码如下:
* [DISPATCH]() {
// define --help and --version by default
this.yargs
// .reset()
.completion()
.help()
.version()
.wrap(120)
.alias('h', 'help')
.alias('v', 'version')
.group([ 'help', 'version' ], 'Global Options:');
// get parsed argument without handling helper and version
const parsed = yield this[PARSE](this.rawArgv);
const commandName = parsed._[0]; //获取命令行参数
if (parsed.version && this.version) {
console.log(this.version);
return;
}
// if sub command exist
if (this[COMMANDS].has(commandName)) {
const Command = this[COMMANDS].get(commandName);
const rawArgv = this.rawArgv.slice();
rawArgv.splice(rawArgv.indexOf(commandName), 1);
debug('[%s] dispatch to subcommand `%s` -> `%s` with %j', this.constructor.name, commandName, Command.name, rawArgv);
const command = new Command(rawArgv);
yield command[DISPATCH]();
return;
}
// register command for printing
for (const [ name, Command ] of this[COMMANDS].entries()) {
this.yargs.command(name, Command.prototype.description || '');
}
debug('[%s] exec run command', this.constructor.name);
const context = this.context;
// print completion for bash
if (context.argv.AUTO_COMPLETIONS) {
// slice to remove `--AUTO_COMPLETIONS=` which we append
this.yargs.getCompletion(this.rawArgv.slice(1), completions => {
// console.log('%s', completions)
completions.forEach(x => console.log(x));
});
} else {
// handle by self
//对不同类型的函数进行调用(generator/promise)
yield this.helper.callFn(this.run, [ context ], this);
}
}首先会去执行yargs中一些方法,这里common-bin只是保留了yargs中一些对自己有用的方法,比如completion()、wrap()、alias()等,具体关于yargs的API可以移步这里。接着是执行this[PARSE]将rawArgv进行处理,处理后的parse对象结构如下:
接着就是对获取到的命令进行校验,如果存在this[COMMAND]对象中就执行。在当前例子中也就是去执行DevCommand,而由于DevCommand最终也是继承于common-bin的,然后执行 yield command[DISPATCH]();又是递归开始执行this[DISPATCH]了,直到所有的子命令递归完毕,才会去使用helper(common-bin中支持异步的关键所在)类继续执行每个command文件中的* run()函数。
egg-bin中的子命令文件
dev.js
作为在egg项目中本地开发最为重要的开发命令,dev.js无疑肩负着比较重要的职责。在dev.js中,主要是定义了一些默认端口号,以及入口命令等。* run()的源码如下:
* run(context) {
const devArgs = yield this.formatArgs(context);
const options = {
execArgv: context.execArgv,
env: Object.assign({ NODE_ENV: 'development' }, context.env),
};
debug('%s %j %j, %j', this.serverBin, devArgs, options.execArgv, options.env.NODE_ENV);
yield this.helper.forkNode(this.serverBin, devArgs, options);
}主要是对当前的上下文参数进行转化并对端口进行了一些处理,然后就开始调用helper的forkNode来执行入口命令,其中this.serverBin的值为:/Users/uc/Project/egg-example/node_modules/egg-bin/lib/start-cluster,下面的事情可以移步这里进行了解
debug.js
由上分析可知,DebugCommand继承于DevCommand,所以在constructor的时候就会去执行dev中的一些options,而且在debug.js中的* run()函数中直接调用的是dev.js中的formatArgs()参数处理。关键源码(有删减)如下:
* run(context) {
const proxyPort = context.argv.proxy;
context.argv.proxy = undefined;
const eggArgs = yield this.formatArgs(context);
//省略部分
// start egg
const child = cp.fork(this.serverBin, eggArgs, options);
// start debug proxy
const proxy = new InspectorProxy({ port: proxyPort });
// proxy to new worker
child.on('message', msg => {
if (msg && msg.action === 'debug' && msg.from === 'app') {
const { debugPort, pid } = msg.data;
debug(`recieve new worker#${pid} debugPort: ${debugPort}`);
proxy.start({ debugPort }).then(() => {
console.log(chalk.yellow(`Debug Proxy online, now you could attach to ${proxyPort} without worry about reload.`));
if (newDebugger) console.log(chalk.yellow(`DevTools → ${proxy.url}`));
});
}
});
child.on('exit', () => proxy.end());
}此处首先是开启egg,做的是和dev里面一样的东西。然后则是实例化InspectorProxy进行debug操作,在命令行打印出一行devtools的地址。
test.js
这个命令主要是用来运行egg项目中的*test文件的,也就是跑我们自己写的测试用例,关于如何写单元测试,可以移步单元测试,在这个文件,* run()形式也和上面类似,然后调用this.formatTestArgs(),formatTestArgs源码如下(有删减):
formatTestArgs({ argv, debug }) {
//省略
// collect require
let requireArr = testArgv.require || testArgv.r || [];
/* istanbul ignore next */
if (!Array.isArray(requireArr)) requireArr = [ requireArr ];
// clean mocha stack, inspired by https://github.com/rstacruz/mocha-clean
// [mocha built-in](https://github.com/mochajs/mocha/blob/master/lib/utils.js#L738) don't work with `[npminstall](https://github.com/cnpm/npminstall)`, so we will override it.
if (!testArgv.fullTrace) requireArr.unshift(require.resolve('../mocha-clean'));
requireArr.push(require.resolve('co-mocha'));
if (requireArr.includes('intelli-espower-loader')) {
console.warn('[egg-bin] don\'t need to manually require `intelli-espower-loader` anymore');
} else {
requireArr.push(require.resolve('intelli-espower-loader'));
}
testArgv.require = requireArr;
// collect test files
let files = testArgv._.slice();
if (!files.length) {
files = [ process.env.TESTS || 'test/**/*.test.js' ];
}
// expand glob and skip node_modules and fixtures
files = globby.sync(files.concat('!test/**/{fixtures, node_modules}/**/*.test.js'));
// auto add setup file as the first test file
const setupFile = path.join(process.cwd(), 'test/.setup.js');
if (fs.existsSync(setupFile)) {
files.unshift(setupFile);
}
testArgv._ = files;
// remove alias
testArgv.$0 = undefined;
testArgv.r = undefined;
testArgv.t = undefined;
testArgv.g = undefined;
return this.helper.unparseArgv(testArgv);
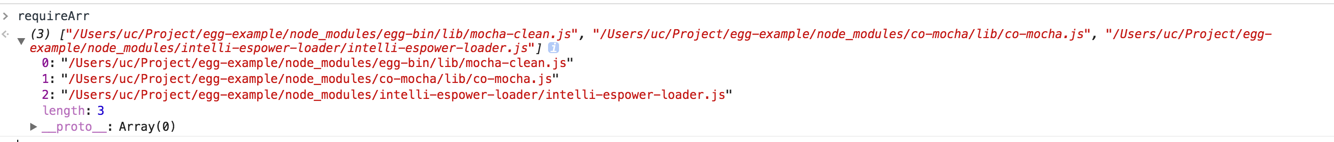
}代码里面的英文注释很清楚了,就是将单元测试的一些库push进requireArr中,requireArr的值如下:
其中mocha-clean是清除上一次mocha遗留的堆栈了,后面两个就是egg选用的测试框架和断言库了。
然后就是加载egg项目中除掉node_modules和fixtures里面的test文件,即项目层面的*.test.js,后面也就是开启进程来进行单元测试。
cov.js
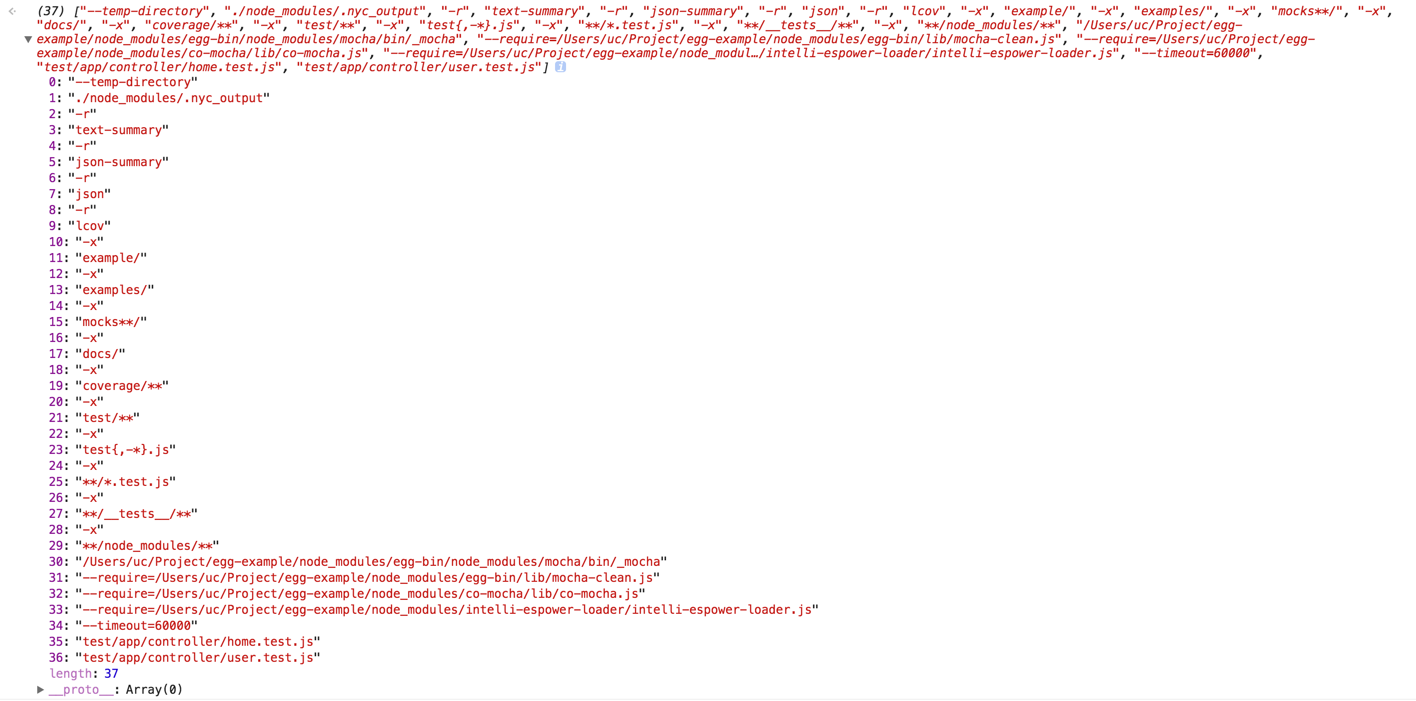
cov.js是用来测试代码覆盖率的。其中CovCommand继承自TestCommand,在cov的* run()中主要定义了字段,比如excludes、nycCli、coverageDir、outputDir等,根据英文命名也知道是什么意思了。然后继续执行getCovArgs是对参数的一些处理,源码也很简单,就不贴出来了,在getCovArgs中将上面test.js中的参数一起concat进来了,最后返回的covArgs的样子是这样的:
然后又是开启进程了。
autod.js和pkgfiles.js
这两个比较简单,这里就不赘述了
总结
整个egg-bin看下来,还是很厉害的,涉及的都是我之前没听过或者听过但是没用过的高大尚的东西,比如commander.js,yargs,mocha,co-mocha,power-assert,istanbuljs,nyc,所以分析起来还是比较吃力的。肯定也有很多分析不到位的地方或者有很多厉害的功能被一笔带过了,还望大神们指出~
感谢~~ 受益匪浅