Dead simple course schedule generator for University of Waterloo courses.
By using a SAT solver, this service can handle extremely complex schedules with ease. See the "Implementation notes" section for details.
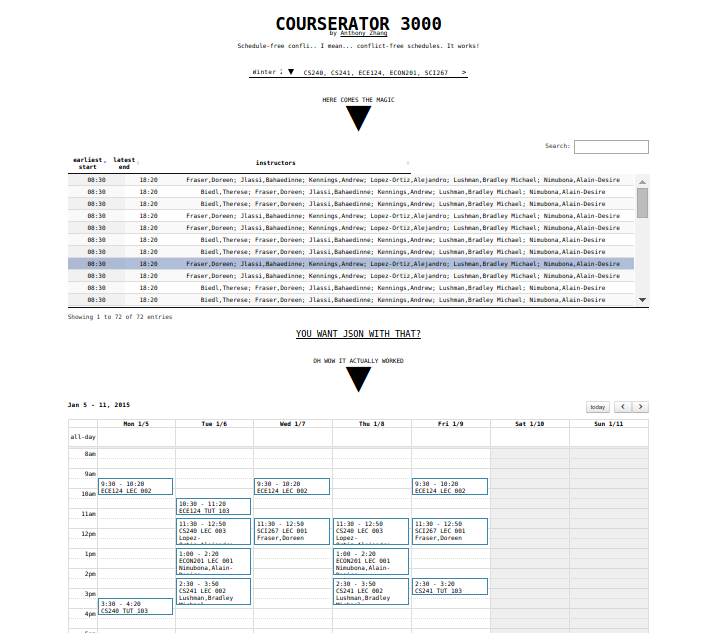
- Enter your courses in the provided field as a comma separated list. For example,
CS240, CS241, ECON201, ECE124, SCI267. - The schedules should now be displayed in a table below the entry field. Select a schedule from the list to view it.
- Selected schedules are displayed below the schedule table.
Is the site down? Want to set up your own Courserator instance? On Debian and Debian-like environments like Ubuntu, run the following commands:
git clone https://github.com/Uberi/COURSERATOR3000.git
cd COURSERATOR3000
python3 -m venv venv && ./venv/bin/activate # set up and enter virtual environment (optional)
./build.sh # install dependencies
python3 COURSERATOR3000/__init__.py # start server (press Ctrl + C to exit)
deactivate # exit virtual environment (optional)For "real" (production-grade) hosting, we'll be using Apache 2 and Flask over WSGI. These instructions target Ubuntu DigitalOcean Droplets, but should work on any Debian-based system.
Make sure you have all the dependencies:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install git python3 python3-pip apache2 libapache2-mod-wsgi-py3
Set up the application in the desired directory (in this case, /var/www):
cd /var/www
sudo git clone https://github.com/Uberi/COURSERATOR3000.git # if setting this up without an internet connection, just copy the folder containing this README to `/var/www` instead of using `git clone`
cd /var/www/COURSERATOR3000/
sudo bash build.sh
sudo chmod +x COURSERATOR3000.wsgi # this needs to be executable for Apache to run it
Now to configure Apache to recognize the site, open /etc/apache2/sites-available/COURSERATOR3000.conf and give it the following contents:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName anthony-zhang.me
ServerAdmin azhang9@gmail.com
WSGIScriptAlias / /var/www/COURSERATOR3000/COURSERATOR3000.wsgi
<Directory /var/www/COURSERATOR3000/COURSERATOR3000/>
Order allow,deny
Allow from all
</Directory>
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log
LogLevel warn
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log combined
</VirtualHost>
The site can now be enabled:
sudo a2enmod wsgi
sudo a2ensite COURSERATOR3000
sudo service apache2 reload
sudo service apache2 restart
Done! Now you can monitor it with tail -f /var/log/apache2/error.log.
The schedule conflict solver uses Pycosat as a constraint solver to directly calculate schedules with no conflicts. This eliminates a lot of the work in searching for non-conflicting schedules. For example, out of a search space of roughly 38,000 possible schedules in the code examples, we can solve for the 72 possibilities within 5 milliseconds.
Reducing the schedule conflicts to SAT clauses is simple. Let
To avoid multiple sections of the same course being selected, we specify the clauses
The conflict detector is responsible for detecting every possible pair of conflicting sections. This means that we run it once over all the sections and obtain a list of conflicting pairs, which is a good thing since its time complexity is pretty bad (but still polynomial). However, in practice it completes quickly enough, helped by the fact that we only need to run it once per query.
The conflict detector outputs pairs
Solving for all these clauses using the SAT solver, we obtain solutions of the form
Essentially:
- User requests courses to attempt to schedule.
- Course data for each course is requested from the uWaterloo Open Data API, computing the start/end times of each individual block for each section. A simple caching mechanism cuts down on unnecessary requests.
- Conflicts are detected by looking for overlapping blocks.
- Constraints are generated from the course sections and conflicts between them.
- Schedules are solved for using PycoSAT.
- Schedules are formatted and displayed to the user.
Copyright 2014-2017 Anthony Zhang.
This program is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License.
Basically, this means everyone is free to use, modify, and distribute the files, as long as these modifications are also licensed the same way.
Most importantly, the Affero variant of the GPL requires you to publish your modifications in source form, even if the program is hosted as a service, without being distributed.