If you use RIs-Calib in a scientific publication, please cite the following paper 👇:
- S. Chen, X. Li*, S. Li, Y. Zhou and S. Wang, RIs-Calib: An Open-Source Spatiotemporal Calibrator for Multiple 3D Radars And IMUs Based on Continuous-Time Estimation. arXiv:2408.02444 [cs.RO]. [paper-arXiv] [code] [video]
Todo List »
- support more radar ros messages.
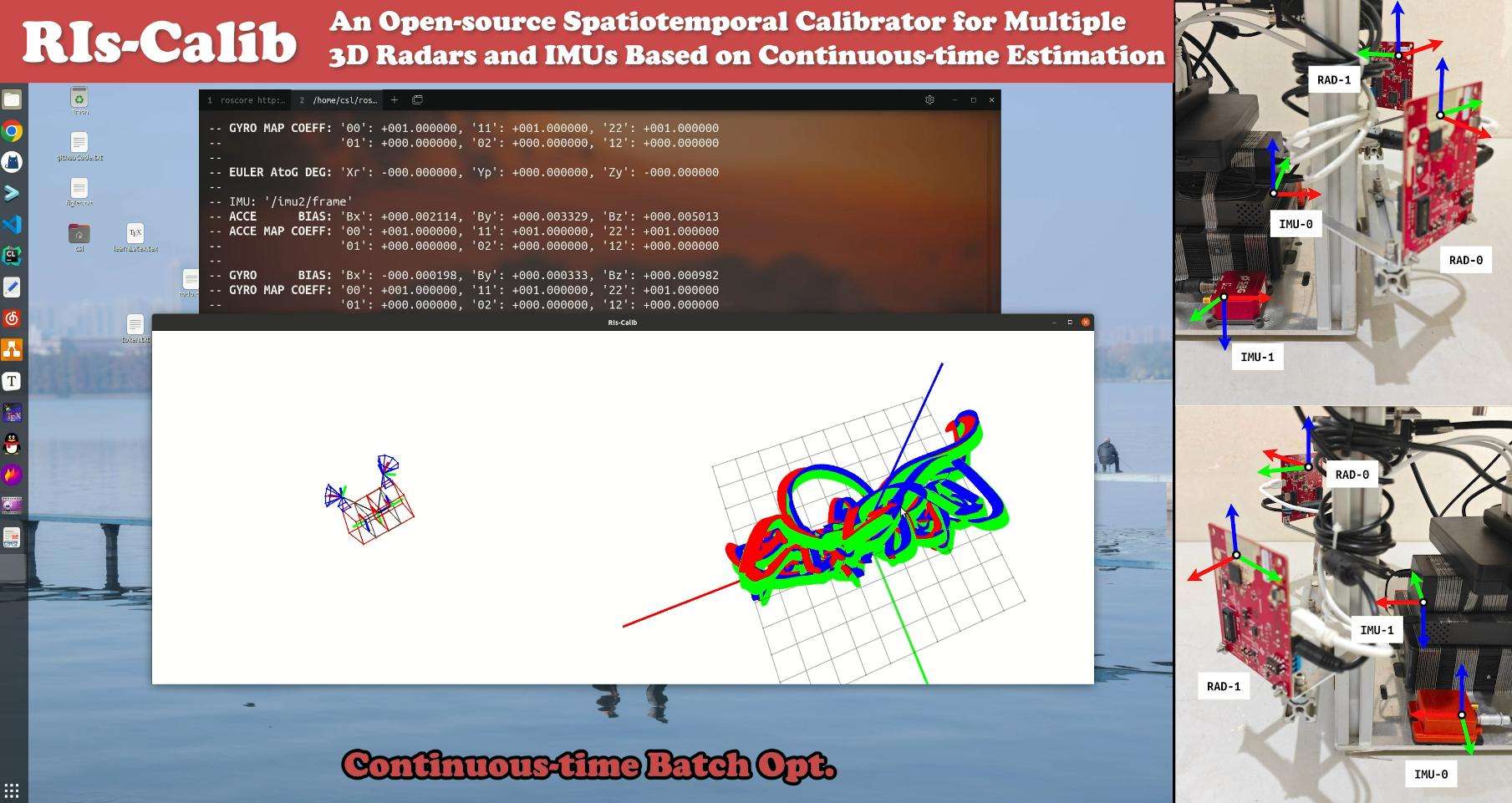
Aided inertial navigation system (INS), typically consisting of an inertial measurement unit (IMU) and an exteroceptive sensor, has been widely accepted and applied as a feasible solution for navigation. Compared with other aided INS, such as vision-aided INS and LiDAR-aided INS, radar-aided INS has better performance in adverse weather conditions such as fog and rain, due to the low-frequency signals radar utilizes. For such a radar-aided INS, accurate spatiotemporal transformation is a fundamental prerequisite to achieving optimal information fusion. In this paper, we present RIs-Calib: a spatiotemporal calibrator for multiple 3D radars and IMUs based on continuous-time estimation, which enables accurate spatial, temporal, and intrinsic calibration, and does not require any additional artificial infrastructure or prior knowledge.
Our accompanying videos are now available on YouTube (click below images to open) and Bilibili.
-
install
ROS1(Ubuntu 20.04 is suggested, Ubuntu 18.04 (ros melodic) is also available):sudo apt install ros-noetic-desktop-full echo "source /opt/ros/noetic/setup.bash" >> ~/.bashrc source ~/.bashrc
Requirements: ROS1 & C++17 Support
-
install
Ceres:see the
GitHubProfile of Ceres library, clone it, compile it, and install it. Make sure that the version ofCerescontains theManifoldmodule. (Ceresversion equal to 2.2.0 or higher than that) -
install
Sophus:see the
GitHubProfile of Sophus library, clone it, compile it, and install it. Set optionSOPHUS_USE_BASIC_LOGGINGon when compile (cmake) the Sophus library, this would avoid to involvefmtlogger dependency (as the followingspdlogwould use internalfmttoo, which may lead to conflict). -
install
magic-enum:see the
GitHubProfile of magic-enum library, clone it, compile it, and install it. -
install
Pangolin:see the
GitHubProfile of Pangolin library, clone it, compile it, and install it. -
install
cereal,yaml-cpp, andspdlog:sudo apt-get install libcereal-dev sudo apt-get install libyaml-cpp-dev sudo apt-get install libspdlog-dev
-
create a ros workspace if needed and clone
RIs-Calibtosrcdirectory asris_calib:mkdir -p ~/RIs-Calib/src cd ~/RIs-Calib/src git clone --recursive https://github.com/Unsigned-Long/RIs-Calib.git ris_calib
change directory to '
ris_calib', and run 'build_thirdparty.sh'.cd ris_calib chmod +x build_thirdparty.sh ./build_thirdparty.shthis would build '
tiny-viewer' and 'ctraj' libraries. -
Prepare for thirdparty ros packages:
clone ros packages '
ainstein_radar', 'ti_mmwave_rospkg', 'serial', 'sbg_ros_driver' to 'ris_calib/..' (directory at the same level asris_calib):cd .. git clone https://github.com/AinsteinAI/ainstein_radar.git git clone https://github.com/Unsigned-Long/ti_mmwave_rospkg.git git clone https://github.com/wjwwood/serial.git git clone https://github.com/SBG-Systems/sbg_ros_driver.gitthen change directory to the ros workspace to build these packages:
cd .. catkin_make -DCATKIN_WHITELIST_PACKAGES="ainstein_radar;ti_mmwave_rospkg;serial;sbg_driver"
Note that these packages will depend on many other ros packages, you need to install them patiently.
-
compile
RIs-Calib:catkin_make -DCATKIN_WHITELIST_PACKAGES=""
datasets, launch, result visualization
datasets, launch, result visualization
Find a configure file named config-real-world.yaml in /ris_calib/config or from the open-source datasets below:
# Google Drive
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1_SPdmBnWIJTYyOIkyS0StbPMGVLdV_fw?usp=drive_linkThen change the fields in the configure files to be compatible with your dataset (there are detailed comments for each field). You only need to change a few fields related to io (input and output), perhaps some additional fields related to optimization.
Then give the path of your configuration file to the launch file of RIs-Calib named ris-calib-prog.launch in folder ris_calib/launch, Then, we launch 'RIs-Calib':
roslaunch ris_calib ris-calib-prog.launchThe corresponding results would be output to the directory you set in the configure file.
Attention: Sufficiently excited motion is required for accurate spatiotemporal calibration in RIs-Calib!