🚀 A practical and imaginary Modular Monolith for implementing an infrastructure for up and running Modular system with the latest technology and architecture like Vertical Slice Architecture, Event Sourcing, CQRS, DDD, gRpc, MongoDB, RabbitMq, Masstransit in .Net 8.
💡 This project is not business-oriented and most of my focus was in the thechnical part for implement a Modular system with a sample project. In this project I implemented some concept in Modular Monolith like Inmemory Broker, Tracing, Event Driven Architecture, Vertical Slice Architecture, Event Sourcing, CQRS, DDD and gRpc.
- The Goals of This Project
- Plan
- Technologies - Libraries
- The Domain and Bounded Context - Service Boundary
- Structure of Project
- Prerequisites
- How to Run
- Documentation Apis
- Support
- Contribution
- ❇️ Using
Vertical Slice Architecturefor architecture level. - ❇️ Using
Domain Driven Design (DDD)to implement all business processes in modules. - ❇️ Using
InMememoryBrokeron top ofCapforEvent Driven Architecturebetween our modules. - ❇️ Using
Inbox Patternon top ofCapfor ensuring message idempotency for receiver andExactly once Delivery. - ❇️ Using
Outbox Patternon top ofCapfor ensuring no message is lost and there is atLeast One Delivery. - ❇️ Using
CQRSimplementation withMediatRlibrary. - ❇️ Using
SqlServerfor database in our modules. - ❇️ Using
Event Storeforwrite sideof Booking-Module to store allhistorical stateof aggregate. - ❇️ Using
Unit Testing,Integration Testingfor testing level. - ❇️ Using
Fluent Validationand aValidation Pipeline Behaviouron top ofMediatR. - ❇️ Using
Docker-ComposeandKubernetesfor our deployment mechanism. - ❇️ Using
OpenTelemetryfor distributed tracing. - ❇️ Using
IdentityServerfor implementation authentication and authorization base onOpenID-ConnectandOAuth2.
🌀This project is a work in progress, new features will be added over time.🌀
I will try to register future goals and additions in the Issues section of this repository.
High-level plan is represented in the table
| Feature | Status |
|---|---|
| API | Completed ✔️ |
| Identity Module | Completed ✔️ |
| Flight Module | Completed ✔️ |
| Passenger Module | Completed ✔️ |
| Booking Module | Completed ✔️ |
| Building Blocks | Completed ✔️ |
- ✔️
.NET 6- .NET Framework and .NET Core, including ASP.NET and ASP.NET Core - ✔️
MVC Versioning API- Set of libraries which add service API versioning to ASP.NET Web API, OData with ASP.NET Web API, and ASP.NET Core - ✔️
EF Core- Modern object-database mapper for .NET. It supports LINQ queries, change tracking, updates, and schema migrations - ✔️
Cap- An EventBus with local persistent message functionality for system integration in SOA or Microservice architecture. - ✔️
MediatR- Simple, unambitious mediator implementation in .NET. - ✔️
FluentValidation- Popular .NET validation library for building strongly-typed validation rules - ✔️
Swagger & Swagger UI- Swagger tools for documenting API's built on ASP.NET Core - ✔️
Serilog- Simple .NET logging with fully-structured events - ✔️
Polly- Polly is a .NET resilience and transient-fault-handling library that allows developers to express policies such as Retry, Circuit Breaker, Timeout, Bulkhead Isolation, and Fallback in a fluent and thread-safe manner - ✔️
Scrutor- Assembly scanning and decoration extensions for Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection - ✔️
Opentelemetry-dotnet- The OpenTelemetry .NET Client - ✔️
DuendeSoftware IdentityServer- The most flexible and standards-compliant OpenID Connect and OAuth 2.x framework for ASP.NET Core - ✔️
EasyCaching- Open source caching library that contains basic usages and some advanced usages of caching which can help us to handle caching more easier. - ✔️
Mapster- Convention-based object-object mapper in .NET. - ✔️
Hellang.Middleware.ProblemDetails- A middleware for handling exception in .Net Core - ✔️
IdGen- Twitter Snowflake-alike ID generator for .Net - ✔️
MagicOnion- gRPC based HTTP/2 RPC Streaming Framework for .NET, .NET Core and Unity. - ✔️
EventStore- The open-source, functional database with Complex Event Processing.
-
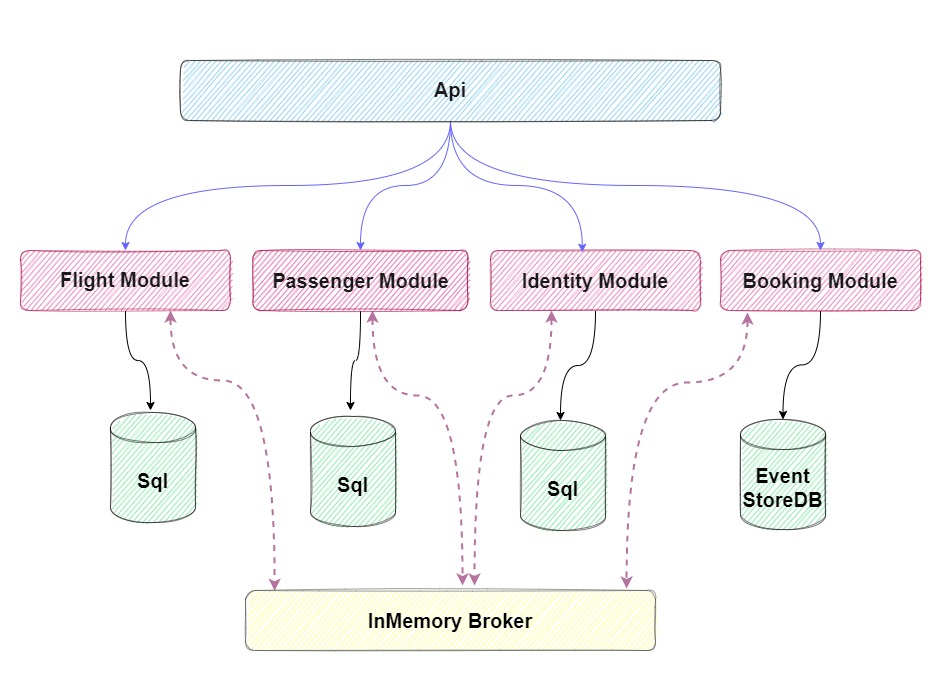
Identity Module: The Identity Service is a bounded context for the authentication and authorization of users using Identity Server. This service is responsible for creating new users and their corresponding roles and permissions using .Net Core Identity and Jwt authentication and authorization. -
Flight Module: The Flight Service is a bounded contextCRUDservice to handle flight related operations. -
Passenger Module: The Passenger Service is a bounded context for managing passenger information, tracking activities and subscribing to get notification for out of stock products. -
Booking Module: The Booking Service is a bounded context for managing all operation related to booking ticket. -
Api: The Api Project use for hosting all modules in one place.
Note: We don't have separated API project for each module because they are not microervice and shouldn't host separately, so for hosting all modules, we just use one Api project.
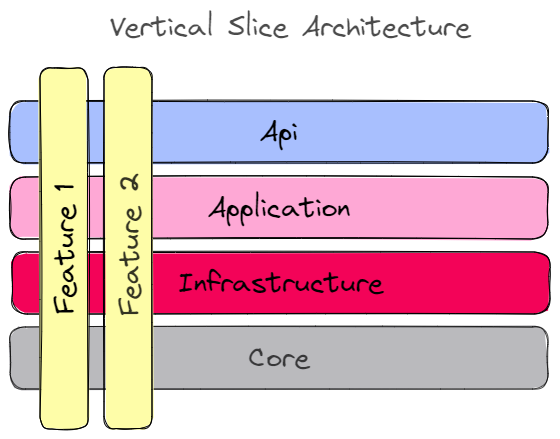
In this project I used a mix of clean architecture, vertical slice architecture and I used feature folder structure to structure my files.
We have a separate module (IdentityServer) for authentication and authorization of each request. Once signed-in users are issued a JWT token. This token is used by other module to validate the user, read claims and allow access to authorized/role specific endpoints.
I used MagicOnion for sync communication between our modules. This framework is based on gRPC, which is a fast and compact binary network transport for HTTP/2. However, unlike plain gRPC, it treats C# interfaces as a protocol schema, enabling seamless code sharing between C# projects without .proto (Protocol Buffers IDL).
I used In-Memory Queue as my MessageBroker for async communication between modules using the eventual consistency mechanism. Each modules uses Cap to interface with In-Memory Queue for easy use messaging, availability, reliability, etc.
modules are event based which means they can publish and/or subscribe to any events occurring in the setup. By using this approach for communicating between modules, each module does not need to know about the other module or handle errors occurred in other modules.
I treat each request as a distinct use case or slice, encapsulating and grouping all concerns from front-end to back.
When adding or changing a feature in an application in n-tire architecture, we are typically touching many "layers" in an application. We are changing the user interface, adding fields to models, modifying validation, and so on. Instead of coupling across a layer, we couple vertically along a slice. We minimize coupling between slices, and maximize coupling in a slice.
With this approach, each of our vertical slices can decide for itself how to best fulfill the request. New features only add code, we're not changing shared code and worrying about side effects.
Instead of grouping related action methods in one controller, as found in traditional ASP.net controllers, I used the REPR pattern. Each action gets its own small endpoint, consisting of a route, the action, and an IMediator instance (see MediatR). The request is passed to the IMediator instance, routed through a Mediatr pipeline where custom middleware can log, validate and intercept requests. The request is then handled by a request specific IRequestHandler which performs business logic before returning the result.
The use of the mediator pattern in my controllers creates clean and thin controllers. By separating action logic into individual handlers we support the Single Responsibility Principle and Don't Repeat Yourself principles, this is because traditional controllers tend to become bloated with large action methods and several injected Services only being used by a few methods.
I used CQRS to decompose my features into small parts that makes our application:
- Maximize performance, scalability and simplicity.
- Easy to maintain and add features to. Changes only affect one command or query, avoiding breaking changes or creating side effects.
- It gives us better separation of concerns and cross-cutting concern (with help of mediatr behavior pipelines), instead of bloated service classes doing many things.
Using the CQRS pattern, we cut each business functionality into vertical slices, for each of these slices we group classes (see technical folders structure) specific to that feature together (command, handlers, infrastructure, repository, controllers, etc). In our CQRS pattern each command/query handler is a separate slice. This is where you can reduce coupling between layers. Each handler can be a separated code unit, even copy/pasted. Thanks to that, we can tune down the specific method to not follow general conventions (e.g. use custom SQL query or even different storage). In a traditional layered architecture, when we change the core generic mechanism in one layer, it can impact all methods.
Run the following commands for Config SSL in your system
dotnet dev-certs https -ep %USERPROFILE%\.aspnet\https\aspnetapp.pfx -p {password here}
dotnet dev-certs https --trustNote: for running this command in
powershelluse$env:USERPROFILEinstead of%USERPROFILE%
We have a separate Docker file for setting up and running the infrastracture.yaml independently.
docker-compose -f ./deployments/docker-compose/infrastracture.yaml up -dTODO 👷♂️ Deployment App in Docker-Compose
To build all microservices, run this command in the root of the project:
dotnet buildTo run each microservice, run this command in the root of the Api folder of each microservice where the csproj file is located:
dotnet runTo test all microservices, run this command in the root of the project:
dotnet testEach microservice has a Swagger OpenAPI. Browse to /swagger for a list of endpoints.
As part of API testing, I created the booking.rest file which can be run with the REST Client VSCode plugin.
If you like my work, feel free to:
- ⭐ this repository. And we will be happy together :)
Thanks a bunch for supporting me!
Thanks to all contributors, you're awesome and this wouldn't be possible without you! The goal is to build a categorized community-driven collection of very well-known resources.
Please follow this contribution guideline to submit a pull request or create the issue.
- https://github.com/jbogard/ContosoUniversityDotNetCore-Pages
- https://github.com/kgrzybek/modular-monolith-with-ddd
- https://github.com/oskardudycz/EventSourcing.NetCore
- https://github.com/thangchung/clean-architecture-dotnet
- https://github.com/jasontaylordev/CleanArchitecture
This project is made available under the MIT license. See LICENSE for details.