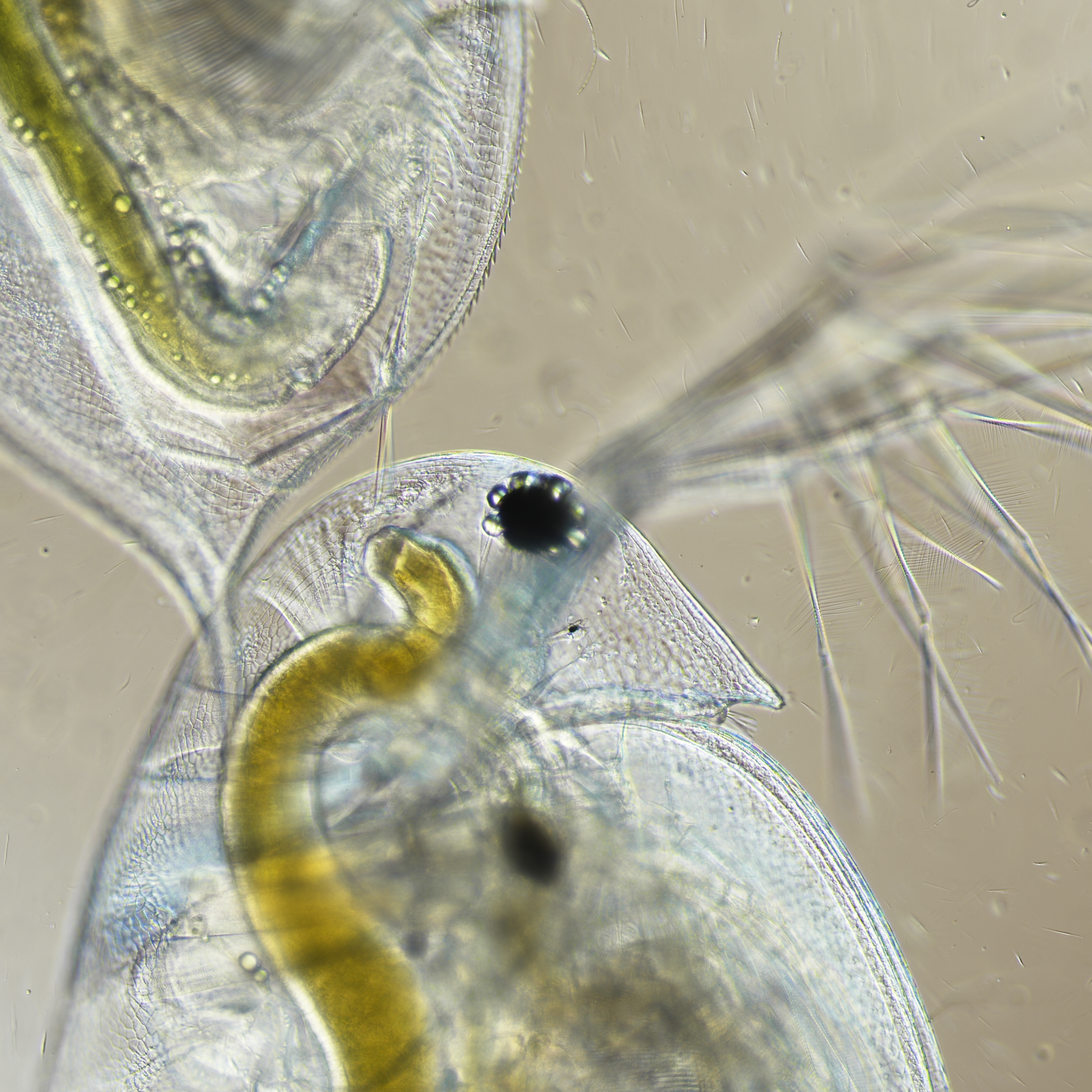
Photo Credit: Angelea Belfiore and Matt Gladfelter
Daphnia species are well-suited for studying local adaptation and evolutionary responses to stress(ors) including those caused by algal blooms. Algal blooms, characterized by an overgrowth (bloom) of cyanobacteria, are detrimental to the health of aquatic and terrestrial members of freshwater ecosystems. Some strains of Daphnia pulicaria have demonstrated resistance to toxic algae and the ability to mitigate toxic algal blooms. Understanding the genetic mechanism associated with this toxin resistance requires adequate genomic resources. Using whole-genome sequence data mapped to the Daphnia pulex reference genome (PA42), we present reference-guided draft assemblies from one tolerant and one sensitive strain of D. pulicaria, Wintergreen-6 (WI-6), and Bassett-411 (BA-411), respectively. Assessment of the draft assemblies reveal low contamination levels, and high levels (95%) of genic content. Reference scaffolds had coverage breadths of 98.9–99.4%, and average depths of 33X and 29X for BA-411 and WI-6, respectively. Within, we discuss caveats and suggestions for improving these draft assemblies. These genomic resources are presented with a goal of contributing to the resources necessary to understand the genetic mechanisms and associations of toxic prey resistance observed in this species.
Amanda D Clark, Bailey K Howell, Alan E Wilson, Tonia S Schwartz, Draft genomes for one Microcystis-resistant and one Microcystis-sensitive strain of the water flea, Daphnia pulicaria, G3 Genes|Genomes|Genetics, 2021;, jkab266, https://doi.org/10.1093/g3journal/jkab266
This repository contains all scripts used to perform reference-guided genomic assembly from paired end sequence reads and screen for contaminants as was done in Clark et al. 2021. These scripts are designed to assemble the genomes for two strains of Daphnia pulicaria using Daphnia pulex (PA42) as a reference. This repository presents a simplified workflow/pipeline to run these analyses on a supercomputer and are separated into two parts, reference-guided genomic assembly and contamination screening.
To use these scripts, you will need to update the header information in the array scripts based on your HPC (see HPC Scheduler Modifications below). Certain regions of the code need to be specified for the user and their system. The main regions of the code that require these updates are the variables within the array scripts (which can be fitted for a single job by hard-coding the sm variable). The save directory (sd) for the additional script will also need an update of the path.
- Reference-Guided Genome Assembly Pipeline
- refg_assem_array.sh
- array script for running reference guided assembly
- support scripts:
- run_fastqscreen.sh
- running
fastqscreenfor quality control
- running
- run_indexgen.sh
- indexing the reference genome
- run_bwa.sh
- mapping using Burrows-Wheeler Aligner (
bwa)
- mapping using Burrows-Wheeler Aligner (
- run_GATK.sh
- performing local realignment, identifying SNPs and INDELs, and filtering identified variants with
gatk
- performing local realignment, identifying SNPs and INDELs, and filtering identified variants with
- run_consensus.sh
- inserting SNPs into the reference genome to create consensus sequence and masking zero coverage and INDEL regions
- run_fastqscreen.sh
- refg_assem_array.sh
- Blobtools Contamination Screening Pipeline
- blobtools_array.sh
- array script for screening for contaminants
- support scripts:
- download_ncbi.sh
- downloads NBCI databases for contaminant identification
- run_nrdmnd.sh
- runs
diamond blastxagainst the NCBI NR database (alternativelyrun_ntdcblast.shusesblastntagainst the NCBI NT database)
- runs
- run_blobtaxify.sh
- runs
blobtools taxifyto add TaxIDs to blast output from NCBI
- runs
- run_blobfin.sh
- runs
blobtools createand all downstream commands to produce all plot outputs
- runs
- download_ncbi.sh
- blobtools_array.sh
- Additional Scripts
- download_blastdb.sh
- script for downloading nr database
- download_blastdb.sh
PBS and SLURM schedulers use slightly different commands to run jobs. These scripts were run on both schedulers. Below are example headers for bash scripts that demonstrate the subtle differences in commands between the two.
#PBS -M usr@host.edu