This project consists of a template Android application and a set of Colab notebooks that can be used to build a custom Android computer vision application. Minor modifications to the Android application need to be made in Java to include the custom trained model, which can be generated using the provided set of Jupyter Notebooks.
The Jupyter Notebooks are written in Python and can be opened in Google Colab or Anaconda. The notebooks are written to download datasets from Kaggle using the Kaggle API. This allows the user to have access to thousands of datasets with minimal changes to the original code. Due to the time it takes to train a custom model, the notebooks are configured to automatically save the models in Google Drive once training is complete.
- Android Studio -> Android IDE
- Google Colab -> Cloud IDE - Python3
- Google Drive -> Model Storage
- Android phone -> Test device (API 21 or greater)
# Git the project
git clone https://github.com/af001/vision.git
# Connect Android phone to adb
apt install adb-tools
adb devices
# Install debug Apk on Android Phone
gradle installDebug
# Open the app - alt: Click app icon on the phone
adb shell am start -n com.msds.vision/.MainActivityThe first thing you need is to identify the dataset you intend on using. The easiest place to find datasets if through Kaggle. This is the preferred method due to the notebooks already being setup to integrate with the Kaggle API. Users could upload their datasets to Kaggle for easier long-term integration, if desired.
Once a Kaggle dataset is identified, look at the dataset to see if it includes annotations. Annotations are normally created with tools such as LabelImg and they are often used to create labels for new datasets. This means that each image contains a label as well as a bounding box with coordinates of the object in the image. If annotations are present, then use the with_annotations template under notebooks. If the dataset is a directory containing sub-directories of images, then the sub-directories will act as the labels and the template notebook will be the without_annotations notebook.
Open the notebook that you identified as a starting point and click the "Open with Colab" link at the top. This will open the notebook in a user's personal Google Colab environment. The first thing to do once the notebook is important into a user's personal Colab environment is set the runtime. This can be done by clicking Runtime -> Change runtime type and setting Hardware Accelerator -> GPU then clicking Ok.
The next step is to change the dataset. The API command to download the dataset from Kaggle can be obtained by going to the Kaggle website and clicking the Copy API command button as seen in the screenshot below:
The three lines that need to be modified in the notebook are:
# Download the dataset
!kaggle datasets download -d jessicali9530/stanford-dogs-dataset
# Unzip the dataset
!unzip stanford-dogs-dataset.zip
# Cleanup
!rm stanford-dogs-dataset.zipThe next step is to obtain a Kaggle API key. This can be achieved on the Kaggle website under My Account -> Create New API Token.
This will download a file called kaggle.json to your computer. Prior to starting to train the model, it is recommended to change the URLS for each test image at the bottom of the notebook. These URLs should point to images that your model can classify, and can be identified by searching for download_and_predict. Once complete, it is time to start training the custom model. To begin, click Runtime -> Run all. As the Python libraries are imported, users will be asked to link their Colab account to their Google account. Click the link for the authorization code and paste the code into Google Colab. The next part will ask to upload you Kaggle API token. Click the upload button and select the kaggle.json file that was previously downloaded to your computer.
The notebooks provide metrics that can be used to determine the accuracy, precision, and recall of you trained model. Ideally, the model accuracy will be above 70% with a loss below 1.5. An example of a model that generalized will look similar to the following images. This model does not show signs of over/underfitting and is capable of classifying dog breeds with a relatively high degree of accuracy. The notebook also provides a list of classes that are commonly misclassified.
Training loss and accuracy
Accuracy, precision, recall
Common misclassifications
Predictions - Note: These URLs should point to the user's test images and should not be images contained in the dataset.
After training, the models will be zipped and placed in the users Google Drive. The zip will contain images from training, model weights, a saved copy of the model, and models converted to tflite format.
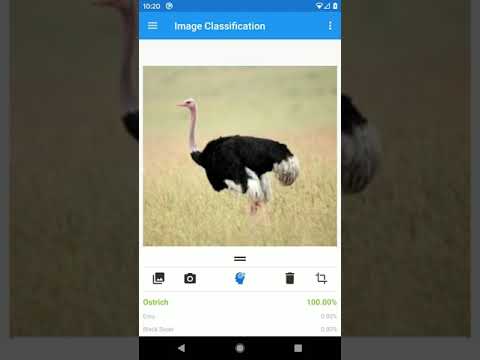
After the new models have been trained, both .tflite files from models.zip will be imported into the Android application assets folder so they can be used by the app.
Open Android Studio and import the project from this repo.