Size Limit is a performance budget tool for JS. It checks every commit on CI, calculates the real cost of your JS for end-users and throws an error if the cost exceeds the limit.
- Size Limit calculates the time it would take a browser to download and execute your JS. Time is a much more accurate and understandable metric compared to the size in bytes.
- Size Limit calculations include all dependencies and polyfills used in your JS.
- Add Size Limit to Travis CI, Circle CI, or another CI system to know if a pull request adds a massive dependency.
- Size Limit is modular to fits different use cases like big JS application with own bundler or small npm libraries with many files.
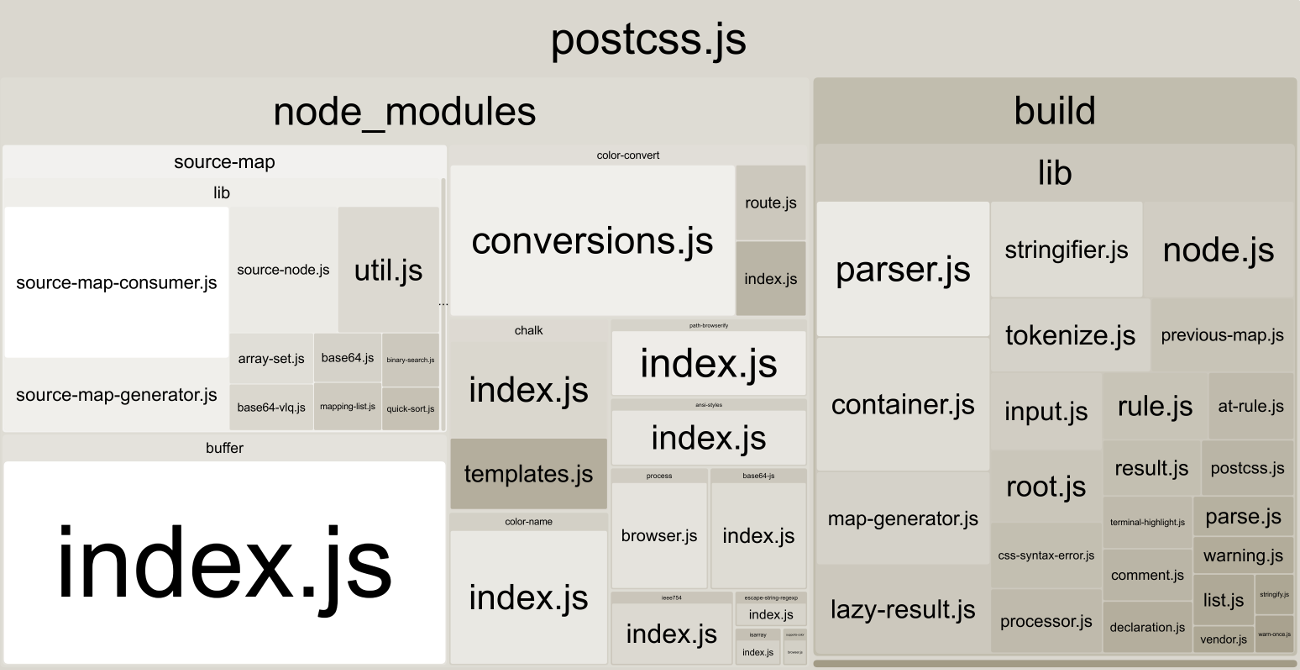
With --why, Size Limit can tell you why your library has this size
and show the real cost of all your internal dependencies.
- MobX
- Material-UI
- Autoprefixer
- PostCSS reduced 25% of the size.
- Browserslist reduced 25% of the size.
- EmojiMart reduced 20% of the size
- nanoid reduced 33% of the size.
- React Focus Lock reduced 32% of the size.
- Logux reduced 90% of the size.
- Size Limit contains CLI tool, 3 plugins (
file,webpack,time) and 3 plugin presets for popular cases (app,big-lib,small-lib). CLI tool finds plugins inpackage.jsonand load the config. - If you use
webpackplugin, Size Limit bundles JS files into the single file. It is important to track dependencies and webpack polyfills. It is also useful for small libraries with many small files and without bundler. webpackplugin creates an empty webpack project, adds your library and looks for the bundle size difference.timeplugin compares current machine performance with low-priced Android devices to calculate CPU throttling rate.- Then
timeplugin runs headless Chrome (or desktop Chrome if it available) to tracks the time using by browser to compile and execute JS.
Application has its own bundler and sends JS bundle directly to a client (without publish it to npm).
Show instructions
-
Install preset:
$ npm install --save-dev @size-limit/preset-app
-
Add
size-limitsection topackage.jsonandsizescript:+ "size-limit": [ + { + "path": "dist/app-*.js" + } + ], "scripts": { "build": "webpack ./webpack.config.js", + "size": "npm run build && size-limit", "test": "jest && eslint ." }
-
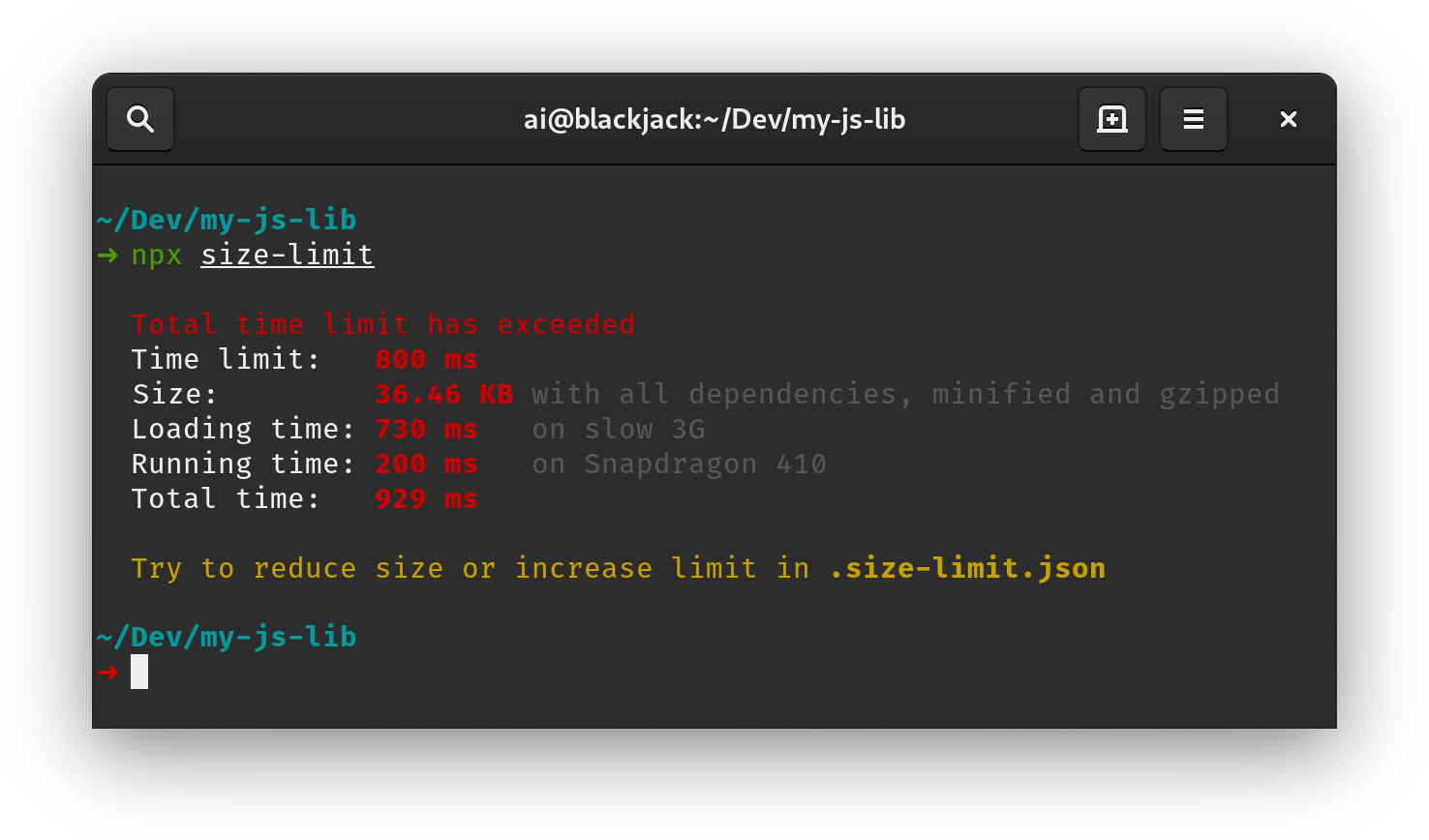
Here’s how you can get the size for your current project:
$ npm run size Package size: 30.08 KB with all dependencies, minified and gzipped Loading time: 602 ms on slow 3G Running time: 214 ms on Snapdragon 410 Total time: 815 ms
-
Now, let’s set the limit. Add 25% for current total time and use that as a limit in your
package.json:"size-limit": [ { + "limit": "1 s", "path": "dist/app-*.js" } ], -
Add the
sizescript to your test suite:"scripts": { "build": "webpack ./webpack.config.js", "size": "npm run build && size-limit", - "test": "jest && eslint ." + "test": "jest && eslint . && npm run size" } -
If you don’t have a continuous integration service running, don’t forget to add one — start with Travis CI.
JS libraries > 10 KB. React is a good example.
Show instructions
-
Install preset:
$ npm install --save-dev @size-limit/preset-big-lib
-
Add
size-limitsection topackage.jsonandsizescript:+ "size-limit": [ + { + "path": "dist/react.production-*.js" + } + ], "scripts": { "build": "webpack ./scripts/rollup/build.js", + "size": "npm run build && size-limit", "test": "jest && eslint ." }
-
Here’s how you can get the size for your current project:
$ npm run size Package size: 30.08 KB with all dependencies, minified and gzipped Loading time: 602 ms on slow 3G Running time: 214 ms on Snapdragon 410 Total time: 815 ms
-
Now, let’s set the limit. Add 25% for current total time and use that as a limit in your
package.json:"size-limit": [ { + "limit": "1 s", "path": "dist/react.production-*.js" } ], -
Add the
sizescript to your test suite:"scripts": { "build": "rollup ./scripts/rollup/build.js", "size": "npm run build && size-limit", - "test": "jest && eslint ." + "test": "jest && eslint . && npm run size" } -
If you don’t have a continuous integration service running, don’t forget to add one — start with Travis CI.
JS libraries < 10 KB. Nano ID or Storeon could be a good example.
Show instructions
-
First, install
size-limit:$ npm install --save-dev @size-limit/preset-small-lib
-
Add
size-limitsection topackage.jsonandsizescript:+ "size-limit": [ + { + "path": "index.js" + } + ], "scripts": { + "size": "size-limit", "test": "jest && eslint ." }
-
Here’s how you can get the size for your current project:
$ npm run size Package size: 177 B with all dependencies, minified and gzipped
-
If your project size starts to look bloated, run
--whyfor analysis:$ npm run size -- --why
-
Now, let’s set the limit. Determine the current size of your library, add just a little bit (a kilobyte, maybe) and use that as a limit in your
package.json:"size-limit": [ { + "limit": "9 KB", "path": "index.js" } ], -
Add the
sizescript to your test suite:"scripts": { "size": "size-limit", - "test": "jest && eslint ." + "test": "jest && eslint . && npm run size" } -
If you don’t have a continuous integration service running, don’t forget to add one — start with Travis CI.
Size Limits supports three ways to define config.
-
size-limitsection topackage.json:"size-limit": [ { "path": "index.js", "limit": "500 ms" } ]
-
or separated
.size-limit.jsonconfig file:[ { "path": "index.js", "limit": "500 ms" } ]
-
or more flexible
.size-limit.jsconfig file:module.exports = [ { path: "index.js", limit: "500 ms" } ]
Each section in the config could have options:
- path: relative paths to files. The only mandatory option.
It could be a path
"index.js", a pattern"dist/app-*.js"or an array["index.js", "dist/app-*.js", "!dist/app-exclude.js"]. - entry: when using a custom webpack config, a webpack entry could be given. It could be a string or an array of strings. By default, the total size of all entry points will be checked.
- limit: size or time limit for files from
pathoption. It should be a string with a number and unit. Format:100 B,10 KB,500 ms,1 s. - name: the name of this section. It will be useful only if you have multiple sections.
- webpack: with
falsewill disable webpack. - running: with
falsewill disable calculating running time. - gzip: with
falsewill disable gzip compression. - config: a path to custom webpack config.
- ignore: an array of files and dependencies to ignore from project size.
If you use Size Limit to track the size of CSS files, only set webpack: false.
Otherwise, you will get wrong numbers, because of webpack inserts style-loader
runtime (≈2 KB) into the bundle.