DynamoDB global tables is a feature that provides fully-managed, multi-active, multi-Region replication, making it easier to build highly available applications. A Regional DynamoDB table is converted to a global table by adding one or more replicas.
If you use CloudFormation to manage your DynamoDB tables, you cannot simply edit an existing Regional table that uses the AWS::DynamoDB::Table resource to a AWS::DynamoDB::GlobalTable resource, as CloudFormation will process these as two different resources, resulting in deletion of the AWS::DynamoDB::Table resource and creation of a new (empty) AWS::DynamoDB::GlobalTable resource. See the AWS:DynamoDB:GlobalTable documentation for more information.
This guide contains the steps necessary to safely convert your Regional DynamoDB table to a global table when using CloudFormation to manage your DynamoDB resources.
This repository details the steps required to change the CloudFormation resource type of a DynamoDB table (with provisioned capacity mode and auto-scaling enabled) from AWS::DynamoDB::Table to AWS::DynamoDB::GlobalTable. It does so by executing the process on a test table you create, so you can understand the steps required while minimizing risk. The instructions, scripts and templates provided here are intended as guides for you to create your own procedure for your tables.
This example uses the AWS-provided auto-scaling role: aws-service-role/dynamodb.application-autoscaling.amazonaws.com/AWSServiceRoleForApplicationAutoScaling_DynamoDBTable.
You can choose to use another role you've defined, but it must have sufficient permissions to execute all tasks.
You can find more information about each step (in the form of comments) in the CloudFormation templates in this repository. It is important to read the comments carefully to understand the changes happening in each step, so you understand each change and its effects changes when performing the process on existing tables. In this example, us-east-1 is used as the primary region and us-east-2 will serve as the replica region.
-
If your Regional table is configured to use provisioned capacity mode, auto-scaling for write capacity must be enabled for your table and any GSIs before it can be converted to a global table.
-
You must have sufficient permissions to run these commands in your own AWS account in order to complete the process.
- If DynamoDB streams is not enabled for your table, it will automatically be enabled as part of the conversion to global table.
- The resulting global table resource (
AWS::DynamoDB::GlobalTable) will be version 2019.11.21.
It is critical to complete each step successfully before performing the next step. Failure to wait for a step to complete may result in unpredictable outcomes.
Review the AWS resources in the file cloudformation-1-initial.yaml.
Using an AWS profile with sufficient permissions, run the following CLI command to deploy the example stack named cfn-demo-dynamodb.
aws cloudformation deploy \
--template-file cloudformation-1-initial.yaml \
--stack-name cfn-demo-dynamodb \
--region us-east-1 \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM \
--parameter-overrides DBTableName=CfnTestPrices
This creates a DynamoDB table named CfnTestPrices with the partition key of price and a sort key ofdate.
Notice that StreamSpecification is set to StreamViewType: KEYS_ONLY for the table.
If DynamoDB streams is not enabled for the table, you will receive an error message when creating a replica in later steps.
After the stack is deployed, open the AWS console for CloudFormation at https://console.aws.amazon.com/cloudformation, and find the stack called cfn-demo-dynamodb.
Check that you are in the same AWS Region, us-east-1, as the stack you deployed.
Clicking on the name of the stack cfn-demo-dynamodb, shows the details of deployed AWS resources in this stack.
You will be asked later to review the details of this stack as well as created change sets.
Make the following settings changes in cloudformation-2-deletionPolicy.yaml. These changes are required to safely execute this step:
-
Set
DeletionPolicy: Retainfor theAWS::DynamoDB::Table,AWS::ApplicationAutoScaling::ScalableTarget, andAWS::ApplicationAutoScaling::ScalingPolicyresources. This is important to protect the resources from deletion. Later, you will remove these resources from the template so they are no longer managed by CloudFormation. This setting ensures that these resources will not be deleted when performing that step. -
Add
DeletionProtectionEnabled: trueto the DynamoDB table resource in the CloudFormation template. Deletion protection was released in March of 2023 and ensures that a table can not be deleted without the proper IAM permissions. TheDeletionProtectionEnabledattribute will be moved to the replica specification in step 4 when the resource type changes fromAWS::DynamoDB::TabletoAWS::DynamoDB::GlobalTable.
The following example shows the changes made so far to protect the table and auto-scaling resources from deletion:
TableReadCapacityScalableTarget:
Type: AWS::ApplicationAutoScaling::ScalableTarget
DeletionPolicy: Retain
...
TableWriteScalingPolicy:
Type: AWS::ApplicationAutoScaling::ScalingPolicy
DeletionPolicy: Retain
...
CfnTestPrices:
Type: AWS::DynamoDB::Table
DeletionPolicy: Retain
Properties:
TableName: !Ref DBTableName
DeletionProtectionEnabled: true
...
- Set
DisableScaleIn: FalseforAWS::ApplicationAutoScaling::ScalingPolicyresources in the CloudFormation template. This ensures the scaling policies are retained and adopted by the new global table resource. The following example has all properties required for the CloudFormation process to execute properly. SeeTableReadScalingPolicyandTableWriteScalingPolicyresources in cloudformation-2-deletionPolicy.yaml for more details. When running these steps on your own table, review that yourAWS::ApplicationAutoScaling::ScalingPolicyresources have all of these properties.
TableWriteScalingPolicy:
Type: AWS::ApplicationAutoScaling::ScalingPolicy
DeletionPolicy: Retain
Properties:
PolicyName: TableWriteScalingPolicy
PolicyType: TargetTrackingScaling
ScalingTargetId: !Ref TableWriteCapacityScalableTarget
TargetTrackingScalingPolicyConfiguration:
TargetValue: 70.0
ScaleInCooldown: 61
ScaleOutCooldown: 61
DisableScaleIn: false
PredefinedMetricSpecification:
PredefinedMetricType: DynamoDBWriteCapacityUtilization
DependsOn: CfnTestPrices
- Note that
MyEmptyResourceis added to thecloudformation-2-deletionPolicy.yamltemplate to ensure that this template will have at least one resource after the DynamoDB table and auto-scaling resources are removed from the template. CloudFormation deletes empty templates, which would result in an error while the process completes.
MyEmptyResource:
Type: AWS::CloudFormation::WaitConditionHandle
Now that the template is properly configured, the next step is to create a CloudFormation change set to review the infrastructure changes before executing them (for more information on change sets, see Viewing a change set in the CloudFormation documentation).
Using an AWS profile with sufficient permissions, run the following CLI command to create the CloudFormation Change Set:
aws cloudformation create-change-set \
--template-body file://./cloudformation-2-deletionPolicy.yaml \
--stack-name cfn-demo-dynamodb \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM \
--region us-east-1 \
--change-set-name create-retain \
--parameters ParameterKey=DBTableName,ParameterValue=CfnTestPrices
You should see a response similiar to below:
{
"Id": "arn:aws:cloudformation:us-east-1:<your-aws-accountId>:changeSet/create-retain/96xxx9b8-a368-494b-b13e-fe3xxx36d167",
"StackId": "arn:aws:cloudformation:us-east-1:<your-aws-accountId>:stack/cfn-demo-dynamodb/0e2xxxe00-7fb2-11ee-b66f-0axxx18d9"
}
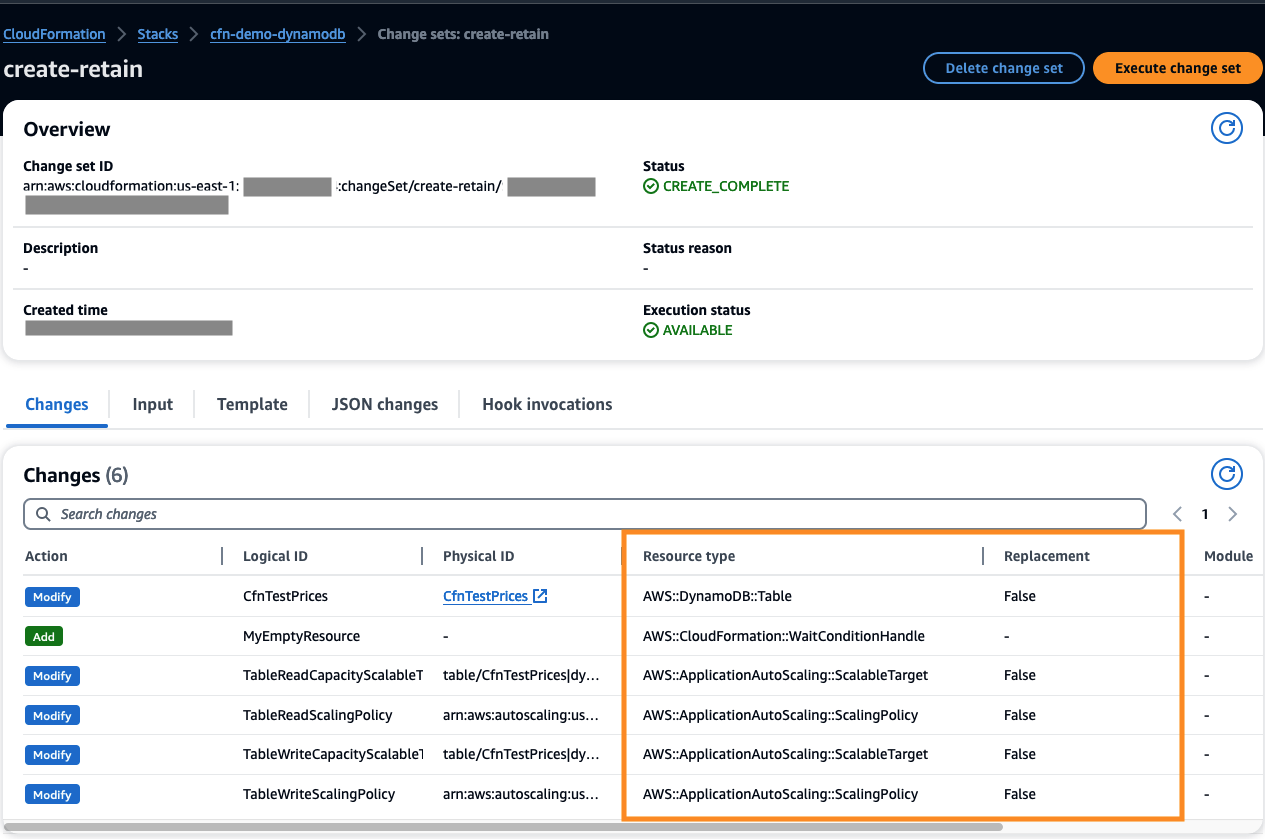
Review the change set to ensure no resources are deleted or re-created.
In the AWS console for CloudFormation, find the cfn-demo-dynamodb stack, go to the Change Sets table, and review the create-retain change set.
If you prefer to use the AWS CLI instead of the AWS console, using an AWS profile with sufficient permissions, run the following CLI command to verify that the AWS::DynamoDB::Table,AWS::ApplicationAutoScaling::ScalableTarget, and AWS::ApplicationAutoScaling::ScalingPolicy resources created in step 1 were not replaced in step 2:
aws cloudformation describe-change-set --region us-east-1 --change-set-name <"Id" from the output of 'create-change-set' command that you run earlier>
To execute the change set, use the AWS console to execture the Change Set.
If you prefer to use the AWS CLI instead of the AWS console, using an AWS profile with sufficient permissions run the following AWS CLI command to execute the Change Set:
aws cloudformation execute-change-set --region us-east-1 --change-set-name <"Id" from the output of 'create-change-set' command that you run earlier>
You can follow the execution of the change set in AWS console:
Wait until the execution is successfully completed:
If you prefer to use the AWS CLI, run the following command to check the status of the change set:
## Wait until the change set finishes and status is UPDATE_COMPLETE
aws cloudformation describe-stack-events --region us-east-1 --stack-name cfn-demo-dynamodb --max-items 1
You get a similar output as below. Don't proceed to the next step until you see "ResourceStatus": "UPDATE_COMPLETE".
{
"StackEvents": [
{
"StackId": "...",
"EventId": "...",
"StackName": "cfn-demo-dynamodb",
"LogicalResourceId": "cfn-demo-dynamodb",
"PhysicalResourceId": "...",
"ResourceType": "AWS::CloudFormation::Stack",
"Timestamp": "...",
"ResourceStatus": "UPDATE_COMPLETE"
}
...
Review the table and auto-scaling resources to ensure the required preparations were successfully executed:
## Validate resources and creation time
aws dynamodb describe-table --table-name CfnTestPrices --region us-east-1
aws application-autoscaling describe-scalable-targets --service-namespace dynamodb --resource-id "table/CfnTestPrices" --region us-east-1
aws application-autoscaling describe-scaling-policies --service-namespace dynamodb --resource-id "table/CfnTestPrices" --region us-east-1
It is VERY IMPORTANT that you successfully completed the required preparation in step 2 before unmanaging the table and auto-scaling resources from CloudFormation:
a) set the DeletionPolicy: Retain for
AWS::DynamoDB::Table, AWS::ApplicationAutoScaling::ScalableTarget, and AWS::ApplicationAutoScaling::ScalingPolicy resources
b) added DeletionProtectionEnabled: true to AWS::DynamoDB::Table resource
If these deletion protections are not in place, when you remove the table and related auto-scaling resources from the CloudFormation template, these resources will be deleted. Because you added the deletion protections explained in step 2, when you remove the table and related auto-scaling resources from the template, these resources will not be deleted. And they will no longer be managed by CloudFormation.
When the table and related auto-scaling resources are not managed by CloudFormation,
you are able to import these existing resources to the CloudFormation template as AWS::DynamoDB::GlobalTable resource type. This is explained in step 4.
As you review the cloudformation-3-unmanage.yaml,
you see that there is only MyEmptyResource resource remaining in the template.
The table and related auto-scaling resources are removed from the template.
Create a change set by running the following AWS CLI command:
aws cloudformation create-change-set \
--template-body file://./cloudformation-3-unmanage.yaml \
--stack-name cfn-demo-dynamodb \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM \
--region us-east-1 \
--change-set-name unmanage-resources \
--parameters ParameterKey=DBTableName,ParameterValue=CfnTestPrices
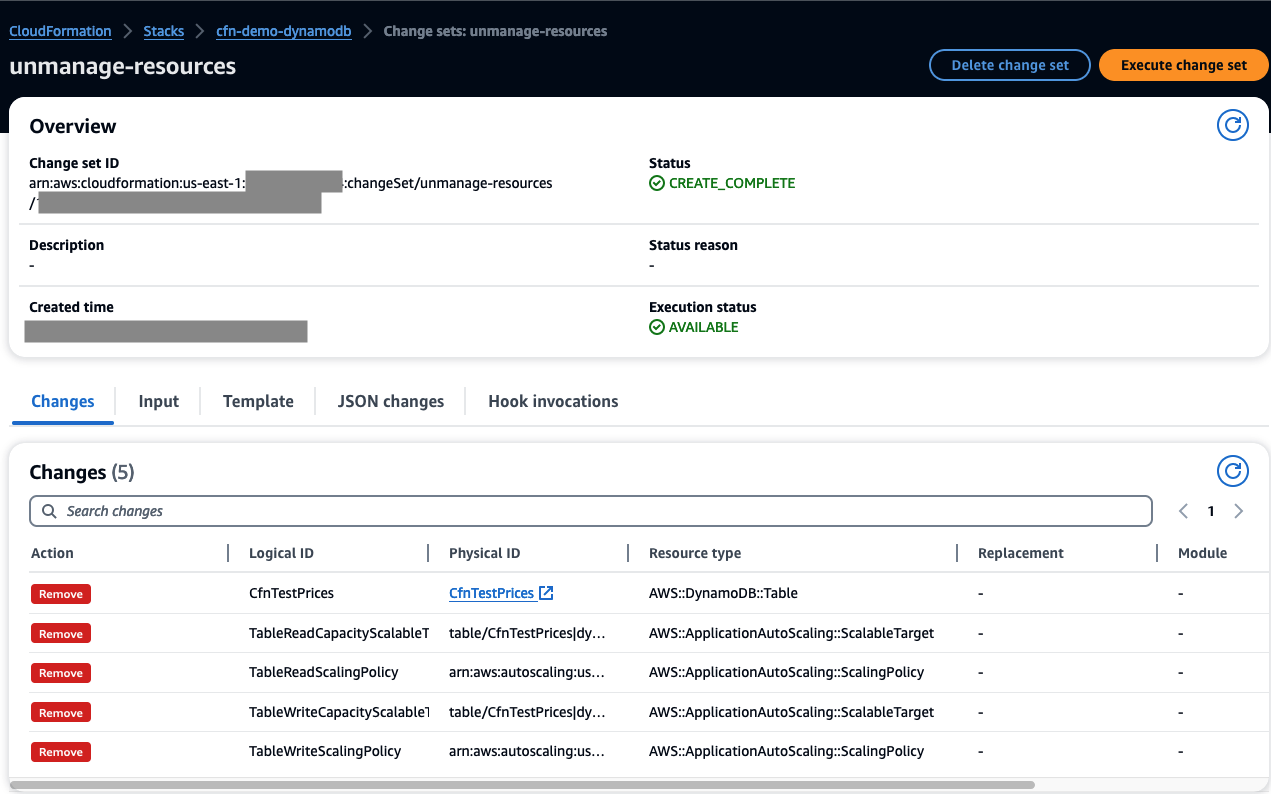
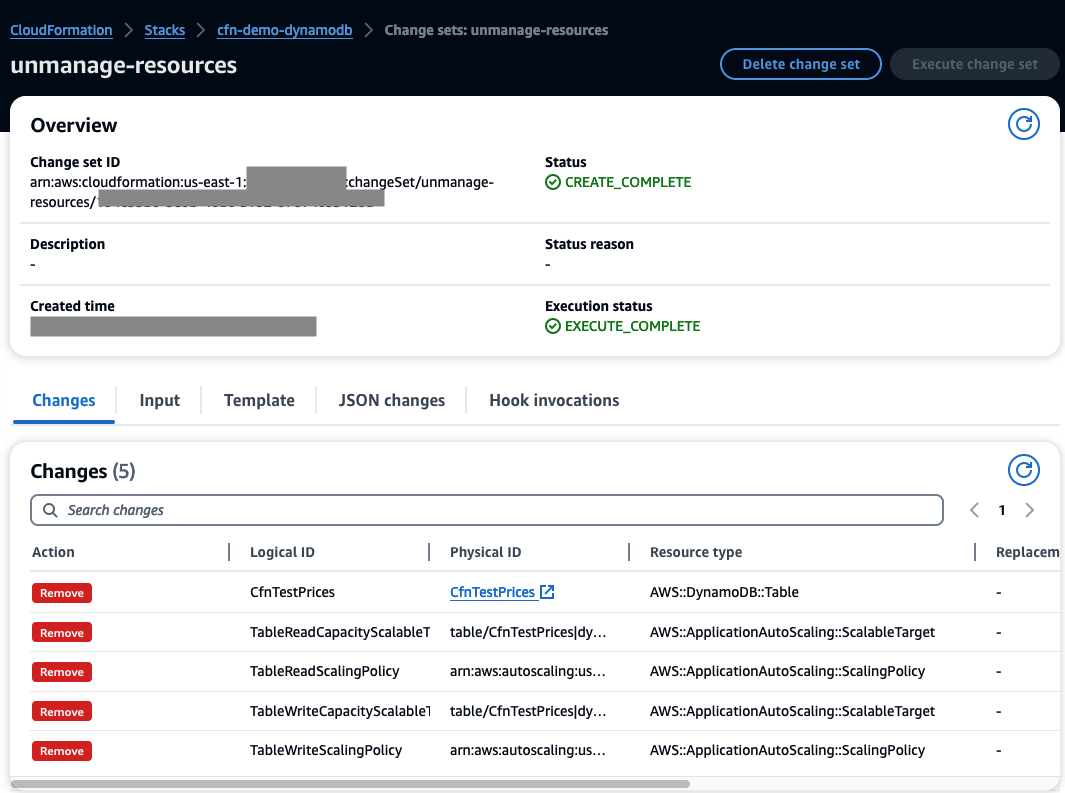
As you review the change set, unmanage-resources, in AWS console, you see:
Using AWS CLI, run the following command to review this change set:
aws cloudformation describe-change-set --region us-east-1 --change-set-name <"Id" from the output of 'create-change-set' command that you run earlier>
Execute the change set using AWS console or run the following command:
aws cloudformation execute-change-set --region us-east-1 --change-set-name <"Id" from the output of 'create-change-set' command that you run earlier>
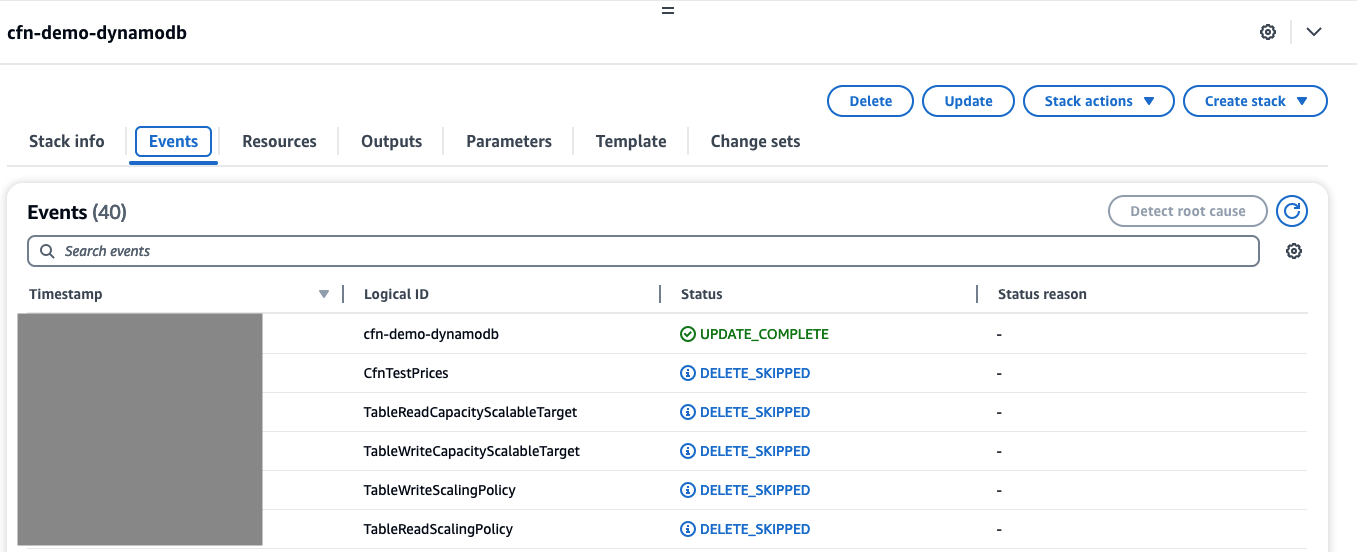
In AWS console, go to Events tab, you see DELETE_SKIPPED for the table and related auto-scaling resources:
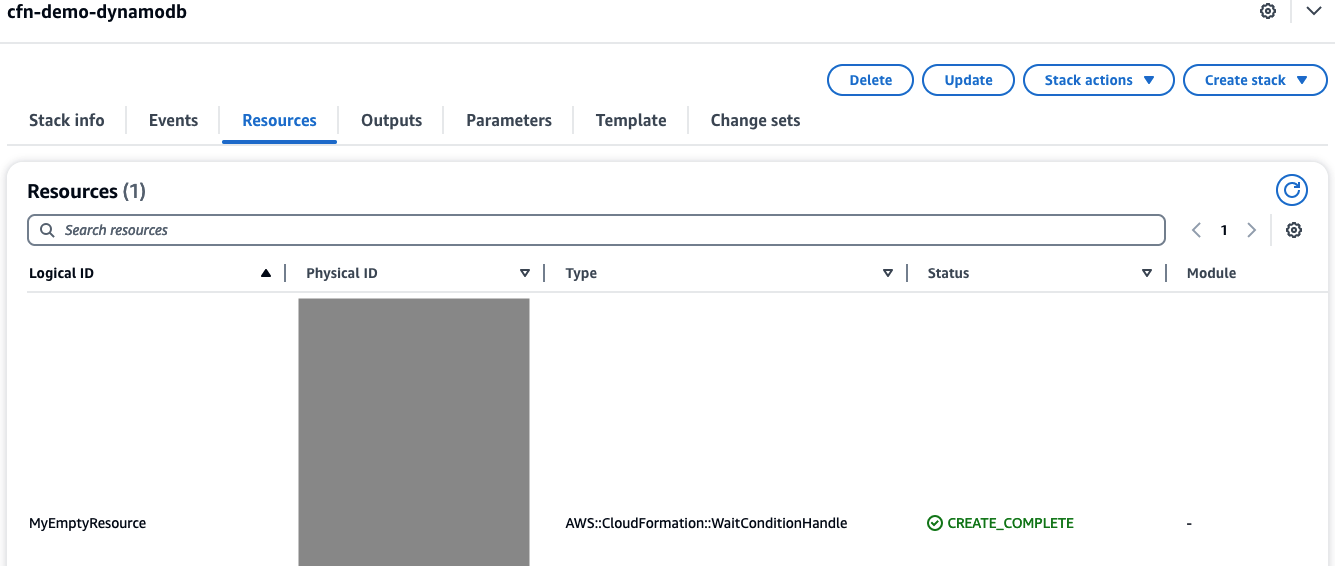
As you see in Resources tab, the table and related auto-scaling resources are no longer managed by CloudFormation:
Using the AWS CLI, check the stack status by running the following command:
aws cloudformation describe-stack-events --region us-east-1 --stack-name cfn-demo-dynamodb --max-items 1
Run the following commands to review the table and related auto-scaling resources. You will see that these resources were not deleted by executing the change set. They are just not managed by CloudFormation any longer.
aws dynamodb describe-table --table-name CfnTestPrices --region us-east-1
aws application-autoscaling describe-scalable-targets --service-namespace dynamodb --resource-id "table/CfnTestPrices" --region us-east-1
aws application-autoscaling describe-scaling-policies --service-namespace dynamodb --resource-id "table/CfnTestPrices" --region us-east-1
At this point, the DynamoDB table and related auto-scaling resources are not managed by CloudFormation.
Review cloudformation-4-import-table.yaml file where AWS::DynamoDB::GlobalTable resource definition is added to the template.
It is recommended to familiarize yourself with the differences between AWS::DynamoDB::GlobalTable and
AWS::DynamoDB::Table resource definition.
For a table with provisioned capacity mode, when using AWS::DynamoDB::GlobalTable resource type,
you must enable auto-scaling for write for your table and its global secondary indexes.
Write auto-scaling for table is directly defined as
WriteProvisionedThroughputSettings
property in the AWS::DynamoDB::GlobalTable resource. This write policy will be applied to all replicas of the table.
Configure auto-scaling for read as
ReadProvisionedThroughputSettings
property in the AWS::DynamoDB::GlobalTable resource.
If the table has a global secondary index, the write auto-scaling is configured as WriteProvisionedThroughputSettings property
in GlobalSecondaryIndex property
in the AWS::DynamoDB::GlobalTable resource. This write policy will be applied to all replicas of the global secondary index.
Configure auto-scaling for read as
ReadProvisionedThroughputSettings
property in ReplicaGlobalSecondaryIndexSpecification property of the AWS::DynamoDB::GlobalTable resource.
When using AWS::DynamoDB::GlobalTable resource, there should not be any AWS::ApplicationAutoScaling::ScalableTarget and AWS::ApplicationAutoScaling::ScalingPolicy resources for
the table replicas or secondary indexes.
Read policies can differ between replicas for table and global secondary index, however write policies are shared between all replicas of the table to keep them in sync with a low latency. All the replicas of a global secondary index would have the same write policies too.
The DeletionProtectionEnabled property should be set under
ReplicaSpecification
property of Replicas property in the global table.
You should specifically define this setting for each replica of a global table because this property is supported only as a replica specific.
In cloudformation-4-import-table.yaml, you don't find any of
the AWS::ApplicationAutoScaling::ScalingPolicy and AWS::ApplicationAutoScaling::ScalableTarget resources that
were part of cloudformation-1-initial.yaml
and cloudformation-2-deletionPolicy.yaml templates.
The reason for that is auto-scaling is defined aligned with the global table resource definition (as explained earlier).
To import the AWS::DynamoDB::GlobalTable resource defined in cloudformation-4-import-table.yaml to cfn-demo-dynamodb stack,
create a change set using the following command:
aws cloudformation create-change-set \
--stack-name cfn-demo-dynamodb \
--change-set-name ImportChangeSet \
--change-set-type IMPORT \
--region us-east-1 \
--resources-to-import "[ \
{\"ResourceType\":\"AWS::DynamoDB::GlobalTable\",\"LogicalResourceId\":\"CfnTestPrices\",\"ResourceIdentifier\":{\"TableName\":\"CfnTestPrices\"}}
]" \
--template-body file://./cloudformation-4-import-table.yaml \
--parameters ParameterKey=DBTableName,ParameterValue=CfnTestPrices \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM
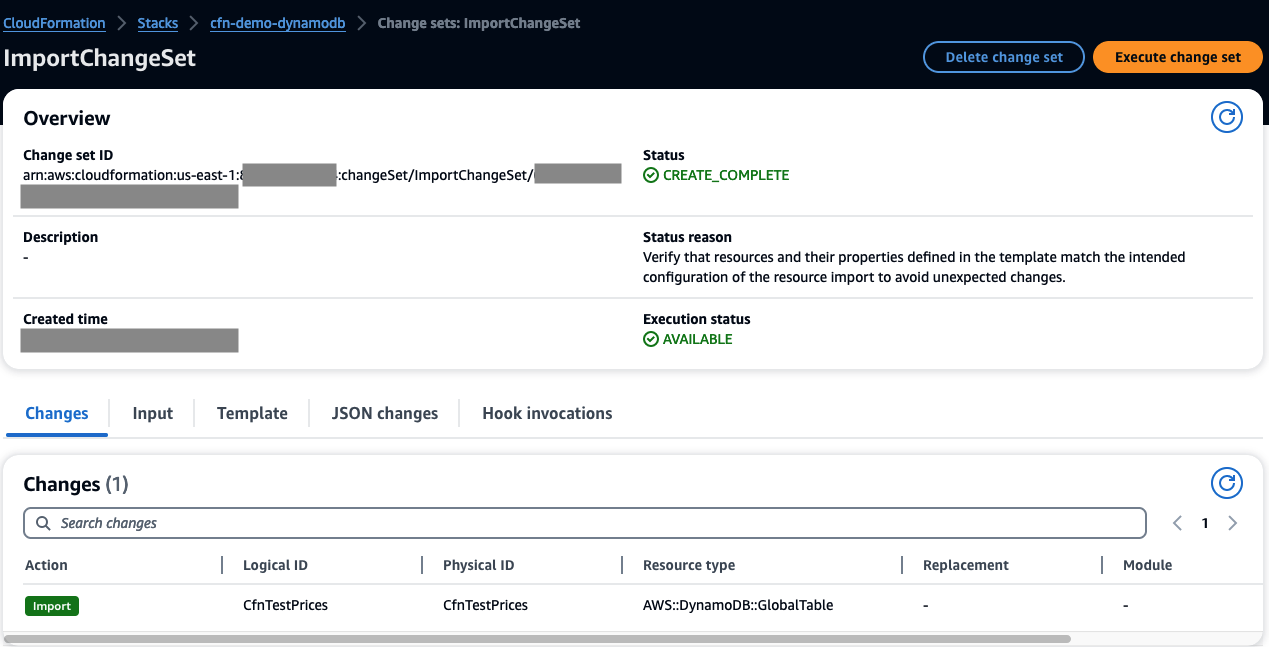
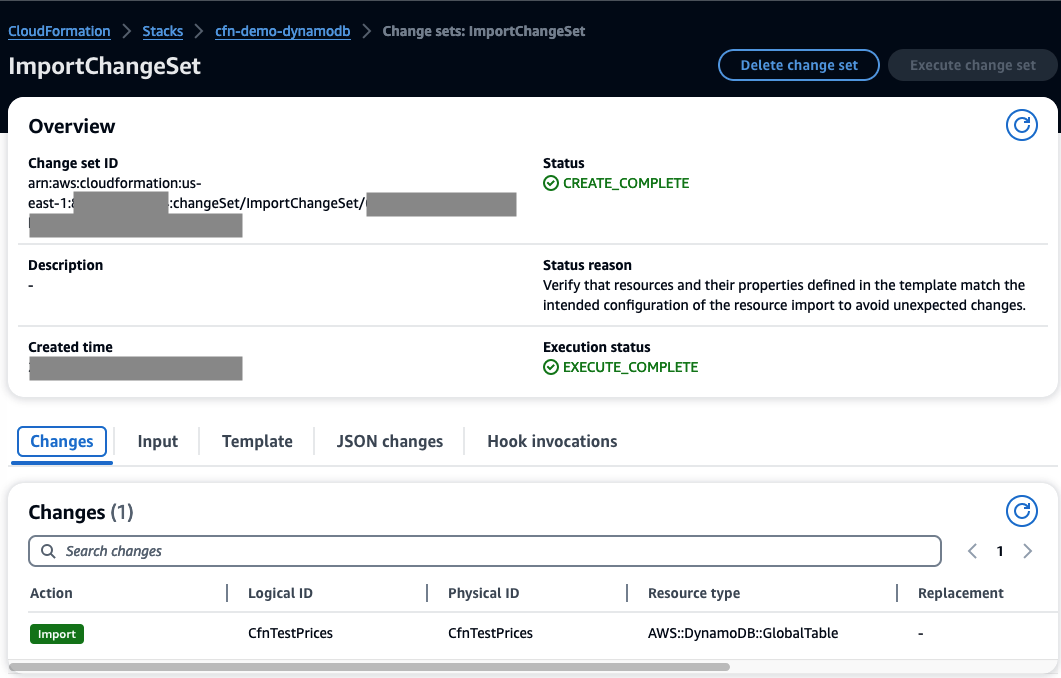
As you review the change set, ImportChangeSet, in AWS console, you see:
Using AWS CLI, run the following command to review this change set:
aws cloudformation describe-change-set --region us-east-1 --change-set-name <"Id" from the output of 'create-change-set' command that you run earlier>
Execute the change set using AWS console or run the following command:
aws cloudformation execute-change-set --region us-east-1 --change-set-name <"Id" from the output of 'create-change-set' command that you run earlier>
In AWS console, you should see a similar execution status:
Using AWS CLI, run the following command to check the stack.
You should see "ResourceStatus": "IMPORT_COMPLETE" in the output.
aws cloudformation describe-stack-events --region us-east-1 --stack-name cfn-demo-dynamodb --max-items 1
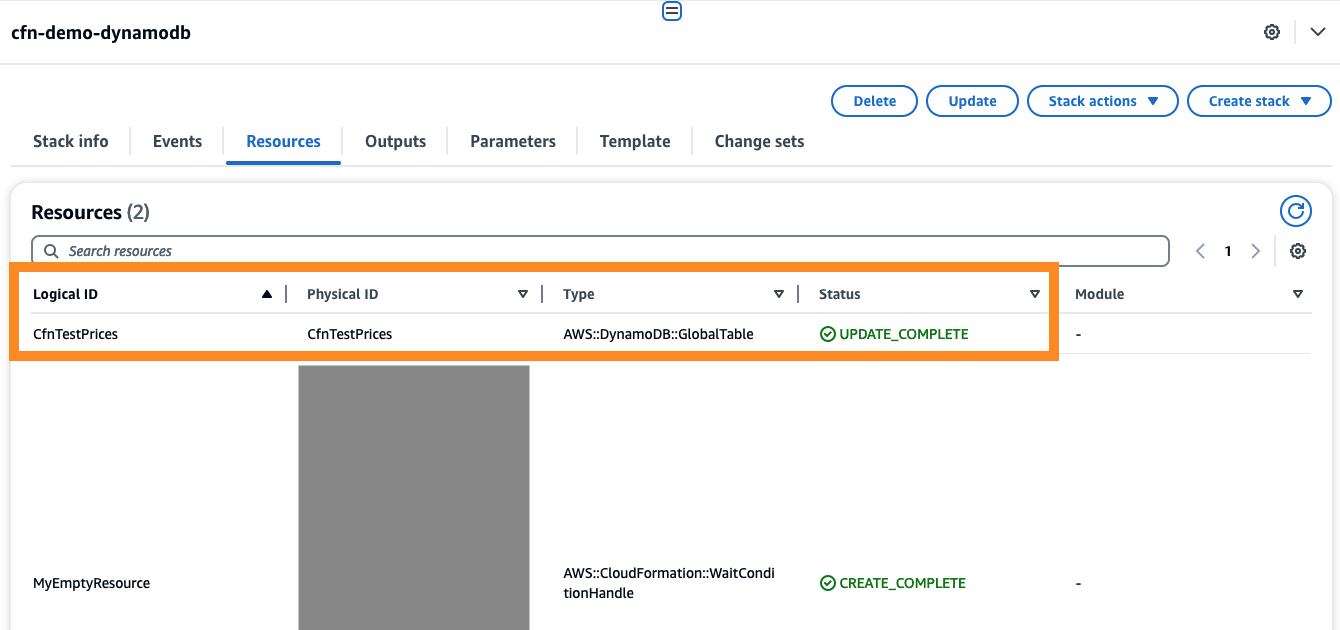
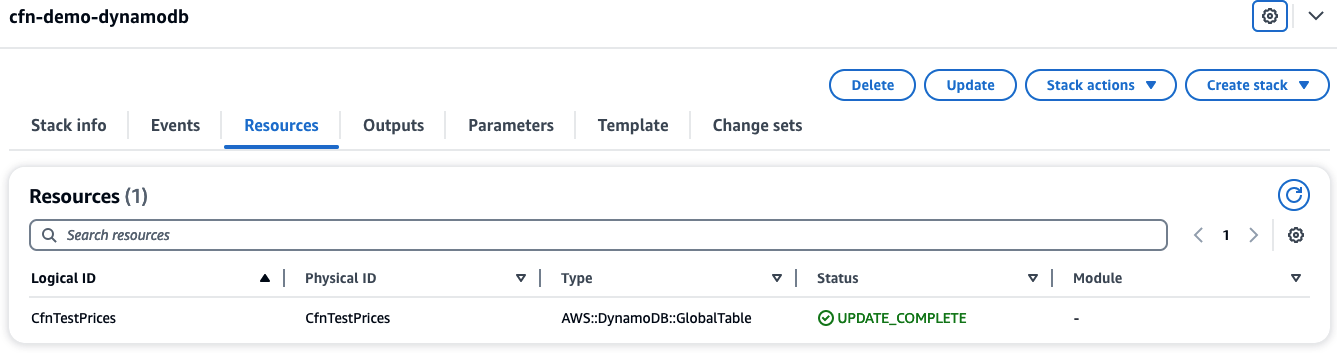
In AWS console, when checking cfn-demo-dynamodb stack,
you should see that CfnTestPrices resource with AWS::DynamoDB::GlobalTable type is now managed by CloudFormation.
Similar to the previous steps, using AWS CLI, you can run the following commands to check the table and related auto-scaling resources:
aws dynamodb describe-table --table-name CfnTestPrices --region us-east-1
aws application-autoscaling describe-scalable-targets --service-namespace dynamodb --resource-id "table/CfnTestPrices" --region us-east-1
aws application-autoscaling describe-scaling-policies --service-namespace dynamodb --resource-id "table/CfnTestPrices" --region us-east-1
Now that the DynamoDB table, CfnTestPrices, is managed by CloudFormation as a AWS::DynamoDB::GlobalTable resource,
add a new replica in the us-east-2 AWS Region.
When adding a replica to a large table (GB to TB range), work with your AWS account team. See the default quotas for Global Tables and DynamoDB Streams. Request to increase the default quotas if needed for your global table. This step can take up to an hour to complete based on the size of the table.
Review cloudformation-5-create-replica.yaml before creating a change set.
Run the following command to create a change set:
aws cloudformation create-change-set \
--template-body file://./cloudformation-5-create-replica.yaml \
--stack-name cfn-demo-dynamodb \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM \
--parameters ParameterKey=DBTableName,ParameterValue=CfnTestPrices \
--region us-east-1 \
--change-set-name add-replica
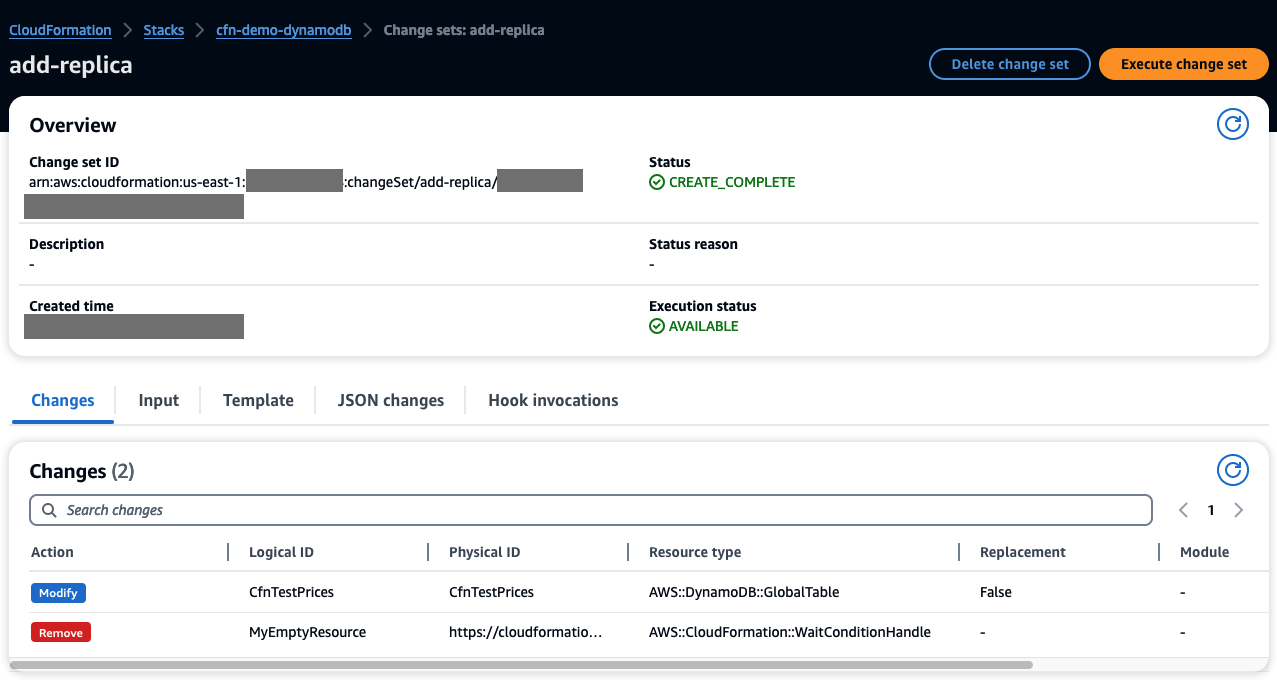
As you review the change set, add-replica, in AWS console, you see:
Using AWS CLI, run the following command to review this change set:
aws cloudformation describe-change-set --region us-east-1 --change-set-name <"Id" from the output of 'create-change-set' command that you run earlier>
Execute the change set using AWS console or run the following command.
aws cloudformation execute-change-set --region us-east-1 --change-set-name <"Id" from the output of 'create-change-set' command that you run earlier>
Adding a replica to CfnTestPrices table may take several minutes.
In AWS console, you see a similar execution status for the change set:
When the execution of the change set is complete, you should see:
Using AWS CLI, run the following command to check the stack.
You should see "ResourceStatus": "UPDATE_COMPLETE" in the output.
aws cloudformation describe-stack-events --region us-east-1 --stack-name cfn-demo-dynamodb --max-items 1
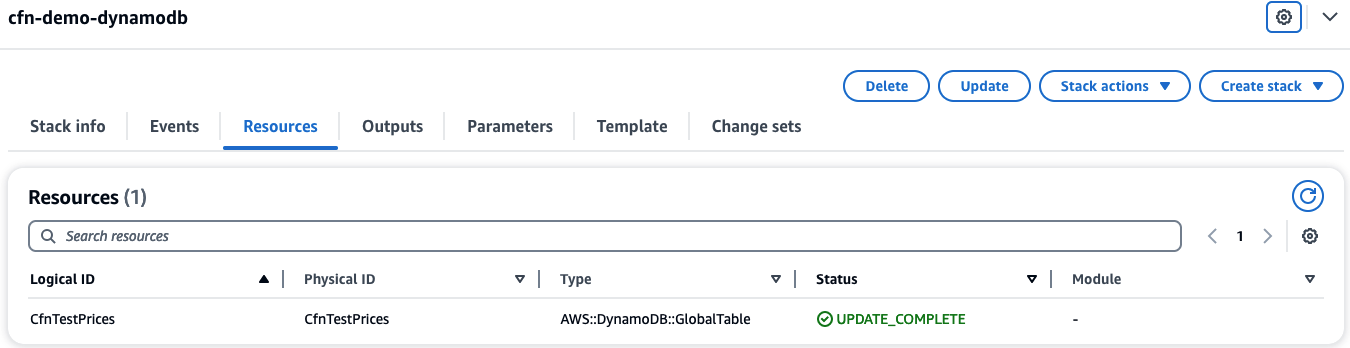
In AWS console, when checking cfn-demo-dynamodb stack,
you see that CfnTestPrices is the only resource in the stack.
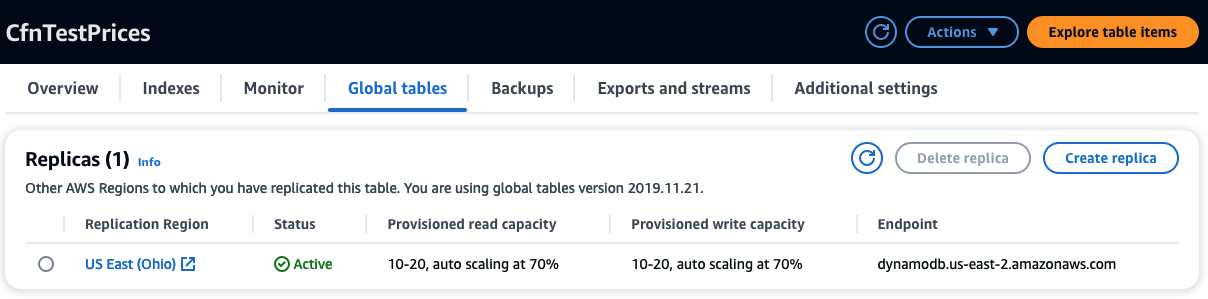
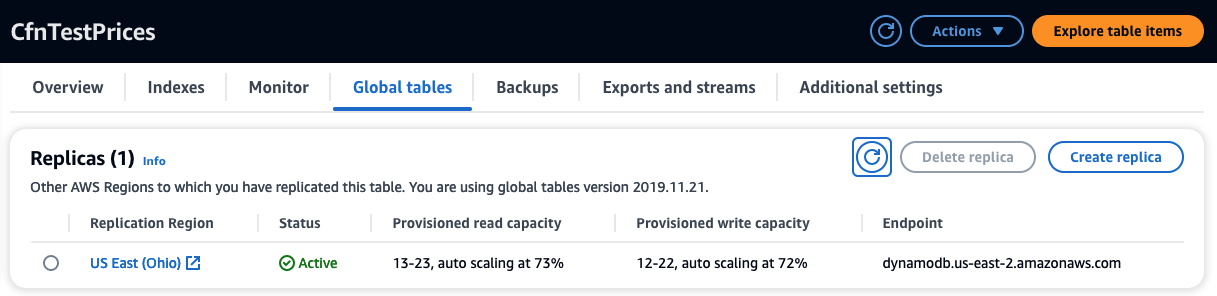
In AWS console, check the CfnTestPrices table, go to Global tables tab where you find the newly added replica:
Using AWS CLI,
you can run the following commands to check the two replicas of the CfnTestPrices global table:
aws dynamodb describe-table --table-name CfnTestPrices --region us-east-1
aws dynamodb describe-table --table-name CfnTestPrices --region us-east-2
Run the following commands to verify scaling policies for the two replicas of the CfnTestPrices global table:
aws dynamodb describe-table-replica-auto-scaling --table-name CfnTestPrices --region us-east-1
aws dynamodb describe-table-replica-auto-scaling --table-name CfnTestPrices --region us-east-2
In this optional step, to validate that the scaling policies are working as expected, change all the scaling policies. Review cloudformation-6-test-scaling.yaml before creating a change set.
Run the following command to create a change set:
aws cloudformation create-change-set \
--template-body file://./cloudformation-6-test-scaling.yaml \
--stack-name cfn-demo-dynamodb \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM \
--parameters ParameterKey=DBTableName,ParameterValue=CfnTestPrices \
--region us-east-1 \
--change-set-name change-scaling
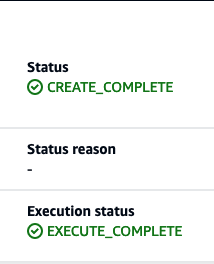
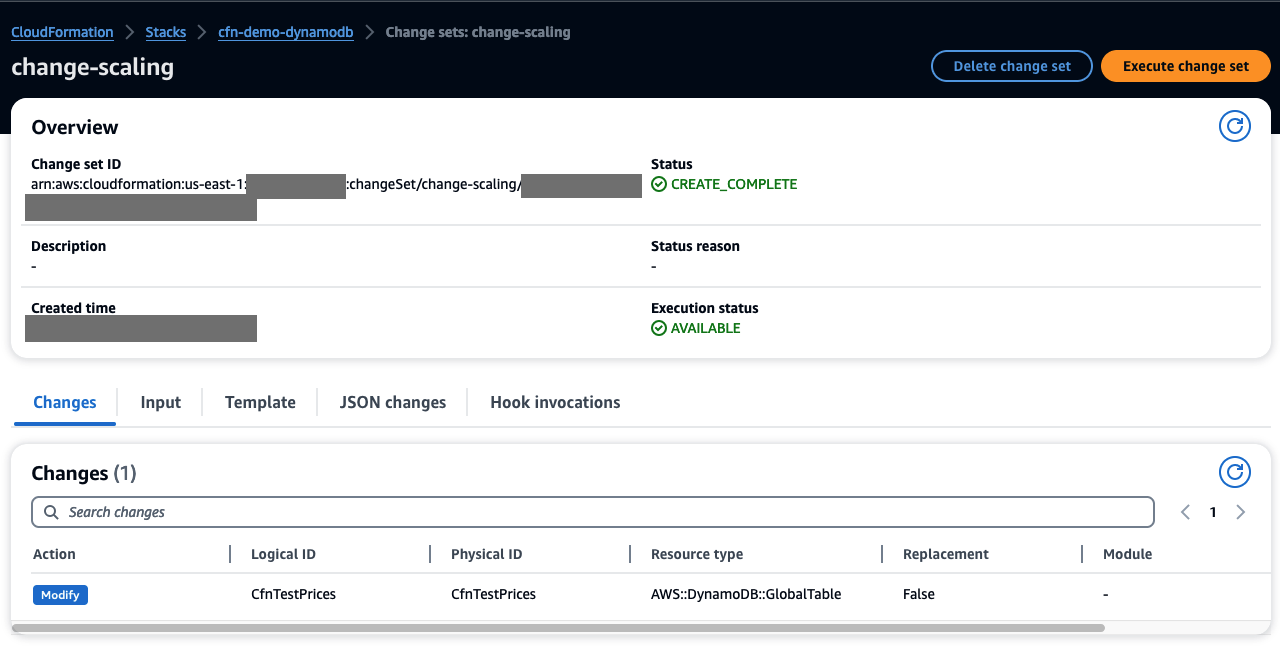
As you review the change set, change-scaling, in AWS console, you see:
Using AWS CLI, run the following command to review this change set:
aws cloudformation describe-change-set --region us-east-1 --change-set-name <"Id" from the output of 'create-change-set' command that you run earlier>
Execute the change set using AWS console or run the following command.
aws cloudformation execute-change-set --region us-east-1 --change-set-name <"Id" from the output of 'create-change-set' command that you run earlier>
When the execution of the change set is complete, you should see:
Using the AWS CLI, run the following command to check the stack.
You should see "ResourceStatus": "UPDATE_COMPLETE" in the output.
aws cloudformation describe-stack-events --region us-east-1 --stack-name cfn-demo-dynamodb --max-items 1
In the AWS console, check CfnTestPrices table, go to the Global tables tab,
check the updated auto-scaling policies for the replica in us-east-2:
Using AWS CLI,
you can run the following commands to check the two replicas of the CfnTestPrices global table:
aws dynamodb describe-table --table-name CfnTestPrices --region us-east-1
aws dynamodb describe-table --table-name CfnTestPrices --region us-east-2
Run the following commands to verify scaling policies for the two replicas of the CfnTestPrices global table:
aws dynamodb describe-table-replica-auto-scaling --table-name CfnTestPrices --region us-east-1
aws dynamodb describe-table-replica-auto-scaling --table-name CfnTestPrices --region us-east-2
Now that you learned about the changes and commands required for each step,
you have the option to use cfn-execution.sh script to execute the commands for each step of the instruction provided in this repository.
For example, the following command executes step 1:
## Execute step 1
./cfn-execution.sh 1
When using the script for your own account and table, you may want to update the following fields in the top of the script:
### OPTIONS
TABLE_NAME='CfnTestPrices'
STACK_NAME='cfn-demo-dynamodb'
PRIMARY_REGION='us-east-1'
REPLICA_REGION='us-east-2'
DEFAULT_STEP=1
To delete the stack, run the following command:
### Deletes the stack
./cfn-execution.sh 86
Do not forget to delete the stack and the table from your AWS account after running the example.
In step 4, DeletionProtectionEnabled: true and DeletionPolicy: Retain
were added to the global table to protect the table from deletion.
To delete the CfnTestPrices global table and cfn-demo-dynamodb CloudFormation stack,
you need to disable these deletion protections.
Review cloudformation-7-remove.yaml
and cloudformation-8-remove.yaml templates.
You can have this setting DeletionProtectionEnabled: false for both replicas in one step but for educational purpose in this example,
run them in two steps using the following commands:
## disables deletion protection on replica
aws cloudformation deploy \
--template-file cloudformation-7-remove.yaml \
--stack-name cfn-demo-dynamodb \
--region us-east-1 \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM \
--parameter-overrides DBTableName=CfnTestPrices
## deletes replica / disables deletion protection on primary
aws cloudformation deploy \
--template-file cloudformation-8-remove.yaml \
--stack-name cfn-demo-dynamodb \
--region us-east-1 \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM \
--parameter-overrides DBTableName=CfnTestPrices
## deletes table and stack
aws cloudformation delete-stack --region us-east-1 --stack-name cfn-demo-dynamodb
Another option is to run the following command if you configured your stack and database name in the script:
./cfn-execution 86
See CONTRIBUTING for more information.
This library is licensed under the MIT-0 License. See the LICENSE file.