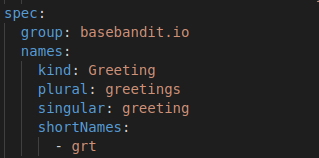
The CustomResourceDefinition API resource allows you to define custom resources:
In this project we create a CRD using the below approach:
- Define CustomResourceDefinition using YAML
- Create custom resources using YAML
Later we will add more functionality, for example if we want our CRDs to work like Pods?
- Once CRD is created, Create new Custom Controller on resource handling create/update/delete events.
- To achieve that, we will build a Custom Controller and deploy it to work as an aggregated API for declarative resources using Kubernetes CRDs and kubectl.
- Have a k8s cluster up and running. (minikube would do perfectly fine)
- Create the CRD.
kubectl apply -f crd-greeting.yaml - Confirm the resource has been successfully created.
└──╼ $ k api-resources
NAME SHORTNAMES APIVERSION NAMESPACED KIND
...
greetings grt basebandit.io/v1alpha1 true Greeting
...- Go ahead and now create a resource using our above CRD.
kubectl apply -f test-greeting.yaml - Confirm it is successfully created.
└──╼ $ k get greetings
NAME AGE
basebandit-greeting 19m
┌─[lab@basebandit]─[~/github.com/basebandit/kubernetes/crd-greeting] [main ⚡]
└──╼ $ k get greeting
NAME AGE
basebandit-greeting 19m
┌─[lab@basebandit]─[~/github.com/basebandit/kubernetes/crd-greeting] [main ⚡]
└──╼ $ k get grt
NAME AGE
basebandit-greeting 19mNote: You can switch the name resource name greetings with any of the names you declared in the CRD spec definition.