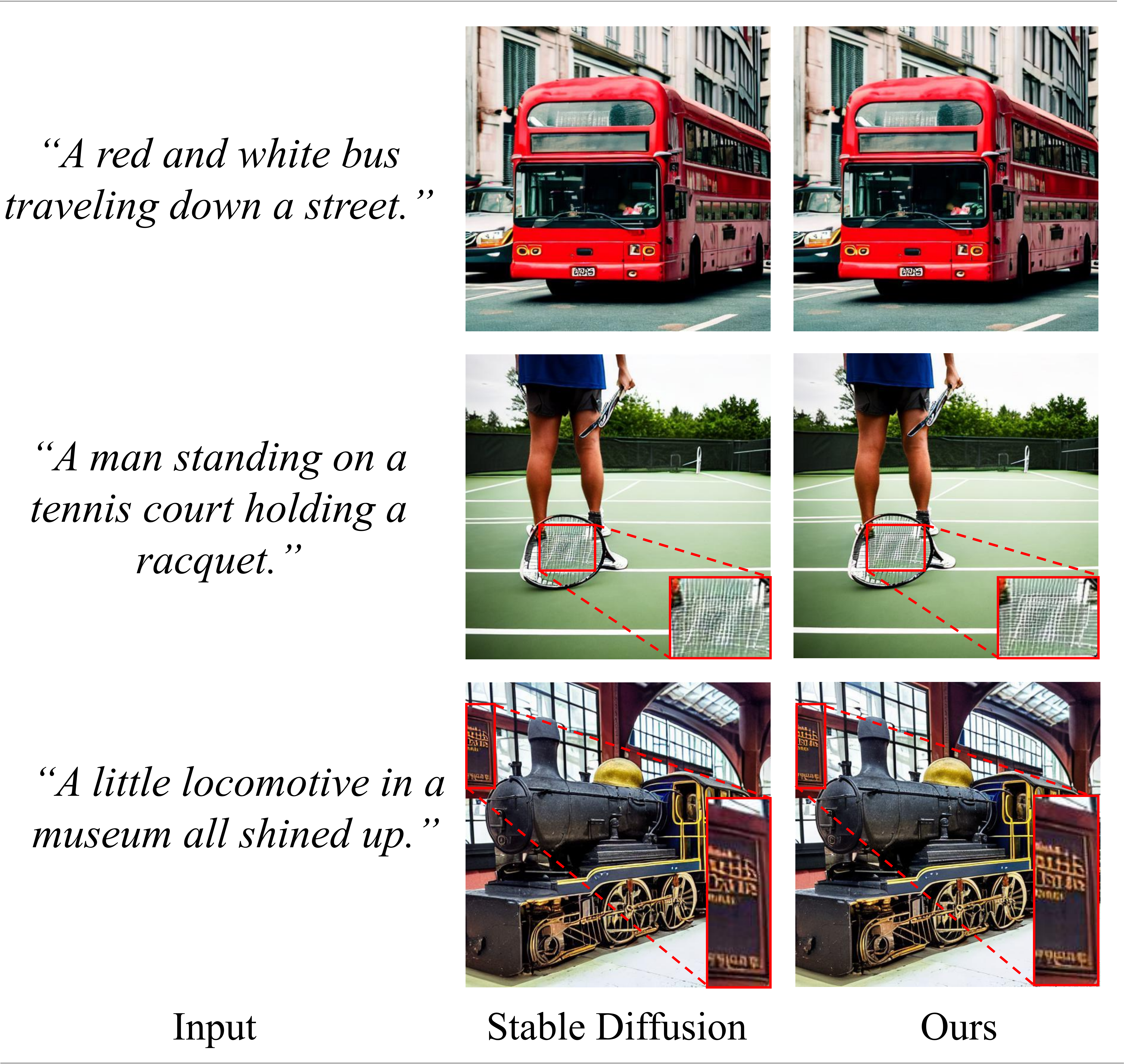
Designing a Better Asymmetric VQGAN for StableDiffusion
We propose the Asymmetric VQGAN, to preserve the information of conditional image input. Asymmetric VQGAN involves two core designs compared with the original VQGAN as shown in the figure. First, we introduce a conditional branch into the decoder of the VQGAN which aims to handle the conditional input for image manipulation tasks. Second, we design a larger decoder for VQGAN to better recover the losing details of the quantized codes.
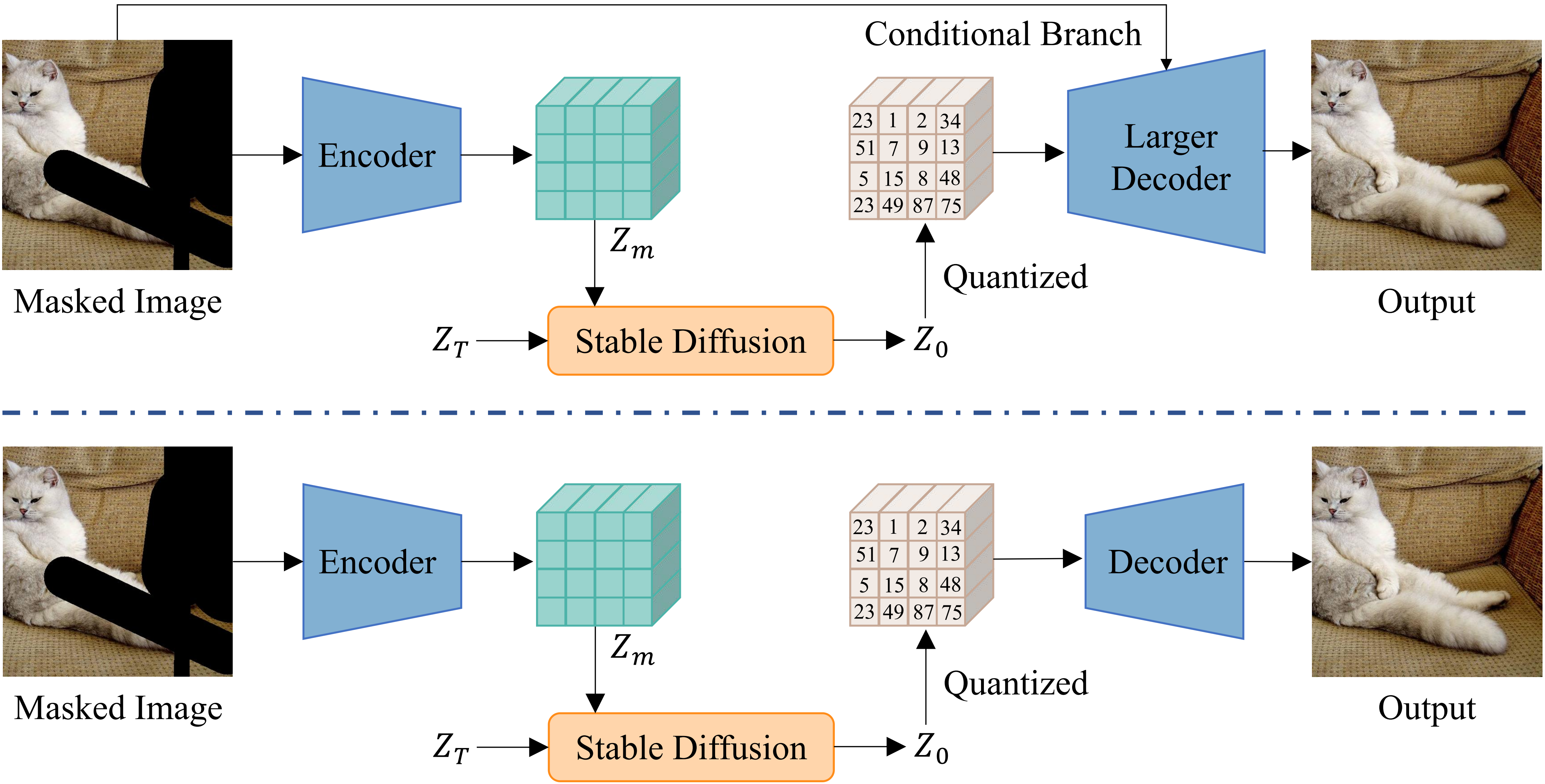 Top: The inference process of our symmetric VQGAN. Bottom: The inference process of vanilla VQGAN.
Top: The inference process of our symmetric VQGAN. Bottom: The inference process of vanilla VQGAN.
- Our pre-trained models are available:
pip install -r requirements.txt
pip install wandb
pip install -e git+https://github.com/CompVis/taming-transformers.git@master#egg=taming-transformers
pip install -e git+https://github.com/openai/CLIP.git@main#egg=clip
The inpainting model sd-v1-5-inpainting.ckpt of StableDiffusion is here
The text2image model v1-5-pruned-emaonly.ckpt of StableDiffusion is here
Download our images and masks .
python inpaint_st.py --config {config_spec}
where config_spec is one of {autoencoder_kl_32x32x4.yaml(base decoder), autoencoder_kl_32x32x4_large.yaml(large decode 1.5x),
autoencoder_kl_32x32x4_large2.yaml(large decoder 2x).
| model | pretrain | resolution | fid | lpips | pre_error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| StableDiffusion + vanilla VQGAN | ImageNet-1K | 224x224 | 9.57 | 0.255 | 1082.8e^-5 |
| StableDiffusion + asymmetric VQGAN (base) | ImageNet-1K | 224x224 | 7.60 | 0.137 | 5.7e^-5 |
| StableDiffusion + asymmetric VQGAN (Large 1.5x) | ImageNet-1k | 224x224 | 7.55 | 0.136 | 2.6e^-5 |
| StableDiffusion + asymmetric VQGAN (Large 2x) | ImageNet-1k | 224x224 | 7.49 | 0.134 | 2.1e^-5 |
python txt2img.py --plms --config_c {config_spec}
where config_spec is one of {autoencoder_kl_woc_32x32x4.yaml(base decoder), autoencoder_kl_woc_32x32x4_large.yaml(large decode 1.5x),
autoencoder_kl_woc_32x32x4_large2.yaml(large decoder 2x).
| model | fid | is |
|---|---|---|
| StableDiffusion + vanilla VQGAN | 19.88 | 37.55 |
| StableDiffusion + asymmetric VQGAN (base) w/o mask | 19.92 | 37.52 |
| StableDiffusion + asymmetric VQGAN (Large 1.5x) w/o mask | 19.75 | 37.64 |
| StableDiffusion + asymmetric VQGAN (Large 2x) w/o mask | 19.68 | 37.73 |
The code will try to download (through Academic
Torrents) and prepare ImageNet the first time it
is used. However, since ImageNet is quite large, this requires a lot of disk
space and time. If you already have ImageNet on your disk, you can speed things
up by putting the data into
./datasets/ImageNet/train. It should have the following structure:
./datasets/ImageNet/train/
├── n01440764
│ ├── n01440764_10026.JPEG
│ ├── n01440764_10027.JPEG
│ ├── ...
├── n01443537
│ ├── n01443537_10007.JPEG
│ ├── n01443537_10014.JPEG
│ ├── ...
├── ...
First, download weights of the autoencoder stable_vqgan.ckpt obtained from StableDiffusion.
Second, input your own key of wandb in main.py (line 679).
Configs for training a KL-regularized autoencoder on ImageNet are provided at configs/autoencoder.
Training can be started by running
python main.py --base configs/autoencoder/{config_spec} -t --gpus 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7 --tag <yourtag>
where config_spec is one of {autoencoder_kl_32x32x4_train.yaml(base decoder), autoencoder_kl_32x32x4_large_train.yaml(large decode 1.5x),
autoencoder_kl_32x32x4_large2_train.yaml(large decoder 2x). It is worth noting that the parameter num_gpus in config_spec is still needed to be set as the same as the number of gpus which you use.
- Our codebase for the diffusion models builds heavily on StableDiffusion. Thanks for open-sourcing!
@misc{zhu2023designing,
title={Designing a Better Asymmetric VQGAN for StableDiffusion},
author={Zixin Zhu and Xuelu Feng and Dongdong Chen and Jianmin Bao and Le Wang and Yinpeng Chen and Lu Yuan and Gang Hua},
year={2023},
eprint={2306.04632},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV}
}