MLSS 2019 will have interactive and practical tutorials in the following subjects
- Deep Learning
- Optimization
- Variational Inference
- Reinforcement Learning
- Gaussian Processes
- Kernels
- Markov Chain Monte Carlo
- Approximate Bayesian Computation
- Speech Processing
- ML in Computational Biology
Since many of these tutorials require the participants to install software with sometimes complex dependencies which means the installation process will differ between platforms (e.g Linux, OSX and Windows) and to make sure the tutorials run smoothly, we have prepared ways for everyone to come prepared and reduce technical issues to minimum.
This means we will get more time for the actual content!
Since the tutorials differ in terms of programming languages used and how the tutorials will be run, each tutorial will get its own section where instructions on how to get started and get the environment for this tutorial up and running.
Most of the tutorials will be run from a docker image that we have created. If you want to read more about docker this can be done here.
We have created a docker image that runs a jupyter notebook with kernels for the
tutorials which you will be access through localhost:8888 in your browser
after you follow the guide below.
Follow these instruction to install docker. If you follow the guide, everything should be fine. If you still have problem, please ask in the Slack general channel or ping me (@Isak Falk) anywhere on the MLSS2019 Slack :)
-
Install docker on your platform (Community Edition (CE), not Enterprise Edition (EE))
-
(Linux only) Add your user to the docker group by running
sudo usermod -a -G docker $USERin a terminal. This will enable you to run
dockercommands without usingsudo. -
Make sure Docker works
- Command line / terminal: In a terminal run
docker run hello-world, this will give an output similar to this - Application: Make sure the Docker application is installed and that you can find the icon when you search for it (this will depend on your system)
- Command line / terminal: In a terminal run
Pull the MLSS docker image to your computer, this image is located here.
Run the following in a terminal
docker pull isakfalk/mlss:latest
This will make the image available to you on your system. The image is a bit large (3gb compressed, 7gb uncompressed), this is normal, don't worry about it.
In order to get jupyter working, do the following from a terminal (note: this is how I do it on Linux, let me know if we need to do it another way on another platform)
- Run
docker run --name mlss -p 8888:8888 isakfalk/mlss, this will start the image we pulled (isakfalk/mlss), name ismlssand forward port 8888 on the image to the port 8888 on our machine. - You should see the following in your terminal
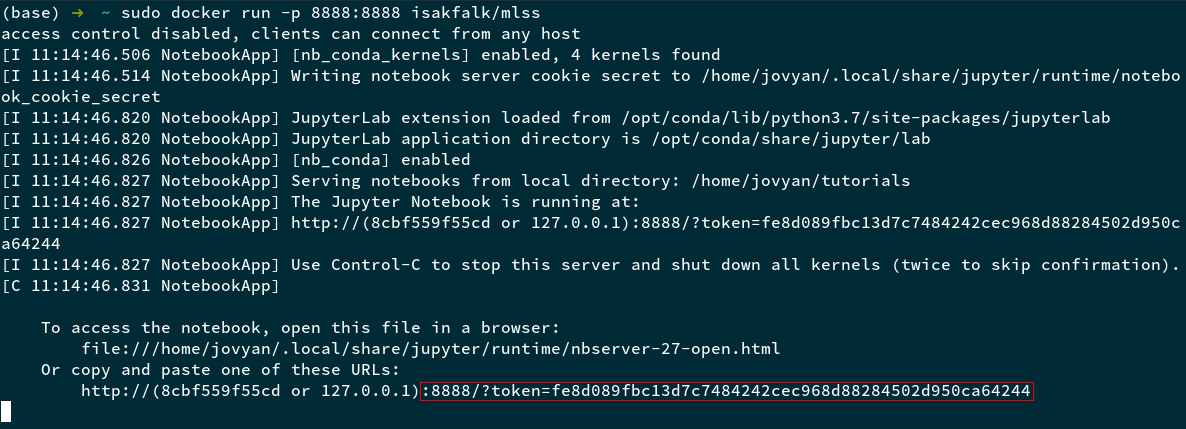 Copy the outlined part (you can do this using the command
Copy the outlined part (you can do this using the command ctrl-shift-cin a terminal on Linux at least) - In your browser of choice, do the following: paste the copied part into the
browser and prefix it with
localhost, like the image below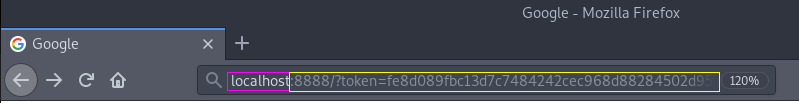
- Congratulations! It should be working now. You can change the kernel to the tutorial kernel by clicking on the notebook you want to run and then go to the tab Kernel and choose Change kernel, you will be presented with the available kernels.
When you are done with the jupyter notebook, we need to clean up the container as else it will not exit. Do the following to stop the jupyter notebook and clean up
- Run
docker container stop mlss - Run
docker container rm mlss
Some tutorials do not use jupyter notebooks. In this case, make sure you have
anaconda installed on your machine. Then run the following in a terminal where
$TUTORIALS_DIR is the path to the git directory of the mlss2019 tutorials that you can
clone from here and $ENV_NAME.yml is the name of the environment yaml file:
cd $TUTORIALS_DIR/environments/
conda env create -f $ENV_NAME.yml
conda activate $ENV_NAME
You should now be in the conda environment and can run the necessay files (e.g.
python tutorial.py) successfully.
Alternatively, this could be done from the anaconda application directly.
Running the notebooks in colab gives you access to GPU which will be good to have. They run out of the box since the colab has all the needed libraries pre-installed.
See Docker, or go directly to how to run jupyter with docker if you have already installed and pulled the docker image.
NOTE: the docker image is getting very big. I have provided a new image which you can pull using docker pull isakfalk/mlss_dl and then follow the guide as before.
See Docker, or go directly to how to run jupyter with docker if you have already installed and pulled the docker image.
There will be a kernel called Julia 1.1.1 which you will have to choose.
To run the Optimization notebooks, you'll need to install Julia (to run locally). An easy guide to follow can be found here. You'll need to have a recent version of Python installed (3.x), and it's easiest if this is from the Anaconda distribution. I'll assume you have this.
For Julia, you'll need to install some packages as well to run things. From a Julia terminal, execute the following code:
using Pkg
Pkg.add("Distributions");
Pkg.add("SpecialFunctions");
Pkg.add("PyPlot");Best to run this in colab as you will get access to GPU. Upload the jupyter notebook
$TUTORIALS_DIR/VAE/MLSS2019_VAEs_exercise.ipynb to Google Colab and run it
there.
If you want / need to run it locally, see Docker, or go directly to how to run jupyter with docker if you have already installed and pulled the docker image.
See Docker, or go directly to how to run jupyter with docker if you have already installed and pulled the docker image.
If you are using docker, don't run the following cells
# install required packages
!pip install --upgrade chainer opencv-python gym matplotlib==3.0.3 numpy# uncomment to install minerl
!pip install --upgrade minerlsince the conda kernel already has these packages installed.
See Docker, or go directly to how to run jupyter with docker if you have already installed and pulled the docker image.
-
Lab1 - Sampling a GP.ipynbIf you find that the first cell
import numpy as np import matplotlib matplotlib.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (14, 6) plt = matplotlib.pyplotdoesn't work, change this cell to
import numpy as np import matplotlib matplotlib.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (14, 6) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt -
Lab2 - GPflow and GP Regression.ipynbSee Lab1
TODO
See Conda with $ENV_NAME.yml set to mlss_mcmc.yml. After activating the
environment, go to $TUTORIALS_DIR/betancourt/ and then run each tutorial by
using
python $TUTORIAL_NAME.py
Install scipy, matplotlib and tqdm via conda/pip. Then run jupyter notebook and launch abc_filippi/ABC.ipynb.
Import abc_filippi/ABC.ipynb either from your local copy or the GitHub repository.
Install simplejson and pytorch via conda/pip and editdistance and soundfile via pip. Then run jupyter notebook and launch speech/tutorial.ipynb.
Place and rename the speech folder in this repository into your personal Google Drive folder (Google Drive is needed) at MLSS2019/tutorials (note that speech needs to be renamed to tutorials). Import speech/tutorial.ipynb either from your local copy or the GitHub repository.
TODO
The tutorial is in $TUTORIALS_DIR/submodular/submodular-opt.ipynb and should work in Colab out of the box.
Alternatively, you can set up Conda with $ENV_NAME.yml set to mlss_submod.yml.
After activating the Conda environment, ensure jupyter can access the environment by running
python -m ipykernel install --user --name mlss_submod --display-name "Python (mlss_submod)"
Then, launch the notebook via jupyter notebook and open the tutorial.
TODO: can we add this to the docker image?