This program is an 8 channel PWM generator to be run on a raspberry PI4 model. It will then control the voltage on the GPIO output 2 to 9.
The program may be run on a non-raspberry computer in which case it behaves exactly as on the raspberry but without GPIO interaction.
Communication with the program is trough a normal TCP connection over witch messages are exchanged. A message is a line of text ended by the newline character (\n not \r\n).
The program generates PWMs only when there is an active connection and it has been configured to do so. When the connection is closed, whatever the reason (e.g client crash), the generator is stopped and all output are set to 0v.
The generator may generate constant or varying pwm values in parallel and idependently on any combination of the 8 channels. The variation may be sinusoidal or triangular with specified amplitude, frequency and phase. The phase is specified as a fraction of the period with a value in the range 0 to 1.
To control this behavior, each channel has 5 parameters:
- type: constant(0), sinusoidal(1), triangular(2)
- average: average value
- amplitude: amplitude of variation around the average
- period: duration in second of a variation period
- start: percentage of period where to start
These parameters must respect the following constrains.
- 0 <= average <= 1
- amplitude >= 0
- average + amplitude <= 1
- average - amplitude >= 0
- period >= 0
- 0 <= start < 1
For constant PWM generation, the amplitude, period and start must all be 0. Setting the average to 0, will keep the GPIO output to 0v. Setting the average to 1, will keep the GPIO output to 3.3v.
For varying PWM generation, the average, amplitude and period must be non-zero.
The generator also continuously measure the frequency of pulse generation and its standard deviation. The value is a mobile value with exponentional decaying weighting with the alpha coefficient 0.9.
The commands supported by the generator are
- GPRM : returns the parameters of all the channels
- SPRM : sets the parameters of channels
- FREQ : returns the mobile mean frequency and its standard deviation
Multiple channels may be configured at once when setting the parameters. The change is atomic (in one step) to ensure that the phase difference between the varying signals is exactly the one requested.
Channels not configured with an SPRM request remain unaffected and continue to generate their output as before.
To stop the generation of PWM on a channel, configure it to CST and all parameters to 0.
The PWM generator accepts only one active TCP connection. When another connection is attempted to be made, the program will respond that it is busy and will provide the IP address and port used for the active connection. This allows to identify the host and process that currently uses the PWM generator.
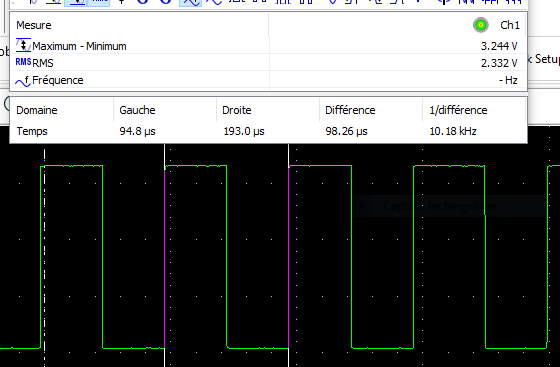
The following image shows a screen capture of a constant PWM generation with an average of .5. We can see that the puls frequency is 10kHz.
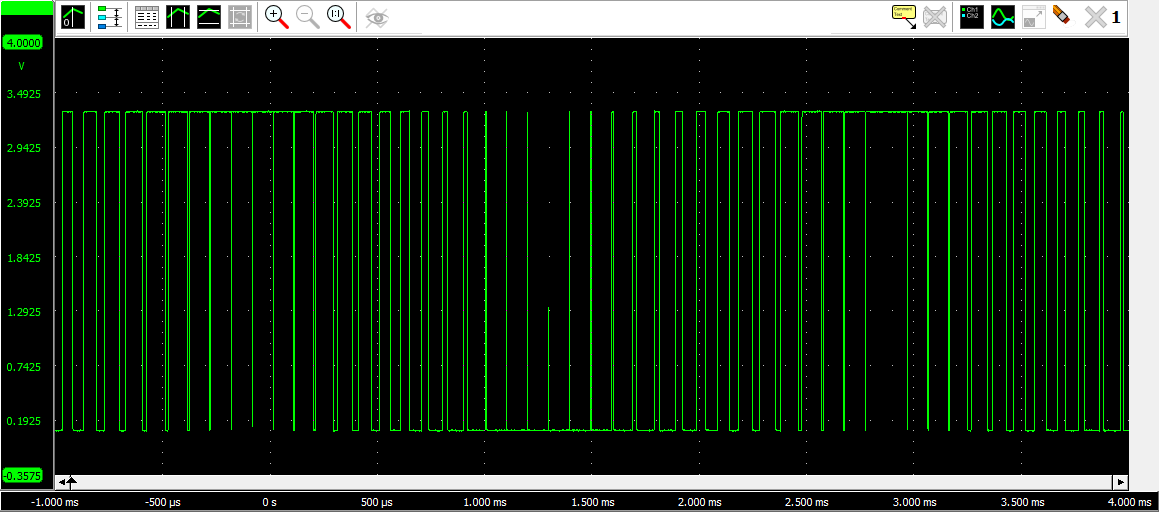
The following image shows a sinusoidal PWM generation. The average and amplitude are .5 and the period is .003.
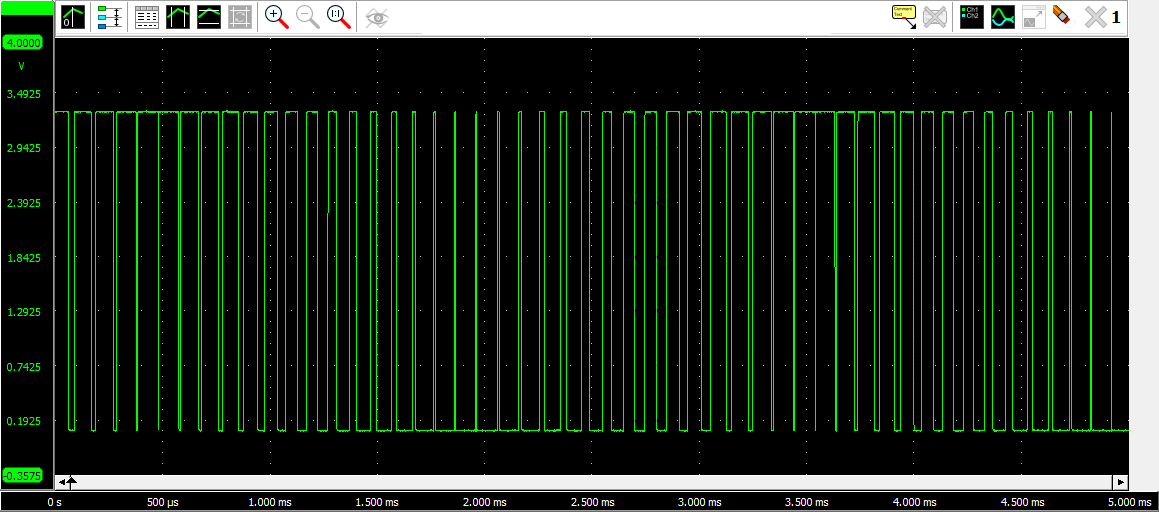
The following image shows a triangular PWM generation with the same parameters as the sinusoidal generation.
Create the file /etc/systemd/system/generator.service with the following content:
[Unit]
Description=PWM Generator on GPIO 02 -> 09
Wants=network.target
After=syslog.target network-online.target
[Service]
Type=simple
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/generator 4000
User=root
Group=root
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec=10
KillMode=process
StandardOutput=append:/var/log/generator.log
StandardError=append:/var/log/generator.err.log
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Build and install the program for the first time.
gcc -I. *.c -O3 -latomic -lm -lpthread -Wall -o pwmgenerator
sudo cp pwngenerator /usr/local/bin/generatorEnable the service for automatic restart when reboot and start it.
sudo systemctl enable generator.service
sudo systemctl start generator.serviceWhen the source files are modified, you may use the ./build command
to recompile, install and start the new code version.
The PWM generator communicates over a TCP IP connection by exchanging text messages ending with a newline character (\n not \r\n). The first character of response message is > in case of success, and ! in case of error. In the later case the ! is followed by a human readable text explaining the reason of error.
Once a TCP connection is established, the client must proceed with the greeting message exchange. Failing to do so result in the connection closing by the generator. This protects generator from rogue visitors or bogus clients.
When the TCP connection is established, the client has 500ms to send the message "PWM0" to which the generator respond with ">HELO v0.1 12bits". The version and resolution might evolve in future versions.
If there is already an active connection, the generator respond with "!busy with xx.xx.xx.xx:yy" where xx.xx.xx.xx:yy is the IP address and port of the active connection. This allows to identify the process that is currently using the generator. After sending back this message, the generator closes the connection.
When the client sends the message "GPRM" to the generator, it respond with the list of parameters of the 8 channels. Example:
"8, 0 CST 0.1 0 0 0, 1 TRI 0.5 0.5 0.003 0, 2 CST 0.3 0 0 0, 3 CST 0.4 0 0 0, 4 CST 0.5 0 0 0, 5 CST 0.6 0 0 0, 6 CST 0.7 0 0 0, 7 CST 0.8 0 0 0"
The first number is the number of channels. It is followed by the parameters of each chanel preceeded by a comma. The first value of the chanel parameters is the channel number. The second parameter is the type of generation (CST, SIN, TRI), and the fours following parameters are respectively the average, the amplitude, the period and the start values.
When the client sends the message "FREQ" to the generator, it respond with the frequency and its standard deviation. Example:
"10156.55 0.012345"
The first number is the frequency and the second number the standard deviation.
To set the channel parameters, the client must send a message starting with "SPRM" and followed by the parameters. Example:
"SPRM 2, 3 CST 0.4 0 0 0, 5 CST 0.6 0 0 0"
The first number after SPRM is the number of channels to be set and whose parameters follow. The channel parameters encoding is the same as for GPRM. The first integer number is the channel number. It is followed by "CST", "SIN" or "TRI" to specify the type of variation. The next four floating point parameters encoded with the formatting code %g, are respectively the average, the amplitude, the period and start values.
A simple Go client program is also provided with PWM generator driver package (Go's library).
To install Go, follow the directives at https://go.dev/dl/.
- add
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/go/binto your .bashrc file - execute the following instructions to download and install Go.
wget -P /tmp https://go.dev/dl/go1.17.7.linux-amd64.tar.gz sudo rm -rf /usr/local/go sudo tar -C /usr/local -xzf /tmp/go1.17.7.linux-amd64.tar.gz go version
cd goClient
go install ./...By default, go creates the directory ~/go where it stores
all the users go related information. You can define a different
location by setting the GOPATH environment variable. The compiled
binaries will be stored in GOPATH/bin. Add this directory to
your PATH environment variable.
The program name is testPWM and it accept the IP address and port
of the PWM generator server as unique optional argument. Example
testPWM 192.168.1.80:4000
This small program simply get and displays the current parameters of the 8 channels, set som channels to some values, and then get again all parameters and display them. It finally waits 2 minutes. It gives time to check the generated output at the GPIO, or test the effect of a connection attempt when there is an active connection.
The channels 0 to 7 are mapped to the GPIO output 2 to 9.
- Establish a connection on file descriptor 5:
$ exec 5<>/dev/tcp/192.168.1.11/4000 - Immediately send the handshake:
$ echo "PWM0" >&5 - Read the response:
$ head -r 1 <&5should be>HELO v0.1.1 12bits - Configure all the channels:
echo "SPRM 8, 0 CST 0.1 0 0 0, 1 CST 0.2 0 0 0, 2 CST 0.3 0 0 0, 3 CST 0.4 0 0 0, 4 CST 0.5 0 0 0, 5 CST 0.6 0 0 0, 6 CST 0.7 0 0 0, 7 CST 0.8 0 0 0" >&5 - Read result:
$ head -r 1 <&5should be ">DONE" - Close the connection:
exec 5>&-
- create logger function with levels
- run fuzzer to test robustness