GraphQL Context and Services
Simple example showing how to use
Contextas aclasswithin GraphQL, along withcontext.servicesfor abstracting away downstream API complexity.For extra credit, this also shows off Apollo's REST Data Source with built in caching!
Demo
Use the following example query:
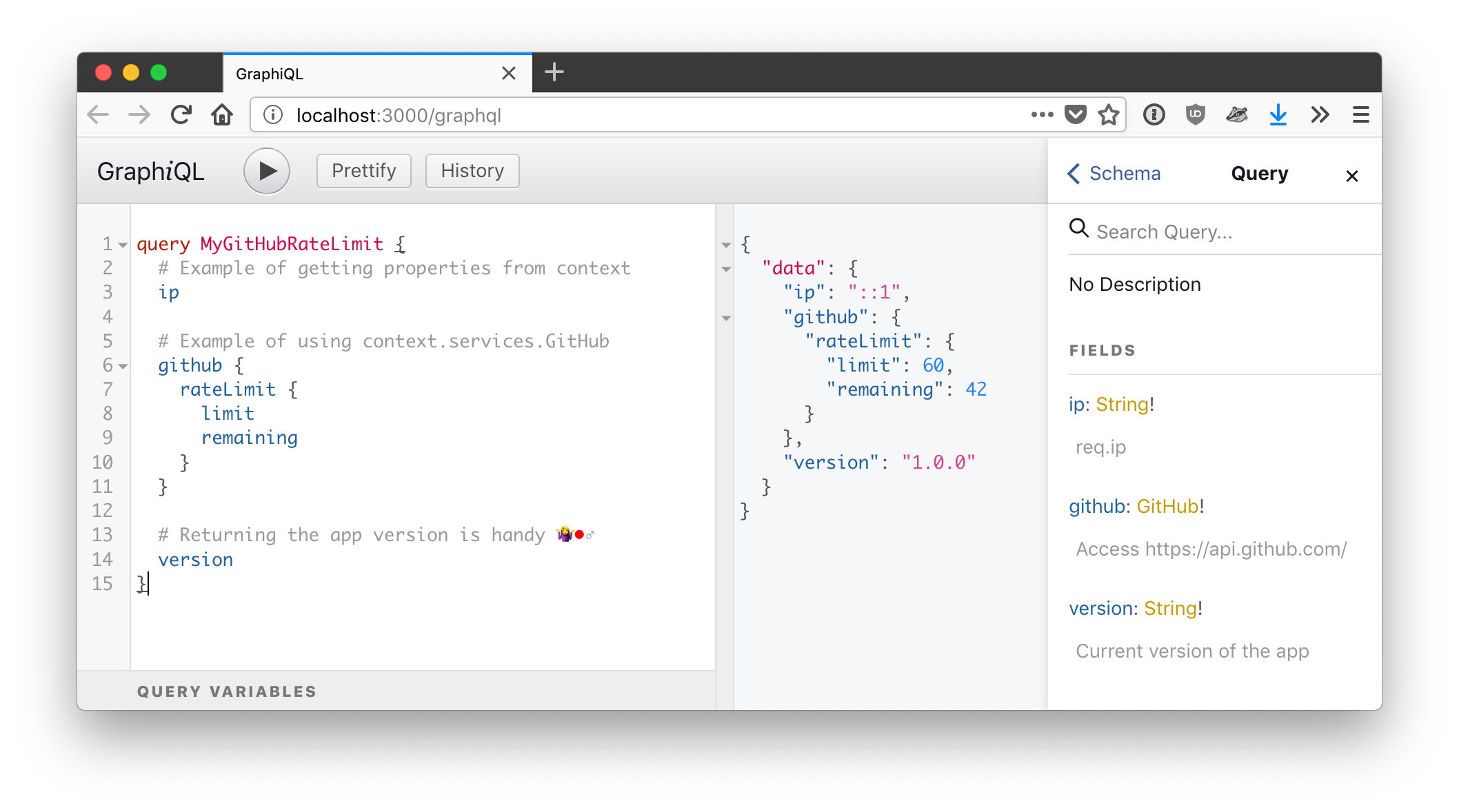
query MyGitHubRateLimit {
# Example of getting properties from context
ip
# Example of using context.services.GitHub
github {
rateLimit {
limit
# 👇 Cached automatically!
remaining
}
}
# Returning the app version is handy 🤷♂️
version
}Rationale
-
Using
Context(instead of a plain{...}object) moves complexity from within your middleware to a separate, testable layer:.use( "/graphql", graphql((req, res) => { const context = new Context({ req }) return { context, graphiql: true, pretty: true, schema, } })
-
Contextcan have a strict, testable API for your resolvers to use, instead of ad-hoc reliance onreq.queryorreq.body:// Before ip: (parent, args, context, info) => { if (req.header("x-forwarded-for")) { return req.header("x-forwarded-for").split(",").shift() } if (req.connection.remoteAddress) { return req.connection.remoteAddress } return req.ip } // After ip: (parent, args, context, inf0) => { return context.ip }
-
API calls within resolvers are simplified:
rateLimit: (parent, args, context, info) => { const { GitHub } = context.services return GitHub.getRateLimit() }
-
The same as Apollo's
dataSources, but works with the standardexpress-graphqllibrary: