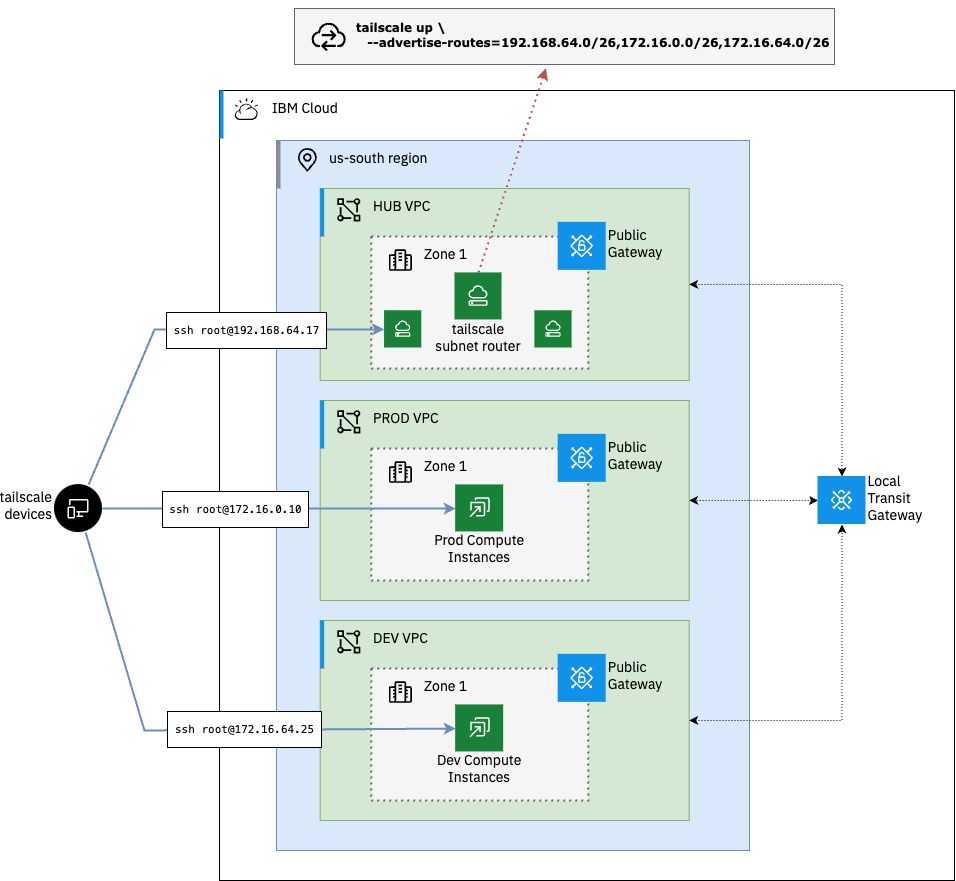
Use the Tailscale Subnet Router feature to expose routes across multiple VPCs. Subnet routers act as a gateway, relaying traffic from your tailnet to the VPC subnets without the need for each device to be running the tailscale agent.
In this example we will connect a hub VPC, where our Subnet Router instance is running, to our prod and dev VPCs in the same region via a local IBM Cloud Transit Gateway.
The first step is to clone the repository and configure the terraform variables.
git clone https://github.com/cloud-design-dev/ibmcloud-vpc-ts-router.git
cd ibmcloud-vpc-ts-routerCopy the example terraform variables file and update the values with your own.
cp tfvars-template terraform.tfvars| Name | Description | Type | Default | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| dev_prefix | The address prefix to use for the dev_vpc VPC | string |
"172.16.64.0/18" |
no |
| existing_resource_group | The IBM Cloud resource group to assign to the provisioned resources. | string |
n/a | yes |
| existing_ssh_key | The name of an existing SSH key to use for provisioning resources. If one is not provided, a new key will be generated. | string |
"" |
no |
| hub_prefix | The address prefix to use for the hub VPC | string |
"192.168.0.0/18" |
no |
| ibmcloud_api_key | The IBM Cloud API key to use for provisioning resources | string |
n/a | yes |
| ibmcloud_region | The IBM Cloud region to use for provisioning VPCs and other resources. | string |
n/a | yes |
| prod_prefix | The address prefix to use for the prod_vpc VPC | string |
"172.16.0.0/18" |
no |
| project_prefix | The prefix to use for naming resources. If none is provided, a random string will be generated. | string |
"" |
no |
| tailscale_api_key | The Tailscale API key | string |
n/a | yes |
| tailscale_tailnet_id | The Tailscale tailnet ID | string |
n/a | yes |
Once you have the required variables set, you can initialize the terraform configuration and create a plan for the deployment.
terraform init
terraform plan -out=plan.outIf no errors are returned, you can apply the plan to create the VPCs, subnets, and compute instances.
terraform apply plan.outWhen the provosion is complete, you should see the output of the plan, including the private IP addresses of the compute hosts.
Apply complete! Resources: 41 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
Outputs:
dev_node_ip = "172.16.64.4"
dev_vpc_subnet = "172.16.64.0/26"
hub_vpc_subnet = "192.168.0.0/26"
prod_node_ip = "172.16.0.4"
prod_vpc_subnet = "172.16.0.0/26"
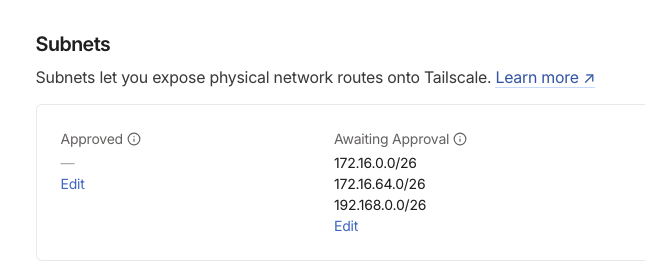
ts_router_ip = "192.168.0.4"By default the subnet router will not advertise any of the subnets until they are approved in the Tailscale admin console. From the admin console, navigate to the Machines tab and click the subnet router instance name. On the machine details page you should see the subnets that are available to be advertised.
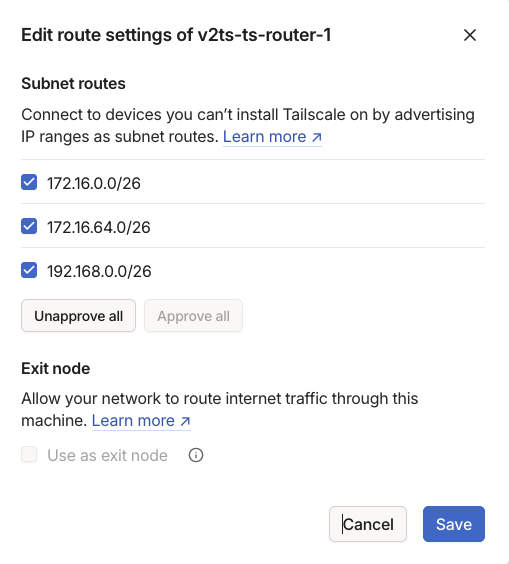
Under Approved click Edit and select the subnets you want to advertise and click Save.
Once the subnets are approved, you can start the Tailscale app on your local machine and start testing connectivity to the private IP addresses of our VPC compute instances.
ssh root@<dev_node_ip>
# or
ssh root@<prod_node_ip>To remove the resources created by the terraform configuration, you can run the destroy command.
terraform destroyIn this example we have deployed a Tailscale subnet router in a hub IBM Cloud VPC and connected it to two spoke VPCs in the same region using a Transit Gateway. This allows us to connect in to our compute in these VPCs without the need for each device to be running the Tailscale agent.