
A decentralized NFT geocaching application
Preview
·
Live Demo
·
Report Bug
·
Request Feature
This project is designed and implemented by Volker Dufner and Tim Schmitz as part of the Solana Summer Hackathon.
Geocaching is an outdoor recreational activity, in which participants use a Global Positioning System (GPS) receiver or mobile device and other navigational techniques to hide and seek containers, called "geocaches" or "caches", at specific locations marked by coordinates all over the world. A typical cache is a small waterproof container containing a logbook and sometimes a pen or pencil. The geocacher signs the log with their established code name and dates it, in order to prove that they found the cache. After signing the log, the cache must be placed back exactly where the person found it. Larger containers such as plastic storage containers (Tupperware or similar) or ammunition boxes can also contain items for trading, such as toys or trinkets, usually of more sentimental worth than financial. Geocaching shares many aspects with benchmarking, trigpointing, orienteering, treasure-hunting, letterboxing and waymarking.
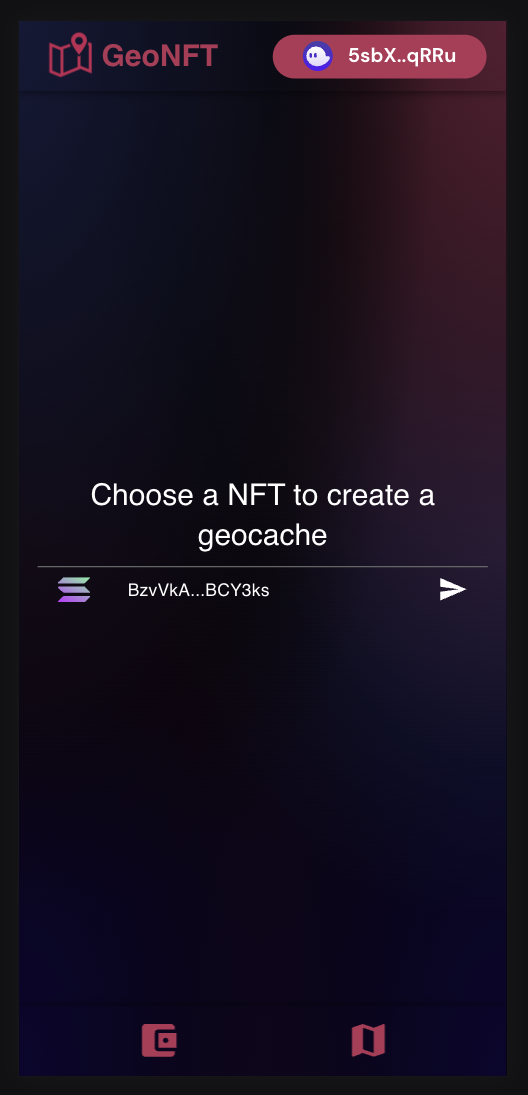
The concept behind NFT geocaching is that with our mobile app, the community can drop off their Non-Fungible Token (NFT) at a specific location of their choice and the finder can pick them up. This creates an incentive to get outside and look for potentially valuable NFTs.
Geocaching offers something for everyone, from families with children to retirees. Some geocachers play the game to see how many total “finds” they can get, while others play to see how many new states or countries they can visit. Geocaching is a great way to find remarkable destinations that you would not have otherwise discovered. It is also an excellent education tool and an excuse to get off the couch.
Since the hackathon is hosted by Solana, we also use the corresponding Solana blockchain and the newly developed Solana Mobile Stack.
Happy hunting!
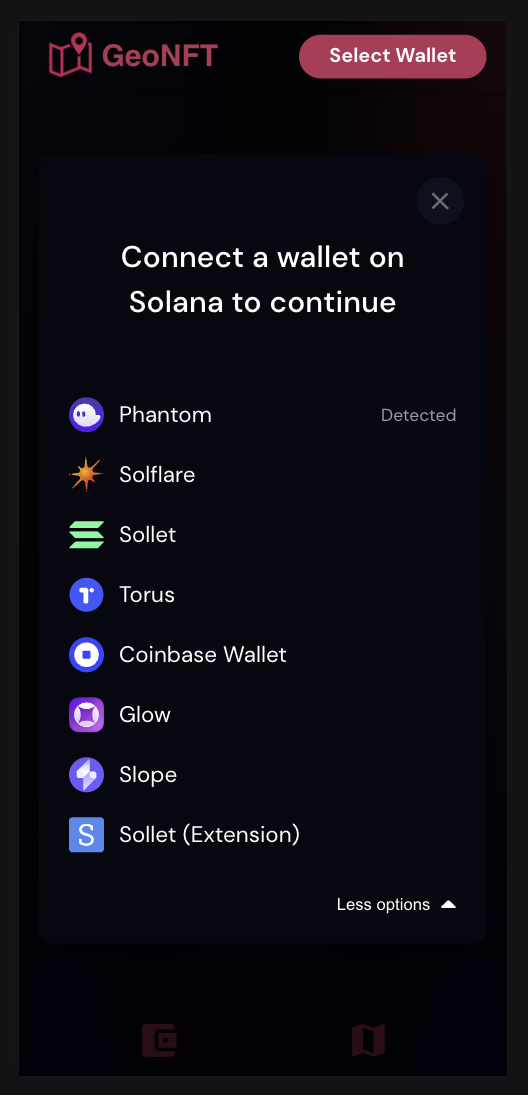
- Connect a Solana compatible wallet of your choice e.g. Phantom
- The NFT holder goes to a location of his/her choice where he/she would like to place the NFT.
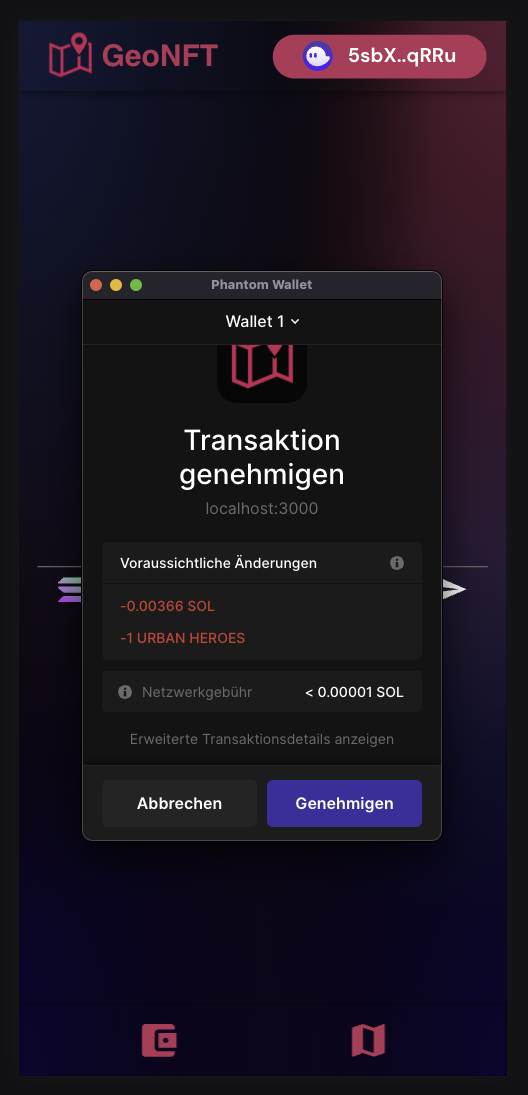
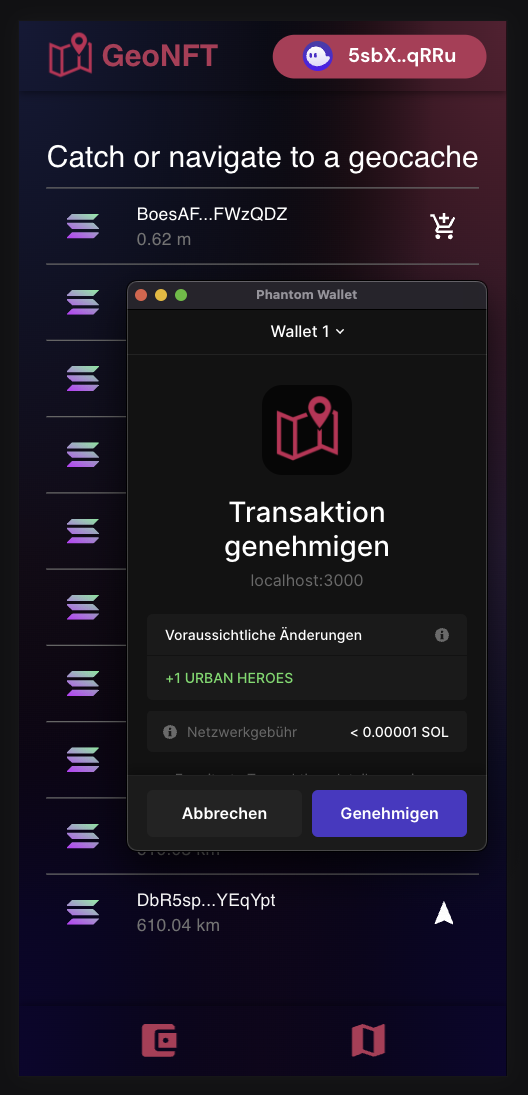
- The NFT and the location coordinates are then sent from the holders wallet to our smart contract. The coordinates are additionally encrypted to prevent misuse or theft of the NFTs.
- Searchers can now use the app to see where the nearest NFTs are and make their way there.
- The first person who finds the NFT gets the opportunity to take it. This is transferred from the smart contract to the finders wallet.
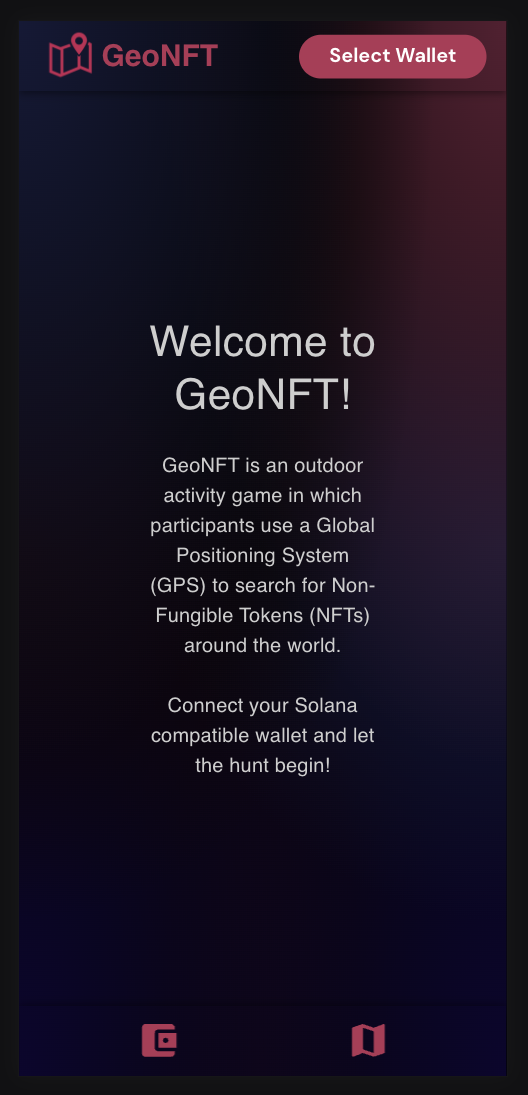
| Starter Page | Connect Wallet | Create Geocache from Token | Confirm Transaction |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Geocache created | Navigate to Geocache | Catch Geocache with Token | Geocache caught |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
First of all, we had the major challenge in general of never having worked with Solana, Rust or React-Native before. But of course we embraced that and started by researching the best practices for creating and deploying smart contracts on Solana. We quickly came across Anchor and familiarized ourselves with its Anchor book and the basics of Solana Contracts.
It seems trivial at first, but after we had finished the basic contract for setting a geolocation of the geocache, we asked ourselves how we can transfer the associated NFT to the contract. The examples of something like this are significantly less common. At some point we found a solution called Program Derived Addresses (PDAs).
The NFTs in the Smart Contract can be taken by everyone who claims to have the coordinates that the NFT was stored on. In practice hackers could call the functions without playing along the rules and steal the NFTs. To solve the problem we plan to put a key into out application that is stored on-chain as hash to make sure only users of the application can extract NFTs.
After the contract was deployed, we wanted to start with the app. Here we quickly encountered limitations caused by the new mobile wallet adapter. Among other things, only Android and not iOS is currently supported, and you also need a fake wallet (also only Android) to sign transactions. There are also no examples of how to use an Anchor contract with it. When we asked the developers, we were told that everything is still under development. So after some tests, we decided to implement a React app as a Progressive Web App (PWA) for mobile devices.
We started the implementation and everything worked at the browser level without any major incidents. But when we tested the app on a smartphone, we could not link a wallet, even though the Phantom app was also installed. After a Github search, we found out that the deep links to the wallet are not yet supported by the Solana wallet adapter and would therefore only work in the in-app Phantom browser. Of course we tested this and ended up with the SSL requirement. We have also built a solution for this, but then we came to the next problem.
After we linked the wallet and tried to create a new geocache, we could not determine the current geolocation of the smartphone. This is because Phatom's internal browser does not support this feature. So we were faced with the decision to create a web-only application, which is of course very impractical for geocaching, or to switch back to the React-Native version.
Currently, the mobile wallet adapter has still limited functionality, using our app in Google Chrome with a wallet extension offers the best user experience. In the future, we plan to switch back to React-Native to make the game playable on mobile devices. A Solana wallet integration, a GPS functionality and a integration of a map such as Google Maps is needed for a proper integration of our app on mobile devices.
Since the hackathon is now coming to an end and we are far from having reached our goal with our idea, we would like to record some planned features. And of course the native app is just one of many.
The sustainability aspect does not stop at blockchain and mobile games, which is why we want to follow the basic idea of Solana and encourage people to use less energy and focus sustainable solutions. With the help of our app we want to bring people back to nature so that they can regain their lost appreciation. GeoNFT allows users to place their valuables in difficult and inaccessible places where vehicles are disadvantageous and walking or cycling is the means of choice. A bonus program and time-limited challenges could provide additional incentives.
With a ranking system, we want to be able to guarantee our participants long-lasting fun. For example, an additional GeoNFT could be issued for each geocache collected, thus creating a global ranking list.
Permanent geocaches are also planned at certain points of interest. If a user reaches this point, it gives him the opportunity to mint an NFT with the location and thereby receive proof of his presence e.g. on a summit cross on Mount Everest.
- Volker Dufner based in D-Stuttgart | Blockchain Developer
- Tim Schmitz based in D-Frankfurt | Blockchain Developer
- Volker Dufner: dufnervolker@gmail.com
GeoNFT is an outdoor activity game in which participants use a Global Positioning System (GPS) to hunt down Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) around the world.
So far there is no established competitor with the same functionality. However, this is only a matter of time, so we as GeoNFT need to stay tuned to the development and possibly also consider a cross-chain solution to reach the masses. First of all, the app should continue to be built on Solana in terms of its UI/UX so that it enables a good gaming experience. With the planned features, we think we can create a versatile solution that can also be used in countless other sports activities.
GeoNFT should appear as a non-profit organization because we don't want to make money - the sustainability and environmental aspects are much more important to us in this project. Of course, the development costs have to be covered, which is why we depend on donations from investors in addition to the hoped-for hackathon prize. In the extreme case, a small fee when transferring the NFTs would be conceivable. However, we would like to consciously avoid placing advertising in the app.
The chances of a possible success or even hype are very good. Consider traditional geocaching used for years, the number of active caches is over a million. If we take a look at Pokemon Go, which was released a few years ago and is based on a similar game principle, then we even reach 166 million possible players.
The Solana-Blockchain is one of the most famous Smart Contract platforms with a fast growing user base. As a leading ledger to create and trade NFTs, Solana can be seen as a large competition to Ethereum.
Smart Contracts on Solana are called 'programs' and they are usually written in the Rust programming language.
Solana announced to develop Saga, an Android phone with special features to integrate cryptocurrencies and decentralized apps in a mobile device. Aditionally, there is a SDK to integrate Solana on classical Android applications. Unfortunately, our game is currently only available as a web application because of the ongoing development of the mobile wallet adapter SDK.
In the project structure, you will see the following files and folders.
- packages - This is an Yarn workspace, new way to set up your package architecture. It allows you to setup multiple packages in such a way that you only need to run yarn install once to install all of them in a single pass.
- achnor - Anchor is a framework for Solana's Sealevel runtime providing several convenient developer tools for writing smart contracts.
- program — This is the directory of Solana programs (Smart contracts)
- test — This is where javascript test code lives
- migrations — This is the deploy script
- react-app — This is where the web-frontend is going to be built
- react-native-app - This is where the mobile-frontend is going to be built
- achnor - Anchor is a framework for Solana's Sealevel runtime providing several convenient developer tools for writing smart contracts.
Go here to install Rust.
Go here to install Solana and then run solana-keygen new to create a keypair at the default location. Anchor uses this keypair to run your program tests.
Switch to the Solana Devnet by running solana config set devnet and fund this wallet with solana airdrop 2 or on https://solfaucet.com/.
Go here to install Yarn.
Installing using Anchor version manager (avm) (recommended)
Anchor version manager is a tool for using multiple versions of the anchor-cli. It will require the same dependencies as building from source. It is recommended you uninstall the NPM package if you have it installed.
Install avm using Cargo. Note this will replace your anchor binary if you had one installed.
cargo install --git https://github.com/project-serum/anchor avm --locked --force
On Linux systems you may need to install additional dependencies if cargo install fails. E.g. on Ubuntu:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade && sudo apt-get install -y pkg-config build-essential libudev-dev
Install the latest version of the CLI using avm, and then set it to be the version to use.
avm install latest
avm use latest
Verify the installation.
anchor --version
To create your own NFT and then place it around the world, you can do this via https://app.strataprotocol.com/launchpad/create.
- Run
yarn installto install related dependencies. - Go to the packages/anchor folder and run
anchor buildto build the Smart Contract. - Run
anchor deploy:<network>to deploy the Smart Contract to the Solana blockchain. - a) Go to the packages/react-app folder and run
yarn startto start the development server which will serve the app on http://localhost:3000
b) Using Docker 🐳docker build . -t geonft-react-app -f packages/react-app/Dockerfile
Copyright: Volker Dufner | 2022





