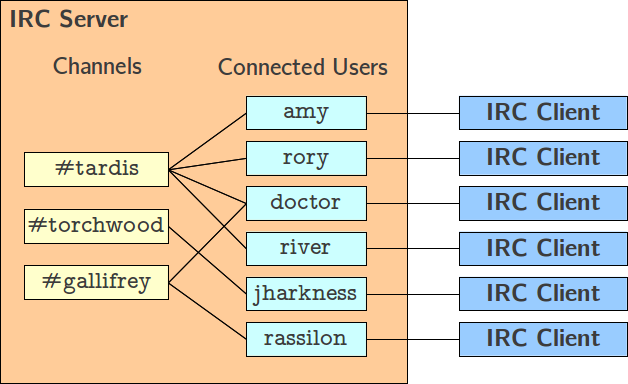
Created an Irc server.
The objective of this project is to reproduce the operation of an IRC (Internet Relay Chat) server, so that several IRC clients can connect; carried out in a group 😊.
- Basic bash
- Terminal
- Irssi client
- Netcat client (nc)
- Work on Linux
- Command make for the Makefile
- How to run the program
- First clone it
git clone https://github.com/balkisous/Ft_Irc.git ``` - Change directory and make to compile
~ cd Ft_Irc && make ~ ./ircserv [port] [password] Ex : ./ircserv 1555 123pass - Open a new terminal and Test with irssi client or nc client
- With irssi :
~ irssi -c localhost -p [port] - With nc :
~ nc localhost [port] PASS serverpass NICK marie USER marie 0 * :marie JOIN #chan PART #chan
Read the IRC documentation to understand how to connect and how it's works. L-> https://modern.ircdocs.horse/ (Go in client Messages)
Names of contributors :
- @marieines7
- @dediane
- @balkisous
- Made at 42Paris
You will find the subject in the repository.
http://chi.cs.uchicago.edu/chirc/index.html
https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc2810
https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc2812
https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc2811
A message is a string of maximun 510 characters and ends by "\r\n"(so 512 characters in total). There is no null terminator.
"\r\n" = CR-LF (Carriage Return - Line Feed)
Any message with more than 510 characters (not counting the delimiter) will be truncated, with the last two characters replaced with “\r\n”.
A message contains at least two parts: the command and the command parameters. ex:
NICK amy
WHOIS doctor
MODE amy +o
JOIN #tardis
QUIT
Some messages also include a prefix before the command and the command parameters. The presence of a prefix is indicated with a single leading colon character.
:borja!borja@polaris.cs.uchicago.edu PRIVMSG #cmsc23300 :Hello everybody
:doctor!doctor@baz.example.org QUIT :Done for the day, leaving
Special type of message called a reply. When a client sends a command to a server, the server will send a reply.
Replies are used to acknowledge that a command was processed correctly, to indicate errors, or to provide information when the command performs a server query. A reply is a message with the following characteristics: It always includes a prefix. The command will be a three-digit code. The full list of possible replies is specified in [RFC2812 §5]. The first parameter is always the target of the reply, typically a nick.
:irc.example.com 001 borja :Welcome to the Internet Relay Network borja!borja@polaris.cs.uchicago.edu
:irc.example.com 433 * borja :Nickname is already in use.
:irc.example.org 332 borja #cmsc23300 :A channel for CMSC 23300 studen
socket() create endpoint and return fd.
getsockopt() to get socket options you need to send the fd returned by socket() function
getsockname() return 0 on success and -1 on error, return the current address to which the socket is bound.
gethostbyname() return a struct type hostent and copy name into the h_name of the struct.
getaddrinfo() returns struct addrinfo: struct addrinfo { int ai_flags; int ai_family; int ai_socktype; int ai_protocol; socklen_t ai_addrlen; struct sockaddr *ai_addr; char *ai_canonname; struct addrinfo *ai_next; }; freeaddrinfo -> to free.
bind() assigns the address specified by addr to the socket referred to by the file descriptor sockfd
fcntl() performs one of the operations described below on the open file descriptor fd. The operation is determined by cmd.
https://modern.ircdocs.horse/#connection-registration
When user connect for the first time, client will send commands: PASS, NICK and USER. We need to split the received buffer and parse it to make first registration. We need to make sure the Nickname is available and the password correct. Then we can set up our user as registered and reply to the client with: RPL_WELCOME, RPL_YOURHOST, RPL_CREATED, RPL_MYINFO.
irssi -c localhost -p 1050