This repo contains the code and data of the following paper:
RF-Net: A Unified Meta-Learning Framework for RF-enabled One-Shot Human Activity Recognition, Shuya Ding, Zhe Chen, Tianyue Zheng, Jun Luo, Sensys2020 [pdf]
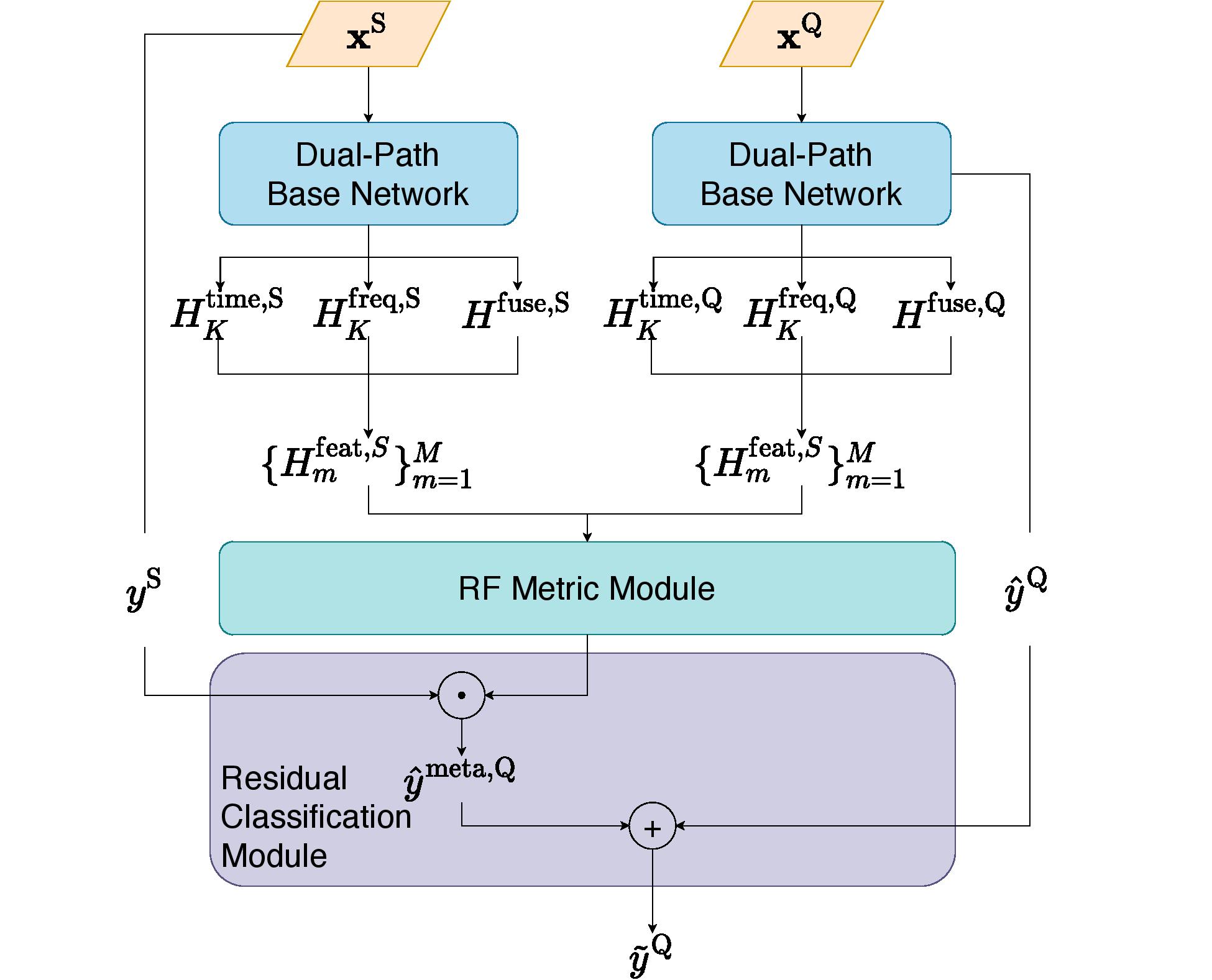
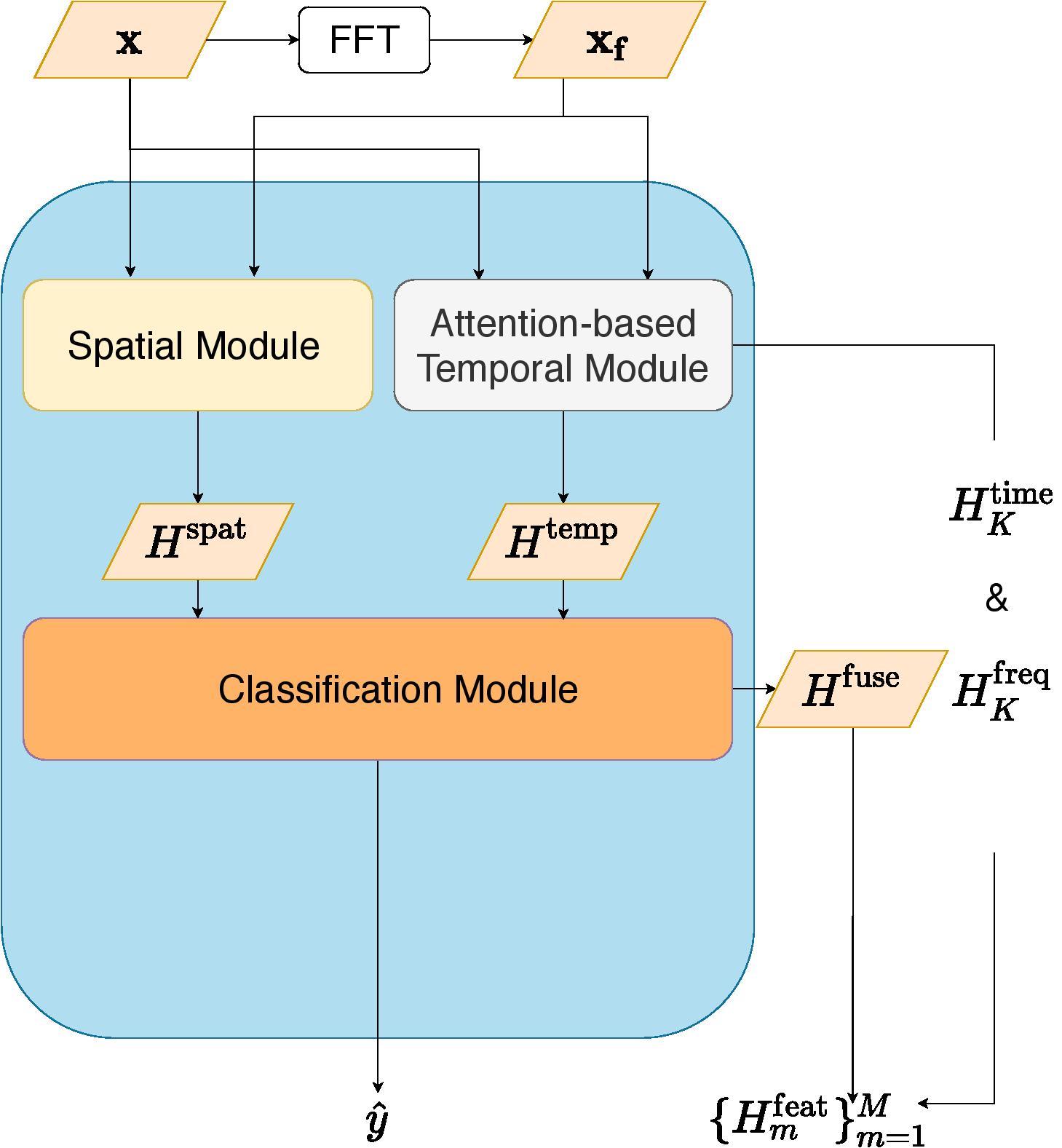
Radio-Frequency(RF) based device-free Human Activity Recognition(HAR) rises as a promising solution for many Internet-of-Things(IoT) applications, such as elderly care and baby monitoring. However, device-free (or contactless) sensing is often more sensitive to environment changes than device-based (or wearable) sensing. Also, RF datasets strictly require on-line labeling during collection, starkly different from image and text data collections where human interpretations can be leveraged to perform off-line labeling. Consequently, existing learning algorithms to achieve RF-HAR entail a laborious process to gather sufficient data for being adaptive to new environments. To this end, we propose RFNet as a meta-learning based neural network for one-shot RF-HAR, so that the labeling efforts for environment adaptation are reduced to the minimum level. In particular, we first examine three representative RF sensing techniques and two major meta-learning approaches. The results motivate us to innovate in two designs: i) a dual-path base HAR network, where both time and frequency domains are dedicated to learning powerful RF features including spatial and attention-based temporal ones, and ii) a metric-based meta-learning framework to enhance the fast adaption capability of the base network, including an RF-specific metric module along with a residual classification module. We conduct extensive experiments based on all three RF sensing techniques in multiple real-world indoor environments; all results strongly demonstrate the efficacy of RFNet compared with state-of-the-art baselines.
- Please provide setting in config.py
- Run python main.py for training RF-Net
If it is useful for your research, please consider cite the following reference paper:
@inproceedings{10.1145/3384419.3430735,
author = {Ding, Shuya and Chen, Zhe and Zheng, Tianyue and Luo, Jun},
title = {RF-Net: A Unified Meta-Learning Framework for RF-Enabled One-Shot Human Activity Recognition},
year = {2020},
isbn = {9781450375900},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3384419.3430735},
doi = {10.1145/3384419.3430735},
abstract = {Radio-Frequency (RF) based device-free Human Activity Recognition (HAR) rises as a promising solution for many applications. However, device-free (or contactless) sensing is often more sensitive to environment changes than device-based (or wearable) sensing. Also, RF datasets strictly require on-line labeling during collection, starkly different from image and text data collections where human interpretations can be leveraged to perform off-line labeling. Therefore, existing solutions to RF-HAR entail a laborious data collection process for adapting to new environments. To this end, we propose RF-Net as a meta-learning based approach to one-shot RF-HAR; it reduces the labeling efforts for environment adaptation to the minimum level. In particular, we first examine three representative RF sensing techniques and two major meta-learning approaches. The results motivate us to innovate in two designs: i) a dual-path base HAR network, where both time and frequency domains are dedicated to learning powerful RF features including spatial and attention-based temporal ones, and ii) a metric-based meta-learning framework to enhance the fast adaption capability of the base network, including an RF-specific metric module along with a residual classification module. We conduct extensive experiments based on all three RF sensing techniques in multiple real-world indoor environments; all results strongly demonstrate the efficacy of RF-Net compared with state-of-the-art baselines.},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 18th Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems},
pages = {517–530},
numpages = {14},
keywords = {RF sensing, human activity recognition, meta-learning},
location = {Virtual Event, Japan},
series = {SenSys '20}
}