Requirments
- Ansible
- Terraform
- Yandex Cloud account
- Yandec Cloud cli (yc)
- GitLab account
Implementation
Terraform part
First we need to build cloud infrastructure. For that we need to create the following resources:
- VPC
- IAM
- Compute Instance
Note: before running all the commands execute terraform init in terraform folder
Setup for that resources in terraform shown down below:
IAM
resource "yandex_iam_service_account" "gitlab-sa" {
name = "gitlab-runner-service-account"
description = "A separate sa for managing gitlab runners"
}
resource "yandex_iam_service_account_iam_binding" "gitlab-sa-binding" {
service_account_id = yandex_iam_service_account.gitlab-sa.id
role = "compute.admin"
members = [
"serviceAccount:${yandex_iam_service_account.gitlab-sa.id}"
]
}VPC
resource "yandex_vpc_network" "gitlab-runner-vpc" {
name = "gitlab-runner-vpc"
description = "VPC for gitlab-runner vm instance"
}
resource "yandex_vpc_subnet" "gitlab-runner-vpc-subnet" {
name = "gitlab-runner-vpc-subnet"
description = "Subnet for gitlab-runner instance"
v4_cidr_blocks = ["10.2.0.0/16"]
zone = var.zone
network_id = yandex_vpc_network.gitlab-runner-vpc.id
}And finally compute instance with nat_ip_address output
resource "yandex_compute_instance" "default" {
name = "gitlab-runner-${uuid()}"
service_account_id = yandex_iam_service_account.gitlab-sa.id
description = "Instance for self-hosted gitlab-runner"
zone = var.zone
resources {
cores = 2
memory = 4
}
network_interface {
subnet_id = yandex_vpc_subnet.gitlab-runner-vpc-subnet.id
nat = true
}
metadata = {
ssh-keys = "ubuntu:${file("~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub")}"
}
boot_disk {
initialize_params {
image_id = var.image-id
size = 30
description = "Ubuntu 22:04 boot os"
}
}
}
data "yandex_compute_instance" "gitlab-runner-vm" {
instance_id = yandex_compute_instance.default.id
}
output "gitlab-runner-vm-external-ip" {
value = data.yandex_compute_instance.gitlab-runner-vm.network_interface.0.nat_ip_address
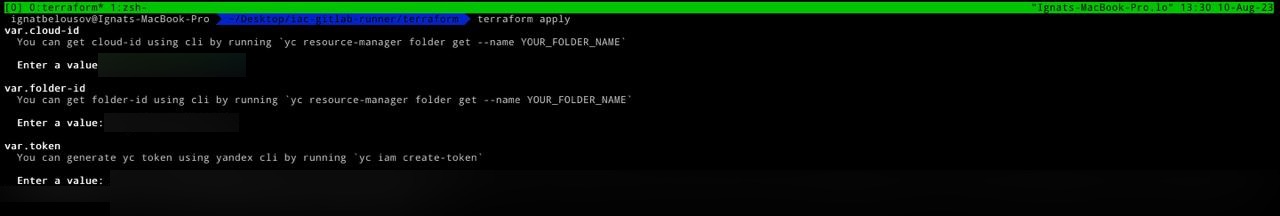
}Now we can apply this configuration by using terraform apply (NOTE: for succesfully running you need 3 required vars such as: cloud-id, folder-id, token. For obtaining and generating it I've provide a guide in each variable description field)
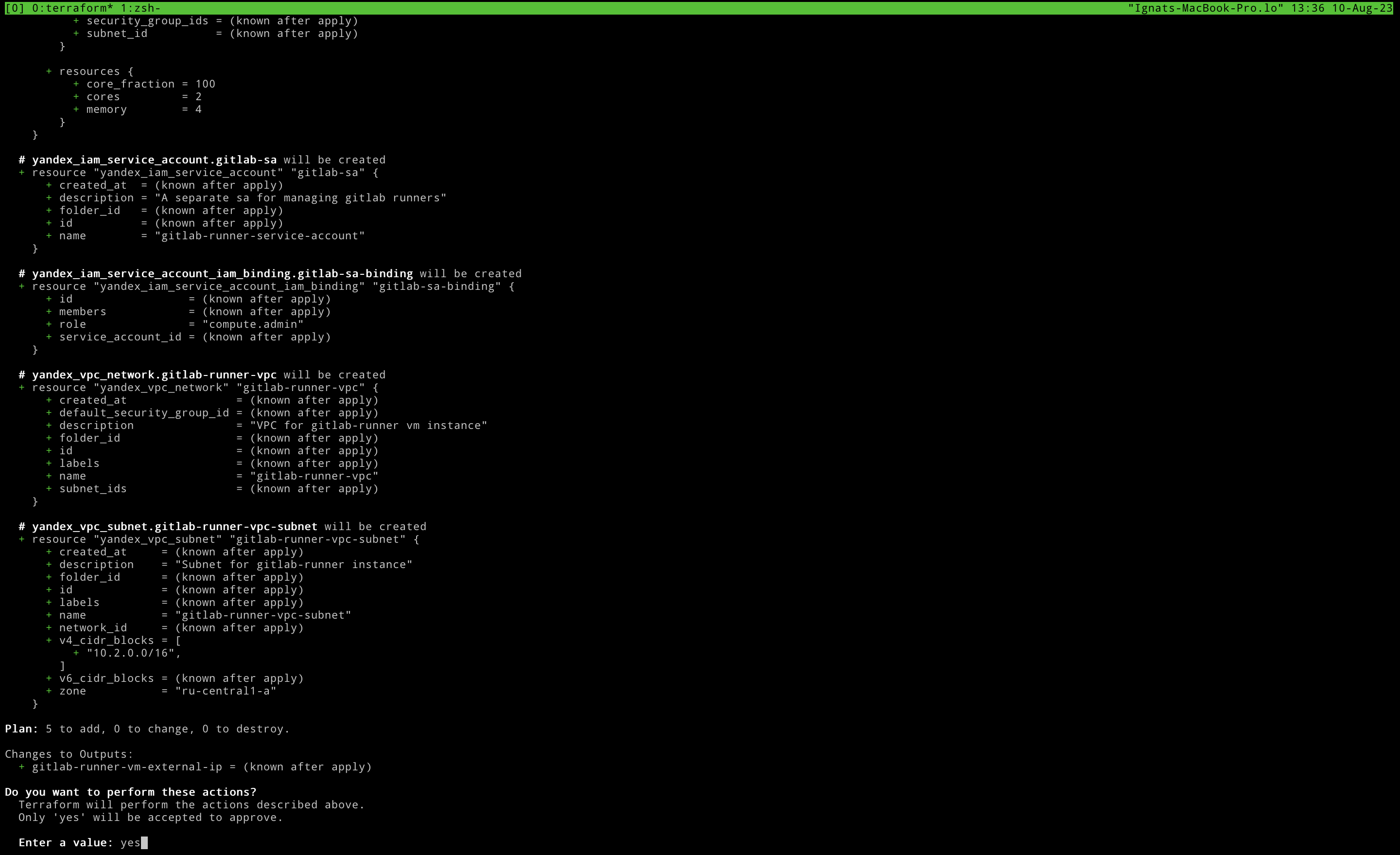
After hitting Enter we can inspect out infrasstructure code and if it seems good type yes in prompt field and click Enter.
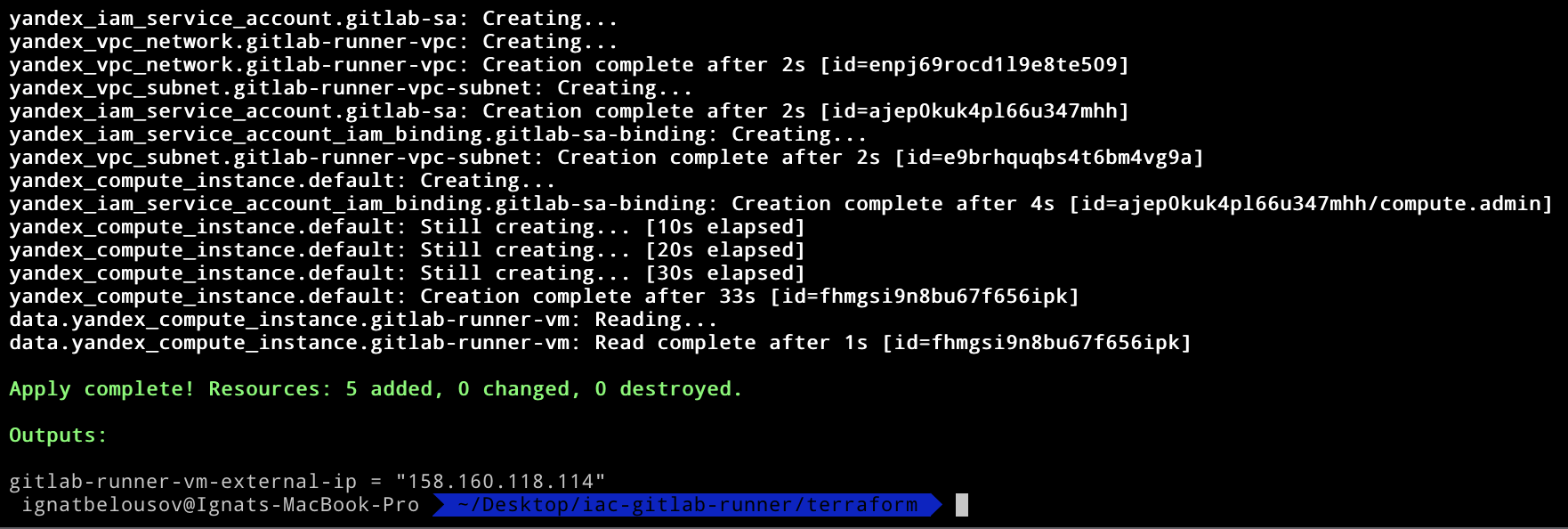
In output you should copy the nat_ip_address and move to the ansible part.
Ansible part
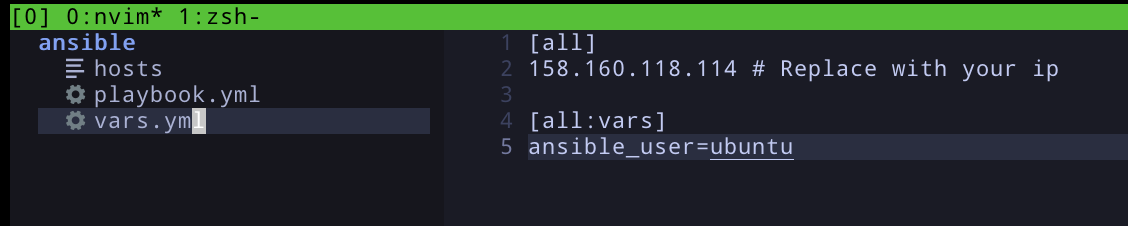
You need to place that address in hosts file in ansible directory
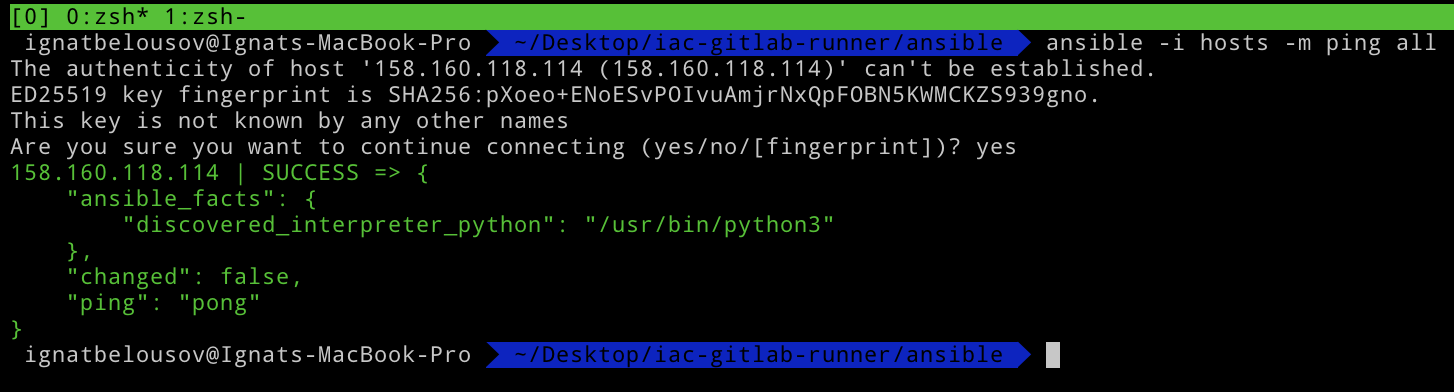
Now we can test the connection to our server by running ansible -i hosts -m ping all
So by running ansible-playbook command it will do this:
- Installing Docker gpg key
- Adding repository for Docker
- Installing Docker from deb repository
- Creating new user
gitlab-runnerand adding it in Docker group - Downloading gitlab runner sh script into
/tmp/gitlab-runner-setup.shand gives it755permissions - Execute
gitlab-runner-setup.shscript using bash - Installing
gitlab-runnerbinary using apt - Register a new Gitlab Runner
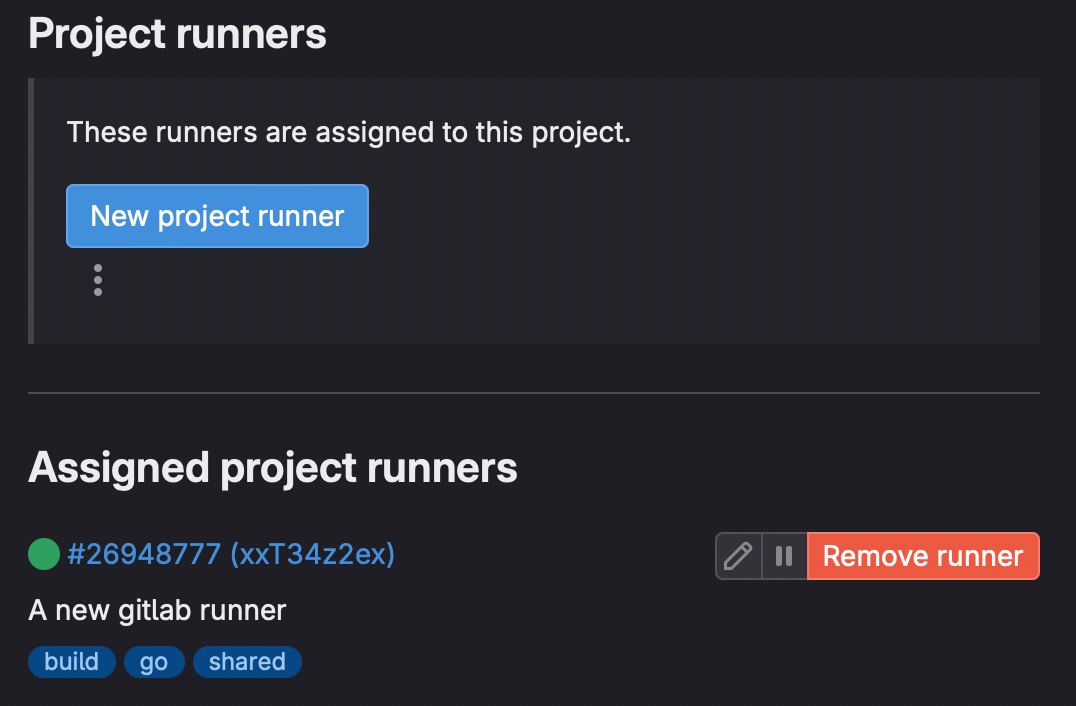
For obtaining this creds let's jump into GitLab website and register a new runner (create a new empty repo and go to the Settings > CI/CD > Runners > New project runner)
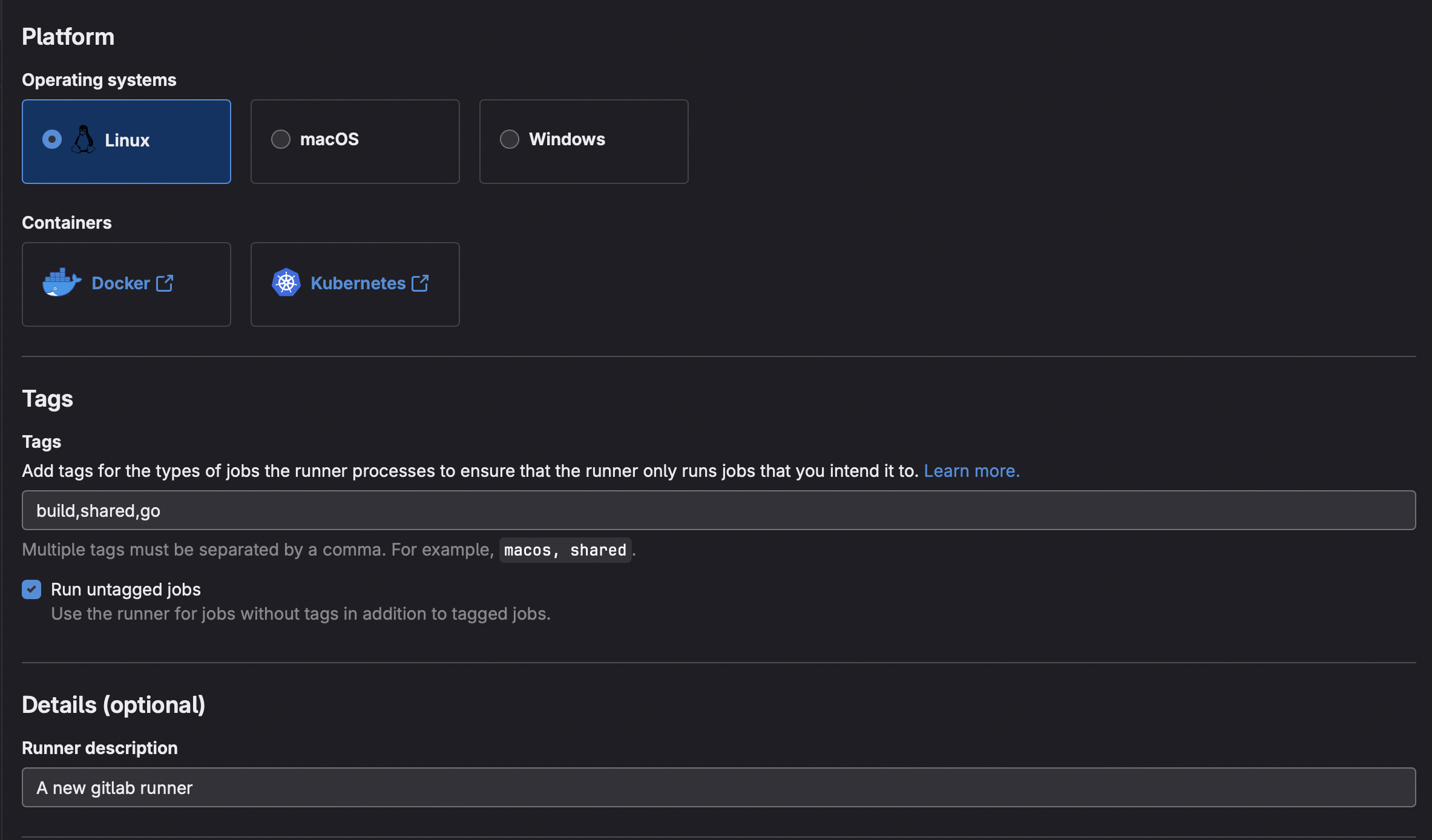
In order to create a new runner give it a tags and description and click Create runner as shown down below
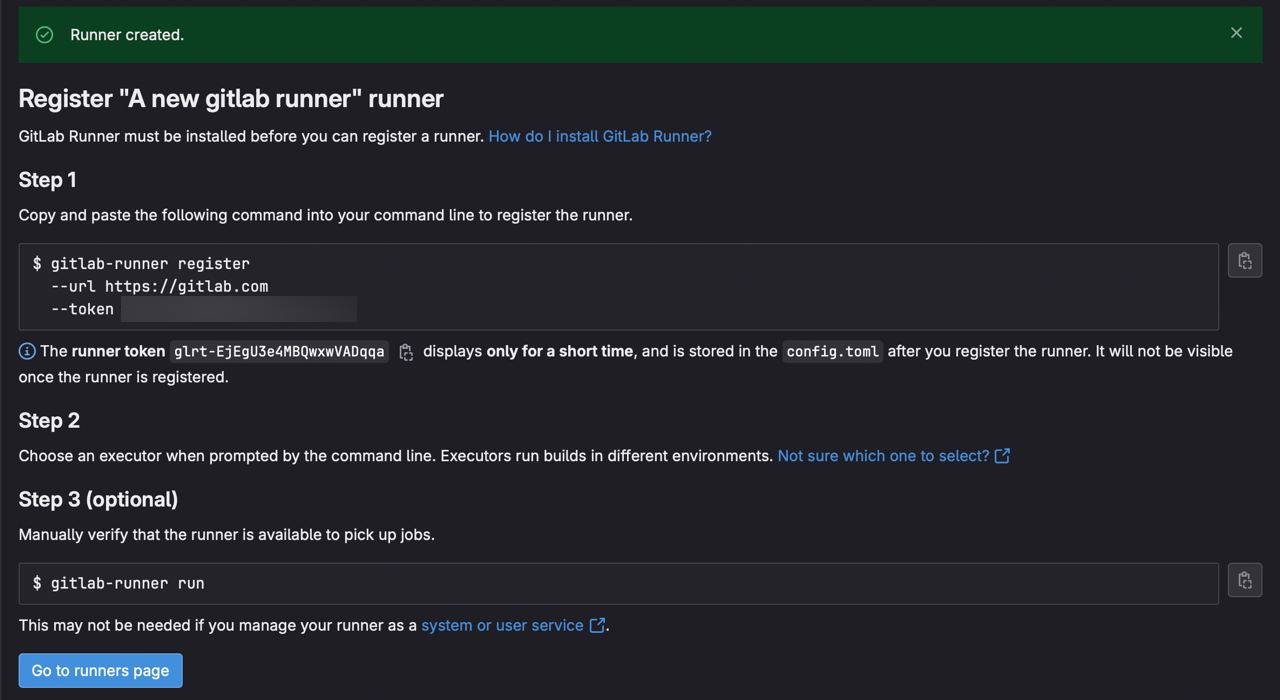
Now we can copy our registration token
Edit vars.yml file and fill it with your description and your registration_token
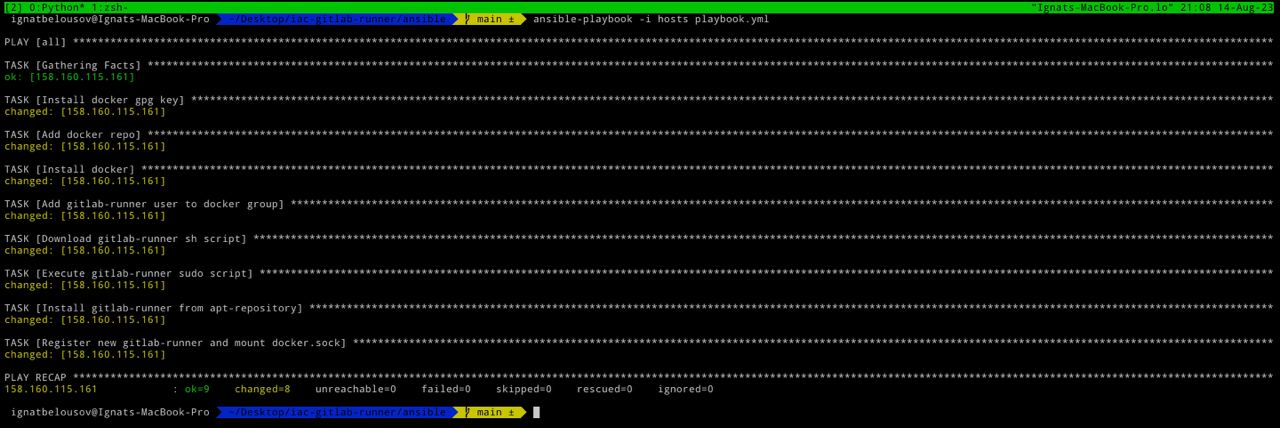
Then execute ansible-playbook -i hosts playbook.yml
The output should be like this:
Finally our gitlab-runner is up and running