Learn how to set up a clean, minimal, and efficient terminal geared towards Python development. This guide assumes a Windows 10 or 11 and a Visual Studio Code installation.
We will be using Visual Studio Code, the most popular code editor out today, along with some extensions:
- Python: Support extension for Python
- Remote - WSL: Virtual environment integration with WSL
As per the official Microsoft description, "The Windows Subsystem for Linux lets developers run a GNU/Linux environment." Put into simple terms, you can use a Linux environment without waiting an hour for your dual-boot or VM configuration to load. Still confused? Check out this video.
We'll be using version 2 since it's supposedly faster. You can check out the official Microsoft Comparison here. Install and configure with:
wsl --install
wsl --set-default-version 2A simple installation isn't enough, so you'll need to enable a feature to use WSL.
- Navigate to
Task Managerthrough 🪟 or with Ctrl+Shift+Esc.- Make sure
Virtualizationis enabled in theCPUsection of your task manager'sPerformancepage
- Make sure
- Navigate to
Turn Windows features on or offthrough the Windows search bar - Enable
Windows Subsystem for Linuxif it isn't already
Now go ahead and reboot your computer.
The most popular and beginner-friendly Linux distribution out there, Ubuntu has collaborated with Microsoft to make WSL possible. This is the Linux distribution that we'll be running atop WSL.
Install Ubuntu from the Microsoft Store. Once finished, enter Ubuntu through the 🪟, and it'll bring up a window and start installing the distribution.
Once finished, launch the app and run its installation course. Then you'll be prompted to enter a username, which you can just set to your Windows username, or whatever you like. Same goes for your password, although it's advisable to keep this the same as your Windows password so you don't have to reach for a sticky note or use your brain every time. Your keyboard won't output to the screen while you type out your password, as this is an intentional feature to keep your credentials secure.
root, run the following in PowerShell (retrieved from issue) to briefly reinstall and re-enter a username.
wsl --unregister Ubuntu
ubuntu install --ui=noneNow you can exit out of that bland default Ubuntu terminal. Go ahead and open up Windows Terminal through 🪟, and pin it to your taskbar. You may have to install it from the Microsoft Store due to what version you're on (specific releases of Windows 10 don't come with it).
Since we don't want PowerShell and the generic color scheme opening up by default, we're going to change it up.
- Click the dropdown by the
+symbol and go toSettings(or with Ctrl+,) - In the
Startuptab- Change your
Default profiletoUbuntu(with the orange logo) - Make sure you hit
Saveon the bottom right (easy to forget)
- Change your
- In the
Defaults>Appearancetab- Set your
Color SchemetoOne Half Dark - Set your
Background opacityto50% - Set your
Enable acrylic materialtoon - Again, make sure you hit
Save - Modify however else you desire
- Set your
Now you can exit and re-open it to see the changes.
Now for the most technical part of the guide, we'll set up your terminal to mimic that of a professional. I'll try my best to explain what the hell the commands you are punching in do.
Don't worry, you're not touching with any Windows system files here. If you mess up, you can go to Add or remove programs through your Windows search bar, search for Ubuntu and click ⋮ > Advanced options > Reset.
We'll install everything involving the look and functionality of your terminal. Starting off, let's upgrade everything. It'll ask for your password because we are running it with sudo, which means "super user do." The -y flag answers yes to all Y/n prompts.
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -yupdate just retrieves new versions of updatable packages, upgrade actually upgrades them. This command could take a while depending on your hardware, so go make a cup of coffee.
Now we'll install zsh (a shell built on bash, the Ubuntu default) and oh-my-zsh (a customization framework for zsh). Don't forget to indicate yes when it prompts you to make zsh your default shell.
sudo apt install zsh -y
sh -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.github.com/ohmyzsh/ohmyzsh/master/tools/install.sh)"Now we'll install our theme. This is separate from what we did back on Windows Terminal settings because we are modifying how the terminal actually displays informational text. The theme we are installing is called Typwritten: a "minimal, lightweight, informative zsh prompt theme" as per its author. Learn how to install a different theme of your liking here.
The first command is retrieving the theme from its repository and the following two commands set up symbolic links for it. Following that, we're "echoing" some settings for the theme into our .zshrc file: the shell startup file.
git clone https://github.com/reobin/typewritten.git $ZSH_CUSTOM/themes/typewritten
ln -s "$ZSH_CUSTOM/themes/typewritten/typewritten.zsh-theme" "$ZSH_CUSTOM/themes/typewritten.zsh-theme"
ln -s "$ZSH_CUSTOM/themes/typewritten/async.zsh" "$ZSH_CUSTOM/themes/async"
echo 'TYPEWRITTEN_PROMPT_LAYOUT="singleline"' >> ~/.zshrc
echo 'TYPEWRITTEN_CURSOR="block"' >> ~/.zshrc
echo 'TYPEWRITTEN_RELATIVE_PATH="adaptive"' >> ~/.zshrcNow we'll install some plugins, stuff that'll make your life easier. Everything except the echo line and the last command fetches a plugin. The statement we "echoed" into .zshrc sets an alias as bat for the plugin's default command, batcat. The last one installs tools for VS Code and opens up a file called .zshrc.
sudo apt install bat -y
echo "alias bat=/usr/bin/batcat" >> ~/.zshrc
sudo apt install tig
git clone https://github.com/zsh-users/zsh-autosuggestions ${ZSH_CUSTOM:-~/.oh-my-zsh/custom}/plugins/zsh-autosuggestions
git clone https://github.com/zsh-users/zsh-syntax-highlighting.git ${ZSH_CUSTOM:-~/.oh-my-zsh/custom}/plugins/zsh-syntax-highlighting
git clone https://github.com/agkozak/zsh-z ${ZSH_CUSTOM:-~/.oh-my-zsh/custom}/plugins/zsh-z
code ~/.zshrcTo make our theme and plugins work, we will need to add them to our .zshrc file so our shell uses them for every new session. Hit Ctrl+F and find ZSH_THEME to change it to:
ZSH_THEME="typewritten"
Hit Ctrl+F, find =(g, and change the line to:
plugins=(copybuffer copypath copyfile dirhistory git jsontools tig web-search zsh-autosuggestions zsh-syntax-highlighting zsh-z)
The reason we have more plugins in addition to the ones we installed is because oh-my-zsh comes with some default ones, which we are simply enabling. You can browse the functionalities of these plugins through these resources: Article | Masterlist | Wiki
Once you've saved .zshrc, you can load your changes with:
source ~/.zshrcNow you have a nice looking terminal, but you actually need language-specific tools. The latest version of Ubuntu on the Windows Store includes Python 3.10. You can make sure by running python3 -V. If you have a different version, check out this article for instructions on how to upgrade. To install and manage project dependencies like any normal developer, you'll need package managing tools. Install pip and venv with:
sudo apt install python3-pip -y
sudo apt install python3.10-venv -yYou can make sure you have correctly installed pip by running pip -V. Currently, the only way to run Python is by tediously typing out python3, so let's minimize this and reload your session with:
sudo apt install python-is-python3
echo "alias py=/usr/bin/python3" >> ~/.zshrc && source ~/.zshrcRun python to make sure you can enter the REPL. Run exit() to hop out. Repeat this with py.
We installed venv in the previous section, so you could just run the following for the standard virtual environment setup inside your project directory.
python -m venv venv && source venv/bin/activateHowever this directory will grow larger with your project over time. Each virtual environment can take up a lot of space with just the base install.
Enter PDM, a package manager that takes advantage of PEP 582 which allows Python to automatically recognize a __pypackages__ folder in your project directory. You can skip having to activate a virtual environment every time and run your project directly. In the background, Python uses the same global interpreter and imports packages from each project's __pypackages__ folder. This enhancement is still pretty new, available in versions 3.8 and up. PDM also offers many more features to use in coalition with this feature with a great user interface.
If you're down to try it out, install PDM and configure PEP 582 mode with:
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pdm-project/pdm/main/install-pdm.py | python3 -
echo "export PATH=/home/$USER/.local/bin:\$PATH" >> ~/.zshrc && source ~/.zshrc
pdm --pep582 >> ~/.zshrc && source ~/.zshrcVS Code's Python extensions include linting tools that will display an error for imported packages they cannot find. This will happen because they currently don't look inside your __pypackages__ directory. pdm-vscode fixes this issue by generating a settings.json file in your workspace to point your Python extensions to your project's dependencies within PEP 582 mode. Install the plugin with:
pdm plugin add pdm-vscodeYou can check out other pdm plugins you might want in your development environment here. Also, I recommend these resources to jump into using pdm: Documentation | Short | Long
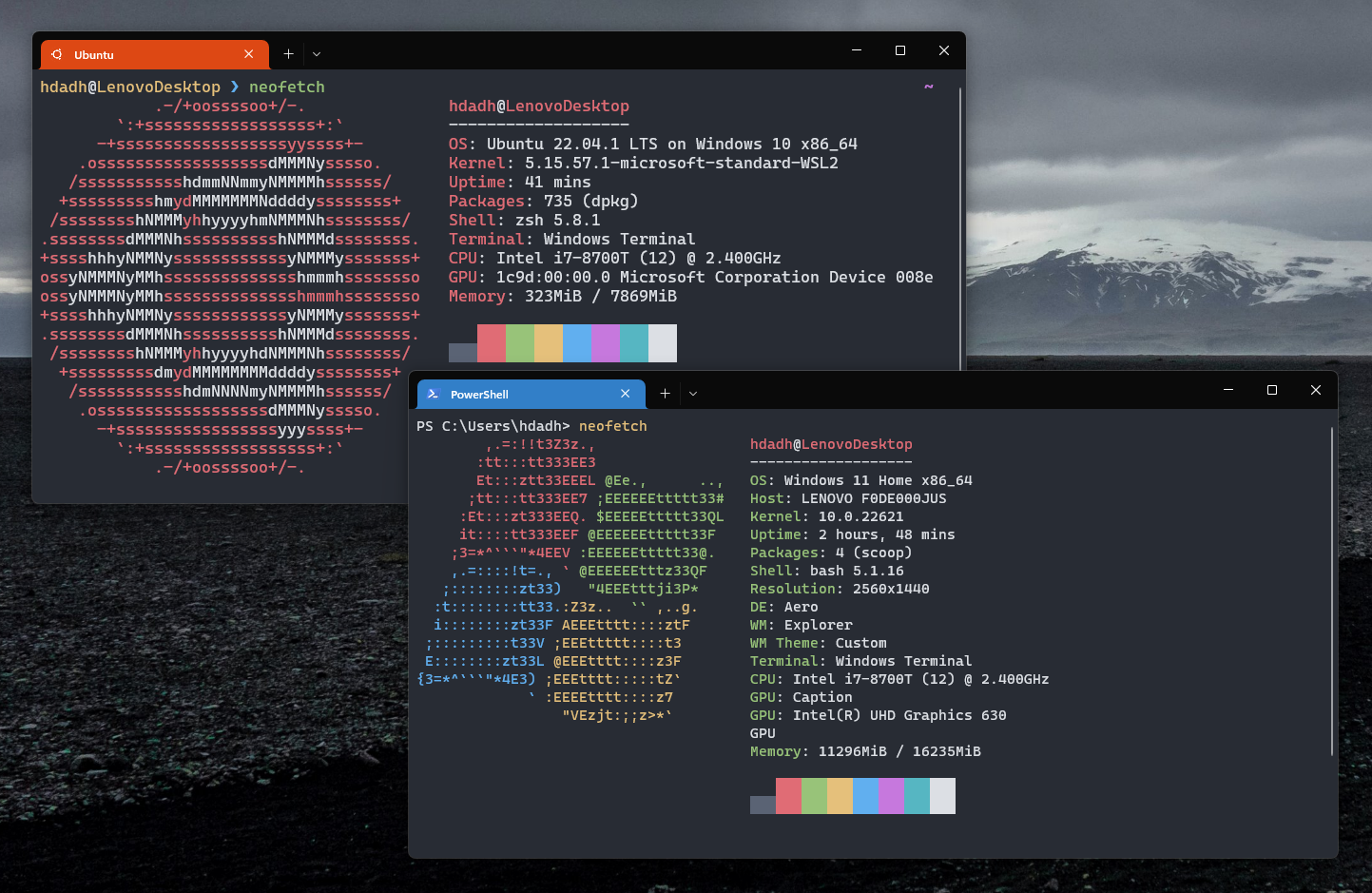
Installing a Linux distribution without Neofetch is something unheard of. To pull up some ASCII art and system information, install it with:
sudo apt install neofetch -y && exec zshYou can also install Neofetch on Windows through a PowerShell terminal with:
iwr -useb get.scoop.sh | iex
scoop install neofetch
scoop install gitTo view the tool, run neofetch.
Ubuntu has its own special file system, you can explore it here.
cd/cd ~will take you to/home/$USERdirectory- This is the default landing directory for every new session
cd /will take you to your root or/directorycd /mntwill take you to your Windows file system- ex:
/mnt/c/Users/$USER/Desktop=C:\Users\$USER\Desktop'
- ex:
pwdwill list the directory you are currently in
Run cd && mkdir dev to make a dev folder in your landing directory. Store your projects within this folder so you can easily access them whenever you open up a new session. Microsoft recommends to store your projects stored inside the Ubuntu file system as opposed to your Windows file system for faster performance and avoiding errors during package installation.
If you didn't like the theme used in this guide, you can modify it for another look.
- Modify current (Typewritten) theme
- Use the instructions on the theme's website to modify your prompt, color, etc.
- Use a theme from the internal library
- Run
code ~/.zshrc> modifyZSH_THEME> save, exit, and runsource ~/.zshrc
- Run
- Use a theme from the external library
- Install using the
oh-my-zshorUbuntu/Manualinstructions - Run
code ~/.zshrc> modifyZSH_THEME> save, exit, and runsource ~/.zshrc
- Install using the
Sometimes you want to layout the complete history of the commands you punched in to your terminal. Setting up a screen recording software or making lengthy logs is inefficient. Instead, you can use asciinema to quickly record and upload sessions. Make an account on their website and install it with:
sudo apt-add-repository ppa:zanchey/asciinema -y
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install asciinemaStart recording with:
asciinema recand stop with:
exit
Save recordings to your account with:
asciinema authSometimes you will start programming away, and when you finally reach the point of wanting to test it, you have to manually build your requirements.txt file with each package you import in your project. pipreqs will automatically go through your project directory files and fetch every imported module. Install it with:
pip install pipreqsYou can view the full documentation to add specific flags to suit your needs. Unfortunately, this module will generally import modules already present in the dependency lists of other modules. However, it's easier to delete/modify those than manually adding all your packages.
Having to format your code manually by running commands every time before committing is pretty annoying. Install pre-commit globally with:
pip install pre-commitNow obviously you wouldn't want it to run on every single project you are working on. This is why you have to run the following in your project's directory in order to use this tool. This project should already be initialized with git. This installs a "hook," or an action, that will run every time you attempt to commit. Hence the name, pre-commit. Enable it in your project with:
pre-commit installNow you can start integrating some hooks you want to use into a .pre-commit-config.yaml file that will executed before you commit. Check out the one for this repository here. If you want the same functionality for your contributors, you should check out pre-commit ci. This basically has the same functionality except that your contributors don't have to care about any of this stuff because it's all handled by the CI. Check out its usage in this project denoted by the green checkmark on the file section header.
GPG is an encryption tool that comes packaged with Ubuntu. It helps you verify your commits to ensure that every modification comes from you. Also, it looks more professional when committing to reasonably sized community projects. Configure it for use with:
echo "export GPG_TTY=$(tty)" >> ~/.zshrc && source ~/.zshrcBefore generating the key, make sure you enter 1, 4096, 0, y, your name, and your email for the prompts, respectively. Generate a key with:
gpg --full-generate-keyOnce generated, copy the key string between the square brackets:
gpg: key [COPY THIS] marked as ultimately trusted
Add your key to git and enable commit signing with:
git config --global user.signingkey COPIED_KEY
git config --global commit.gpgsign true
To integrate this with source control in VS Code, turn on Git: Enable Commit Signing in User settings. Now, GitHub just needs a way to verify that it is actually you committing to a repository, which means you will give it the key you generated so it can check it against every commit's signature. Get the full key with:
gpg --armor --export COPIED_KEYCopy (include the header/footer) and save the key to GitHub here by hitting New GPG key and pasting it into the Key field. The name can be set as anything, but preferably go for your device's name (ex: Lenovo Laptop). Now when you attempt to commit, you will be prompted for the passphrase that you encrypted your key with. Once pushed, you will see a green Verified box next to every single commit you make on GitHub.
Tracking how much time you are spending on your projects each day helps you develop a sense of priority and consistency. Head over to WakaTime to set up an account.
As per the tools used in this guide, you can set it up for VS Code and zsh. If you've got other editors, check out this page to install their plugin(s).
Upgrade everything and force reboot your distribution.
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
sudo reboot -fYou're good to go, welcome to your new development environment.
You might run into an error where you might have restarted your computer and open up your terminal to see the following layout, wondering where your original layout went. This is the WSL GUI interface, an addition to only WSL2 enabling you to run native Linux apps. If you're interested, check out its functionality here.
wslg [ ~ ]$
To fix this, open up a PowerShell terminal and run:
wsl --shutdown
wslNow relaunch your session to restore your original layout.