WGAN-GP Tensorflow 2.0
This repo is the TF2.0 implementation of Improved Training of Wasserstein GANs.
Note that this implementation is not totally the same as the paper. There might be some differences.
Algorithm
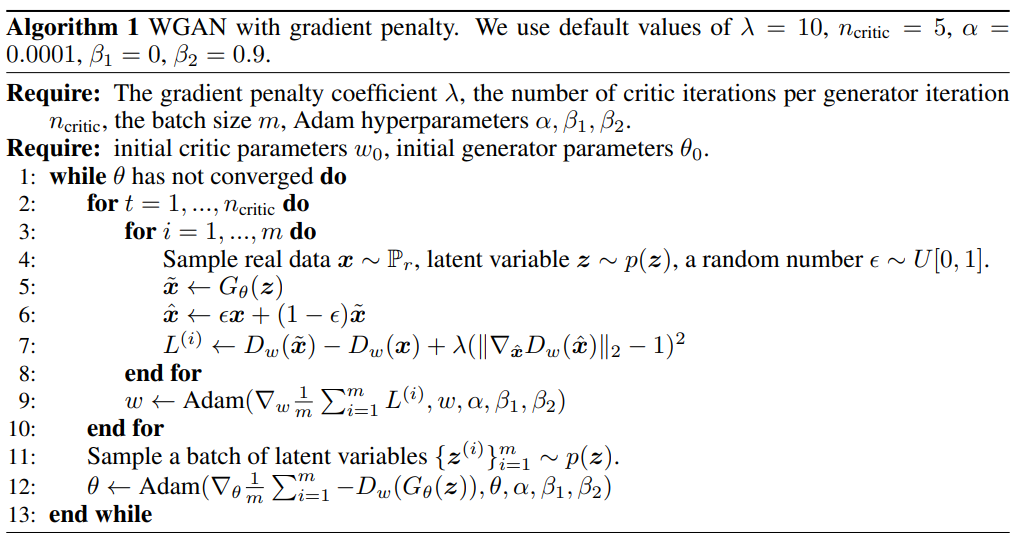 This image is from the original paper. The code below is functions of single training step.
This image is from the original paper. The code below is functions of single training step.
@tf.function
def WGAN_GP_train_d_step(real_image, batch_size, step):
noise = tf.random.normal([batch_size, NOISE_DIM])
epsilon = tf.random.uniform(shape=[batch_size, 1, 1, 1], minval=0, maxval=1)
###################################
# Train D
###################################
with tf.GradientTape(persistent=True) as d_tape:
with tf.GradientTape() as gp_tape:
fake_image = generator([noise], training=True)
fake_image_mixed = epsilon * tf.dtypes.cast(real_image, tf.float32) + ((1 - epsilon) * fake_image)
fake_mixed_pred = discriminator([fake_image_mixed], training=True)
# Compute gradient penalty
grads = gp_tape.gradient(fake_mixed_pred, fake_image_mixed)
grad_norms = tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(grads), axis=[1, 2, 3]))
gradient_penalty = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(grad_norms - 1))
fake_pred = discriminator([fake_image], training=True)
real_pred = discriminator([real_image], training=True)
D_loss = tf.reduce_mean(fake_pred) - tf.reduce_mean(real_pred) + LAMBDA * gradient_penalty
# Calculate the gradients for discriminator
D_gradients = d_tape.gradient(D_loss,
discriminator.trainable_variables)
# Apply the gradients to the optimizer
D_optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(D_gradients,
discriminator.trainable_variables))
@tf.function
def WGAN_GP_train_g_step(real_image, batch_size, step):
noise = tf.random.normal([batch_size, NOISE_DIM])
###################################
# Train G
###################################
with tf.GradientTape() as g_tape:
fake_image = generator([noise], training=True)
fake_pred = discriminator([fake_image], training=True)
G_loss = -tf.reduce_mean(fake_pred)
# Calculate the gradients for generator
G_gradients = g_tape.gradient(G_loss,
generator.trainable_variables)
# Apply the gradients to the optimizer
G_optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(G_gradients,
generator.trainable_variables))
Dataset
The notebook trains WGAN-GP using aligned CelebA dataset, the image resolution is adjusted to 64*64. Due to the limitation of computation resource, I train the models for only 40 epochs. It may be able to produce better images if trained for more epochs.
Environments
- Python 3
- jupyter or jupyterlab
- numpy
- matplotlib
- tensorflow 2.0
How to Run
There are two ways to run this repo.
-
-
Download the dataset you want.
-
Clone this repo, then use Juypter Notebook or Lab to open the
WGAN-GP-celeb64.ipynbfile, and modify the dataset path in the Prepare dataset section.
-
-
Run in Google Colab 😺
(In the default setting, training one epoch would take about 300~500 seconds.)
Results
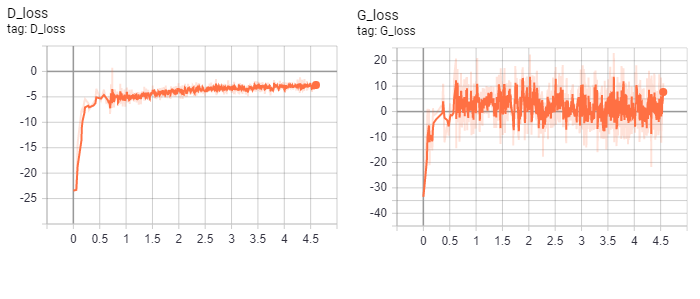
Result at 40 epoch
Training losses (Did not multiply negative)
Acknowledges
Ishaan Gulrajani, Faruk Ahmed, Martin Arjovsky, Vincent Dumoulin, and Aaron Courville, "Improved Training of Wasserstein GANs", https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.00028
Alec Radford, Luke Metz, Soumith Chintala, "Unsupervised Representation Learning with Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Networks", https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.06434
TKarras's PGGAN repository, https://github.com/tkarras/progressive_growing_of_gans