This is the official repo of ALRIGHT and MAXRIGHT algorithms for efficient trade-off in LLM post-training (see the paper Mitigating Forgetting in LLM Supervised Fine-Tuning and Preference Learning).
The widely adopted approach in post-training popular open-source LLMs is to sequentially perform SFT and DPO. However, sequential training is sub-optimal in terms of SFT and DPO trade-off: when trained with preference data, LLM inevitably forgets about the knowledge learnt during SFT, despite the presence of KL regularization. Similar issue persists when performing DPO first and then SFT in LLM continual learning. A simple solution like directly mixing the DPO and SFT objectives greatly increases the computational cost and slows down the training speed.
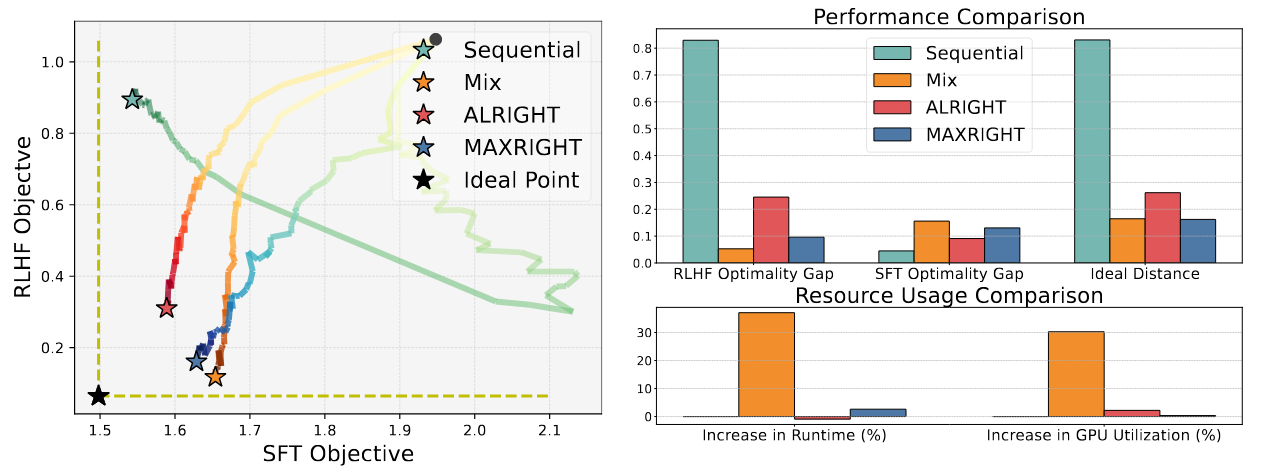
As a remedy for these issues, we implement the ALRIGHT and MAXRIGHT algorithms. The algorithms demonstrate the following merits:
-
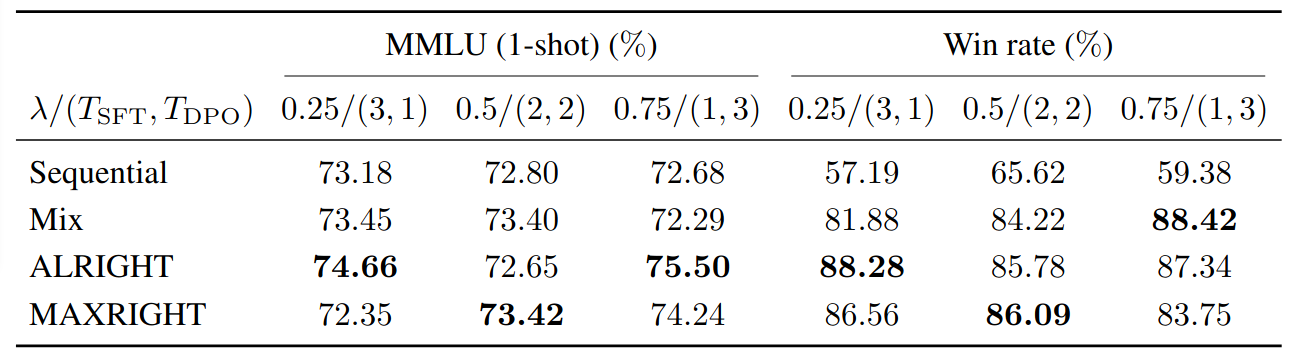
Improved post-training performance: Models such as Llama-3-8b trained with ALRIGHT/MAXRIGHT demonstrates superior quality than those trained with sequential method. Experiments showcase a 3% increase on MMLU (1-shot) and a 31% win rate increase on Anthropic HH.
-
Similar computational cost as sequential training: The computational cost compared to sequential SFT/DPO is similar, with a worst-case increase of 2% in GPU utilization when training Llama-3-8b.
We give some examples here. For complete results, please see paper.
Loss trade-off plot for training Pythia-1b with this implementation (ALRIGHT and MAXRIGHT), sequential method (SFT then DPO) and mix(combining DPO and SFT objectives):
Result on Llama-3-8b. Here
The win percent metric follows AlpacaEval, which is commonly used for human preference evaluation.
Create conda environment
conda create -n xright python=3.10
conda activate xrightTo install xright, navigate to the top-level of the repo and run
pip install -e .Then, run the following command to install the needed FlashAttention version
pip install flash-attn==2.6.1 --no-build-isolationHere we provide example implementations of ALRIGHT and MAXRIGHT, using Pythia-1b model. The following variables need to be specified, an example specification (for training distributed between 2 GPUs) would be
beta=0.1
lambd=0.5
learning_rate=5e-5
max_len=2048
train_batch_size=2
sft_max_samples=24000
rlhf_max_samples=8000
sft_micro_train_batch_size=12
rlhf_micro_train_batch_size=4
max_epochs=6
max_eval_steps=10
sft_opt=1.4980
dpo_opt=0.0647Note that, for the current implementation of ALRIGHT and MAXRIGHT, lengths of trainloaders for RLHF and SFT datasets should be same, thus the variable specification should satisfy sft_max_samples/sft_micro_train_batch_size = rlhf_max_samples/rlhf_micro_train_batch_size. This constraint will be removed in the future. sft_opt, dpo_opt can be pre-computed by a procedure similar to training a reference policy (given next), or they can be set to 0 if the value is not known.
First, we need to train the reference policy that will be needed for the DPO objective. This can be trained by
deepspeed --module xright.cli.train_sft_pref\
--save_path ./checkpoint/pythia-1b-beta=$beta-learning_rate=$learning_rate-epoch=$max_epochs-sft-pref-optim \
--save_steps -1 \
--logging_steps 1 \
--eval_steps -1 \
--train_batch_size $train_batch_size \
--pretrain EleutherAI/pythia-1b \
--bf16 \
--max_epochs $max_epochs \
--zero_stage 2 \
--dataset Dahoas/rm-hh-rlhf \
--max_samples $sft_max_samples \
--max_len $max_len \
--eval_split dummy \
--rlhf_micro_train_batch_size $(($sft_micro_train_batch_size/2)) \
--flash_attn \
--learning_rate $learning_rate \
--lora_rank 32 \
--lora_alpha 32 \
--use_wandb {wandb_token} \
--target_module query_key_valueNext, we can implement ALRIGHT for joint DPO and SFT optimization by running
deepspeed --module xright.cli.train_sft_dpo_alright \
--save_path ./checkpoint/pythia-1b-beta=$beta-learning_rate=$learning_rate-sft_dpo_alright-temp \
--save_steps -1 \
--logging_steps 1 \
--eval_steps 100 \
--rlhf_dataset Dahoas/rm-hh-rlhf \
--train_batch_size $train_batch_size \
--rlhf_micro_train_batch_size $rlhf_micro_train_batch_size \
--rlhf_max_samples $rlhf_max_samples \
--rlhf_max_len $max_len \
--rlhf_eval_split dummy \
--sft_dataset vicgalle/alpaca-gpt4 \
--sft_max_samples $sft_max_samples \
--sft_max_len $max_len \
--sft_micro_train_batch_size $sft_micro_train_batch_size \
--lambd $lambd \
--pretrain EleutherAI/pythia-1b \
--ref_pretrain ./checkpoint/pythia-1b-beta=$beta-learning_rate=$learning_rate-epoch=$max_epochs-sft-pref-optim \
--bf16 \
--max_epochs $max_epochs \
--zero_stage 2 \
--beta $beta \
--flash_attn \
--learning_rate $learning_rate \
--lora_rank 32 \
--lora_alpha 32 \
--use_wandb True \
--target_module query_key_valueSimilarly, we can implement MAXRIGHT for joint DPO and SFT optimization by running
deepspeed --module xright.cli.train_sft_dpo_maxright \
--save_path ./checkpoint/pythia-1b-beta=$beta-learning_rate=$learning_rate-sft_dpo_maxright-temp \
--save_steps -1 \
--logging_steps 1 \
--eval_steps 100 \
--rlhf_dataset Dahoas/rm-hh-rlhf \
--train_batch_size $train_batch_size \
--rlhf_micro_train_batch_size $rlhf_micro_train_batch_size \
--rlhf_max_samples $rlhf_max_samples \
--rlhf_max_len $max_len \
--rlhf_eval_split dummy \
--sft_dataset vicgalle/alpaca-gpt4 \
--sft_max_samples $sft_max_samples \
--sft_max_len $max_len \
--sft_micro_train_batch_size $sft_micro_train_batch_size \
--lambd $lambd \
--sft_opt $sft_opt \
--dpo_opt $dpo_opt \
--ref_pareto_sft "$ref_pareto_sft" \
--ref_pareto_dpo "$ref_pareto_dpo" \
--max_eval_steps $max_eval_steps \
--pretrain EleutherAI/pythia-1b \
--ref_pretrain ./checkpoint/pythia-1b-beta=$beta-learning_rate=$learning_rate-epoch=$max_epochs-sft-pref-optim \
--bf16 \
--max_epochs $max_epochs \
--zero_stage 2 \
--beta $beta \
--flash_attn \
--learning_rate $learning_rate \
--lora_rank 32 \
--lora_alpha 32 \
--use_wandb True \
--target_module query_key_valueTo run experiments given in the paper, run the following commands at the top level of this repo. All the scripts needed to run these commands can be found in the directory examples/scripts/.
For training the optimal SFT and DPO models needed either as reference policies or for optimal SFT and DPO objective value calculation, run
./run_sft_dpo_optim_pythia1b.shThen, to train the model sequentially, with SFT first and then DPO, run
./run_sft_dpo_seq_pythia1b.shTo train the model sequentially, with DPO first and then SFT, run
./run_dpo_sft_seq_pythia1b.shTo train the joint optimization methods with SFT optimum model as the reference model (corresponding to SFT first then DPO sequential training) run
./run_moo_sft_ref_training_pythia1b.shTo train the joint optimization methods with the model trained on the chosen responses of the preference dataset as the reference model (corresponding to DPO first then SFT sequential training) run
./run_moo_pref_ref_training_pythia1b.shFor training the optimal SFT and DPO models needed either as reference policies or for optimal SFT and DPO objective value calculation, run
./run_sft_dpo_optim_llama3.shThen, to train the model sequentially, with SFT first and then DPO, run
./run_sft_dpo_seq_llama3.shTo train the joint optimization methods with SFT optimum model as the reference model (corresponding to SFT first then DPO sequential training) run
./run_moo_sft_ref_llama3.shTo generate the inference outputs which will be used to compute the win rates, run
./run_inference_llama3.shTo compute the win rates compared to the Anthropic-HH test data using AlpacaEval, run (make sure you specify a valid OPEN_AI_KEY in the script)
./run_alpaca_eval_rm_hh_rlhf.shTo evaluate the trained models using MMLU benchmark of DeepEval, run
./run_MMLU_benchmark.shWe would like to thank all packages this repo is built on, especially