- About
- Usage
- Support us
- Buy Hardware
- DIY Hardware
- Flash Software
- Scripting
- CLI Commands
- How to Debug
- Development
- Disclaimer
- License
- Credits
This open-source project aims to provide a user-friendly tool to learn about keystroke injection attacks and 'BadUSBs'.
By emulating a USB keyboard, tools like this can gain full access to any computer with a USB port in a matter of seconds!
This is made possible by the fact that keyboards are trusted by computers. You can have full control over a computer with just a keyboard.
A BadUSB pretends to be a keyboard to the computer to send keystrokes.
But unlike a human, it can type hundreds of characters per second.
By using a simple scripting language, it's easy to make BadUSBs type whatever you want.
With the WiFi Duck, you can simply connect via WiFi to manage all scripts from within a web interface. This means that, unlike other BadUSBs, you don't need to install an app, log in, compile or copy scripts to an SD card.
- Plug in your WiFi Duck
- Connect to the WiFi network
wifiduckwith the passwordwifiduck - Open a browser and visit
192.168.4.1 - Write, save and run your first Ducky Script
- [Recommended] Open
Settings(top right corner) and update SSID and password
Help I forgot the password:
Flash the ESP8266, but make sure that you select Erase Flash: Sketch + WiFi Settings
under Tools in the Arduino IDE.
If you have further questions, check out the issue section.
Hey, do you like this kind of project?
It took a huge amount of effort to create!
To make sure we can keep working on free and open-source projects like this,
please consider becoming a ❤️ Sponsor or support us via ☕ Ko-fi.
Visit spacehuhn.com to learn more about us. 🐔
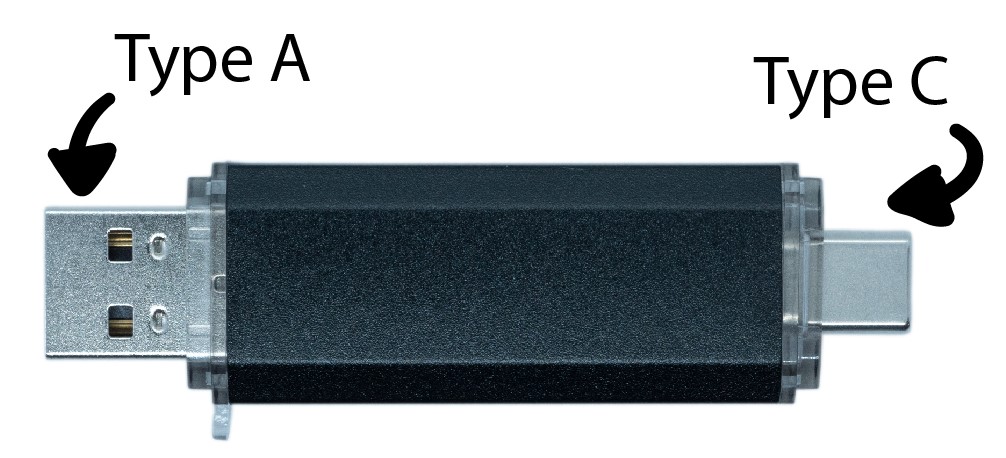
A nicely encased, inconspicuous looking BadUSB by Maltronics.
Having USB-A and USB-C makes it compatible with all kind of devices.
It comes flashed with the WiFi Duck firmware and works plug and play.
ℹ️ Documentation can be found here
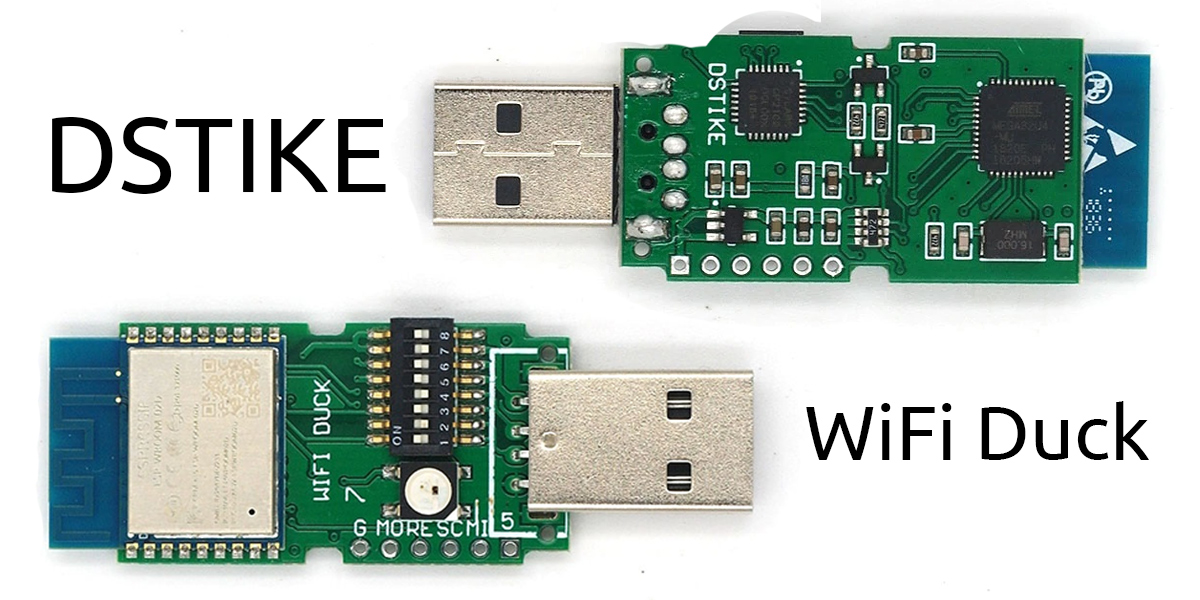
A custom designed development board which comes preflashed with this software by Travis Lin.
You can update the ESP8266 over the air and flash the Atmega32u4 via Arduino, all while enclosed in its neat little case.
📺 Watch the How to Update Tutorial here.
If you wish to develop your own software or help improve this one, the 8-bit DIP-switch makes it easy for you to access the Atmega32u4 or ESP8266 independently. For more info see Flash Software.
| Mode | Atmega32u4 | ESP8266 | DIP-switch | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Default Operating Mode | USB | On | 10101101 |  |
| Atmega32u4 Flash Mode | USB | Off | 10101010 | 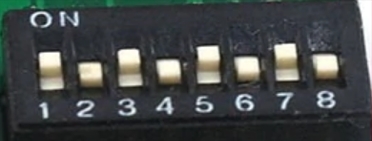 |
| ESP8266 Flash Mode | Off | USB | 01011101 |  |
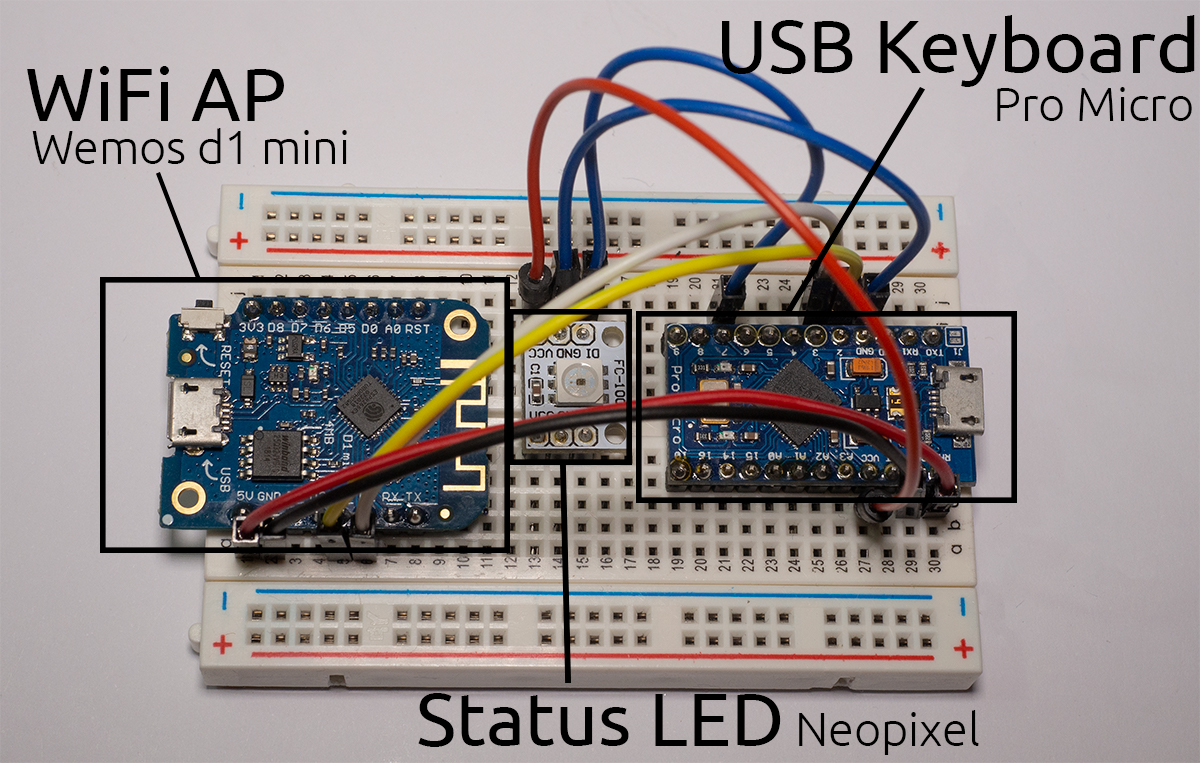
To build a WiFi Duck yourself, you need the following hardware:
- An Atmega32u4 development board (see the list below)
- An ESP8266 or ESP8285 development board (see the list below)
- Optional: A single Neopixel (WS2812b) or Dotstar (APA102) LED
To flash the microcontrollers you need a computer and USB cable.
If you're a beginner, it's recommended you wire everything together on a breadboard first!
In this case, you'd also need a breadboard with a couple of jumper wires.
If you wish to solder everything together into a small gadget, you also need soldering equipment.
You can use any Atmega32u4 or ESP8266 based development board,
but if you have no idea where to start, here's a list.
The Atmega32u4 to act as USB keyboard, and the ESP8266 for WiFi.
- Arduino Leonardo
- Arduino Micro
- Sparkfun Pro Micro
- CJMCU Beetle
- SS Micro
- NodeMCU 1.0 (ESP-12E Module)
- LOLIN(WEMOS) D1 Mini
- LOLIN(WEMOS) D1 Mini Pro
- LOLIN(WEMOS) D1 Mini Lite
A map of pins that need to be connected.
| ESP8266 | Atmega32u4 |
|---|---|
D1 alias GPIO 5 |
3 alias SCL |
D2 alias GPIO 4 |
2 alias SDA |
GND |
GND |
Ideally, you want the Atmega32u4 to power the ESP8266, so it can run on one USB connection, instead of having to always plug in both.
To share power between both chips, you need a voltage regulator that takes 5V and turns it into 3.3V.
That's because USB runs on 5V, but the ESP8266 only takes 3.3V. Luckily most development boards have such a regulator on board.
DO NOT CONNECT ESP8266 VCC to the ATMEGA32u4 VCC, it will kill the ESP826. Instead look for the 5V or VIN pin on your dev board, as those will be connected to the regulator.
| ESP8266 Dev Board | Atmega32u4 |
|---|---|
5V or VIN |
RAW, 5V or VIN |
To add a Neopixel (WS2812b) LED:
| Atmega32u4 | Neopixel LED |
|---|---|
7* |
DI alias Data, In |
5V alias VCC |
5V alias VCC |
GND |
GND |
* The Data pin can be changed later on in the software, pin 7 is just an example.
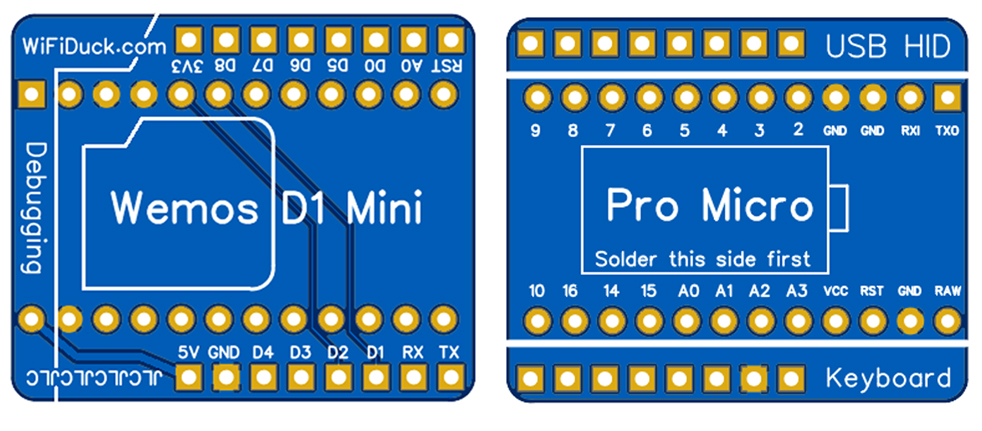
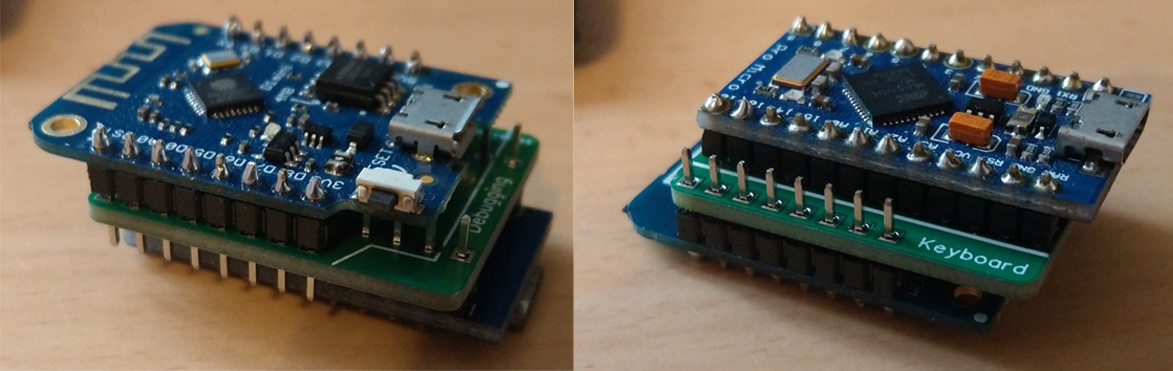
To make the DIY process easier, I designed a little PCB.
You solder a Pro Micro board on one side and a Wemos d1 mini or NodeMCU board (depending on the PCB) on the other side.
That's it. You don't even have to solder all pins,
just the ones mentioned in Connections, excluding the LED.
Design Files:
- Pro Micro + Wemos d1 mini: https://easyeda.com/Spacehuhn/wifi-duck
- Pro Micro + NodeMCU: https://easyeda.com/Spacehuhn/diy-wifi-duck-pro-micro-nodemcu
You can also order them on OSHPark:
- Pro Micro + Wemos d1 mini: https://oshpark.com/shared_projects/ARCED9je
- Pro Micro + NodeMCU: https://oshpark.com/shared_projects/XUuUH1HB
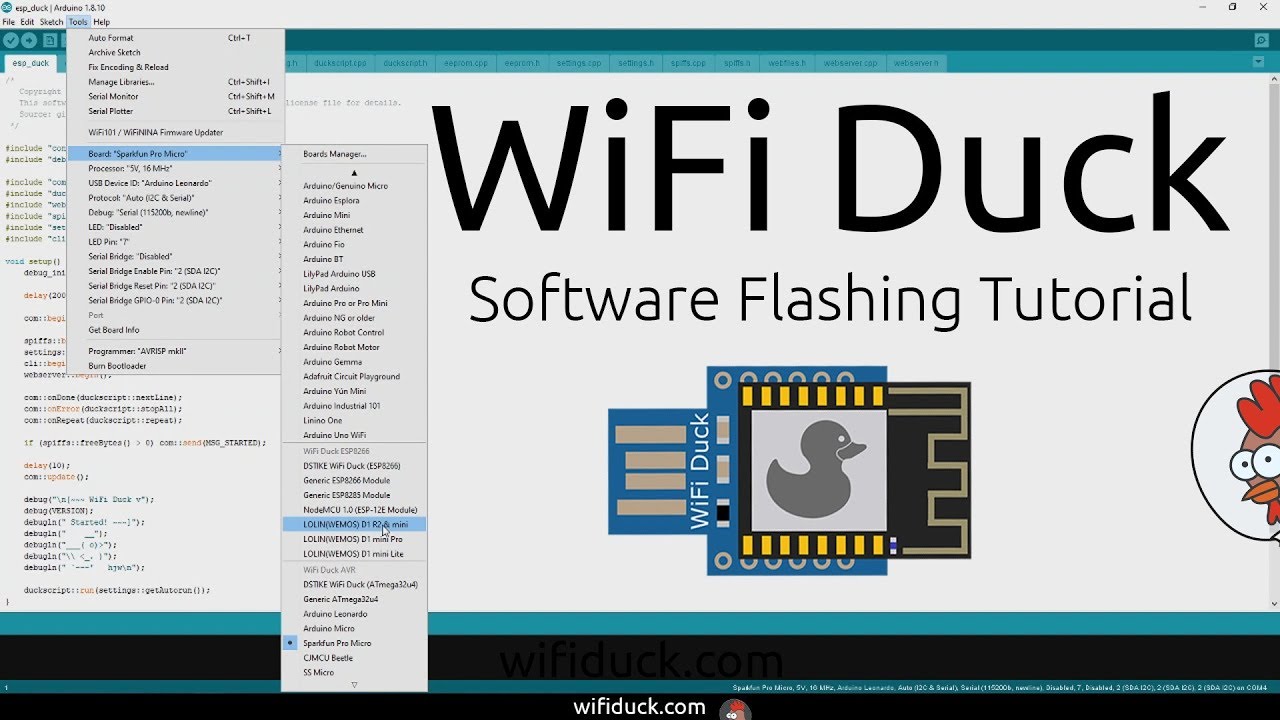
- Download and install the Arduino IDE.
- Start the Arduino IDE, go to
File>Preferences. - At Additional Board Manager ULRs enter
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/spacehuhn/hardware/master/wifiduck/package_wifiduck_index.json. You can add multiple URLs, separating them with commas. - Go to
Tools>Board>Board Manager, search forwifi duckand installWiFi Duck AVR BoardsandWiFi Duck ESP8266 Boards. - Download and extract this repository or git clone it.
If you can't find the COM port of ESP8266 board, then you're probably missing the right drivers. Here are links to drivers of the 2 most used UART chips on ESP8266 development boards:
- Open
atmegaduck/atmega_duck.inowith the Arduino IDE. - Under
Tools>Boardin theWiFi Duck AVRsection, select your board; for example,Sparkfun Pro Micro. - Connect the Atmega32u4 board via USB and select its port under
Tools>Port. - Optional: Under
Toolsyou can enable the LED and set its pin. You can also change the USB ID to make it appear as a certain type of keyboard. - Press Upload.
- Open
esp_duck/esp_duck.inowith the Arduino IDE. - Under
Tools>Boardin theWiFi Duck ESP8266section, select your board. For exampleNodeMCU 1.0 (ESP-12E Module). - Connect the ESP8266 board via USB and select its port under
Tools>Port. - Press Upload.
Pro Tip: If the ESP8266 is already running this software
and you just want to update it, you don't have to connect it via USB.
You can update it over the air! Simply connect to the wifiduck network (default password is wifiduck).
Then in Arduino at Tools > Port you should now see a network port.
Select it and press Upload.
Note: After the initial flashing, the ESP8266 has to format its memory, so it might take a minute until it's fully ready.
If you connected the RGB LED:
- Blue LED = Connection working
- Green LED = Device ready
If you flashed your Atmega32u4 board with the wrong bootloader,
it will no longer appear in the port selection after you connect it.
To solve this, you need to:
- Connect the reset pin
RSTto groundGND. Preferably with a jumper wires, because you need to be able to disconnect it quickly. - Open a sketch,
atmegaduck/atmega_duck.inoor an empty sketch.
Make sure to have the correct board selected underTools>Board! - Connect the board with the wire still connected.
- Press
Uploadand as soon as you seeCompiling...turn toUploading..., disconnect the wire.
Now it should flash the sketch and the correct bootloader.
Keys are separated by a single space.
Everything written in a single line gets pressed and released at the same time.
To write text, use the STRING function.
It's compatible to Ducky Script, which was developed by the wonderful people at Hak5.
| Example | Explanation |
|---|---|
| WINDOWS r |
Type the Windows key and then the r key |
| WINDOWS r | Press the Windows key and the r key simultaneously |
| STRING WINDOWS r | Write WINDOWS r |
| Command | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
REM |
REM Hello World! |
Comment |
DEFAULTDELAY or DEFAULT_DELAY |
DEFAULTDELAY 200 |
Time in ms between every command |
DELAY |
DELAY 1000 |
Delay in ms |
STRING |
STRING Hello World! |
Types the following string |
REPEAT or REPLAY |
REPEAT 3 |
Repeats the last command n times |
LOCALE |
LOCALE DE |
Sets the keyboard layout. Available: DE, ES, GB, US, DK, RU, FR |
KEYCODE |
KEYCODE 0x02 0x04 |
Types a specific key code (modifier, key1[, ..., key6]) in decimal or hexadecimal |
LED |
LED 40 20 10 |
Changes the color of the LED in decimal RGB values (0-255) |
| Key |
|---|
a - z |
A - Z |
0 - 9 |
F1 - F12 |
| Key |
|---|
CTRL or CONTROL |
SHIFT |
ALT |
WINDOWS or GUI |
| Key |
|---|
ENTER |
MENU or APP |
DELETE |
HOME |
INSERT |
PAGEUP |
PAGEDOWN |
UP or UPARROW |
DOWN or DOWNARROW |
LEFT or LEFTARROW |
RIGHT or RIGHTARROW |
TAB |
END |
ESC or ESCAPE |
SPACE |
PAUSE or BREAK |
CAPSLOCK |
NUMLOCK |
PRINTSCREEN |
SCROLLLOCK |
REM Hello World for Windows PCs
DEFAULTDELAY 200
GUI r
STRING notepad
ENTER
STRING Hello World!
The command line interface or CLI is accessible using a serial connection to the ESP8266 (115200 baud, Newline ending) or via the web interface at 192.168.4.1/terminal.html.
| Command | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| help | Returns all available commands | help |
| ram | Returns available memory in bytes | ram |
| version | Returns version number | version |
| settings | Returns list of settings | settings |
| set -n/ame -v/alue | Sets value of a specific setting | set ssid "why fight duck" |
| reset | Resets all settings to their default values | reset |
| status | Returns status of i2c connection with Atmega32u4 | status |
| run <...> | Starts executing a Ducky script | run example.txt |
| stop <...> | Stops executing a Ducky script | stop example.txt |
| Command | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| mem | Returns available, used and free memory of SPIFFS in bytes | mem |
| format | Formats SPIFFS | format |
| ls <...> | Returns list of files | ls / |
| create <...> | Creates file | create example.duck |
| remove <...> | Deletes file | remove example.duck |
| cat <...> | Returns content of file | cat example.duck |
| rename -fileA,a -fileB,b | Renames file | rename example.duck example.txt |
| write -f/ile -c/ontent | Writes (appends) data to file | write example.txt "Hello World!" |
| stream <...> | Opens file stream | stream example.txt |
| close | Closes file stream | close |
| read | Read and return the result from file stream | read |
If a stream is open, everything you type (except messages containing exactly close or read) will be written to the file until you type close!
To properly debug, you need to have both the Atmega32u4 and the ESP8266 connected via USB to your computer.
That can be tricky when you only have a all in one board, so it might be useful you built one yourself. You don't need to solder it, for example you can use an Arduino Leonardo and a NodeMCU and connect them with jumper cables.
Now open 2 instances of Arduino (so they run as separate processes!), select the COM port and open the serial monitor for each device. You might need to reset the Atmega32u4 to see serial output. If that causes problems with the i2c connection, try to reset the ESP8266 too.
If you would like to modify the web interface, you can!
The web/ folder contains all .html, .css, .js files.
You can edit and test them locally as long as you're connected to the WiFi Duck
network thanks to the websocket connection handled by JavaScript in the background.
To get the new files onto the ESP8266, run python3 webconverter.py in the
repository folder.
It gzips all files inside web/, converts them into a hex array
and saves it in esp_duck/webfiles.h.
Now you just need to flash the ESP8266 again.
Currently supported keyboard layouts:
All standard keys are defined in usb_hid_keys.h.
To translate a keyboard layout, you have to match each character on
your keyboard to the one(s) of a US keyboard.
This stuff is hard to explain in writing and requires a lot of manual work and testing.
- Copy one of the existing layouts files, like locale_us.h.
Preferably one that is close to your keyboard layout, it will save you time! - Add
#include "locale_xx.h"to the end of the locales.h file. - Rename the file and its variables to your language code.
For example:
locale_xx.h->locale_de.h,
ascii_xx->ascii_de,
locale_xx->locale_de,
extended_ascii_xx->extended_ascii_de,
utf8_xx->utf8_de. - Modify the ASCII array.
The ASCII array has a fixed size. Each row describes a key. First a modifier key likeKEY_MOD_LSHIFT, then a character key. Some ASCII characters can't be typed or don't require a modifier, that's where you must placeKEY_NONE. Check usb_hid_keys.h for the available keys.
If multiple modifiers are required, you must use a bitwise OR to connect them:KEY_MOD_RALT | KEY_MOD_LSHIFT.
For example, in locale_de.hZis saved asKEY_MOD_LSHIFT, KEY_Y.
This is because German keyboards use QWERTZ instead of the QWERTY layout and since the letter is uppercase, shift must be pressed as well.
Thankfully you don't have to trial and error everything, the Hak5 Community translated a lot of layouts already here. It's just written in a different syntax. For example,ASCII_20(20 in hexadecimal) is the 32th character in our ascii array. - Modify or create the extended ASCII array.
The extended ASCII array doesn't have a fixed size and is only as long as you make it. First the character code. For example, ä has the index 132, or 84 in hex. It doesn't use a modifier and sits where the apostrophe key is on a US keyboard:0x84, KEY_NONE, KEY_APOSTROPHE, // ä. - Modify or create the UTF-8 array.
The UTF-8 array is variable in length, too.
The first 4 bytes are the character code.
For example, Ä has the hex code c384 or 0xc3 0x84. The other 2 bytes are not used so we set them to 0. Because the letter is uppercase, we need to press the shift key and like before, the letter is typed by pressing the same key as the apostrophe key of a US keyboard:0xc3, 0x84, 0x00, 0x00, KEY_MOD_LSHIFT, KEY_APOSTROPHE, // Ä. - Edit the hid_locale_t structure.
If you renamed all variables accordingly, there's nothing left to do. - Go to duckparser.cpp at
// LOCALE (-> change keyboard layout)you can see a bunch of else if statements. You need to copy one for your layout.
Before adding GB layout:
if (compare(w->str, w->len, "US", CASE_SENSETIVE)) {
keyboard::setLocale(&locale_us);
} else if (compare(w->str, w->len, "DE", CASE_SENSETIVE)) {
keyboard::setLocale(&locale_de);
}After adding GB layout:
if (compare(w->str, w->len, "US", CASE_SENSETIVE)) {
keyboard::setLocale(&locale_us);
} else if (compare(w->str, w->len, "DE", CASE_SENSETIVE)) {
keyboard::setLocale(&locale_de);
} else if (compare(w->str, w->len, "GB", CASE_SENSETIVE)) {
keyboard::setLocale(&locale_gb);
}- Test your layout with a Ducky Script that contains all characters of your keyboard. For example:
LOCALE DE
STRING !"#$%&'()*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz{|}~²³äöüÄÖÜ߀°§`
ENTER
- Add a link to your layout to README, to web/index.html and please feel free to improve this tutorial to help future translators!
- Create a Pull Request
This tool is intended to be used for testing, training, and educational purposes only.
Never use it to do harm or create damage!
The continuation of this project counts on you!
This software is licensed under the MIT License. See the license file for details.
Software libraries used in this project: