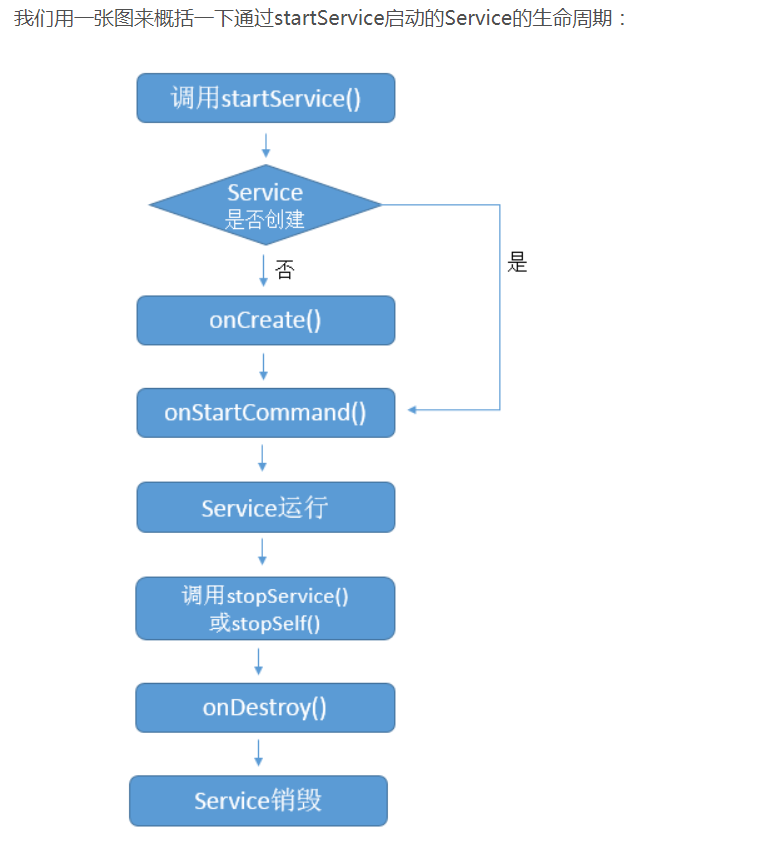
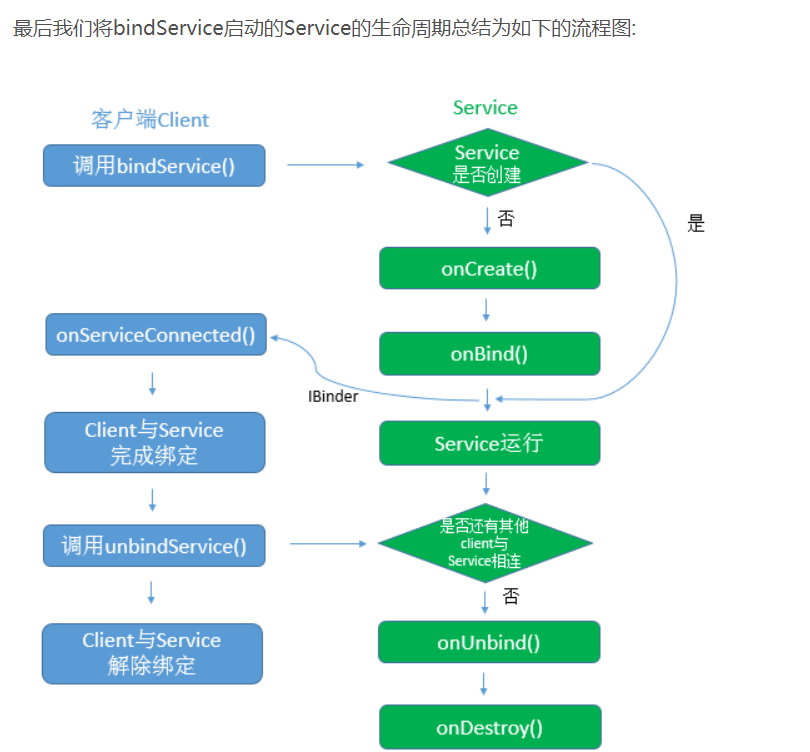
Service是Android中实现程序后台运行的解决方案,它非常适合去执行那些不需要和用户交互而且还要求长期 运行的任务。服务的运行不依赖于任何用户界面,即使程序被切换到后台,或者用户打开了另外一个应用程序, 服务仍然能够保持正常运行。 需要注意的是,服务并不是运行在独立的进程中,而是依赖于创建服务的应用程序 进程。当某个应用程序被杀掉的时候,所有依赖于该进程的服务也会停止运行。
另外,服务并不会自动开启线程,所有的代码都是默认运行在主线程当中的。也就是说,我们需要在服务内部手动创建子线程,并在这里执行具体 的任务,否则就可能出现主线程被阻塞的情况。
- 停止一个服务可以使用Context的stopService或Service的stopSelf方法
- 绑定服务并不会调用Service的onStartCommand()方法
当Android面临内存匮乏的时候,可能会销毁掉你当前运行的Service,然后待内存充足的时候可以重新创建Service,Service被Android系统强制销毁并再次重建的行为依赖于Service中onStartCommand方法的返回值。
我们常用的返回值有三种值,START_NOT_STICKY、START_STICKY和START_REDELIVER_INTENT,
这三个值都是Service中的静态常量。
-
START_NOT_STICKY=2:如果Service运行的进程被杀死以后,Service不再处于启动状态并且不会重新创建Service,除非再次调用
Context.startService(Intent)方法。在什么时候适用这种返回值呢?在我们启动服务做一些工作,这个服务 在内存紧张时可以被停止。然后在晚些时候再次启动服务来进行工作。例如,我们可以启动一个服务来定时轮询服务器获取一些数据,当我们启动Service以后 可以在onStartCommand方法中使用定时器再次启动服务,达到定时轮询的功能。 -
START_STICKY=1:如果Service运行的进程被杀死以后,Service会保留在启动状态,但是不会保留
intent--就是Context.startService(Intent)传递过来的Intent。 随后系统会试着重新创建服务,因为Service处于运行状态,在新的服务实例创建以后,一定会调用onStartCommand方法,但这时在onStartCommand方法中获取不到 Intent信息。这个返回值适用场景:服务被确切的启动或者停止,并且不需要intent信息,例如后台播放音乐。 -
START_REDELIVER_INTENT=3:如果Service运行的进程被杀死以后,系统会再次创建该Service,并执行onStartCommand回调方法, Android系统会将Service在被杀掉之前最后一次传入onStartCommand方法中的Intent保留下来并传入到重新创建后的Service的onStartCommand方法中, 这样我们就能读取到intent参数。只要返回START_REDELIVER_INTENT,那么onStartCommand方法参数中的intent一定不是null。如果我们的Service需要 依赖具体的Intent才能运行(需要从Intent中读取相关数据信息等),并且在强制销毁后有必要重新创建运行,那么这样的Service就适合返回 START_REDELIVER_INTENT。
在启动前台服务的时候,如果Android版本8.0及以上,要创建通知渠道,不然通知显示在通知栏里。
###Service#onCreate()
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
Log.e(TAG, "onCreate: ");
if(Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.O) {
NotificationChannel primaryChannel = new NotificationChannel(
PRIMARY_CHANNEL_ID, PRIMARY_CHANNEL_NAME,
NotificationManager.IMPORTANCE_DEFAULT);
getManager().createNotificationChannel(primaryChannel);
}
Intent intent = new Intent(this, MainActivity.class);
PendingIntent pi = PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0, intent, 0);
Notification notification = new NotificationCompat.Builder(this,
PRIMARY_CHANNEL_ID)
.setContentTitle("title")
.setContentText("content text")
.setWhen(System.currentTimeMillis())
.setSmallIcon(R.mipmap.ic_launcher)
.setLargeIcon(BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.mipmap
.ic_launcher))
.setDefaults(NotificationCompat.DEFAULT_ALL)
.setContentIntent(pi)
.build();
startForeground(1, notification);
}
private NotificationManager getManager() {
if(manager == null) {
manager = (NotificationManager) getSystemService(Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
}
return manager;
}
I java.lang.Throwable
at com.dmw.servicedemo.MainActivity$1.onServiceConnected(MainActivity.java:29)
at android.app.LoadedApk$ServiceDispatcher.doConnected(LoadedApk.java:2210)
at android.app.LoadedApk$ServiceDispatcher$RunConnection.run(LoadedApk.java:2242)
at android.os.Handler.handleCallback(Handler.java:900)
at android.os.Handler.dispatchMessage(Handler.java:103)
at android.os.Looper.loop(Looper.java:219)
at android.app.ActivityThread.main(ActivityThread.java:8673)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Native Method)
at com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit$MethodAndArgsCaller.run(RuntimeInit.java:513)
at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.main(ZygoteInit.java:1109)