Apify SDK simplifies the development of web crawlers, scrapers, data extractors and web automation jobs.
It provides tools to manage and automatically scale a pool of headless Chrome / Puppeteer instances,
to maintain queues of URLs to crawl, store crawling results to a local filesystem or into the cloud,
rotate proxies and much more.
The SDK is available as the apify NPM package.
It can be used either stand-alone in your own applications
or in actors
running on the Apify Cloud.
View full documentation, guides and examples on the dedicated Apify SDK project website
Thanks to tools like Puppeteer or Cheerio, it is easy to write Node.js code to extract data from web pages. But eventually things will get complicated. For example, when you try to:
- Perform a deep crawl of an entire website using a persistent queue of URLs.
- Run your scraping code on a list of 100k URLs in a CSV file, without losing any data when your code crashes.
- Rotate proxies to hide your browser origin and keep user-like sessions.
- Disable browser fingerprinting protections used by websites.
Python has Scrapy for these tasks, but there was no such library for JavaScript, the language of the web. The use of JavaScript is natural, since the same language is used to write the scripts as well as the data extraction code running in a browser.
The goal of the Apify SDK is to fill this gap and provide a toolbox for generic web scraping, crawling and automation tasks in JavaScript. So don't reinvent the wheel every time you need data from the web, and focus on writing code specific to the target website, rather than developing commonalities.
The Apify SDK is available as the apify NPM package and it provides the following tools:
-
BasicCrawler- Provides a simple framework for the parallel crawling of web pages whose URLs are fed either from a static list or from a dynamic queue of URLs. This class serves as a base for more complex crawlers (see below). -
CheerioCrawler- Enables the parallel crawling of a large number of web pages using the cheerio HTML parser. This is the most efficient web crawler, but it does not work on websites that require JavaScript. -
PuppeteerCrawler- Enables the parallel crawling of a large number of web pages using the headless Chrome browser and Puppeteer. The pool of Chrome browsers is automatically scaled up and down based on available system resources. -
PuppeteerPool- Provides web browser tabs for user jobs from an automatically-managed pool of Chrome browser instances, with configurable browser recycling and retirement policies. Supports reuse of the disk cache to speed up the crawling of websites and reduce proxy bandwidth. -
RequestList- Represents a list of URLs to crawl. The URLs can be passed in code or in a text file hosted on the web. The list persists its state so that crawling can resume when the Node.js process restarts. -
RequestQueue- Represents a queue of URLs to crawl, which is stored either on a local filesystem or in the Apify Cloud. The queue is used for deep crawling of websites, where you start with several URLs and then recursively follow links to other pages. The data structure supports both breadth-first and depth-first crawling orders. -
Dataset- Provides a store for structured data and enables their export to formats like JSON, JSONL, CSV, XML, Excel or HTML. The data is stored on a local filesystem or in the Apify Cloud. Datasets are useful for storing and sharing large tabular crawling results, such as a list of products or real estate offers. -
KeyValueStore- A simple key-value store for arbitrary data records or files, along with their MIME content type. It is ideal for saving screenshots of web pages, PDFs or to persist the state of your crawlers. The data is stored on a local filesystem or in the Apify Cloud. -
AutoscaledPool- Runs asynchronous background tasks, while automatically adjusting the concurrency based on free system memory and CPU usage. This is useful for running web scraping tasks at the maximum capacity of the system. -
Puppeteer Utils- Provides several helper functions useful for web scraping. For example, to inject jQuery into web pages or to hide browser origin. Additionally, the package provides various helper functions to simplify running your code on the Apify Cloud and thus take advantage of its pool of proxies, job scheduler, data storage, etc. For more information, see the Apify SDK Programmer's Reference.
This short tutorial will set you up to start using Apify SDK in a minute or two. If you want to learn more, proceed to the Getting Started tutorial that will take you step by step through creating your first scraper.
Apify SDK requires Node.js 10.17 or later, with the exception of Node.js 11. Add Apify SDK to any Node.js project by running:
npm install apify --saveRun the following example to perform a recursive crawl of a website using Puppeteer. For more examples showcasing various features of the Apify SDK, see the Examples section of the documentation.
const Apify = require('apify');
Apify.main(async () => {
const requestQueue = await Apify.openRequestQueue();
await requestQueue.addRequest({ url: 'https://www.iana.org/' });
const pseudoUrls = [new Apify.PseudoUrl('https://www.iana.org/[.*]')];
const crawler = new Apify.PuppeteerCrawler({
requestQueue,
handlePageFunction: async ({ request, page }) => {
const title = await page.title();
console.log(`Title of ${request.url}: ${title}`);
await Apify.utils.enqueueLinks({
page,
selector: 'a',
pseudoUrls,
requestQueue,
});
},
maxRequestsPerCrawl: 100,
maxConcurrency: 10,
});
await crawler.run();
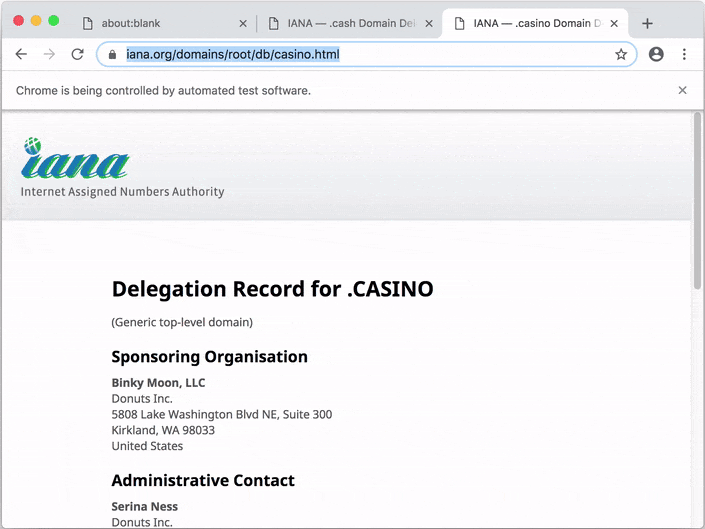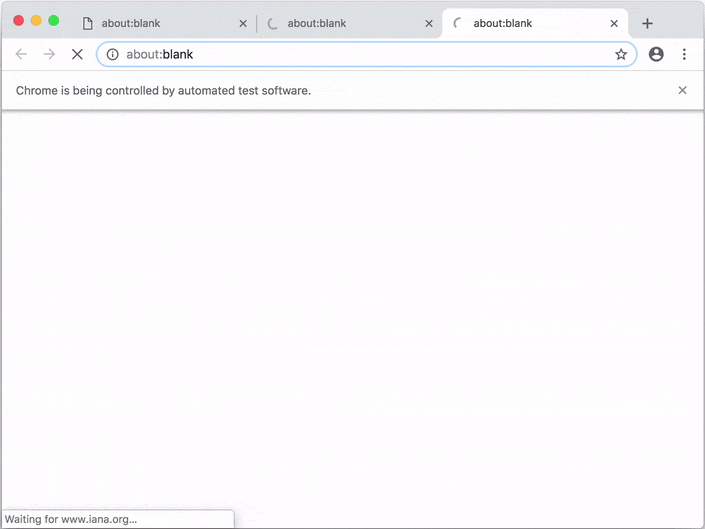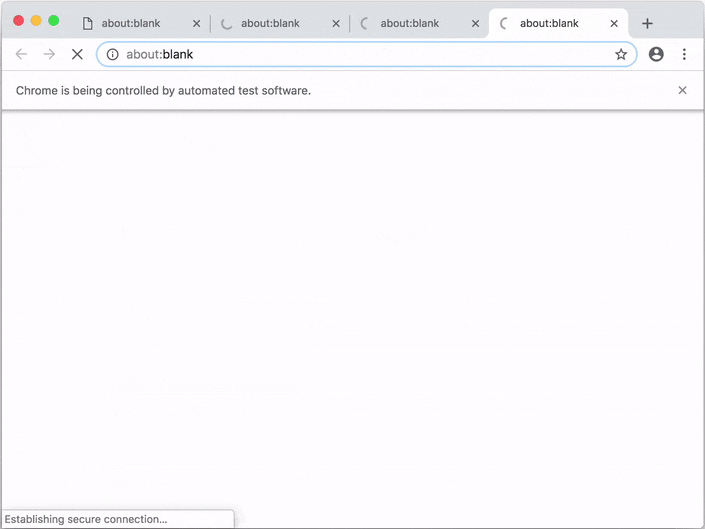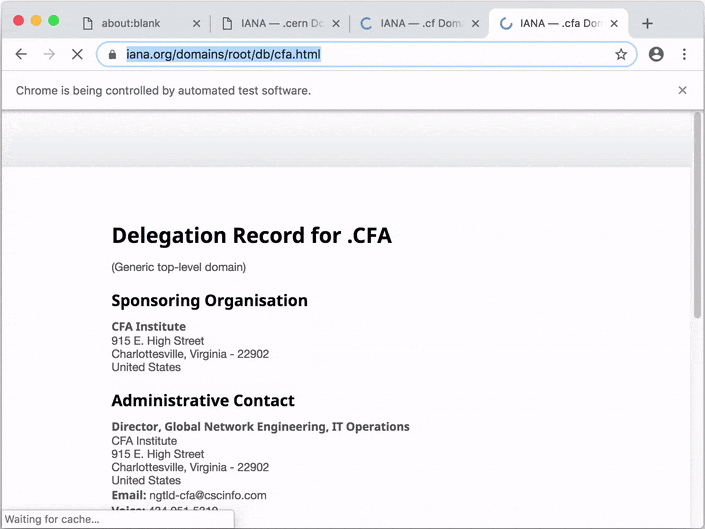
});When you run the example, you should see Apify SDK automating a Chrome browser.
By default, Apify SDK stores data to ./apify_storage in the current working directory. You can override this behavior by setting either the
APIFY_LOCAL_STORAGE_DIR or APIFY_TOKEN environment variable. For details, see Environment variables and
Data storage.
To avoid the need to set the environment variables manually, to create a boilerplate of your project, and to enable pushing and running your code on the Apify platform, you can use the Apify command-line interface (CLI) tool.
Install the CLI by running:
npm -g install apify-cliYou might need to run the above command with sudo, depending on how crazy your configuration is.
Now create a boilerplate of your new web crawling project by running:
apify create my-hello-worldThe CLI will prompt you to select a project boilerplate template - just pick "Hello world". The tool will create a directory called my-hello-world
with a Node.js project files. You can run the project as follows:
cd my-hello-world
apify runBy default, the crawling data will be stored in a local directory at ./apify_storage. For example, the input JSON file for the actor is expected to
be in the default key-value store in ./apify_storage/key_value_stores/default/INPUT.json.
Now you can easily deploy your code to the Apify platform by running:
apify loginapify pushYour script will be uploaded to the Apify platform and built there so that it can be run. For more information, view the Apify Actor documentation.
You can also develop your web scraping project in an online code editor directly on the Apify platform. You'll need to have an Apify Account. Go to Actors, page in the app, click Create new and then go to the Source tab and start writing your code or paste one of the examples from the Examples section.
For more information, view the Apify actors quick start guide.
If you find any bug or issue with the Apify SDK, please submit an issue on GitHub. For questions, you can ask on Stack Overflow or contact support@apify.com
Your code contributions are welcome and you'll be praised to eternity! If you have any ideas for improvements, either submit an issue or create a pull request. For contribution guidelines and the code of conduct, see CONTRIBUTING.md.
This project is licensed under the Apache License 2.0 - see the LICENSE.md file for details.
Many thanks to Chema Balsas for giving up the apify package name
on NPM and renaming his project to jsdocify.