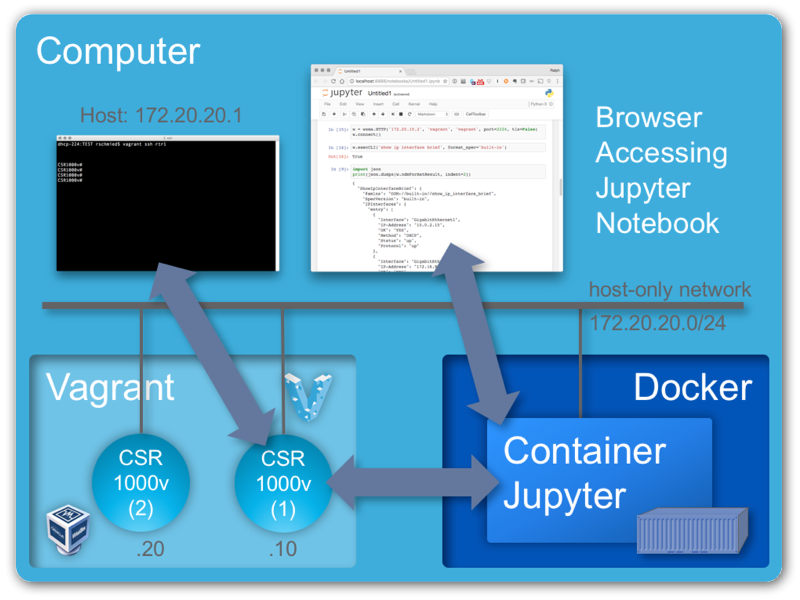
This repository provides a framework for an interactive device programability learning class. It is intended to be used with individual workstations where each workstation hosts the complete environment consisting of
- 1-2 CSR1000V virtual routers running IOS XE 16.3.2 Denali. The platform for the virtual machines is Vagrant using the VirtualBox provider.
- Docker Container running Jupyter to serve the content notebooks with Python 3.5 as the kernel.
This is a rough guideline how to bring up / prepare the entire environment. It has a couple of dependencies:
- Git client
- VirtualBox 5.0.28
- Vagrant 1.8.7 (be aware of this issue)
- Docker 1.12.3
- cdrtools (in particular
mkisofs) - a build environment (e.g. compiler, make, ...), suggest to use MacPorts or Brew if running on a Mac
- Clone the
iso-xrv-x64-vboxrepository from GitHub - IOS XE image from Cisco.com (e.g. here, then go to IOS XE Software and download the Denali-16.3.2 .iso file in the Latest tree branch, ~350MB in size)
Note: Version numbers mentioned were the ones that have been used when testing / creating the environment. Upgrading to latest code of the various components might simply work -- ymmv. Recommend to stick with 16.3.2 for the time being, though. Proper RESTCONF support should be included with 16.6.
Go to the directory where you cloned the iso-xrv-x64-vbox repository. Start the Vagrant box image build by running the following command
iosxe_iso2vbox.py -v ~/Downloads/csr1000v-universalk9.16.03.02.iso
This will take a while. When done, you need to install the resulting box into Vagrant:
vagrant box add --name iosxe csr1000v-universalk9.16.03.02.box
(See the output at the end of the script. It has the exact location of the generated box file and also the command to add / replace the Vagrant box file).
The next steps are required to prepare configuration disks for the routers and then either launch both or only one of them
- Clone this repo from GitHub into a new directory
- Make sure that the Vagrant box name matches the one configured in the Vagrant file
- Ensure you have the required tools installed
- run
maketo create the ISO files with the router configurations - Bring up the routers using
vagrant up(brings up both) orvagrant up rtr1to only start rtr1
-
Change into the DOCKER directory
-
Build the container using
docker build . -t dp-workbenchThis will take a while. The resulting image should be around 400MB in size.
-
Run the container. If you want to make the content read-only then don't provide a volume. Otherwise providing the DOCKER directory as the volume enables to edit the content. Additional build is required to update files in container image if content is changed.
docker run -p8888:8888 -v$(pwd):/home/docker/notebooks -d dp-workbenchThe above command runs the container with a mapped volume.
docker run -p8888:8888 --name workbench -d dp-workbenchThis command runs without a mapped volume, therefore using the content from within the container as read-only content. It also assigns the name
workbenchto it to refer to the container.
Point your browser on your local machine to http://localhost:8888. Everything should be working at this point.
-
Run the container without Volume (e.g. readonly files)
docker run -p8888:8888 -d dp-workbench -
Run the container with the Volume (need to build the image again after changing files)
docker run -p8888:8888 -v$(pwd):/home/docker/notebooks -d dp-workbench -
Execute a shell into the container
docker exec -it -u 0 ${CONTAINER_ID} /bin/sh -
Build the image
docker build . -t dp-workbench -
When building in a lab that requires a proxy:
docker build . -t dp-workbench --build-arg http_proxy=$http_proxy