#Super cat
An ECMAScript 6(ES6) features project.
- Node.js/NPM (v6.9.5)
The framework uses SystemJs for dependencies management ,Incremental DOM as the view engine for dynamic html templates and Gulp for build tasks including pre-compiling ES6 scripts and dynamic view templates. The framework is for the traditional multi-page application, it aims to reduce writing boilerplate code for interactions between DOM elements and components. More information is provided below.
To get started on this project, you can use the node version manager NVM to switch different versions of nodeJs in your local development environment. Install Node.js v6.9.5 after the installation with
nvm install 6.9.5
Then run
node -v
to check whether the node version is 6.9.5.
It recommends a global installation for JSPM and Gulp:
$ [sudo] npm install -g jspm jspm-git gulp jspm-github
Config github registry
jspm registry config github
connect bitbucket
$ jspm config registries.bitbucket.baseurl ssh://git@bitbucket.org
$ jspm config registries.bitbucket.handler jspm-git
Now you can install node modules and jspm packages
$ npm install
$ jspm install
To start a local live reload server with gulp watch task
gulp watch
Then open one of the page below in your browser
http://localhost:9000/demo/examples/cat-clicker.html http://localhost:9000/demo/examples/cat-list-counter.html
src/components/_cat-clicker
A typical component package
a-component.js controller
a-component-tpl.html SuperviewJs view template
a-component-tpl.js `gulp build-view-templates` compiles tpl.html into Incremental DOM tpl.js
a-component.scss scss file
demo.a-component.html component demo html
controller -> view
Example
src/components/_cat-clicker/cat-list-counter/cat-list-counter.js
controller -> View model -> view
Examples
src/components/_cat-clicker/cat-list
src/components/_cat-clicker/cat-detail-panel
src/components/_cat-clicker/cat-description-panel
A component controller can have different views or view models
controller 1 -> view model 1 -> view 1
-> view 2
controller 1 -> view model 1 -> view 1
-> view model 2 -> view 2
controller 1 -> view model 1 -> view 1
controller 2 -> view model 2 -> view 1
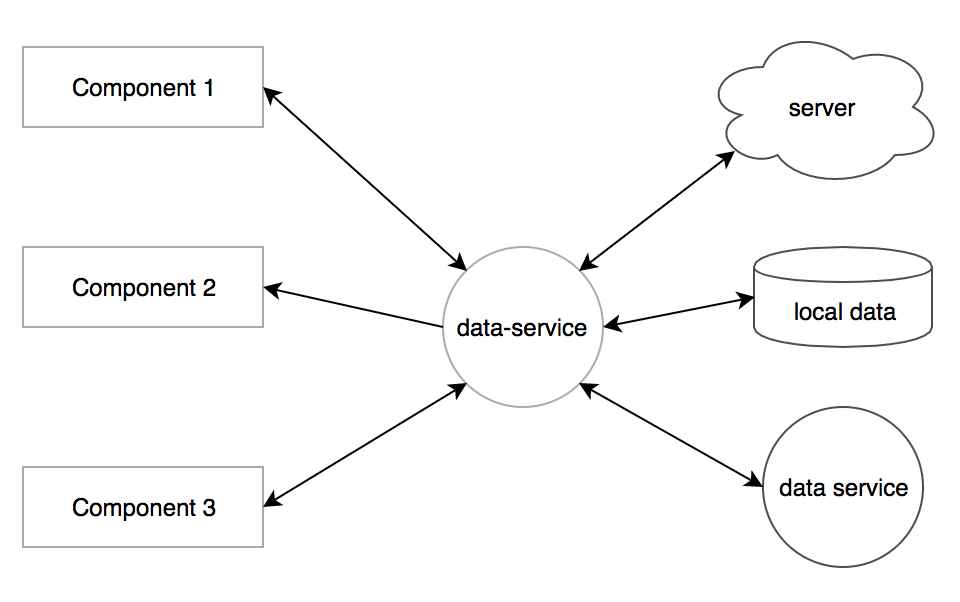
Source: src/js/lib/data-service.js
Example: src/components/_cat-clicker/cat-service.js
The data service follows the observer pattern, it observers and broadcasts data changes between different components with data-driven processing. Recommend to use it as a central control to manage interactions or state changes for a group of components, or synchronise data with other modules such as the server side module and the local storage and so on. As the chart shown below, it provides a clear data flow among a group of components and modules.
Each of components in a group subscribes to an object and gets the (ES6) proxy of the object:
cat-list | this._data.selectedCat cat-service cat-detail-panel | this._data.selectedCat
-> subscriber | | subscriber <-
_subscribeToData("selectedCat") | this._data.selectedCat | _subscriberToData("selectedCat")
<- proxy | | proxy ->
The object proxy observes changes, the service broadcasts the object changes to its subscribers, each of components gets a notification and update its view:
cat-service cat-list
_handleObservingDataChanges() -> broadcastDataChanges("cats") -> handleNotification() -> this._dynamicPartial.view.render() / update dynamic view
cat-detail-panel
-> handleNotification() -> update static view dom element values
Shared functions or data between components
international student <->
student-data-service (addStudent(), deleteStudent()) <-> [ helpers/data-services ]
domestic student <->
Data synchronisation between the local storage or the server side API
international student <->
student-service <-> server side API/local storage
(validate, filter, sort, find)
domestic student <->
Interactions with nested components
current student
- international student
- domestic student
current student <-> student-service <-> international student
(list, add, find, delete) <-> domestic student
Component dependencies management
login teacher -> student-service -> international student
(setTheListOfSelectedStudents, setTheListOfAvaiableStudents) -> domestic student
Group data services
international student <->
student-sevice <-> teacher-service <-> teacher
domestic student <->
OR
international student <->
student-sevice <-> student-teacher-service <-> teacher-service <-> teacher
domestic student <->
Unit test for the complex business logic Comparing to the end to end test, it is easier to write the unit test for a data service as it doesn't require DOM interactions. For example, using Mocha writes a BDD test for the student service or teacher service.
The framework uses Incremental DOM for the dynamic view. SuperviewJs is a template engine to convert a html template into an incremental-dom render function. The
The SuperviewJs playground http://davidjamesstone.github.io/superviews.js/playground/index.html
###Example###
View
<ul each="student in students">
<li><h3 class="{vm.handlers.getStudentState(student)}">{student.name}</h3></li>
<li><h3 class="{vm.handlers.getStudentState(student)}">{student.name}</h3></li>
</ul>Handler for the implement details
getStudentState(student) {
return (selectedStudent === student) ?
student.type === "international" ?
"b-student--internal b-student--selected" :
"b-student--domestic b-student--selected" :
student.type === "international" ?
"b-student--internal" :
"b-student--domestic" ;
}The benefit is the same view can be used with different handlers from the same or different controllers:
getStudentState(student) {
return (loginUser === student) ? "b-user--login" : "b-user" ;
} BDD test script for data service examples