One week until final presentation demos and the end of the course! I'm excited to see the realization of these projects. Lets go into details on what to expect next Monday.
Everyone will spend ~5 minutes presenting. This doesn't have to be a huge production.
Talk about:
- Your site's purpose
- Your challenges, victories
- What you learned that we didn't cover in FEWD
IMPORTANT Also, if you have not submitted all of your homework assignments to schoology, please do so ASAP. In order to recieve a passing grade in the class, I have to have received your homework throughout the course.
By the end of this class you will be able to:
- Understand the uses and advantages of using Version Control
- Differentiate between Git and GitHub
- Create a Github repository and push it to an online repo.
- Install Bootstrap and add it to an existing project
- Explain Bootstrap's 12-column grid system
Version control is a way to keep track your project as it changes over time. It also is the easiest way to collaborate with other developers working on the same codebase.
Have you ever run into this problem?
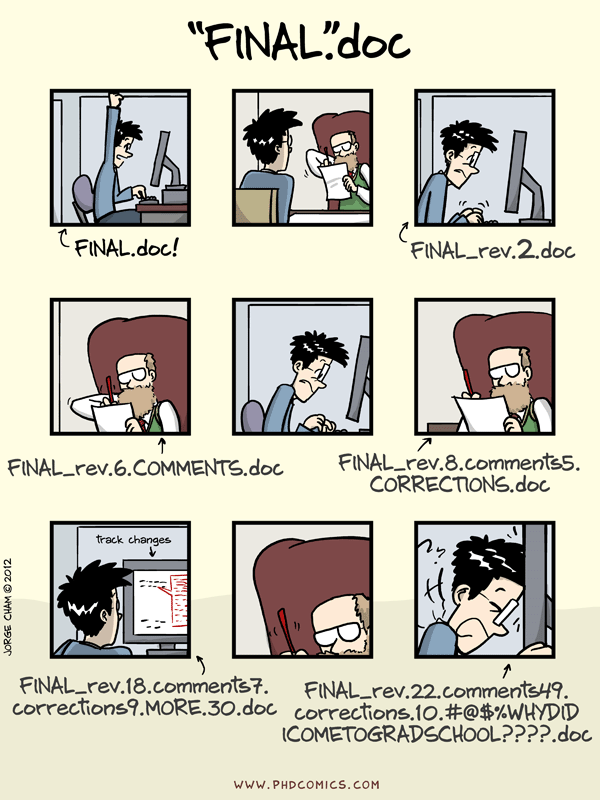
This is what version control solves. Using version control you can incrementally change and modify your project, while still having a history of your previous work.
Imagine these scenarios
- You've been working on a project for weeks that you're pretty happy with. Unfortunately, you start working on a new feature that breaks a lot of the things you were happy with. How could you backtrack and retrieve the version you were happy with?
- You're working on a project with 3 other developers. How do you manage who makes changes? How to you make sure that the code one developer writes doesn't affect the code that you write? How do you make comments and suggestions about these code changes?
Git is:
- A program you run from the command line or the desktop
- A distributed version control system
Programmers use Git so that they can keep the history of all the changes to their code. This means that they can rollback changes (or switch to older versions) as far back in time as they started using Git on their project.
Note: We don't have enough time to talk about using Git from the command line, but I highly recommend learning how to. Github provides a great tutorial here.
A codebase in Git is referred to as a repository, or repo, for short.
Repositories are kind of like "projects" in Git
- Each repository is independent of others.
- No specific definition, can be whatever you want it to be.
- Usually one project per repo, e.g:
- Relaxr Website
- Startup MatchMaker
- Final Project
Git is pretty confusing and complex at first, but I have full confidence that you will pick it up before you know it. When we talk about repos and codebases we're really just talking about a directory that has a file in it named .git. This .git is very importanta. It tells git binary to treat the directory as a repo and listen for changes, track files, and do git-related tasks when asked.
Git was created by Linus Torvalds, the principal developer of Linux.
GitHub is:
- A hosting service for Git repositories
- A web interface to explore Git repositories
- A social network of programmers
- We all have individual accounts and put our codebases (repos, directories) on our GitHub account
- You can follow users and star your favorite projects
- Developers can access codebases on other public accounts
- You can use it to work on open source project
- GitHub uses Git
Repos exist both locally on your computer and can be pushed to services like Github for online storage.
You can "clone" repositories from github onto your computer. (Demo for class)
As you make changes, you can "commit" them to your local git folder... then "push" them to your GitHub repository
Think about this quote: “Git is software. GitHub is company that happens to use Git software.”
Exercise: If you think this statement is true, react to with a thumbs up or a thumbs down if you think it is false. Why?
- Visit GitHub and sign up for an account.
- Download the Desktop Client (Don't download the new Beta just yet)
- Sign into your new GitHub account through the Desktop client.
- Add your Final Project folder to GitHub by using the '+' button in the top left corner
- You will see that there are changes to be made to your git repo (because this is the first time you've made a commit)
- Create a commit message and description, then click 'commit to master'
- Now let's make some changes
- Create a README.md file.
- This is a file that Github uses to show text when you visit a page on Github. Think of it as a place where you can describe what your app does, how to install it, etc.
- .md means it is a Markdown file. Think of it as a hybrid between regular text files and html
- Cheatsheet here
- Check out the Github Desktop again, and you'll see that it has tracked your changes.
- Let's make another commit.
- Now we have our project and a couple commits. Let's push it to GitHub to share with others.
- Click Publish in the top right corner.
- Visit your personal GitHub page. Voila!
Exercise: Let's spend ~20 minutes adding onto your github portfolio. Add the Relaxr exercises, Startup Matchmaker, etc.
Bootstrap is the world's most popular styling library. It was originally created by Twitter and has since been used all over the web. Through using Bootstrap you can easily create responsive layouts, utilize components built by CSS experts, and more rapidly build projects that look great.
Bootstrap Website: Get Bootstrap
Some examples of sites built with Bootstrap: Build with Bootstrap
One of Bootstrap's biggest features is that it is focused on mobile first design, and easily scales up.
Thanks to the documentation, it's pretty clear how to install Bootstrap. However, there are so many choices that it may be confusing.
- Compiled Bootstrap - This is what we want
- Source Code - written in LESS
- Sass - similar to Source Code
- CDN
- Bower/NPM/Composer - package managers
For now, lets install either the compiled Bootstrap or grab a CDN link.
REMEMBER: Bootstrap is dependent on jQuery, so make sure it is also present on your page.
Bootstrap uses a 12 column responsive grid in order to control the layout of the page. This grid is an invisible set of measurements used to determine the size of your HTML elements on screen.
Through Bootstrap, we can define how many of these columns we want our HTML element to cover.
When using bootstrap, you define a row of content using the row class. And within the row, you can declare the sizing of your HTML components through the col-* classes.
Lets look at the Bootstrap Documentation for more details.
As the page changes size, Bootstrap uses breakpoints defined in it's code to change whether an element stacks or is in line with others.
Code Along: Lets use Bootstrap to create a responsive layout
Another benefit of using Bootstrap is the resusable components available to help build your application quickly.
These components include:
- Dropdown Menus
- Styled Buttons
- Alerts
- and More...
Exercise: Bootstrap Scavenger Hunt
As a class, we're going to compile an appendix to the Bootstrap documentation, providing tips and tricks on the implementation of some of Bootstrap's Greatest Hits.
Group One
- Jumbotron
- Well
- Modal
- Glyphicon
Group Two
- Badge
- Progress bar
- List groups
- Tooltip
Group Three
- Navbar
- Dropdowns
- Panels
Each group should create Codepen demo of their three components and write up the answers to the following questions for each:
- What is it?
- What's it good for?
- Where can I read more about it?
- Any tips/tricks for implementation? (Think: What value can I add to the existing docs?")
Lab/Homework:
Bootstrapify (or Foundation-ify or Materialize-ify or Picnic-ify or Pure-ify or…) something that you built earlier in the course. If you don't want to overwrite your previous styling, you're welcome to work on an branch.
http://getbootstrap.com/components/
http://getbootstrap.com/customize/
https://github.com/twbs/bootstrap-sass
http://www.tutorialspoint.com/bootstrap/
http://tutorialzine.com/2015/06/12-time-saving-bootstrap-examples/
http://builtwithbootstrap.com/
https://bootstrapbay.com/blog/built-with-bootstrap/
https://scotch.io/bar-talk/bootstrap-3-tips-and-tricks-you-might-not-know
https://scotch.io/tutorials/understanding-the-bootstrap-3-grid-system
