Google Colab is essentially a virtual machine (Ubuntu 20.04) that people with a google-account can get in the cloud. You configure it yourself and can have it for up to 12 hours and then it is closed. Next time you need to configure it again. It is pre-configured with Python 3.7 and some common libraries and you interact through a Colab notebook that is based on the Jupyter notebook. More about it you can find here Colab.
I have made a notebook that set-up PyFMI 2.9.8 and needed libraries and run a small example with microbial batch cultivation. The model is an example taken from Bioprocess Library and the example is available as an FMU. You can interact with it through a simplified command-line interface using: newplot(), par(), inut(), simuI() etc. More about the command-line interface you find here FMU-explore and is a layer on top of PyFMI.
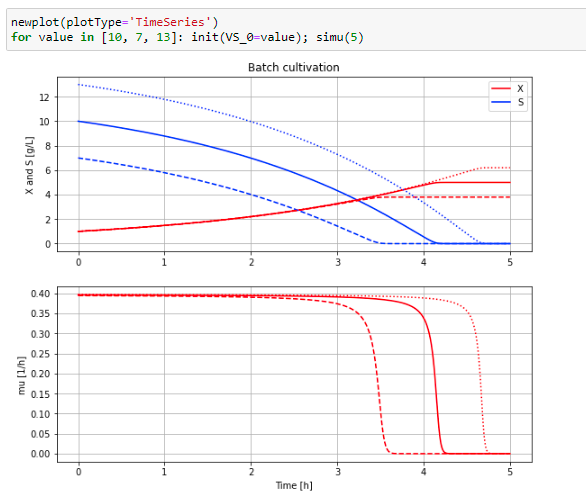
Below script and diagram with three simulations of batch growth with different initial substrate level that you will get at the end of the notebook.
You start up the notebook in Colab by pressing here start BPL notebook or alternatively (experimentally) start BPL notebook with FMPy. Then you in the menu choose Runtime/Run all. If you have chosen the altarnative with FMPy click first on the symbol Open in Colab.
The installation takes just a few minutes. The subsequent execution of the simulations of microbial growth take just a second or so. You can continue in the notebook and make new simulations and follow the examples given.
See also the related repositories: BPL_TEST2_Batch_calibration and BPL_TEST2_design_space.
Note that:
- The script occassionaly get stuck during installation. Then just close the notebook and start from scratch.
- Remember, you need to have a google-account!
Just to be clear, no installation is done at your local computer.
License information:
- The binary-file with extension FMU is shared under the permissive MIT-license
- The other files are shared under the GPL 3.0 license