Ricochet.js is a backend tool designed for frontend developers, allowing you to host your backend code alongside your frontend code. It provides a document and file store with serverless capabilities, simplifying your application's architecture and data storage needs.
With Ricochet.js, you can integrate your frontend and backend seamlessly, enabling you to focus on building a great user experience. This eliminates the need for a separate backend server and improves your workflow.
Ricochet.js comes packed with a range of useful features, including:
- Multi-tenancy: Deploy Ricochet.js once and use it for multiple websites.
- General APIs: A JSON document store and a file store are ready to use.
- Remote function calls: Call remote JavaScript functions like a Serverless backend or function-as-a-service (FaaS) application.
- Frontend-backend version alignment: Avoid version mismatch by deploying your backend code alongside your frontend code on the same CDN or server.
- Password-less authentication: A secure authentication service that requires zero knowledge from users.
- Cloud compatibility: Choose from a variety of stores, including Memory, NeDB (Disk), MongoDB, S3-compatible, and more.
- Scalability: Easily scale your application to meet growing demand.
- Edge compatibility: Works seamlessly on edges, enabling you to deliver your content to users quickly and efficiently.
Some use cases:
- You don't want to deploy your backend server each time you make a backend modification
- You need a simple backend with only some specific code
- You want to store structured data and files
- You want frontend and backend code to be updated at same time
Creating a web application typically requires a server for three main reasons:
- Data persistence: Structured and binary data must be stored and managed, which can be accomplished with a server.
- Server-side code execution: Certain code needs to be executed on the server-side, which cannot be modified or accessed by the client for security reasons.
- Periodic task execution: Tasks such as automated emails or large data processing often require a server to perform in a timely manner.
Ricochet.js fulfills these requirements with the following features:
- A REST API to store key-value documents, allowing for structured data storage. Binary files, such as images and documents, can also be associated with each stored resource.
- The ability to bundle custom JavaScript code that can be executed in a secured context on the server-side, with access to the two stores mentioned above.
- The ability to schedule hourly or daily actions to perform periodic tasks.
To use Ricochet.js you need a running instance of the server. You have two options:
- Using an hosted version (jump to project initialization section)
- Running your own instance, continue with the next section
First you need to define a random secret string and store it the
RICOCHET_SECRET env variable or in .env file if you prefer.
The following command helps you to create such a file.
echo RICOCHET_SECRET=`cat /dev/urandom | tr -dc 'a-zA-Z0-9' | fold -w 32 | head -n 1` > .envNow you can start a Ricochet.js server by using npx (🚨 you should have npm version >=7
to support mongodb or nedb store backend):
npx ricochetjsOr install Ricochet.js globally and launch the server:
npm install -g ricochetjs
# then
ricochetjsBy default, data are stored in memory so if you restart the server, all data are lost. The default configuration is for development purpose only. See server configuration for more customization and how to use persistent storages.
Now the server is running so you can create a new ricochet site. To do it,
visit the Ricochet.js URL with a browser. By default http://localhost:4000.
Fill the left form with wanted information and click the Create button.
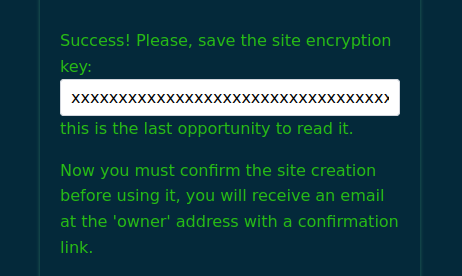
The result should look like the following image:
From the response you MUST save the key value, this key is used to encrypt
your server side code hosted alongside with your frontend code.
This is the ONLY chance to get it so keep it for later and keep it secret.
In the meantime you should have received a mail with a link you must visit to confirm the site creation. This is a security measure to prevent abuse. Click the link to validate the site creation. If you've not yet configured any mail provider, check out the server logs to read the confirmation link.
Now, your server is ready and a site exists. You can follow the next steps to create a new site project.
Since you have a Ricochet.js instance up and running, you can use the project starter to initialize your backend.
Use degit to make your own copy of the starter repository where you want
(A good place can be in the backend folder of your project):
npx degit https://github.com/jrmi/ricochetjs-starterThen install dependencies:
npm installCreate a .env file from the .env.dist file and customize it by adding your
previously generated site key with Ricochet.js.
You can serve the default project by executing:
npm run serveor if you use an external instance of Ricochet.js, you can use the tunnel version:
npm run tunnelTo test the script, a Ricochet.js server must be running.
In the following example we assume that you use your local Ricochet.js instance
available on http://localhost:4000 but you can replace this URL by any ricochet
instance that have access to your backend package server. We also assume that your
backend server is on http://localhost:9000 but if you use a tunnel, use the
address given by the npm command.
You can use curl to test the API:
curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json
X-Ricochet-Origin: http://localhost:9000" -d '{"some":"data"}' http://localhost:4000/exampleSite/store/publicData/And get the of the publicData box:
curl -X GET -H "Content-Type: application/json
X-Ricochet-Origin: http://localhost:9000" http://localhost:4000/exampleSite/store/publicData/You can freely modify src/index.js file to declare your store, hooks,
custom functions, ...
Remember that the server bundle will be encrypted and should be used by ricochet server with related site configuration.
Also remember to define a SECRET environment variable for the server
(Can be defined in same .env file if you start the server from here).
The server should be listening on http://localhost:4000.
Since you finish your code, you must bundle it to prepare the deployment:
npm run buildYes, that's true, you are bundling the backend code with webpack!
This bundle can now be deployed on any content delivery network and can (should?) be deployed alongside with your frontend code.
Each time you call an API you should have at least one of this HTTP header:
x-ricochet-origin, referer, origin. These headers are used to determine the website
where the backend code is stored. Let's call it the <ricochetOrigin>. By default
if you use a browser, referer or origin should be included by default.
On the first call of any API endpoint for a specific siteId, the file
<ricochetOrigin>/ricochet.json is downloaded, decrypted and executed by the
Ricochet.js server.
This is the encrypted server side bundle that configure Ricochet.js for this siteId.
This file MUST exists before being able to call any Rest API.
The script must define and export a main function that will be executed (and cached) on the very first query for this site. The main function is called with an object as parameters that contains the following properties:
- store: Allow to access the JSON store.
- hooks: Add some hooks to the store to modify the queries and the response.
- functions: Add arbitrary custom function to the API.
- schedules: Schedules hourly or daily function calls.
All this parameters are explained in next sections.
This script is executed on Ricochet.js server so it can't rely on browser capabilities.
This script allow you to configure the ricochet server for your siteId in a declarative way.
Once you have initialized your site with the setup script (the ricochet.json file)
you can use the rest API to store data, files or call
custom functions.
To access JSON store from the setup function in your ricochet.json file, you can use the store parameter.
This a store instance scoped to the current siteId. You have access to the following methods:
store.createOrUpdate(boxId, options): create, if not exist, or update a boxId store. Options are:
| Name | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| security | Security model of the box. Values are string: "public", "readOnly", "private" | "private" |
store.list(boxId, options): list box content. Options are:
| Name | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| sort | Name of sort field | "_id" |
| asc | Ascending order ? | true |
| skip | How many result to skip | 0 |
| limit | Limit result count. | 50 |
| onlyFields | Limit result to this fields. | [] |
| q | A query to filter results. The query must be written in the pivotql query language. | "" |
store.save(boxId, id, data): Create or update the given id resource with given data.
store.update(boxId, id, data): Update the resource. Fails if not existing.
store.delete(boxId, id) try to delete the corresponding resource.
Hooks allows you to customize the way data are accessed for one specific
box or for all.
You can add a hook by pushing a function to the hooks array from parameters.
By using hooks you can customize behavior of the generic Rest APIs to change way they work.
Custom functions can be defined by adding a function to the function object.
The key will be the endpoint and the value the executed callback. The key is the
name of the function and the value must be a function executed when the query
is received.
Then you can call the function later using the following endpoint.
Returns the value returned by the function.
Define daily or hourly schedules by pushing functions to this object for the
key daily or hourly.
[More details coming soon...]
This section describe the Rest api of Ricochet.js.
To list available resources in this box.
With a JSON payload.
To create a new ressource in boxId
returns: previously saved resourceId from boxId.
With a JSON payload to update the resource with this Id.
To add a file to this resource.
Returns the file Path for later uses.
List URL of the files associated to the given ressource Id.
Executes a previously defined custom function in the setup and returns the result to the client.
The functions receive an object with following properties:
storethe very same store API used for JSON store API. Allow you to do some protected operationmethodthe http verb usedquerya dict of query parametersbodythe request payloaduserIdthe id of the current user if one is logged inidthe optionalidif provided
By posting a JSON containing a user email:
{"userEmail": "user@example.com"}an email will be sent to this address containing a link to authenticate to the platform.
This link is: <ricochetOrigin>/login/:userId/:token
You frontend should handle this url and extract the userId and the token to
authenticate the user.
userId is the unique user identifier corresponding to the given email address.
The token is valid during 1 hour.
Allow the client to verify the token and authenticate against the service.
Allow the client to verify if a user is authenticated. Returns 403 http code if not authenticated.
To register new site. A mail is send each time you want to create a website to confirm the creation.
The json content should look like this:
{
"siteId": "the new site Id",
"name": "Name displayed in mail",
"owner": "owner email address for security, confirmation mails are send here",
"emailFrom": "email address displayed in email sent for this site"
}In the response you'll get an extra key property. You MUST save it for later use.
This is the ONLY chance to get it. This is the encryption key you need to crypt
your ricochet.json file.
To update a site configuration. To confirm the modification, a mail is send to the site owner.
The json content should look like this:
{
"name": "Name displayed in mail",
"emailFrom": "email address displayed in email sent for this site"
}You can't modify owner email (yet?).
You can configure your instance by settings environment variables or using
.env file:
| Name | description | default value |
|---|---|---|
| SERVER_HOST | '0.0.0.0' to listen from all interfaces. | 127.0.0.1 |
| SERVER_PORT | Server listen on this port. | 4000 |
| SERVER_NAME | Server name displayed on mail for example. | Ricochet.js |
| RICOCHET_SECRET | Secret to hash password and cookie. Keep it safe. | |
| SITE_REGISTRATION_ENABLED | Set to 0 to disable site registration. |
1 |
| FILE_STORAGE | Configure file store type. Allowed values: 'memory', 'disk', 's3'. | memory |
| STORE_BACKEND | Configure JSON store provider. Allowed values: 'memory', 'nedb', 'mongodb'. | memory |
| EMAIL_* | To configure email provider. Put "fake" in EMAIL_HOST to log mail instead of sending them. |
Note: "memory" stores are for development purpose only and remember that you loose all your data each time you stop the server.
Note: for "mongodb" backend, you need to install npm install mongodb@3.
Note: for "nedb" backend, you need to install npm install @seald-io/nedb.
If you use disk file store you need to configure this variables:
| Name | description | default value |
|---|---|---|
| DISK_DESTINATION | Base path of the file store | /tmp/ricochet_file |
If you use S3 file store configure also this variables:
| Name | description | default value |
|---|---|---|
| S3_ACCESS_KEY | S3 access key | |
| SB_SECRET_KEY | S3 secret key | |
| S3_ENDPOINT | S3 endpoint | |
| S3_BUCKET | S3 bucket | |
| S3_REGION | S3 Region | |
| S3_PROXY | Set to "1" to enable to proxy file (otherwise it's a redirect to the file) | 0 |
| S3_SIGNED_URL | Set to "0" to disabled usage of signed URL | true |
| S3_CDN | Set the CDN prefix to enable it |
For nedb JSON store provider:
| Name | description | default value |
|---|---|---|
| NEDB_BACKEND_DIRNAME | NeDB base path for DB storage |
For mongodb JSON store provider:
| Name | description | default value |
|---|---|---|
| MONGODB_URI | Mongodb configuration URI | |
| MONGODB_DATABASE | Database to use |
Clone the repository then install dependencies:
npm ciCreate .env file from .env.dist file and change the values.
and start the instance in dev mode:
npm run dev