Hi, in this step by step article, we will see how we can integrate the Telerik UI for ASP.NET Core (Kendo) components with our Abp MVC app.
ABP Framework offers startup templates to get into business faster.
In this article, I will create a new startup template with EF Core as a database provider and MVC for UI framework. But if you already have a project with MVC UI, you don't need to create a new startup template, you can directly implement the following steps to your existing project.
If you already have a project with the MVC UI, you can skip this section.
- Before starting to development, we will create a solution named
TelerikComponents(or whatever you want). We will create a new startup template with EF Core as a database provider and MVC for UI framework by using ABP CLI:
abp new TelerikComponents --ui mvc --database-provider ef- Our project boilerplate will be ready after the download is finished. Then, we can open the solution in the Visual Studio (or any other IDE) and run the
TelerikComponents.DbMigratorto create the database and seed initial data (which creates the admin user, admin role, permissions, etc.). I prefer changing the db connection string in the DbMigrator project to(localdb)\\mssqllocaldbto be able to just run right away.
"ConnectionStrings": {
"Default": "Server=(localdb)\\mssqllocaldb;Database=TelerikComponents;Trusted_Connection=True"
},- After the database and initial data created,
- Run the
TelerikComponents.Webproject to see our UI working.
Default login credentials for admin: username is admin and password is 1q2w3E*
-
First thing we need to do is downloading the Progress Control Panel to get Telerik Kendo components on our development machine.
-
If you are using Telerik UI for ASP.NET Core components for the first time or you don't have an active license you can click here to download free trial.
You can find the more installation details from here.
- We need to install the
Telerik.UI.for.AspNet.CoreNuGet package to our web project (*.Web). We need to choose the Telerik feed package source to see the package. - If you're using the trial, install
Telerik.UI.for.AspNet.Core.Trialpackage via NuGet.
- In package.json, add the kendo script component as a dependency. This will get the scripts in your
node_modulesdirectory. A note, the npm package from Telerik needs to be transpiled to be able to be used so we're basically following their npm+webpack documentation here with a few adjustments for abp.io setup:
{
{
"version": "1.0.0",
"name": "my-app",
"private": true,
"main": "main.js",
"devDependencies": {
"webpack": "^5.26.3",
"webpack-cli": "^4.5.0"
},
"dependencies": {
"@volo/abp.aspnetcore.mvc.ui.theme.lepton": "^4.2.2",
"@volo/account": "^4.2.2",
"@volo/audit-logging": "^4.2.2",
"@volo/identity": "^4.2.2",
"@volo/saas": "^4.2.2",
"@progress/kendo-theme-bootstrap": "4.33.0",
"@progress/kendo-ui": "2021.1.225",
"css-loader": "^5.1.3",
"expose-loader": "^2.0.0",
"style-loader": "^2.0.0"
},
"scripts": {
"build": "webpack"
}
}
}Create a main.js in the root directory, this is what webpack will use to know what to include in the transpiled js bundle.
import $ from 'jquery';
window.jQuery = $; window.$ = $;
import "@progress/kendo-ui";
import "@progress/kendo-ui/js/kendo.aspnetmvc";
import "@progress/kendo-ui/js/kendo.timezones";
import "@progress/kendo-theme-bootstrap/dist/all.css";Finally, add a webpack.config.js file to the root directory of your web project with the following content:
"use strict"
{
const path = require('path');
const webpack = require('webpack');
module.exports = {
entry: './main.js',
output: {
filename: 'kendo-bundle.js',
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'wwwroot/libs/kendo/dist')
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: [{ loader: 'style-loader' }, { loader: 'css-loader' }]
},
{
test: /jquery.+\.js$/,
use: [{
loader: 'expose-loader',
options: 'jQuery'
}, {
loader: 'expose-loader',
options: '$'
}]
}
]
},
externals: {
jquery: 'jQuery'
}
}
}What this will do is create a single js file that contains all of kendo, transpiled so you don't get 'module' errors. The use of expose-loader, externals jquery and the jquery rules are all there so that abp.io scripts, the way jquery is added and how kendo's js generally includes jquery doesn't conflict with each other.
- In the
abp.resourcemapping.jsfile, add the necessary entries that look like the following:
module.exports = {
aliases: {
},
mappings: {
"@node_modules/@progress/kendo-ui/css/**/*": "@libs/kendo/css",
"@node_modules/@progress/kendo-ui/js/**/*": "@libs/kendo/js"
}
};This will ensure the scripts and styles we need are packed up and in the right place for the next steps.
-
Run
yarn(to get the package) -
Run
gulp(to execute the mapping) -
Run
npm build(to execute the conversion of the js from Telerik into something usable here) -
In the
TelerikComponents.Webproject, under/Bundling, create a new directory we'll callKendo- i.e./Bundling/Kendo
- In
/Bundling/Kendo, create the class fileKendoScriptContributer.cswith the following content:
namespace TelerikComponents.Web.Bundling
{
[DependsOn(
typeof(JQueryScriptContributor)
)]
public class KendoScriptContributor : BundleContributor
{
public override void ConfigureBundle(BundleConfigurationContext context)
{
context.Files.AddIfNotContains("/libs/kendo/dist/kendo-bundle.js"); // This is the output of our webpack step
}
}
}- In
/Bundling/Kendo, create the class fileKendoStyleContributer.cswith the following content:
namespace TelerikComponents.Web.Bundling
{
public class KendoStyleContributor : BundleContributor
{
public override void ConfigureBundle(BundleConfigurationContext context)
{
context.Files.AddIfNotContains("/libs/kendo/css/web/kendo.common-bootstrap.min.css");
context.Files.AddIfNotContains("/libs/kendo/css/web/kendo.bootstrap-v4.min.css");
}
}
}- In the
TelerikComponents.Webproject, under/Components, create a new directory we'll callKendo- i.e./Components/Kendo - Create a
Default.cshtmlwith the following content:
@using TelerikComponents.Web.Bundling.Kendo
@addTagHelper *, Volo.Abp.AspNetCore.Mvc.UI.Bundling
<!-- Kendo -->
<abp-script type="typeof(KendoScriptContributor)" />- Create a KendoViewComponent.cs with the following content:
public class KendoViewComponent : AbpViewComponent
{
public IViewComponentResult Invoke()
{
return View("/Components/Kendo/Default.cshtml");
}
}- In
/Pages/_ViewImports.cshtmladd the tag helper:
@using Kendo.Mvc.UI
@addTagHelper "*, Kendo.Mvc"- Finally, in your
TelerikComponentsWebModule.csfile - let's add the following bits:- In
ConfigureServices, addConfigureKendo(context.Services);. The method implementation looks simply like this:
- In
private void ConfigureKendo(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddKendo();
}- Find the area
Configure<AbpBundlingOptions>and after theGlobaladd, also add our style contributor.AddContributors(typeof(KendoStyleContributor)):
Configure<AbpBundlingOptions>(options =>
{
options
.StyleBundles
.Get(StandardBundles.Styles.Global)
.AddContributors(typeof(KendoStyleContributor)); // add this
});If you don't see this section, add it to ConfigureServices().
* Add a new configure to setup a layout hook, where we add the kendo scripts to the bottom of the page:
Configure<AbpLayoutHookOptions>(options =>
{
options.Add(
LayoutHooks.Head.Last, //The hook name
typeof(KendoViewComponent) //The component to add
);
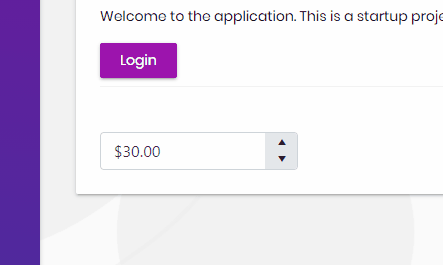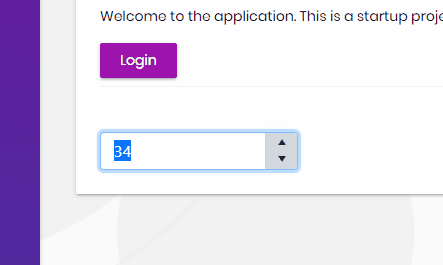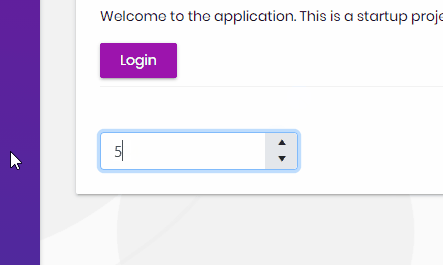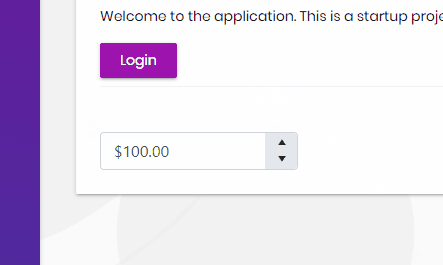
});If we've done everything right, then we should now be able to use the components. On any page, you should now be able to use either the tag helpers or razor syntax:
<kendo-numerictextbox name="currency" format="c" min="0"
enable="true" max="100" value="30">
</kendo-numerictextbox>@(Html.Kendo().NumericTextBox()
.Name("currency")
.Format("c")
.Min(0) // Set the min value of the NumericTextBox.
.Max(100) // Set the min value of the NumericTextBox.
.Value(30) // Set the value of the NumericTextBox.
)