How to fix the arabic display problem in matplotlib
hashirabdulbasheer opened this issue · 5 comments
Here is how I fixed the arabic display problem in matplotlib. I thought I would mention it here, incase it helps someone. Please let me know if there is a better way to do this.
The problem:
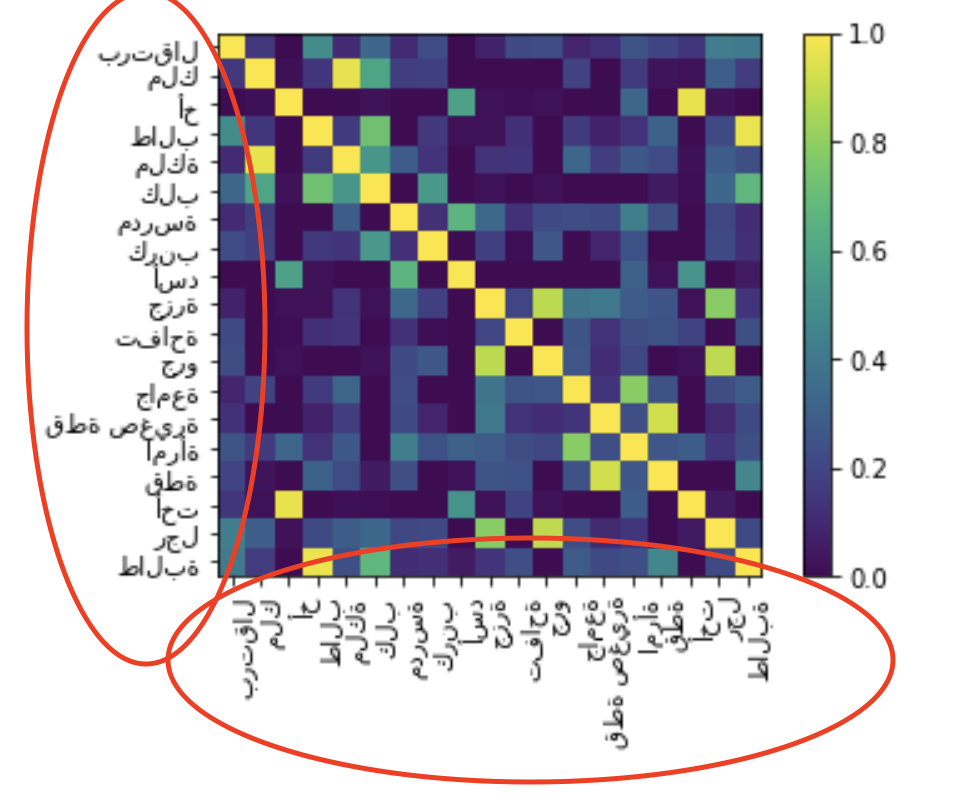
Arabic is not displayed properly in matplotlib, by default. The letters are not joined and are displayed from left to right instead of right to left.
Here is a sample code to reproduce the issue.
from whatlies.language import CountVectorLanguage
from whatlies.transformers import Umap
words = {
"man":"رجل",
"woman":"امرأة",
"king":"ملك",
"queen":"ملكة",
"brother":"أخ",
"sister":"أخت",
"cat":"قطة",
"dog":"كلب",
"lion":"أسد",
"puppy":"جرو",
"male student":"طالب",
"female student":"طالبة",
"university":"جامعة",
"school":"مدرسة",
"kitten":" قطة صغيرة",
"apple" : "تفاحة",
"orange" : "برتقال",
"cabbage" : "كرنب",
"carrot" : "جزرة"
}
lang_cv = CountVectorLanguage(10)
lang_cv[list(set(words.values()))].plot_similarity()
Here is the output.
The Solution:
The solution is to use two python packages to preprocess the arabic strings before providing them to matplotlib. The packages are:
- arabic_reshaper
- bidi.algorithm
Here is the code:
from whatlies.language import CountVectorLanguage
from whatlies.transformers import Umap
import arabic_reshaper
from bidi.algorithm import get_display
words = {
"man":"رجل",
"woman":"امرأة",
"king":"ملك",
"queen":"ملكة",
"brother":"أخ",
"sister":"أخت",
"cat":"قطة",
"dog":"كلب",
"lion":"أسد",
"puppy":"جرو",
"male student":"طالب",
"female student":"طالبة",
"university":"جامعة",
"school":"مدرسة",
"kitten":" قطة صغيرة",
"apple" : "تفاحة",
"orange" : "برتقال",
"cabbage" : "كرنب",
"carrot" : "جزرة"
}
lang_cv = CountVectorLanguage(10)
def handle_arabic(input_string):
reshaped_text = arabic_reshaper.reshape(input_string)
return get_display(reshaped_text)
words = [handle_arabic(word) for word in words.values()]
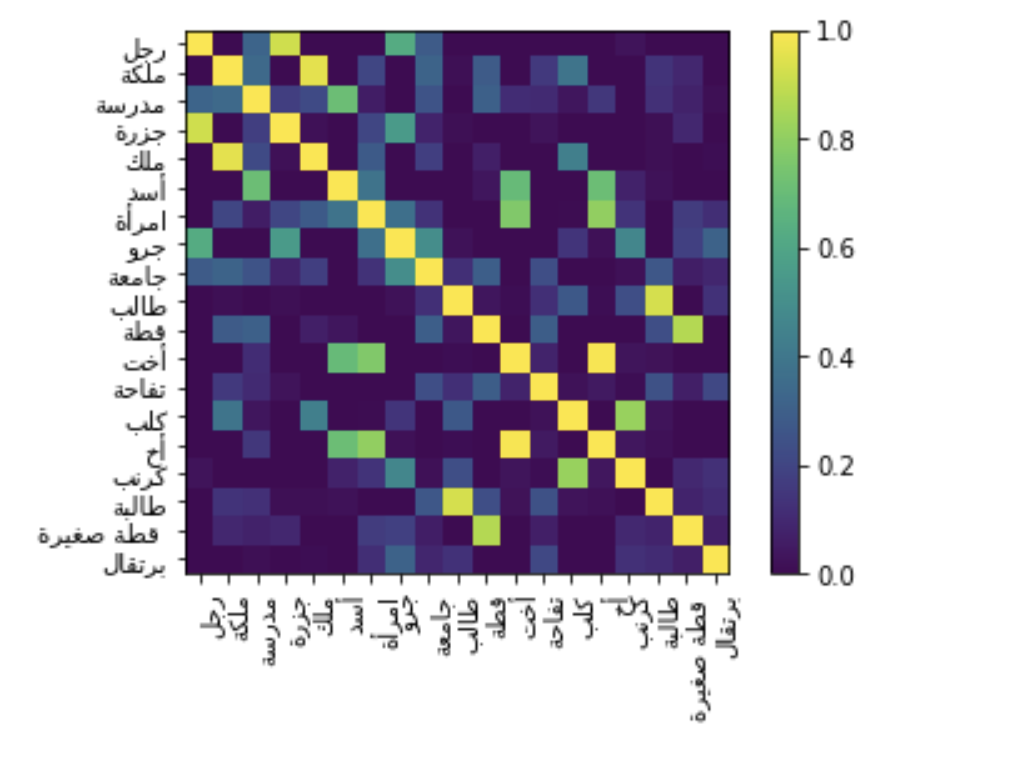
lang_cv[words].plot_similarity()
Here is the output now
As you can see, the arabic is now fixed. The letters appear joined and are displayed from right to left.
Hope that helps.
Thanks for mentioning it explicitly. The tricky thing I wonder about is how to best support this.
Adding a flag to all the matplotlib methods feels a bit "much" so instead it might be more helpful to add a helper function. Something like;
# functions in util.py
def handle_arabic(input_string):
reshaped_text = arabic_reshaper.reshape(input_string)
return get_display(reshaped_text)
def sort_arabic(embset):
return [Embedding(name=handle_arabic(e), vetor=e.vector) for e in embset
# importing and using said functions
from whatlies.util import sort_arabic
embset.pipe(sort_arabic).plot_distance()Your code is doing something slightly different though. I'm assuming that the issue is in matplotlib, not in python. That means that you don't need to resort the strings when you're fetching the embeddings. Rather you'd need to sort just before plotting. Is my assumption correct?
you are right, sorting was not required. It must have got in when I copy pasted the code.
this should work.
lang_cv[words].plot_similarity()
Ideally, the charts should have been flipped too, for RTL. The letters should come on the right side because we start reading from the right, and the color legend on the left. But there is no option to set matplotlib for RTL so that it gets flipped.
I might be able to work on a fix this week. I think sorting just before plotting makes sense.
The example is now live and on the docs. I've decided to start with a simple string reversion helper. That way this project doesn't gain dependencies.