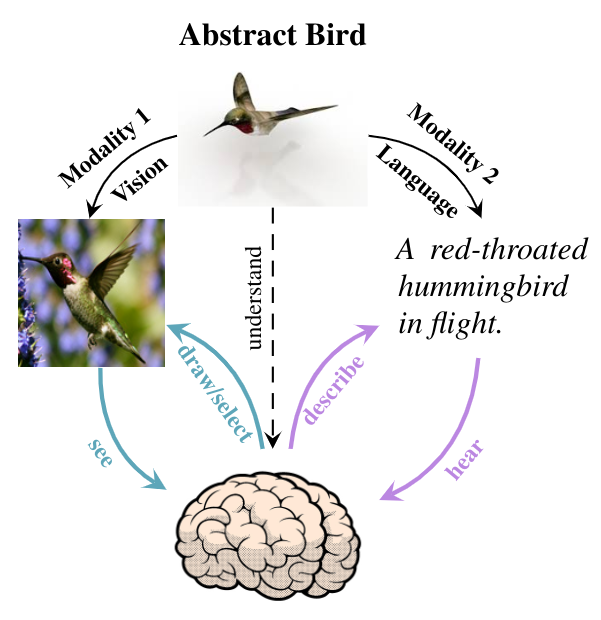
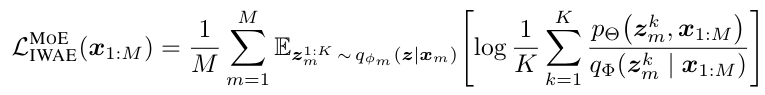This repository contains the code for the framework in Variational Mixture-of-Experts Autoencodersfor Multi-Modal Deep Generative Models (see paper).
List of packages we used and the version we tested the model on (see also requirements.txt)
python == 3.6.8
gensim == 3.8.1
matplotlib == 3.1.1
nltk == 3.4.5
numpy == 1.16.4
pandas == 0.25.3
scipy == 1.3.2
seaborn == 0.9.0
scikit-image == 0.15.0
torch == 1.3.1
torchnet == 0.0.4
torchvision == 0.4.2
umap-learn == 0.1.1
We construct a dataset of pairs of MNIST and SVHN such that each pair depicts the same digit class. Each instance of a digit class in either dataset is randomly paired with 20 instances of the same digit class from the other dataset.
Usage: To prepare this dataset, run bin/make-mnist-svhn-idx.py -- this should automatically handle the download and pairing.
We use Caltech-UCSD Birds (CUB) dataset, with the bird images and their captions serving as two modalities.
Usage: We offer a cleaned-up version of the CUB dataset. Download the dataset here. First, create a data folder under the project directory; then unzip thedownloaded content into data. After finishing these steps, the structure of the data/cub folder should look like:
data/cub
│───text_testclasses.txt
│───text_trainvalclasses.txt
│───train
│ │───002.Laysan_Albatross
│ │ └───...jpg
│ │───003.Sooty_Albatross
│ │ └───...jpg
│ │───...
│ └───200.Common_Yellowthroat
│ └───...jpg
└───test
│───001.Black_footed_Albatross
│ └───...jpg
│───004.Groove_billed_Ani
│ └───...jpg
│───...
└───197.Marsh_Wren
└───...jpg
Pretrained models are also available if you want to play around with it. Download from the following links:
Make sure the requirements are satisfied in your environment, and relevant datasets are downloaded. cd into src, and, for MNIST-SVHN experiments, run
python main.py --model mnist_svhn
For CUB Image-Caption with image feature search (See Figure 7 in our paper), run
python main.py --model cubISft
For CUB Image-Caption with raw image generation, run
python main.py --model cubIS
You can also play with the hyperparameters using arguments. Some of the more interesting ones are listed as follows:
--obj: Objective functions, offers 3 choices including importance-sampled ELBO (elbo), IWAE (iwae) and DReG (dreg, used in paper). Including the--looserflag when using IWAE or DReG removes unbalanced weighting of modalities, which we find to perform better empirically;--K: Number of particles, controls the number of particlesKin IWAE/DReG estimator, as specified in following equation:
--learn-prior: Prior variance learning, controls whether to enable prior variance learning. Results in our paper are produced with this enabled. Excluding this argument in the command will disable this option;--llik_scaling: Likelihood scaling, specifies the likelihood scaling of one of the two modalities, so that the likelihoods of two modalities contribute similarly to the lower bound. The default values are:- MNIST-SVHN: MNIST scaling factor 32323/28281 = 3.92
- CUB Image-Cpation: Image scaling factor 32/64643 = 0.0026
--latent-dimension: Latent dimension
You can also load from pre-trained models by specifying the path to the model folder, for example python --model mnist_svhn --pre-trained path/to/model/folder/. See following for the flag we used for these pretrained models:
- MNIST-SVHN:
K=50, batch_size=256, cuda=True, epochs=50, experiment='mnist_svhn', latent_dim=20, learn_prior=True, llik_scaling=1, logp=False, looser=True, model='mnist_svhn', no_analytics=False, no_cuda=False, num_hidden_layers=1, obj='dreg', pre_trained=None, print_freq=0, projection='' - CUB Image-Caption (feature):
K=50, batch_size=64, cuda=True, epochs=50, experiment='cubISft', latent_dim=64, learn_prior=True, llik_scaling=0.002, logp=False, looser=True, lr=0.0001, model='cubISft', no_analytics=True, no_cuda=False, num_hidden_layers=1, obj='dreg', std=0.0001 - CUB Image-Caption (raw images):
K=50, batch_size=64, cuda=True, epochs=200, experiment='cubIS', latent_dim=128, learn_prior=True, llik_scaling=0.0, logp=False, looser=True, lr=0.0001, model='cubIS', no_analytics=True, no_cuda=False, num_hidden_layers=1, obj='dreg', std=0.001
We offer tools to reproduce the quantitative results in our paper in src/report. To run any of the provided script, cd into src, and
- for likelihood estimation of data using trained model, run
python calculate_likelihoods.py --save-dir path/to/trained/model/folder/ --iwae-samples 1000; - for coherence analysis and latent digit classification accuracy on MNIST-SVHN dataset, run
python analyse_ms.py --save-dir path/to/trained/model/folder/; - for coherence analysis on CUB image-caption dataset, run
python analyse_cub.py --save-dir path/to/trained/model/folder/.
If you have any question, feel free to create an issue or email Yuge Shi at yshi@robots.ox.ac.uk.