I plan to fill this section with what I discovered today - - - AFAP (As Frequently as possible)! These notes are best viewed with MathJax extension in chrome.
"Science isn't good or bad, it's just true." - Hank Green
"One day I will find the right words, and they will be simple." - Jack Kerouac
"Duplication is far cheaper than the wrong Abstraction" - Sandi Metz
"Obstacle is the way" - Marcus Aurelius
"We must run as fast as we can, just to stay in place." - Lewis Carrol
Apr 8, 2024
- Grant Sanderson from 3Blue1Brown dropped visual tutorials about GPT and attention in transformers.
Mar 31, 2024
- convnet-benchmarks Easy benchmarking of all public open-source implementations of convnets. A summary is provided in the section below.
- Soumith Chintala's interview with latent space take away: NVIDIA's moat is their GPU interconnect NVlink. (Google's GPU interconnect is great too but not for sale only for rent)
Mar 27, 2024
- GPU Puzzles by Sasha Rush. (He also has a Pytorch tensor puzzles course that I might skim later)
- The exercises use NUMBA which directly maps Python code to CUDA kernels
- The global index uniquely identifies a thread across the entire grid of blocks being launched by a CUDA kernel. If you have multiple blocks, each block contributes threads, and the global index helps you locate a specific thread within the entire grid
global_index = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x - Within a block, the
threadIdx.xis the local index. - Shared memory is only accessible by threads within the same block.
shared = cuda.shared.array(block_size, numba.float32). - Shared memory operations are often coupled with thread synchronization to ensure that all threads in a block have reached a certain point in the code
cuda.syncthreads(). This is usually enough for within-block-synchronization. - For inter-block synchronization, you can use techniques like:
- Atomic add:
cuda.atomic.add(out, 0, temp_sum) - Multi step reduction. Compute partial sums and put them in an array and then compute a global sum in a separate CUDA kernel.
- Atomic add:
- Organisation of threads in a block (1d vs 2d vs 3d) is just for ease of programming. You will always be limited by max-threads-per-block which is a GPU hardware limitation. (Example nvidia 3090 limitation = max 1024 threads per block - which is logically the same as 32 x 32 threads in a 2d thread arrangement)
Mar 13, 2024
- NVIDIA GTC talks.
- Transforming AI - Attention is all you need collected for this talk.
- Maybe gradient descent is not the way?
- Too much wasted compute at the moment.
- Try to learn everything instead of handcrafting it. (Andrej energy of trying to train the tokenization process).
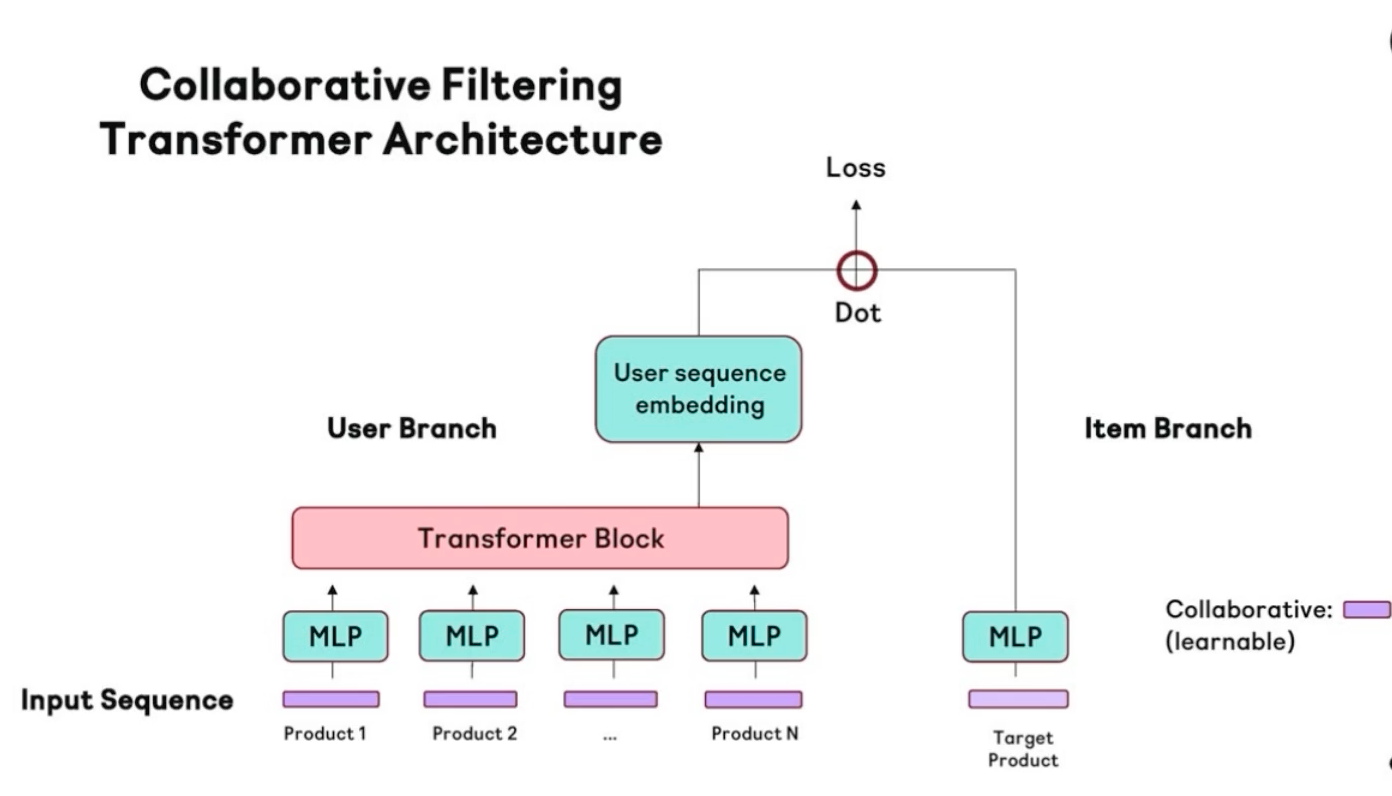
- NVIDIA Merlin library called transformers4rec for building recommendation models.
- Uses Huggingface transformers
- Input data is typically a sequence of interactions such as items that are browsed in a web session or items put in a cart
- A special use case of sequential-recommendation is the session-based recommendation
- Link to paper
-
CUDA tips:
- Try to make use of the L2 cache (memory is good but much much slower)
- Try to pack items in bundles that knapsack well in GPUs.
- Ugly code will usually lead to performance gains.
-
GPU kernel programming in the next post.
Feb 23, 2024
- Recommendation systems:
- Collaborative filtering
- Two tower embeddings
- Siamese networks
- Graph networks
- Train embeddings based on an objective function. If you find a generic enough feedback signal, you could reuse the embeddings for other use cases too (potentially with more linear layers for task specific use cases).
- Karpathy dropped a new Tokenization Video
- Nice LLM course repo
Feb 12, 2024
- Multimodal huggingface process. Nice podcast
- You don't need to train the entire models from scratch like Visual question answering, language mode, and merge them using adapters.
- Only the adapter weights are trained. Adapters can be linear layers or even attention.
- Perplexity score is a way to check the dataset quality for multimodal dataset.
- Most time as always is spent data engineering.
Jan 21, 2024
- Designing ML systems quick summary:
- Sampling data:
- Probability
- Simple random
- Weighted sampling
- Reservoir sampling - (Sampling a random number from a stream of numbers with a fixed probability)
- Getting labels:
- Weak supervision
- Simulation
- Transfer learning
- Active learning - Use ab-test metrics to generate samples
- Class imbalance: (asymetric cost error)
- Right evaluation - (overall accuracy not enough - look at precision/recall/f1-scores)
- Data resampling - (oversample minority/undersample majority)
- Focal loss
- Feature engineer:
- Keep track of data lineage
- Use features that generalise well
- Keep data partitioned
- Golden datasets
- Understand feature importance to the model
- Ensemble:
- bagging - aggregate using majority voting
- boosting - weak learners
- stacking - meta learner model looks at outputs from other models to output.
- Keeping up:
- Stateless retraining
- Stateful training (incremental only using new data)
- Multi armed bandit: (Strike a balance between exploration and exploitation)
- Thompson sampling - Popular in recommendation systems. (Keep sampling from all distributions as the distributions keep getting updated as new results flow in).
- Use this instead of plain AB testing to dynamically scale traffic to the best models.
Sep 19, 2023
-
Building server processes has these common steps:
- Spawn a separate process.
- Run an infinite loop in the process.
- Maintain the process state.
- React to messages.
- Send a response back to the caller.
-
gen_servergeneric server processes (very close to the actor model)use GenServerin your module.init/1accepts one argument. This is the second argument provided toGenServer.start/2, and you can use it to pass data to the server process while starting it.- The result of
init/1must be in the format{:ok, initial_state}. Alternatively, you can return{:stop, some_reason}if for some reason you decide the server process shouldn’t be started. - ASYNC:
handle_cast/2accepts the request and the state and should return the result in the format{:noreply, new_state}. - SYNC:
handle_call/3takes the request, the caller information, and the state. It should return the result in the format{:reply, response, new_state}. :timer.send_interval(5000, :cleanup)inside init will callhandle_info/2every 5 seconds.- Returning
{:stop, reason, new_state}fromhandle_*callbacks causes gen_server to stop the server process.
-
Exceptions/Supervisor:
- There are three types of runtime errors: throws, errors, and exits.
- When a runtime error occurs, execution moves up the stack to the corresponding try block. If an error isn’t handled, a process will crash.
- Process termination can be detected in another process. To do this, you can use links or monitors.
- Links are bidirectional—a crash of either process is propagated to the other process
- By default, when a process terminates abnormally, all processes linked to it terminate as well. By trapping exits, you can react to the crash of a linked process and do something about it.
- Supervisors can be used to start, supervise, and restart crashed processes.
Aug 26, 2023
- Elixir official guide
- Beautiful highlevel scripting language. Runs on the Erlang virtual machine (aka Beam).
- Different Concurrency model: Split your program into processes (when you don't want one process slowness to affect other processes). Each process has a mailbox. You can spawn millions of processes within your program. Each process has a pid and can be killed.
- Quickstart:
- Interactive shell
$ iex - Run programs
$ elixir yourfile.exs(exs means elixir script)$ elixir --no-halt yourfile.exswill not exit after starting concurrent tasks.
IO.puts("Hello world")
- Interactive shell
- Start with Mix:
mix new my_projectmix compilecompiles and puts all beam files inebinmix runmix run --no-haltiex -S mix run
- Types:
iex> 1 # integer
iex> 0x1F # integer
iex> 1.0 # float
iex> true # boolean
iex> :atom # atom / symbol / constant
iex> "elixir" # string
iex> [1, 2, 3] # list
iex> {1, 2, 3} # tuple
- Types:
is_number()/ is_integer/ is_float/ is_boolean/ is_atom- Use div(a,b) and rem(a,b) to get divisor/remainder. Operator
/always returns float. roundandtruncto round a float or to floor it.String.length("hellö")for string length.is_function(..)Anonymous functionsadd = fn a, b -> a + b endneed to be invoked with a.like this:add.(1, 2)- List:
[1, 2, true, 3]length lreturns length of list++to extend a list--to remove itemshd(l), tl(l)returns head and tail (rest of the list).[0 | list]Prepend item to list- Lists are stored in memory as linked lists, meaning that each element in a list holds its value and points to the following element until the end of the list is reached.
- Tuples:
{:ok, "hello"}tuple_size treturns size of tupleput_elem(tuple, 1, "blah")returns a new tuple with item "blah" inserted at index 1- Access item at index
elem(tuple, 1) - Tuples, on the other hand, are stored contiguously in memory. This means getting the tuple size or accessing an element by index is fast. However, updating or adding elements to tuples is expensive because it requires creating a new tuple in memory
- Operators:
"foo" <> "bar"string concat like thisand/or/notwith booleans onlyfalse or is_atom(:example)||, && and !for other types (everything butfalseandnilwill evaluate to true)1 == 1.0true but1 === 1.0false
- PatternMatching:
=is the match operator- A variable can only be assigned on the left side of
= x=1; 2=xwill raise MatchError. You can also use the pin operator^for this use case:x = 1; ^x = 2will give a MatchError too.{a, b, c} = {:hello, "world", 42}[head | tail] = [1, 2, 3]Just like thehd/tlfunctions
- A variable can only be assigned on the left side of
- Conditionals:
case :ok do
:error -> "Won't match"
_ -> "catchall"
end
cond do
2 + 2 == 5 -> "This is never true"
2 * 2 == 3 -> "Nor this"
true -> "This is always true (equivalent to else)"
end
# To change the value of x in an if clause
x = if true do
x + 1
else
x
end
- Bitstrings, Binary:
- A bitstring
denoted by <<>>is a contiguous sequence of bits in memory<<42>> == <<42::8>>by default 8 bits are used to stored any number in this. - If bits are divisible by 8, it is a binary
is_binary - A string is a UTF-8 encoded binary. Given that strings are binaries, we can also pattern match on strings:
<<head::utf8, rest::binary>> = "banana"head isb - Charlists are denoted by
~cthe list is only printed in single-quotes if all code points are within the ASCII range. - "Got hello from #{inspect some_variable}" to convert var to str representation.
- A bitstring
- Keywordlists and Maps:
- As the name implies, keyword lists are simply lists. In particular, they are lists consisting of 2-item tuples where the first element (the key) is an atom and the second element can be any value.
[{:trim, true}] == [trim: true]. keyword lists are used in Elixir mainly for passing optional values. If you need to store many items or guarantee one-key associates with at maximum one-value, you should use maps instead. map = %{:a => 1, 2 => :b}Trying to access not-present key givesnil.Map.get(xx), Map.put(), Map.removeetc.put_inandupdate_infunctions can be used to update map entries.- When working with known data, use map with fixed keys:
%{name: "John", age: 23}where all keys are atoms, it can be denoted just like keyword lists.
- As the name implies, keyword lists are simply lists. In particular, they are lists consisting of 2-item tuples where the first element (the key) is an atom and the second element can be any value.
- Modules and Functions:
- Modules are usually put in separate files with extension
.ex defmodule Math do ... endModule name is capitalised. Inside a module, functions can be defined likedef sum(a,b) do ... endor withdefp(for private methods).elixirc math.exto generate bytecode for the module soiexcan pick it up..exfiles are compiled and.exsfiles are used for scripting.- Question mark at the end of function name means it returns a boolean.
- Capturing
&can let you assign named function to a variable for passing around as arguments. Assume function isMath.zero?(0),fun = &Math.zero?/1then fun can be invoked like an anonymous functionfun.(0)- You can also capture operators:
add = &+/2,add.(1,2) fn x -> x + 1anonymous function is the same as&(&1 + 1)
- You can also capture operators:
- Modules are usually put in separate files with extension
defmodule Concat do
# A function head declaring defaults
def join(a, b \\ nil, sep \\ " ")
def join(a, b, _sep) when is_nil(b) do
a
end
def join(a, b, sep) do
a <> sep <> b
end
end
IO.puts Concat.join("Hello", "world") #=> Hello world
IO.puts Concat.join("Hello", "world", "_") #=> Hello_world
IO.puts Concat.join("Hello") #=> Hello
# Sample reduce impl:
defmodule Math do
def sum_list([head | tail], accumulator) do
sum_list(tail, head + accumulator)
end
def sum_list([], accumulator) do
accumulator
end
end
- Recursion:
- You usually use recursion to create loops in Elixir with different functions with clause matching for end-loop cases. (Sample reduce impl above)
- For list modifications however you use the utilities from Enum:
Enum.reduce([1, 2, 3], 0, fn(x, acc) -> x + acc end)Enum.map([1,2,3], fn(x) -> x*2)is the same using capture syntax:Enum.map([1,2,3], &(&1*2))
- Enumerables and Streams:
- Enumerables are eager and Streams are lazy and composable.
- The
|>symbol is the pipe operator: it takes the output from the expression on its left side and passes it as the first argument to the function call on its right side. 1..100_000 |> Enum.map(&(&1 * 3)) |> Enum.filter(odd?) |> Enum.sum()is the same as:Enum.sum(Enum.filter(Enum.map(1..100_000, &(&1 * 3)), odd?))pipe makes it readable.1..100_000 |> Stream.map(&(&1 * 3)) |> Stream.filter(odd?) |> Enum.sumlazy. Instead of generating intermediate lists, streams build a series of computations that are invoked only when we pass the underlying stream to the Enum module.Stream.unfold("hełło", &String.next_codepoint/1) |> Enum.take(stream, 3)
- Processes:
- In Elixir, all code runs inside processes. Processes are isolated from each other, run concurrent to one another and communicate via message passing. Processes are not only the basis for concurrency in Elixir, but they also provide the means for building distributed and fault-tolerant programs.
pid = spawn(fn -> 1 + 2 end)Process.alive?(pid)current_pid = self()send(self(), {:hello, "world"})send is non blockingreceive do \n{:hello, msg} -> msg\n{:world, _msg} -> "won't match"\n endReceive is blocking. It is possible to set timeout to receive:after \n 1_000 -> "timed out".flush()for flushing and printing items of mailbox.- Links:
spawn(fn -> raise "oops" end)Will not just log the exception and continue, it brings the exception to the current process.
- Tasks:
- Tasks build on top of the spawn functions to provide better error reports and introspection
- Task provides convenience functions, like
Task.async/1andTask.await/1, and functionality to ease distribution.
- State:
defmodule KV do
def start_link do
Task.start_link(fn -> loop(%{}) end)
end
defp loop(map) do
receive do
{:get, key, caller} ->
send caller, Map.get(map, key)
loop(map)
{:put, key, value} ->
loop(Map.put(map, key, value))
end
end
end
- State:
- You can maintain state in elixir using a pattern like above. Spawn a new process that loops and you can interact with it using messages.
{:ok, pid} = KV.start_link(), then use it likesend(pid, {:get, :hello, self()}) - You can register a pid for a started process too:
Process.register(pid, :kv)then use:kvinstead of pid anywhere. - Or you can use an abstraction like Agent.
{:ok, pid} = Agent.start_link(fn -> %{} end)Agent.get(pid, fn map -> Map.get(map, :hello) end)
- You can maintain state in elixir using a pattern like above. Spawn a new process that loops and you can interact with it using messages.
- IO/Filesystem:
- If you don’t want to handle the error outcomes, prefer to use the functions ending with an exclamation mark.
IO.puts("hello world"),IO.gets("Yolo? y/n")- File writing
{:ok, file} = File.open("path/to/file/hello", [:write])IO.binwrite(file, "world")File.close(file)File.read!("path/to/file/hello")will raise error if file not found unlike the regularFile.read/1
- iodata and chardata are lists of binaries and integers. Those binaries and integers can be arbitrarily nested inside lists. Their goal is to give flexibility and performance when working with IO devices and files. The choice between iodata and chardata depends on the encoding of the IO device. If the file is opened without encoding, the file expects iodata, and the functions in the IO module starting with bin* must be used.
- Elixir uses processes for the underlying IO mechanisms.
- Require/Alias/Import/Use
- Alias: Has lexical scope
alias Math.List, as: Listis the same asalias Math.List- These aliases can be defined inside lexical scopes like modules/functions
- Require: Has lexical scope
- Elixir provides macros as a mechanism for meta-programming (writing code that generates code). Macros are expanded at compile time. Public functions in modules are globally available, but in order to use macros, you need to opt-in by requiring the module they are defined in.
Integer.is_odd(3)can't be used withoutrequire Integer
- Import: Has lexical scope
import List, only: [duplicate: 2]duplicate/2can now be used without using the Fully qualified name
- Alias: Has lexical scope
Apr 10, 2023
- Transformer Reinfocement Learning library: https://github.com/lvwerra/trl
- PEFT (parameter efficient fine tuning) of LLMs using adapter layers (keeping the base LLM layer weights frozen).
- Nice hands on guide that uses peft: https://huggingface.co/blog/stackllama
Mar 21, 2023
- chromedp is a nice project in
go. - Here are some nice examples for the same.
- CSS Selectors can be used to find elements.
Jan 27, 2023
- Discord uses elixir to scale up. So few engineers, so much scale.
- Moved all rusty progress here.
Jan 17, 2023
- GoChannels equivalent: Thread safe Queue
- Java ThreadPool equivalent: Concurrent futures library
- We should be able to solve all multiprocessing needs using these without locks.
- Locks anyway:
l = threading.Lock()
l.acquire()
# do stuff
l.release()
Dec 22, 2022
- Auth can-i equivalent example:
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"os"
authv1 "k8s.io/api/authorization/v1"
metav1 "k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/apis/meta/v1"
"k8s.io/client-go/kubernetes"
_ "k8s.io/client-go/plugin/pkg/client/auth/gcp"
"k8s.io/client-go/rest"
"k8s.io/client-go/tools/clientcmd"
)
func main() {
kubeconfig := fmt.Sprintf("%s/.kube/config", os.Getenv("HOME"))
config, err := clientcmd.BuildConfigFromFlags("", kubeconfig)
if err != nil {
panic(err.Error())
}
ns := "dummy-namespace"
config.Impersonate = rest.ImpersonationConfig{
UserName: "system:serviceaccount:" + ns + ":default",
}
clientset, err := kubernetes.NewForConfig(config)
if err != nil {
panic(err.Error())
}
action := authv1.ResourceAttributes{
Namespace: ns,
Verb: "get",
Resource: "configmaps",
}
selfCheck := authv1.SelfSubjectAccessReview{
Spec: authv1.SelfSubjectAccessReviewSpec{
ResourceAttributes: &action,
},
}
resp, err := clientset.AuthorizationV1().
SelfSubjectAccessReviews().
Create(context.TODO(), &selfCheck, metav1.CreateOptions{})
if err != nil {
panic(err.Error())
}
if resp.Status.Allowed {
fmt.Println("allowed")
} else {
fmt.Println("denied")
}
}
Sep 09, 2022
-
Cargo package manager + build system
cargo new <newproject>cargo buildcreates executable intarget/cargo checkchecks compilation errors without producing executablescargo runfrom within a cargo repo, runs the executable
-
Variables
- Immutable by default.
let a: u32 = 5; - Redeclaration of same var names is allowed.
let a = "override previous value"; - Make Mutable.
let mut a = 5;and nowa = 6;is allowed. - Constants:
const THREE_HOURS_IN_SECONDS: u32 = 60 * 60 * 3;
- Immutable by default.
-
Data types
- Int
i8, ...i128,u8...u128- Decimal
98_222 - Hex
0xff - Octal
0o77 - Binary
0b1111_0000 - Byte (u8 only)
b'A'
- Decimal
- Float
f323.0 - Boolean
booltrue/false - Character
char'😻' - Compound types
- tuple
let tup: (i32, f64, u8) = (500, 6.4, 1);- Access elements like this
tup.0,tup.1 - Explode into variables like:
let (x, y, z) = tup;
- Access elements like this
- array
let a = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];- Access elements like
a[0].
- Access elements like
- tuple
- Int
-
Valid program that panics when index is out of bounds
use std::io;
fn main() {
let a = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
println!("Please enter an array index.");
let mut index = String::new();
io::stdin()
.read_line(&mut index)
.expect("Failed to read line");
let index: usize = index
.trim()
.parse()
.expect("Index entered was not a number");
let element = a[index];
println!("The value of the element at index {index} is: {element}");
}
- Functions
- Most assignments are statements (that do not return a value)
- Calling a function is an expression. Calling a macro is an expression. A new scope block created with curly brackets is an expression.
// Sample expression
{
let x = 3;
x + 1
}
fn five() -> i32 {
5
}
-
Control flow
let number = if condition { 5 } else { 6 };
-
Loops
let mut counter = 0;
// loop can also return a value
let result = loop {
counter += 1;
if counter == 10 {
break counter * 2;
}
};
// while loops
let mut number = 3;
while number != 0 {
println!("{number}!");
number -= 1;
}
- Loop over compound types:
let a = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50];
for element in a {
println!("the value is: {element}");
}
for number in (1..4).rev() {
println!("{number}!");
}
- Rules:
- Each value in Rust has an owner.
- There can only be one owner at a time.
- When the owner goes out of scope, the value will be dropped. (when a variable goes out of scope, Rust automatically calls the
dropfunction and cleans up the heap memory for that variable)
- All data stored on the stack must have a known, fixed size.
- Data with an unknown size at compile time or a size that might change must be stored on the heap instead.
let s1 = String::from("hello");
let s2 = s1;
- String is made up of three parts, shown on the left: a pointer to the memory that holds the contents of the string, a length, and a capacity. This group of data is stored on the stack. On the right is the memory on the heap that holds the contents.
move: To ensure memory safety, after the line let s2 = s1, Rust considers s1 as no longer valid.- stack-only-data is
copied. If a type implements the Copy trait, variables that use it do not move, but rather are trivially copied, making them still valid after assignment to another variable. - Rust won’t let us annotate a type with Copy if the type, or any of its parts, has implemented the
Droptrait.
- Rust has a feature for using a value without transferring ownership, called references.
- The Rules of References:
- At any given time, you can have either one mutable reference or any number of immutable references.
- References must always be valid.
- Functions cannot return references of new variables (because the reference variable will go out of scope when the function ends).
fn main() {
let mut s = String::from("hello");
let r1 = &s; // no problem
let r2 = &s; // no problem
println!("{} and {}", r1, r2);
// variables r1 and r2 will not be used after this point (NLL-Non Lexical Lifetime)
let r3 = &mut s; // no problem
change(r3);
}
fn change(some_string: &mut String) {
some_string.push_str(", world");
}
- Slices let you reference a contiguous sequence of elements in a collection rather than the whole collection. A slice is a kind of reference, so it does not have ownership.
- A string slice (
&str) is a reference to part of a String. (Immutable reference)
let s = String::from("hello");
let len = s.len();
let slice = &s[0..2];
let slice = &s[..2]; // same
let slice = &s[3..len];
let slice = &s[3..]; // same
let slice = &s[0..len];
let slice = &s[..]; // same
- Slices work on other types too:
let a = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];,let slice = &a[1..3];This slice has the type&[i32] - The concepts of ownership, borrowing, and slices ensure memory safety in Rust programs at compile time.
Hello GraphQL - Link
- Fields - straight forward. Query the nested fields you want only.
{
hero {
name
# Queries can have comments!
friends {
name
}
}
}
- Arguments - Nested fields can have arguments too (that act like filters). Scalars can also have arguments (to perform trasnformations on the server side).
{
human(id: "1000") {
name
height(unit: FOOT)
}
}
- Aliases - You can't directly query for the same field with different arguments. That's why you need aliases.
{
empireHero: hero(episode: EMPIRE) {
name
}
jediHero: hero(episode: JEDI) {
name
}
}
- Fragments - GraphQL includes reusable units called fragments. (A fragment cannot refer to itself or create a cycle)
{
leftComparison: hero(episode: EMPIRE) {
...comparisonFields
}
rightComparison: hero(episode: JEDI) {
...comparisonFields
}
}
fragment comparisonFields on Character {
name
appearsIn
friends {
name
}
}
- Specifying operation-type and operation-name is optional if the operation is a query. Valid operation-types:
query, mutation, or subscription
query HeroNameAndFriends {
hero {
name
friends {
name
}
}
}
- Variables - pass dynamic arguments directly in the query string. Another dictionary of values is also expected with the query. All declared variables must be either scalars, enums, or input object types. Default values can also be assigned to the variables in the query by adding the default value after the type declaration
query HeroNameAndFriends($episode: Episode = "DefaultValue") {
hero(episode: $episode) {
name
friends {
name
}
}
}
# variables
{
"episode": "JEDI"
}
- Directives - More control to create dynamic queries: default ones
@include(if: Boolean),@skip(if: Boolean). It is possible to create custom directives.
query Hero($episode: Episode, $withFriends: Boolean!) {
hero(episode: $episode) {
name
friends @include(if: $withFriends) {
name
}
}
}
# variables
{
"episode": "EMPIRE",
"withFriends": true
}
- Inline Fragments - If you are querying a field that returns an interface or a union type, you will need to use inline fragments to access data on the underlying concrete type.
query HeroForEpisode($ep: Episode! = "JEDI") {
hero(episode: $ep) {
name
... on Droid {
primaryFunction
}
... on Human {
height
}
}
}
- Meta fields - GraphQL allows you to request __typename, a meta field, at any point in a query to get the name of the object type at that point.
searchin the example below returns a union type.
{
search(text: "an") {
__typename
... on Human {
name
}
... on Droid {
name
}
... on Starship {
name
}
}
}
- query fields are executed in parallel, mutation fields run in series, one after the other.
- Mutations can return an object type which can be useful for fetching the new state of an object after an update
mutation CreateReviewForEpisode($ep: Episode!, $review: ReviewInput!) {
createReview(episode: $ep, review: $review) {
stars
commentary
}
}
# variables
{
"ep": "JEDI",
"review": {
"stars": 5,
"commentary": "This is a great movie!"
}
}
- Objects are defined with
typekeyword.
type Character {
name: String!
appearsIn: [Episode!]!
}
- Arguments. Each field in an object can have arguments. Arguments can have default values and are always named.
type Starship {
id: ID!
name: String!
length(unit: LengthUnit = METER): Float
}
- Special reserved types. Query and Mutation. This is the entrypoint for all graphql queries/mutations.
schema {
query: Query
mutation: Mutation
}
# You need this to expose types for querying
type Query {
hero(episode: Episode): Character
droid(id: ID!): Droid
}
- GraphQL default scalar types:
Int, Float, String, Boolean, ID. It is possible to specify custom scalar types. - Enums
enum Episode {
NEWHOPE
EMPIRE
JEDI
}
- Object types, scalars, and enums are the only kinds of types. Additional modifiers are list
[]and not-null!. - Interfaces abstract type that includes a certain set of fields that a type must include to implement the interface.
interface Character {
id: ID!
name: String!
friends: [Character]
appearsIn: [Episode]!
}
- UnionTypes Similar to interfaces but are not dependent on fields.
union SearchResult = Human | Droid | Starship
- Remember, to query object fields on unionTypes/Interfaces, use inlined fragments
query HeroForEpisode($ep: Episode! = "JEDI") {
hero(episode: $ep) {
name
... on Droid {
primaryFunction
}
}
}
- Input Types: Passing complex variables as arguments. Input types look exactly the same as regular object types, but with the keyword input instead of type. Schema:
input ReviewInput {
stars: Int!
commentary: String
}
Query:
mutation CreateReviewForEpisode($ep: Episode!, $review: ReviewInput!) {
createReview(episode: $ep, review: $review) {
stars
commentary
}
}
# variables
{
"ep": "JEDI",
"review": {
"stars": 5,
"commentary": "This is a great movie!"
}
}
- Input types can't be mixed with output types in your schemas. Also, you can't have arguments on the fields in input types.
__schemais always available at the root type of a Query
{
__schema {
types {
name
}
}
}
- Then you can dig into the schemas per field like so:
{
__type(name: "Droid") {
name
kind
}
}
March 28, 2022
- Scala benchmarking:
jmh:run -t 1 -f 1 -wi 1 -i 1 .*benchFuncRegex.*- -t = threads
- -f = jvm instances
- -wi = warmump iterations
- -i = iterations
- Results: lower score is better.
- Running tests:
sbt testOnly TestFunc - Mutable is always faster. See which steps lead to actual memory allocation.
- Try to make things lazy to avoid allocations.
- Try to use mutable data structures for faster execution times.
Oct 7, 2021
- Semigroups - Sets which have an associative binary operation. (doesn't matter where you put the parenthesis)
(a + b) + c == a + (b + c)
-
See
cats.Semigroup -
Commutativity -
(a + b) == (b + a)position doesn't matter -
Coursier is great for playing with dependencies etc. It is used by sbt for interacting with Artifactories.
- Mac:
~/Library/Caches/Coursier/v1 - Linux:
~/.cache/coursier/v1
- Mac:
-
Dependency Conflict resolution: Add the line:
addDependencyTreePlugintoproject/plugins.sbt- Then use the sbt command
dependencyList/dependencyTree/dependencyBrowseTree/evicted - add setting
conflictManager := ConflictManager.strictto NOT have conflicting dependencies silently evicted. - Another option is add setting
dependencyOverrides ++= Seq("group" % "artifact" % "yourversion") - Or exclude deps per dependency in the setting `libraryDependency ++= Seq("group" % "artifact-dep" % "yourversion" exclude("group", "artifact"))
- Then use the sbt command
Oct 7, 2021
- Scala school basics by twitter.
def timesTwo(i: Int): Int = {
println("hello world")
i * 2
}
- Any function can be partially applied by using
_
def adder(m: Int, n: Int) = m + n
val add2 = adder(2, _:Int)
add2(3)
- This
_magic wildcard syntax also works with curried functions.
def multiply(m: Int)(n: Int): Int = m * n
Sep 30, 2021
- Stateless apps = Simple Deployments (That use ReplicaSets)
- Single instance Stateful app:
- Deployment 1 replica
- PersistentVolume, PersistentVolumeClaim
- Service
- Replicated stateful app:
- StatefulSet
- PersistentVolume, PersistentVolumeClaim are a part of statefulset spec
- Names all the pods as
<statefulset-name>-<ordinal-number>eg.mysql-1 - Scaling up statefulsets creates new pvc but scaling down doesn't delete them automatically.
- Headless service
clusterIp: NoneMakes all pods available on the network individually<pod-name>.<headless-service-name>
- Service (Simple load balancer / clusterIp service)
- Usually a ConfigMap
- A pod disruption budget, so pods are not killed voluntarily (for maintenance, autoscaling etc.)
- StatefulSet
- Get all CRD and resources in your k8s cluster:
kubectl api-resources -o wide
Sep 24, 2021
- GoDoc tips link
- Each comment line should end with a
.otherwise it is considered aheading - Multi line comments over a package/function, only the first line is used for "overview".
- Only exported methods (that begin with a capital letter) are added to documentation.
- Comments that begin with one extra space, are considered code blocks.
- Examples can be added to the same package or in
yourpackage_test
// This is a package-level example:
func Example() {
fmt.Printf("Hi")
}
// Real is just another name for float64.
type Real float64
// Use Real like a general floating type:
func ExampleReal() {
var x Real = 1.23
}
// Multiple examples for a function
// Absolute value.
func Abs(x Real) Real {
}
func ExampleAbs_positive() {
Abs(1.23)
// Output: 1.23
}
func ExampleAbs_negative() {
Abs(-1.23)
// Output: 1.23
}
Sep 24, 2021
ScioContext.scalaSeparation of runner classes (reflection)ContextAndArgs- Cmd line or Luigi specifies args here. (Intercept dataflow args here and pass on the rest)PipelineOptions- Dataflow specificArgs- Scalding handles arg parsing
ScioExecutionContext- Can have runner specific things in the response- Counters are initialized to 0 in the
run()
PCollectionWrapper.scalawraps the basic functionality likeapplyScio coder case class sealed trait is not the same as Beam CoderSCollection.scala- syntactic sugar over beam transformsCoderMaterializer.beam- Takes a Scio coder and converts it to Beam Coder.map,flatMap,filterare justbeam doFns
Functions.scala- Wrapping scala functions to convert them into BeamDoFnsNamedProcessFnto get all stack traces etc.- Closure cleaner to send serialized functions. Scalding came up with it.
SideInput-PairSCollectionFunction- Artisan Join
- Sparse join
- Bloom Filter - When one side has too many inputs compared to the other side.
PairSkewedCollection- CountMinSketch - To get Hot keys.
CodersCoderMaterializer- Sending it to beam happens on SCollection apply- Everything else happens in Scio before that.
Sep 15, 2021
- Link to the blog post.
- The communication is a big part of
flink-runtime. (Not to be confused with job manager and task manager coordination which is handled by Akka RPCs) - These low level components are implemented using Netty.
- Network buffers: At this point in the stack, Flink is not dealing with individual records anymore but instead with a group of serialised records assembled together into network buffers. The number of buffers available to each subtask in its own local buffer pool (one per sending and receiving side each) is limited to at most
channels * buffers-per-channel + floating-buffers-per-gate - In Flink, there are three situations that make a buffer available for consumption by the Netty server:
- a buffer becomes full when writing a record to it, or
- the buffer timeout hits, or
- a special event such as a checkpoint barrier is sent.
- These network buffers can also be hand tuned as described here.
Aug 23, 2021
- Automating policy checks for kubernetes.
- Uses a specialized language to define policy check constraints: Rego
- Before you can define a constraint, you must first define a
ConstraintTemplate(<- This is a CRD), which describes both the Rego that enforces the constraint and the schema of the constraint.
Aug 5, 2021
- Transport layer security great video
- Shor's algorithm. Getting the prime factors of a big number is computationally demanding af. video
- Makes a bad guess and converts it into a better guess.
- This conversion takes loong on conventional compute, but surprisingly fast on quantum computers.
- So you need to guess the power p in this:
g^p = m.N + 1(N = big number, g = crappy initial guess) - 3/8 times you will end up with factors of N or m.N. Euclid's algorithm can be used to get the shared factors from there.
- This power also has a repeating property that the quantum computers can exploit by superposition and find a
pthat solves our equation.
- Grover's algorithm. Search space N tasks can be done in
sqrt(N)time using quantum. - Casper ffg - Vitalyk's consensus paper for proof of stake.
- ETH2 will use Proof of stake instead of Proof of Work that is used by Bitcoin and will need much less compute.
- ETH is all about smart contracts. Smart = code is embedded in the contract to distribute the tied up ethers (wealth) in the contract.
July 19, 2021
k8s
go mod initcreates a new module, initializing the go.mod file that describes it.go build, go test,and other package-building commands add new dependencies to go.mod as needed.go list -m allprints the current module’s dependencies.go list -m -versions <module>prints module's available versions.go getchanges the required version of a dependency (or adds a new dependency).go mod tidyremoves unused dependencies.
July 16, 2021
k8s
- Following this book
:
- Edit
api/v1/project_types.goto make changes in the API (CRD). make installgenerates kustomize template and applies it to your context.- Edit
controllers/project_controller.goto make changes to the Controller.make runto run the controller in a shell for development- Deploying the controller on cluster:
make docker-build docker-push IMG=<some-registry>/<project-name>:tagmake deploy IMG=<some-registry>/<project-name>:tag
- An API Group in Kubernetes is simply a collection of related functionality.
- Each API group-version contains one or more API types, which we call Kinds.
- A resource is simply a use of a Kind in the API.
July 11, 2021
k8s
- In Kubernetes, Admission Controllers enforce policies on objects during create, update, and delete operations. Admission control is fundamental to policy enforcement in Kubernetes.
For example, by deploying OPA as an admission controller you can:
- Require specific labels on all resources.
- Require container images come from the corporate image registry.
- Require all Pods specify resource requests and limits.
- Prevent conflicting Ingress objects from being created.
- Admission controllers can also mutate incoming objects.
By deploying OPA as a mutating admission controller you can: - Inject sidecar containers into Pods. - Set specific annotations on all resources. - Rewrite container images to point at the corporate image registry. - Include node and pod (anti-)affinity selectors on Deployments.
July 11, 2021
Scala
- Following a book by Paul Chiusana, Runar Bjarnason, Martin Odersky.
- Functional programming is a restriction on how we write programs, but not on what programs we can express.
- Pure functions are easier to test, reuse, parallelize, generalize, and reason about. Furthermore, pure functions are much less prone to bugs.
- An expression e is referentially transparent if, for all programs p, all occurrences of e in p can be replaced by the result of evaluating e without affecting the meaning of p.
- When expressions are referentially transparent, we can imagine that computation proceeds much like we’d solve an algebraic equation.
- Currying = convert function of two arguments to a function of one argument and applies f partially.
def curry[A,B,C](f: (A, B) => C): A => (B => C) = (a: A) => (b: B) => f(a,b)- It is often used for assisting with type inference.
- Uncurry = reverse of curry. Convert curried function to a function with multiple arguments.
def uncurry[A,B,C](f: A => B => C): (A, B) => C = (a: A, b: B) => f(a)(b)
- Compose = one function aftet the another. Very common use case. Scala Function1 has this available. (
compose,andThenare similar.f andThen g=g compose f)def compose[A,B,C](f: B => C, g: A => B): A => C = (a: A) => f(g(a))val f = (x: Double) => math.Pi/2-xval cos = f andThen math.sinNEAT
- Functional List:
sealed trait List[+A]
case object Nil extends List[Nothing]
case class Cons[+A](head: A, tail: List[A]) extends List[A]
- Functional Tree:
sealed trait Tree[+A]
case class Leaf[A](value: A) extends Tree[A]
case class Branch[A](left: Tree[A], right: Tree[A]) extends Tree[A]
July 2, 2021
IDE
- Link
- Open file
Cmd + P - Command Pallete
Cmd + Shift + P - Multicursors
Cmd + shift + Lfor taking cursor to all selections.option + click= multicursor arbitraryCmd + option + arrow-up/down= spawn new cursors
Cmd + \Split screen vertical onlyCmd + Bopen close folder view- File diff
code --diff <file1> <file2> - Copy selection up/down
shift option up/down. - Move line up/down
Cmd + option + up/down - Jump to line number
ctrl + g - Jump lines
option + up/down(Install extension line-jumper for this) - Find and replace
Cmd + option + R - Open extensions marketplace
Cmd + shift + x keybindings.jsonshould look like this
// Place your key bindings in this file to override the defaults
[
{
"key": "alt+cmd+up",
"command": "editor.action.moveLinesUpAction",
"when": "editorTextFocus && !editorReadonly"
},
{
"key": "alt+up",
"command": "-editor.action.moveLinesUpAction",
"when": "editorTextFocus && !editorReadonly"
},
{
"key": "alt+cmd+down",
"command": "editor.action.moveLinesDownAction",
"when": "editorTextFocus && !editorReadonly"
},
{
"key": "alt+down",
"command": "-editor.action.moveLinesDownAction",
"when": "editorTextFocus && !editorReadonly"
}
]July 2, 2021
Data
- Storage format initially built by Twitter and Cloudera.
- Informative video
- Hybrid storage format.
- Horizontal partitioning - For splitting up rows into groups called Row Groups. Also known as Blocks. Default size of such a file is 128MB. These files have footers which contain basic stats about the row group columns.
- Vertical partitioning - For splitting up column types so only necessary columns are queried, each block is stored as Column chunks.
- Each column chunk stores data in the form of Pages. Data Pages that also contains metadata along with encoded values.
- On disk it is not a file, it is a directory.
June 10, 2021
- Scala 3 has introduced
inlinevariables and methods. The change here is that wherever the function is called, that call is eliminated and its code is inlined at that point. It is done at compile time. (This could effectively avoid deep stack calls). - Scala has
macros
June 10, 2021
- DBeam is a Apache Beam based single threaded pipeline that reads all the data from single SQL database table, and converts the data into Avro and stores it into appointed location, usually in GCS.
- Monoids and Semigroups
- A monoid is a function that takes two arguments and follows two laws: associativity and identity.
- The general notion here is to separate behavior from the data. The algebraic structure provides the context for describing the desired behavior through operations applied to the data.
- The algebraic structure semigroup is a set and an associated binary operator that combines two elements from the set. A monoid is a semigroup with the added identity element.
trait Semigroup[A] {
def op(x: A, y: => A): A
}
trait Monoid[A] extends Semigroup[A] {
def zero: A
}
- Implicits Given/Using
- Implicit parameters: Your function can have parameters that are labelled with implicits.
- It takes an available default value from a predefined implicit value. (There can only be ONE predefined implicit value though).
def summer(x: Int)(implicit y: Int): Int = x * y
implicit val z: Int = 10
println(summer(5)) // Returns 50
- Another use case is to convert from one type to other which is discouraged in Scala3.
- You can use this syntax with a class as well instead of a def. All the functions in the class become implicit then.
- NOTE: implicit modifier cannot be used for top-level objects.
case class Person(name: String) {
def greet: String = s"Hey my name is $name"
}
implicit def stringToPerson(s: String): Person = Person(s)
println("Alice".greet) // Treats Alice like a person and prints the greeting
- Newer(Scala3) enforced implicit needs to be "explicit"
import scala.language.implicitConversions // This is needed
// And this makes it explicit that you want a conversion
given stringToPerson as Conversion[String, Person] {
def apply(s: String): Person = Person(s)
}
- Given and using can also be used with function parameters instead of implicits
given z as Int = 10
def summer(x: Int)(using y: Int): Int = x * y
println(summer(5)) // 50
println(summer(5)(using 11)) // 55 // This is how you override
- This implicit pattern is used as Pimp my library pattern to make the code more expressive.
- Implicitly is used with the type classes pattern. Suppose you have a bunch of model classes that you don't want to create copies of. You can make them extend a new trait that you created by using this pattern. Also, implicitly works as a “compiler for implicits”. We can verify if there is an implicit value of type T. If no implicit value of type T is available in the scope, the compiler will warn us of the fact.
June 9, 2021
Data
- Following this programming guide.
- Steps:
- Create a driver program using one of Beam SDKs.
- It defines all the steps in your DAG like sources, transforms, sinks etc.
- Set execution options including the Pipeline Runner (with CLI arguments etc.)
- Beam Abstractions:
- Pipeline: A Pipeline encapsulates your entire data processing task, from start to finish.
- PCollection: A PCollection represents a distributed data set that your Beam pipeline operates on. you can also create a PCollection from in-memory data within your driver program. PCollections are the inputs and outputs for each step in your pipeline.
- PTransform: A PTransform represents a data processing operation, or a step, in your pipeline. Every PTransform takes one or more PCollection objects as input, performs a processing function that you provide on the elements of that PCollection, and produces zero or more output PCollection objects.
- Pipeline Options can be implemented by implementing/extending the
PipelineOptionsinterface. - Once a pipeline object is created, the source PCollection is
apply-ed to the pipeline object. - Transforms are applied to PCollection objects. They provide a generic processing framework. You provide processing logic in the form of a function object. Core Beam transforms:
ParDois useful for a variety of common data processing operations like Map, FlatMap, Filter. You'll need to implement aDoFn.GroupByKeyis a Beam transform for processing collections of key/value pairs. It’s a parallel reduction operation, analogous to the Shuffle phase of a Map/Shuffle/Reduce-style algorithm.CoGroupByKeyperforms a relational join of two or more key/value PCollections that have the same key type.- NOTE: If you are using unbounded PCollections, you must use either non-global windowing or an aggregation trigger in order to perform a GroupByKey or CoGroupByKe because a bounded GroupByKey or CoGroupByKey must wait for all the data with a certain key to be collected, but with unbounded collections, the data is unlimited. Windowing and/or triggers allow grouping to operate on logical, finite bundles of data within the unbounded data streams.
Combine- Combine has variants that work on entire PCollections, and some that combine the values for each key in PCollections of key/value pairs.Flatten- merges multiple PCollection objects into a single logical PCollection.Side Inputs- A side input is an additional input that your DoFn can access each time it processes an element in the input PCollection. When you specify a side input, you create a view of some other data that can be read from within the ParDo transform’s DoFn while processing each element.Composite Transforms- Multiple transforms that are seen frequently bundled together.
- Windows
- Triggers
- Splittable DoFns
Apr 16, 2021
- RAID 0 : data split into multiple drives. (No redundancy, high throughput)
- RAID 1 : data duplicated. Half the storage space is wasted on this. Hot swaps not possible.
- RAID 5 : Data is stored with parity bits. Parity bits are used to reconstruct missing data in either of the drives. Great quick video. Zero downtime for maintenance.
Apr 13, 2021
- Find point that is minimum distance from all points on the grid combined. (Sum of distances is minimized).
- We can decide on a precision and move in the direction of descent (x = x + dx * multiplier) with reducing multiplier with each step. Just like gradient descent.
- Find top K for something.
- Another approximation technique for calculating top k items with very low memory footprint.
- 2D grid. Each row means a hash function. When you want to find occurences of a key, you can get minimum from all rows.
- You'll need an additional heap to maintain top k keys.
- Great link.
Apr 08, 2021
- Token bucket algorithm.
- Tokens refill after every x time.
- New requests need tokens to go through.
- In a distributed setting, maintain a separate bucket on each node and share information.
- Distributed key value store to store token information.
- Can also use a coordinator (master slave) to decide correct counts per machine.
- Can also use gossip protocol.
- Can also use mesh connection to share token information among nodes.
Apr 07, 2021
- Index on documents for efficient searching.
- Information Retrieval on steroids.
- Document -> tokens -> inverted index.
- Tokenizing = splitting by whitespace.
- Inverted index = frequency of words, document list.
- such an index created from 3 documents
- Indexed (merged)
- Then the group of 3 is merged to a bigger 9 index.
- Useful for time series. (Newer documents are in a faster index).
Mar 31, 2021
- Heapq has a function nlargest for the same.
- Another approach is an algorithm called quickselect. (Works just like quicksort).
- Select a pivot, fix its position.
- Move pivot element to right.
- Iterate over remaining elements from left to right moving any smaller elements to the left and incrmenting potential pivot index.
- Swap right with pivot index.
- Once the fixed position is the same as the nth largest index, return!
- Complexity worst case = O(Nlog(N)), Average case = O(N)
- Select a pivot, fix its position.
Mar 31, 2021
- Helm project has gained considerable popularity as it solves one of the key problems that enterprises face — creating custom YAMLs for deploying the same application workload with different settings, or deploying it in different environments (dev/test/prod).
- Operators use the kubernetes Custom resource and Controller pattern --> which uses a reconcilliation loop (You always strive to be in the target state). Its API is set towards running stateful application workloads natively on Kubernetes.
- Once deployed, new Custom Resources (e.g. Mysql, Cassandra, etc.) are available to the end users similar to built-in Resources (e.g. Pod, Service, etc.).
- As an Operator developer, it is tremendously useful for your users if you create Helm chart for its deployment. Soo, they go hand in hand and not vs.
Mar 29, 2021
- When you want to also use elements that were not a part of the permutation, there is a neat trick to get them: Thanks to Stefan Poochman:
for a,b,*rest in itertools.permutations(rem):
# rest contains the list of elements apart from a,b
- Brilliant!
- Python programs are inherently not multithreaded because of GIL.
- This is used because of the garbage collection that python uses:
- reference counting.
- Ease of developer work because of this lock.
- One possible solution for the same is using multiprocessing module.
- Or use a different python distribution. (Not Cython).
Mar 25, 2021
- Bots scrape website's pricing data to kick ass.
- Cause unnecessary load on the servers.
- Conversion calculations are unreliable with bots causing a percentage of the traffic.
- A company that does it:
PerimeterX
Mar 22, 2021
- Approximation algorithm like bloom filter.
- Just like bloom filters, have one integer which stores all bits.
- You need one hash function to generate numbers in this integer's range.
- Lets look at last x bits. If we have n 0s there, that means there are 2^n unique items.
- Get max 0s for each bucket. (Buckets are made from bits preceeding the x bits).
- Get the average max 0s from these buckets = avg.
- Total number of unique users is approx: 2^avg.
Mar 21, 2021
- There are 4 possible scenarios when the
abs(left_tree_height - right_tree_height) > 1. - Tree rotations come in handy when tree is left heavy or right heavy.
- BTree is used for databases. Amazing video.
- Multi level indexes. (Rotate it for a tree impression)
- Disc access needs to be optimized.
- Tree grows bottom up. Whenever one node has more than specified elements, it is split up and the middle value is sent up (to parent).
- Each node has a record and block pointer.
- In a B+ tree, only the leaf nodes have record indexes. The higher level nodes are sparse indexes (only block pointers).
- Red Black trees - Root and leaves are always black. If a node is red, the children will be black.
- Number of black nodes from the root to the nil nodes is the same across the tree.
- Longest path is no more than 2 times the shortest path (Path = root to nil).
- Insertions/Removals can cause rotations to maintain red black properties.
- Since the violations have to be resolved all the way up the tree, the complexity of these operations is log(n).
Mar 20, 2021
- Integration considerations.
- Scaling requirements (Storage and Requests/sec).
- Support considerations (Security concerns etc.).
- Keep it simple.
- Internal phone directory: MySQL.
- Internal analytics: If not a lot of people are consuming results constantly, no need for a NoSQL solution. Just a spark job on your hadoop cluster is enough.
- Movie Recommendations: High availability - Cassandra.
- The truth is, you can force Cassandra or MySQL to behave just how you'd like (CAP) with enough effort.
Mar 17, 2021
- 2 phase commit. - prepare - commit
- Use etcd locks.
- Or Zookeeper locks using one of the higher order recipes.
- Hypervisor makes virtualization feasible.
- Software that runs on physical server.
- Type1(Baremetal/KVM) / Type2(Hosted/Sit on top of hostOS)
- It is possible to move VMs from one Hypervisor to another in case of a host going down.
- Containers run on an OS (which in usual cloud scenarios, is a VM).
- Nice video about virtualization.
Mar 16, 2021
- Useful algorithm for finding cycles in a graph (given a list of edges).
- Also useful for finding number of disjoint subsets in the graph at any point in time.
- The data structure maintains one node as a representative of the disjoint subset.
- Initialize with a list which contains parents for all elements.
- Implements a
find_parent(x)function that returns the representative node of the current disjoint subset. - Also implements a
union(x,y)function that makesfind(x) the parent of find(y)
Mar 15, 2021
- Structured as a tree. Each node is called a
zNodeand has a path. - Each node can be
persistentorephemeraland can store data. - zNodes can't be renamed.
- zNodes can be
watchedfor changes. - Recover from partial failures with style.
- Widespread applications that need consistency like:
- Leader election.
- Coordination and Locks.
- Currently available workers.
- Use Apache Curator recipes for working implementations of common zookeeper use cases like
locks,barriers,distributed countersetc.
- Impossible to perform joins. No Joins.
- Query first approach.
- Query one table whenever reading. While writing, write to multiple.
- Rows with same partition key will be stored on the same node.
- Partition key (does not have to be unique) is not the same as Primary key. (Only partition key should be used for querying data in cassandra)
- PRIMARY KEY = PARTITION KEY + CLUSTERING KEY (which is used for order by)
- Each node gets some virtual nodes in Cassandra. (Tunable in case your hosts have varying capacities).
- Set a replication factor for the kind of consistency you need. (It should be less than or equal to the number of nodes).
- Consistency level can be set for reading/writing.
- Keyspaces = logical grouping. Table = Also logical grouping. Only rows with the same partition keys get stored on the same node.
- Some useful commands (for
cqlsh):CREATE KEYSPACE blah WITH replication = {'class': 'SimpleStrategy', 'replication_factor': '1'} AND durable_writes = 'true';DESCRIBE KEYSPACES/TABLESUSE KEYSPACE blah;DROP KEYSPACE blah;CREATE TABLE table (id int PRIMARY KEY, name text, position text);CREATE TABLE carmake (carmake text, id int, car_model text, PRIMARY_KEY(car_make, id));-> Notice the partition key and clustering key(s) here.- You could also have a combination of columns as partition key in case one partition is getting overloaded.
CONSISTENCY xto change consistency level. (JustCONSISTENCYfor querying current consistency level forcqlshsession)SELECT car_make, writetime(car_model) FROM tablename;Writetime can be foundUPDATE table USING TTL 60 SET car_model='TRUCK' WHERE primary_key=2TTLs could be useful.ALTER TABLE emp ADD colname set<text>;Adds column on the fly with set of texts.UPDATE emp SET colname = colname + {'123'} WHERE id=2;Adding (+) or removing (-) from set/list types in cassandra.CREATE INDEX ON emp (name);(When you designed the system wrong initially)
- UUIDs is a col type like (
text,uuid,timeuuid)INSERT INTO emp (id, fname) VALUES (uuid(), 'tom');timeuuidis also a column of type uuid with a time componentINSERT INTO emp (id, fname) VALUES (now(), 'tom');
- Counters in cassandra (Increment or decrement)
CREATE TABLE purchases (id uuid PRIMARY KEY, pur counter);UPDATE purchases SET pur = pur + 1 WHERE id = uuid();
- Snitch - Decides which node is the best to serve a request. Dynamic snitches allow nodes to decide which nodes (closest) to route the request to to serve a query.
- Gossip protocol - Nodes communicate cluster state with all other machines they're aware of. And eventually, exponentially all machines are aware of each other and their health checks etc.
- Data Storage:
- Memtable - In memory - ordered by clustering keys
- Commit Log - On disc - append only - unordered
- SS Table - Created whenever memtable is flushed to disk to create an immutable ordered table. - ordered
- The flush also creates a new commit log and memtable.
- These SSTables are compacted into fewer SSTables over time for better read performance.
- While reading, it compares values in Memtable vs SSTables and returns values with the same timestamp.
- More read optimizations:
- Bloom Filter - To tell you if a value DOES NOT exist in an SSTable.
- Key Cache - For giving locations of a LRU partition keys.
- Partition Index - For giving disk index locations for each partition.
- Paxos has been industry leader since forever but not very easy to understand.
- Raft is a recent and more understandable approach to the same.
- Leader is elected when timer times out. (Timeout is reset on each heartbeat)
- Leader can reset their timer with a heartbeat or some data.
- Term is a time that a leader serves after an election.
- Term can have no leaders in case of split vote and another leader election is triggered after a node timeout.
- Replicated state machine. Video link
- ETCD - Key value state store that kubernetes relies on implements this. One leader at a time. Replicated and consistent. Uses disk.
- etcd has another mode called learner (Which blocks the node from election till it catches up on leader logs).
- Both raft and paxos assume that the nodes are not evil.
- Public ledgers (Like blockchain) use Byzantine failure for consensus assuming everyone is evil.
Mar 8, 2021
- Palindrome checking can be done recursively. Check recursively if the center of the string is a palindrome or not.
Mar 5, 2021
- Bound blocking queues are amazing for producer consumer settings.
- You need two mutexes (Locks) to make produce and consume blocking (when queue is full or empty). Produce lock and consume lock.
- Or a single python
threading.Condition()
- Or a single python
- Guess what buffered Go channels are! 🤯
- Need two separate binary searches. That go left/right when item found at mid.
- Flip the problem! Water to land calculation needs a single pass over each cell. Also BFS, but faster. Maintain a visited set().
- Minimum transactions needed to settle.
- Amazing DP solution with backtracking.
- First calculate debt per person. (Total sum of array = 0)
- Keep checking with the transactions on the right. Move the value at current cell to the right(where sign is different). Then DFS that. Then backtrack that transaction settle to look for other possible paths.
Mar 4, 2021
- It is possible to remove item from an array in O(1) if the order of items is not important.
- Just do a pop. Then replace the index of the item removed with the last item.
l = threading.Lock()- Use it like a mutexl.acquire()l.release()
e = threading.Event()- Use it to wait inside and event can be set from outside.e.wait()e.set()
cv = threading.Condition(lock=None)- This is pretty cool if you need to block a thread till a condition is satisfied.cv.wait_for(lambda: True)Waits for this function to return true.cv.notify_all()Notifies all waiting threads that it is done.
with cv:
cv.wait_for(lambda: condition_satisfied())
# Do your thing here
cv.notify_all()
Feb 23, 2021
- Wiggle sort can be achieved in a single iteration.
- Look at 3 items at a time and make the condition satisfy. a <= b >= c <= d ...
- DP way of looking at it. Create two dp arrays up and down.
- In case of a wiggle up
(n[i] > n[i-1]), up[i] = down[i-1] + 1 - In case of a wiggle down,
down[i] = up[i-1] + 1
- In case of a wiggle up
Feb 22, 2021
- Itineary planning. Make sure all tickets are used at least once. What path will be followed?
- DFS is good. But how to decide valid paths.
- DFS with ticket use each time and mark path in bottom up. Append to a ret variable after the recursive call.
- This will ensure that node is visited (appended to the list) when it is stuck there.
- Hence that should be visited at the end. (If you reverse the list).
- Kind-of like topological sort. DFS in graphs are quite similar!
- Debugging bottom up recursions is not very pleasant.
Feb 18, 2021
- Amazing post on using a memory ballast to trigger fewer GC cycles.
- More on Go GC here.
- Heap is used for dynamic allocations.
- A few takeaways:
- Go's Garbage Collection is Concurrent and not "Stop the world".
- Each goroutine needs to pay some tax (gc marking work)
- GC Pacer: If need be, the Pacer slows down allocation while speeding up marking. At a high level the Pacer stops the Goroutine, which is doing a lot of the allocation, and puts it to work doing marking. The amount of work is proportional to the Goroutine's allocation. This speeds up the garbage collector while slowing down the mutator.
- Go’s default pacer will try to trigger a GC cycle every time the heap size doubles.
GOGC - Marking is the more expensive step in GC.
- Enter "Ballast" — Nautical. any heavy material carried temporarily or permanently in a vessel to provide desired draft and.
// Create a large heap allocation of 10 GiB
ballast := make([]byte, 10<<30)
- Continuing ^:
- It reduced GC cycles by allowing the heap to grow larger
- API latency improved since the Go GC delayed our work less with assists
- The ballast allocation is mostly free because it resides in virtual memory
- Ballasts are easier to reason about than configuring a
GOGCvalue - Start with a small ballast and increase with testing
- Uber engineering production issues with spawning new goroutines on each request. Link
- Goroutine stacks: Every goroutine in Go starts off with a 2 kibibyte stack. As more items and stack frames are allocated and the amount of stack space required exceeds the allocated amount, the runtime will grow the stack (in powers of 2) by allocating a new stack that is twice the size of the previous one, and copying over everything from the old stack to the new one.
- Solution: Don't create a goroutine for each request. Use a worker pool to reuse the already expanded stacks of existing goroutines.
Feb 3, 2021
- Great Link
- That may seem cynical or naive -- that we're "merely" products of our environment -- but as game theory reminds us, we are each others' environment. In the short run, the game defines the players. But in the long run, it's us players who define the game. So, do what you can do, to create the conditions necessary to evolve trust. Build relationships. Find win-wins. Communicate clearly.
Jan 24, 2021
- We want to guarantee that for each message consumed from the input topics, the resulting message(s) from processing this message will be reflected in the output topics exactly once, even under failures. In order to support this guarantee, we need to include the consumer’s offset commits in the producer’s transaction.
- Kafka wire protocol is how to implement a language agnostic client. Phew.
- The txn protocols need to be implemented first before I can proceed with the steps mentioned in the beautiful design.
Jan 23, 2021
-
Idempotent producer: Every message write will be persisted exactly once, without duplicates and without data loss -- even in the event of client retries or broker failures. However, idempotent producers don’t provide guarantees for writes across multiple TopicPartitions.
- To implement idempotent producer semantics, we introduce the concepts of a producer id, henceforth called the PID, and sequence numbers for Kafka messages. Every new producer will be assigned a unique PID during initialization. The PID assignment is completely transparent to users and is never exposed by clients. For a given PID, sequence numbers will start from zero and be monotonically increasing, with one sequence number per topic partition produced to. The sequence number will be incremented for every message sent by the producer. Similarly, the broker will increment the sequence number associated with the PID -> topic partition pair for every message it commits for that topic partition. Finally, the broker will reject a message from a producer unless its sequence number is exactly one greater than the last committed message from that PID -> topic partition pair. This ensures that, even though a producer must retry requests upon failures, every message will be persisted in the log exactly once. Further, since each new instance of a producer is assigned a new, unique, PID, we can only guarantee idempotent production within a single producer session.
-
Transactional Guarantees: A ‘batch’ of messages in a transaction can be consumed from and written to multiple partitions, and are ‘atomic’ in the sense that writes will fail or succeed as a single unit.
- Atomic multi-partition writes and Zombie fencing - To achieve this, we require that the application provides a unique id which is stable across all sessions of the application. For the rest of this document, we refer to such an id as the TransactionalId. TransactionalId is provided by users, and is what enables idempotent guarantees across producers sessions. When provided with such an TransactionalId, Kafka will guarantee:
- Idempotent production across application sessions. This is achieved by fencing off old generations when a new instance with the same TransactionalId comes online.
- Transaction recovery across application sessions. If an application instance dies, the next instance can be guaranteed that any unfinished transactions have been completed (whether aborted or committed), leaving the new instance in a clean state prior to resuming work.
- The API requires that the first operation of a transactional producer should be to explicitly register its transactional.id with the Kafka cluster. When it does so, the Kafka broker checks for open transactions with the given transactional.id and completes them. It also increments an epoch associated with the transactional.id (effectively broker will return same
PIDfor a giventransactionalIdwhich will ensure idempotent writes across producer sessions). The epoch is an internal piece of metadata stored for every transactional.id. Hence it can fence writes from zombie producers which have an older epoch.
- Consuming Transactional Messages: - The transactional guarantees mentioned here are from the point of view of the producer. On the consumer side, the guarantees are a bit weaker. In particular, we cannot guarantee that all the messages of a committed transaction will be consumed all together. This is for several reasons:
- For compacted topics, some messages of a transaction maybe overwritten by newer versions.
- Transactions may straddle log segments. Hence when old segments are deleted, we may lose some messages in the first part of a transaction.
- Consumers may seek to arbitrary points within a transaction, hence missing some of the initial messages.
- Consumer may not consume from all the partitions which participated in a transaction. Hence they will never be able to read all the messages that comprised the transaction.
- Atomic multi-partition writes and Zombie fencing - To achieve this, we require that the application provides a unique id which is stable across all sessions of the application. For the rest of this document, we refer to such an id as the TransactionalId. TransactionalId is provided by users, and is what enables idempotent guarantees across producers sessions. When provided with such an TransactionalId, Kafka will guarantee:
- Planning to contribute to segmentio's kafka-go
- Their API does not deal with transactions at all. Yet ;)
Dec 11, 2020
- Make sure this is added to your server run command
-agentlib:jdwp=transport=dt_socket,server=y,suspend=n,address=5010 - Once this is done, make sure you have this in your IDE run config. (
Remote > Attach to remote JVM>). - Port forward your deployed service using
ssh tunnelsorkubectl port-forward. Cmd + shift + F9to actually hot swap.- Life = Easy.
Dec 11, 2020
- Test your APIs in style with ease.
- Use Collection Runners for sending a particular request multiple times (iterations).
- Also possible to send requests with variables that can be sent via a CSV.
- It is also possible to chaining requests for parsing response from one request and using the response to create variables to use for the upcoming requests. This can help build test suites.
Oct 13, 2020
- Kerberos is a network authentication software that allows safe client-server authentication even on non safe protocols.
- Client applications must authenticate themselves when communicating with (almost) any Hadoop service.
Oct 8, 2020
- Added some tutorial implementations here.
String fileName = "yourfile.txt";
ClassLoader classLoader = getClass().getClassLoader();
URL resource = classLoader.getResource(fileName);
// Now file can be accessed like
... new File(resource.toURI());
Oct 6, 2020
- Flink docs
- Layered API:
- Low level: processFunctions
- Medium level: DataStreams API / DataSet API
- High level: SQL & Table API
- Making updates to a stateful streaming application is not trivial. This is solved by Flink’s Savepoints.
env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();- This will do the right thing depending on the context: if you are executing your program inside an IDE or as a regular Java program it will create a local environment that will execute your program on your local machine.
- Local cluster (
./bin/start-cluster.sh) (UI atlocalhost:8081). You don't need this if running from IDE. - Execution environment provides Multiple ways of reading streams like from file, sockets etc.
val text: DataStream[String] = env.readTextFile("file:///path/to/file") - Buffer Size: Full buffer(wait for buffer to fill up before forwarding) means highest throughput, and empty small buffer means low throughput.
- Operators transform one or more DataStreams into a new DataStream
- List
- map/filter
- Make sure to keyBy before using windows.
- A window is created as soon as the first element that should belong to this window arrives, and the window is completely removed when the time (event or processing time) passes its end timestamp.
- Trigger: Trigger specifies the conditions under which the window is considered ready for the function to be applied.
- Function: The function will contain the computation to be applied to the contents of the window
- Evictors: which will be able to remove elements from the window after the trigger fires and before and/or after the function is applied
- Windows can be defined over long periods of time (such as days, weeks, or months) and therefore accumulate very large state. [link](Windows can be defined over long periods of time (such as days, weeks, or months) and therefore accumulate very large state.)
- The state size of a window depends on the type of function that you apply. If you apply a ReduceFunction or AggregateFunction, arriving data is immediately aggregated and the window only holds the aggregated value. If you apply a ProcessWindowFunction or WindowFunction, Flink collects all input records and applies the function when time (event or processing time depending on the window type) passes the window's end time.
- You can also use them together. This is useful because you have incremental aggregation (due to ReduceFunction / AggregateFunction) but also access to the window metadata like begin and end timestamp (due to ProcessWindowFunction).
- In order to work with event time, Flink needs to know the events timestamps, meaning each element in the stream needs to have its event timestamp assigned.
- Event time can progress independently of processing time (measured by wall clocks). For example, in one program the current event time of an operator may trail slightly behind the processing time (accounting for a delay in receiving the events), while both proceed at the same speed. On the other hand, another streaming program might progress through weeks of event time with only a few seconds of processing, by fast-forwarding through some historic data already buffered in a Kafka topic (or another message queue).
- The mechanism in Flink to measure progress in event time is watermarks. Watermarks flow as part of the data stream and carry a timestamp t.
- In addition to the main stream that results from DataStream operations, you can also produce any number of additional side output result streams
- Only step = declare OutputTag to identify sideOutput.
- Get side output from result stream like this
DataStream<T> lateStream = result.getSideOutput(lateOutputTag);
- Link
- The
ParameterToolprovides a set of predefined static methods for reading the configuration. - Parameters registered as global job parameters in the ExecutionConfig can be accessed as configuration values from the JobManager web interface and in all functions defined by the user.
- Flink needs to be aware of the state in order to make it fault tolerant using checkpoints and savepoints.
- Many operators maintain their own state and async checkpoint when checkpoint barriers pass through them.
- Queryable state allows you to access state from outside of Flink during runtime.
- For processing exactly once, the source must be replayable and the sink must be transactional(idempotent).
Sep 22, 2020
- It is a package manager for Kubernetes like homebrew for mac.
- You can define multiple services/deployments etc. in a single chart.
- Building blocks:
- Charts: Packaged k8s resources
- Chart repository: Registry of consumable charts
- Release: Deployed instance of a chart
- Has a Hub like Docker: HelmHub
- Helm client:
- helm search hub whatToSearch (hub search)
- helm repo add repo-name repo-link
- helm search repo repo-name (local search)
- helm install yourReleaseName chartName
- helm status yourReleaseName
- helm show values chartName (shows configurable options in chart)
- helm get values yourReleaseName (shows configurations applied to a chart)
- helm install -f configWithOptions.yaml yourReleaseName chartName
- helm upgrade -f configWithOptions.yaml yourReleaseName chartName
- helm rollback yourReleaseName revision (revision begins at 1 and keeps incrementing)
- helm history yourReleaseName
- helm create yourChart (creates a template for your chart)
- helm package yourChart (creates a chart for distribution)
Sep 18, 2020
- HDFS operates on the concept of "immutable block storage". It also has a strict requirement that all file creation / deletion MUST be atomic. That is the operation completes entirely, or if it aborts no intermediate state is left behind.
- Writing data has 2 paths:
- If file doesn't exist: write new
- If file does exist: discard old, write new.
- You cannot append to a file in the regular sense when using HDFS. You have to read the file out completely, mutate it, and write it back out entirely.
Sep 17, 2020
- Hello again scala
- Tail recursion. Neat concept of using recursion when the current stack frame can be reused. (No stack overflows). Just decorate the function with
@tailrec
@tailrec
def gcd(a: Int, b: Int): Int = …
- Scala and Java together in the same project with maven link.
case classis advantageous overclassin Scala as it doesn't create a new object and keeps it all functional.
Aug 26, 2020
Serialization is the process of translating data structures or objects state into binary or textual form to transport the data over network or to store on some persisten storage.
- Avro is a language-neutral data serialization system (like thrift, protocol buffers).
- Avro creates a self-describing file named Avro Data File, in which it stores data along with its schema in the metadata section.
- Avro is also used in Remote Procedure Calls (RPCs). During RPC, client and server exchange schemas in the connection handshake.
- Avro schemas can represent Union types, but not Abstract types. It does not make sense to serialize an abstract class, since its data members are not known.
- LogicalTypes in Avro like date etc.
- Using avro with maven.
- Creating complicated schemas with maven
Aug 14, 2020
- Processing exactly once.
- Link to confluent article
- Talk by Matthias J. Sax @ kafka Summit-2018.
- Two phase commits: Two phase commit does not guarantee that a distributed transaction can't fail, but it does guarantee that it can't fail silently without the Transaction Manager being aware of it.
- Given enough data, all the numbers for any given question fit the benford's curve.
- Log curve:
- Numbers beginning with 1 = 30%
- With 2 = 17%
- so on.
- Intuitive (think about it) and useful!
- If a set of numbers seem to not follow this law, they could possibly be tampered with.
Aug 1, 2020
- Covering of a plane with one or more geometric shapes called tiles with no overlaps or gaps.
- M.C. Escher was a genius. 3 Kinds of tessellations.
Jul 21, 2020
- Read about:
- Two phased commits
- Wound wait deadlock prevention algorithm
- Collaborative filtering
- Spanner link: Distributed database with strong consistency.
Jul 19, 2020
- Portable (Runs on any stream processing engine like spark/flink/dataflow) + Flexible (SDKs in many languages).
- flow
Data -> PCollection -(PTransform)> PCollection -> sink - Python/Go SDKs not yet ready for the party :(
- Lack of generics in go makes it painful to build for this use case.
- 101 by Tyler Akidau.
- State management in Stream Processors - by Jay Kreps.
- Joins in streams:
- Streaming join: so you might only need to wait for a few minutes after the impression for the matching click to occur.
- Enriching join: Query user data from another source to enrich your stream.
- Instead of a remote DB, have some state colocated for fast access. This is where in memory dbs like rocksDb/Badger shine.
- Nice post
- The way consumers maintain membership in a consumer group and ownership of the partitions assigned to them is by sending heartbeats to a Kafka broker designated as the group coordinator.
- If the consumer stops sending heartbeats for long enough (
session.timeout.msdefault10s), its session will time out and the group coordinator will consider it dead and trigger a rebalance. (During the rebalance, no messages from the partitions owned by the dead consumer are processed)- At each rebalance, groupCoordinator decides a leader (first consumer) and sends it the list of hearbeat-sending consumers which assigns partitions to them.
auto.offset.resetdecides where should a consumer start reading from when no valid offset is available. (Values can beearliest,latestetc.)partition.assignment.strategycan be set to Range or RoundRobin.- It is possible to add listeners for
partitionRevokedandpartitionAssignedby implementingConsumerRebalanceListenerand passing it to the subscribe method.- So you can commit offsets etc. before the rebalance actually comes into effect.
- It is also possible to seek to a certain offset(+1) per partition. Useful if you use an external database for storing offsets everytime after processing a record.
Jul 13, 2020
- Stefan Pochmann's brilliance.
June 24, 2020
- Varargs
public void printer(String... lst) {}equivalent to passing any number of strings or a list to this function. - Wildcards:
<? extends Building>
June 22, 2020
- Get ascii values of all input characters, multiply them = get a big number.
- Mod big number with a prime number (this will be your size) of your choice. Bigger number = less collisions = size of your hashtable.
- That's it. Your hash function is ready.
- Year wise latency numbers
- System design prep must revisits:
- Consistent Hash ring - Multiple hash functions to decide ranges for each server. Send requests to the next(clockwise) server in the ring.
- Bloom filters - Multiple hash functions to fill in a single array.
- Python Decorators hierarchy:
@dec
def yellow():
pass
# is the same as
yellow = dec(yellow) (decorator should return a callable function basically)
# Decorators with params
decorator_func('decorator', 'arguments')(my_fun)('function', 'arguments')
June 21, 2020
product('ABCD', repeat=2) --> AA AB AC AD BA BB BC BD CA CB CC CD DA DB DC DDpermutations('ABCD', 2) --> AB AC AD BA BC BD CA CB CD DA DB DCcombinations('ABCD', 2) --> AB AC AD BC BD CDcombinations_with_replacement('ABCD', 2) --> AA AB AC AD BB BC BD CC CD DD- All of the above are generators.
- Use
math.factorialfor a fast C implementation for the same. - Use
divmod(numerator, denominator)to getdiv, modfor convenient division results.
June 18, 2020
- Joins:
SELECT * FROM Employee e LEFT JOIN Managers mUSING(id);Column names need to be the same.ON e.id = m.id;Can contain any condition.
- Nth highest salary:
SELECT Salary from Employee ORDER BY Salary DESC LIMIT 1 OFFSET N;. Offset is the key ingredient. - Nested queries:
SELECT * from Employee where Salary > (Select Salary from Employee where Name = "Alex");
June 10, 2020
- For finding minimum paths in graphs.
- Maintain 2 arrays of size
N(N=number of nodes in graph). - At each iteration =
i, maintain the vertices reached in exactlyisteps. - Maintain a global minimum/maximum as necessary.
- Maintain a heap with minimum cost so far.
- With each step (
i) add possible paths to heap. - The First time you reach the destination is the shortest path to that node.
May 27, 2020
- Monitoring a service is an essential part of owning a service and it is as important as the service itself. - Ivan Kruglov
- Resolution determines how fine-grained the resolution of our data is (per second, per 10 seconds).
- Link to documentation.
- Meters: rate of an event over time. Requests per second. Mean rate, (1,5,15 min) moving averages.
- Gauge: A gauge is an instantaneous measurement of a value.
- Counter: A counter is just a gauge for an AtomicLong instance. You can increment or decrement its value.
- Histogram: A histogram measures the statistical distribution of values in a stream of data. In addition to minimum, maximum, mean, etc., it also measures median, 75th, 90th, 95th, 98th, 99th, and 99.9th percentiles.
- Timer: A timer measures both the rate that a particular piece of code is called and the distribution of its duration.
- Timers usefully combine a histogram of the event’s duration and a meter of its rate. (For web requests maybe, not for producer consumer use cases).
- MetricReporter implementations push to a specified sink every few seconds/minutes as configured.
May 23, 2020
- Link.
- Minimum/maximum path to reach a target -
- Use previous min/max of previous results + currentItemCost.
routes[i] = min(routes[i-1], routes[i-2], ... , routes[i-k]) + cost[i]
- Distinct ways to reach a target -
- Sum all possible ways to reach the current state.
routes[i] = routes[i-1] + routes[i-2], ... , + routes[i-k]- (Maintain a dict or list of all sums encountered so far).
- Decision Making
- State Machine thinking: sample. Create state diagram and make sure there is a list for each state and each update checks previous items in the corresponding lists(based on state connections).
April 25, 2020
- Async/Await is a better/cleaner way of writing promises or asynchronous code in general. (Much cleaner than
promise.then(..).catch(..)). C# came up with it and most languages are adopting it. asyncwith function definition- Always
awaitasync function calls. asyncio.sleepfor sleepingasyncio.run(asyncFunc())to run the function from a non async scope.asyncio.create_task(asyncFunc())wraps function into a Task before running.asyncio.gather(asyncFunc("A", 2),asyncFunc("B", 3))wait on multiple asyncs.- Can also write
golike producer consumer code by usingasyncio.Queue- Usage:
q = asyncio.Queue(), Functions: await q.put((i, t))i, t = await q.get()q.task_done()to mark task as doneawait q.join()to wait on all q tasks to be done
- Usage:
April 17, 2020
- Alternative to REST/gRPC.
- GraphQL seems relevant when the network and bandwith matter (mobile) as there will be less calls and data on the wire,
- GraphQL seems relevant when you need a typed schema (less flexibility) and some kind of contract between you and your consumer or maybe you don't know your consumer (public API)
- GraphQL seems relevant when you have a highly connected or hierarchical data. Relations and traversal can be retrieved as a single query
- GraphQL seems relevant when you need to aggregate multiple data sources (mashup).
- For CRUD operations, plain old REST is still the way to go
- For streaming, asynchronous and action/command oriented API, gRPC is our best choice
April 16, 2020
Big Data
- Mapper splits the task into key value pairs
- Partitioner/Shuffler decides which reducer will the mapped keys will go to (sticky). Usually the hash of key is used to do this mapping. Time consuming step of actually performing netowork operations.
- Reducer gets its input and performs aggregations. Usually stores the results on disk for further consumption.
- Types of file input formats:
- Text: key = byte offset of each line, value = line itself.
- Key Value: key = before seperator, value = after separator. (Default separator=tab)
- NLine: Each mapper receives N lines of input
- Sequence File: Map output is stored intermediate in this format (binary key value pairs).
- Spark = Better then MapReduce because of RDDs and high level library.
- Read these notes before continuing
- 2 types of spark processes:
- Driver is where user code runs, converted to map-reduce pattern.
- Spark executors are the executors that run the job. These are launched by the driver in the cluster.
- RDDs vs DataFrames:
- Use Dataframes API always.
- Transformations are steps in a recipe. Aren't actually executed till an action is called. Transformations on a Dataframe returns a dataframe. Only the DAG is computed. (Lazy Evaluation).
df = spark.table('blah')df.where('col="meow"')df.groupBy('col(category)').sum('col2(quantity)')orderBy, selectetc.
- Actions: Data is actually sent through the DAG(
collect, take, count, reduce, saveAsTextFile) - Use
df.cache()when the intermediate result will be reused. It will be cached whenever it is materialized for an action. Simlarly dodf.unpersist()when you don't need it cached anymore.
April 8, 2020
algorithm
- Both players play optimally. Players can pick 1, 2 or 3 items at a time. Solution: start from back of the item list. DP[i] is difference between both players' optimal moves so far, assuming nothing behind A[i] exists yet. As DP progresses backwards, dp[0] will contain final score difference between player 1 and player 2.
April 1, 2020
algorithm
- Naive approach is O(n^2).
- Edges not part of a cycle are bridges.
- Non repeating element in a list - Find XOR of all elements.
reduce(lambda x,y: x^y, lst) - Max Subarray Sum: has a beautiful tiny implementation. We already know that if the subarray sum becomes negative, it is useless for the upcoming subarrays.
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
if nums[i-1] > 0:
nums[i] += nums[i-1]
return max(nums)
- Palindrome hack - Count number of occurances of each character in the string. Number of odd count elements usually gives you hints.
- Axis aligned rectangle: To find the closest point in that rectangle to a circle,
closestX = xc>x2?x2:xc<x1:x1:xc. Similar forclosestYThen distance can be compared to radius to see if there is any intersection. Closest X and closest Y are calculated separately to make life easier. - Stocks when to buy sell - Any number of transactions. 1 transaction at a time. Boils down to finding increasing sub-sequences in the array. Quick hack is to buy today sell tomorrow if tomorrow>today for each pair.
return sum(max(prices[i + 1] - prices[i], 0) for i in range(len(prices) - 1))💣 Neat!
Feb 11, 2020
- 'Stream/Batch' processing engine. Same programming model for both kinds of workloads.
- Available modes:
Standalone, Cluster.- Standalone = pretty much useless.
- Cluster = Can be used on baremetal or using resouce allocator layers like yarn or k8s etc. Yarn who!
- Flink on K8s:
Job cluster- Cluster allocated per job. Long running jobs. Job Manager deployed as a k8s-Job(that submits the task and ends).Session cluster- Single cluster used for multiple short jobs (like ad-hoc queries). Job Manager deployed as a k8s-deployment. Tasks can be submitted by port-forwarding a job manager pod submitting flink job-ar using flink cli.Hybrid(Zalando) - Deploy like session cluster but submit long running jobs.
Feb 6, 2020
- There will always be so much to learn
- Post
- Adds pagination to most command outputs.
ps aux | less mysql Something | less -Sto chomp lines instead of warping them. Useful in case of wide tables.less -N filenamedisplays line numbers.less -X filenameleaves the output on the screen.less +F filenamewatches a file for change.
watch YourscriptRe runs it in full screen every n seconds.watch -n 1 youscripttime intervalwatch -d -n 1 yourscriptPrints differences in successive runs.
- In mysql shell,
\gis equivalent to;to end statements. \Gcan be used at the end of statements instead of;for displaying results vertically! It is much easier to read if the number of columns is a lot.
Feb 4, 2020
- Link
type cat struct{}is like a class and interfaces are like interfaces.- To have a GoLang interface use the following syntax.
type animal interface {func1() int64} - This comes in handy when you want to define function arguments. All the classes that implement this interface just need to implement func1.
structscan also have embedded anonymous types. Usually fields inside structs have:has arelationship, but these anonymous types haveis arelation ship. Like a superclass.type dog struct {Canine}assuming canine struct is also defined with all members and methods.- Several ways to initialize them:
var c Dogc := Dog{}c := new(Dog) //returns a pointerc := Dog{a: 1, b:2}
- Use
time.Now().UnixNano()for high precision. - Convert this int64 back to time.Time using:
time.Unix(0, timestampUnixNano)
Jan 14, 2020
- Shared Lock - aka Read Lock: Multiple locks can exist at the same time. Write transactions should wait for the read to finish.
- Exclusive Lock - aka Write Lock: One lock can exist at a time. Can't be read or written by another transaction.
- Golang package lockedfile
Jan 13, 2020
- gRPC on Kubernetes requires proxies configured on each pod to be able to load balance. Linkerd service mesh helps with just that :D
- Server maintains a keep-alive HTTP2 connection with the client. All requests don't create a new connection.
- Hence the load needs to be balanced on requests instead of open connections.
- Protobuf: Sample message and rpc
syntax = "proto3";
message Burp {
int32 status = 1;
string message = 2;
}
service OesophagusService {
rpc Consume(Swallow) returns (Burp) {}
}
- Proto file can be used to generate client and server side code for the spec.
- Go proto generating command:
protoc --go_out=plugins=grpc:. *.proto - See grpc-gateway for also supporting REST.
- Influx and Grafana setup on Kubernete is fairly simple. Use Persistent volume claim for InfluxDB. Everything else can be stateless.
- Nice Link
- Screen can also be configured for things like scroll up buffer etc.
screen -lsscreen -r <number or name>screenCtrl+a, :sessionname nameCtrl+a, /run screenrc file.
Jan 6, 2020
- Uses etcd - key value store
- Master
- API Server - interact with cluster
- Can have multiple masters
- etcd
- Scheduler - schedules pods
- **Worker
- kubelet - reports status to API server
- kube-proxy - networking
- Docker - container runtime
- Pods
- Atomic unit of Kube
- Can have multiple containers and volumes
- All containers are equal except:
- InitContainer - A Pod can have multiple containers running apps within it, but it can also have one or more init containers, which are run before the app containers are started.
- Runs to completion
- One has to finish before the next init container can start.
- Sidecar Container ?
- InitContainer - A Pod can have multiple containers running apps within it, but it can also have one or more init containers, which are run before the app containers are started.
- Starts a container (pause container) that creates a network for the pod that all the containers in it share.
- Get a shell to a running container in a pod.
kubectl exec -it <pod-name> -- /bin/sh - Debug a pod: Port forward to localhost
kubectl port-forward <podname> 2020:80(localhost-port:pod-port) - Pod logs:
kubectl logs <pod> <-c container-name>container name is not compulsary ofcourse. This is like docker-compose logs. kubectl describe pod <podname>Check status for lifecycle of the container/pod.
- ReplicaSet
- Encapsulates pods
- Pod replication.
- Automatically created in Deployment.
- Deployment
- Encapsulates replicaset - (grouped pods on ReplicaSets)
- Can also roll back to previous deployment. Current state to desired state.
- Namespace
- Separation of concerns in a Kubernetes cluster.
- For different teams.
- Workload patterns
- Stateless Pattern
- Stateful Pattern
- Daemon Pattern
- Batch Pattern
- Deployment
- StatefulSet
- DaemonSet
- Job
- StatefulSet: Manages the deployment and scaling of a set of Pods, and provides guarantees about the ordering and uniqueness of these Pods. Unlike a Deployment, a StatefulSet maintains a sticky identity for each of their Pods. These pods are created from the same spec, but are not interchangeable: each has a persistent identifier that it maintains across any rescheduling.
- Switch kubernetes context from the top in Docker 4 Mac.
- Setting default namespace:
kubectl config set-context <your-context> --namespace=<namespace-name> - Labels: Key value pair attached to an object like a tag
- Objects include Pods, Services
- Used for load-balancing/ deployments etc.
- comma separated (means and), = or !=, in means or.
environment=production,tier!=frontend,partition in (europe, asia)- Useful commands:
kubectl label deployment hello-world env=prodkubectl get deployment -l env=prodkubectl label deployment hello-world env-to remove
- Annotations - Much like Labels except this is arbitrary non-identifying metadata.
- LABEL SELECTORS IS HOW KUBERNETES OPERATES!
- ALWAYS CHECK ENDPOINTS!
- Services -
- Forward traffic to pod or a group of pods that work together
- Decoupled from the lifecycle of Pods
- Stable endpoint like a dns (The IP of a service only changes )
- Types:
spec.type- ClusterIP - Default type. It creates a cluster internal IP for pods that match the selector criterea and can be accessed by all pods by
service-name:port. - NodePort - Also creates a clusterIP and additionally also forwards specified ports (from each pod) to all the Nodes in the cluster.
- LoadBalancer - External LoadBalancer service usually proviced by cloud provider.
kubectl get endpointsto see where the traffic is mapped from a service.- Ingress - With Ingress, you can easily set up rules for routing traffic without creating a bunch of Load Balancers or exposing each service on the node. This makes it the best option to use in production environments.
- ClusterIP - Default type. It creates a cluster internal IP for pods that match the selector criterea and can be accessed by all pods by
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: sample
spec:
type: NodePort # or ClientIP
ports:
- name: http
port: 3000
targetPort: 3000
selector:
app: sample # all pods/deployments with this label will be loadbalanced over
-
ConfigMaps -
- ConfigMaps can be used to send config files to pods.
kubectl create configmap <cmapname> --from-file=<configFile> - Path where to put it is set in pod configuration. It is mounted as a volume.
- ConfigMaps can be used to send config files to pods.
-
Secrets -
- Can be used to send sensitive environment variables to pods.
-
DaemonSets -
- Use this if you want certain pods to be deployed on each Node in the cluster as Nodes are added/removed. Examples: Node monitoring, cluster storage, log collection etc.
Jan 5, 2020
- Your virtualenvironment is not the same as jupyter's virtualenvironment.
- Solution:
- Create your virtualenvironment and activate it
python3 -m virtualenv venv3. - Install ipykernel
pip install ipykernel python -m ipykernel install --user --name <your-env> --display-name "<your-env>"- Change to this kernel from inside the notebook. 🍻
- Jupyter should be installed globally and not inside a virtualenvironment.
- Create your virtualenvironment and activate it
Jan 2, 2020
import threadingthreading.active_count()- current active threadsthreading.current_thread()- current Thread objectthreading.enumerate()- list of all alive Thread objects
- Thread object
threading.Threadstart()/run()/join()/name()/is_alive()daemonmust be set before start is called.
- Lock object
threading.Lockl = Lock()acquire(),release()- Better:
with lock:(equivalent to calling acquire() and then release())
Dec 21, 2019
go mod initto initialize go modules. (Generates go.mod file)go mod tidyto create go.sum file.- These files can be used for quick dockerized builds.
- Dockerfile
- ENTRYPOINT is used to run container as a script
- CMD is used to run commands.
- Multistage alpine images are usually not kept up by docker run.
- To keep them up:
docker run --entrypoint "/bin/sh" --env-file ./.secrets -it dbatheja/repository:tag - NOTE that
--env-file pathcomes before the image name.
Dec 20, 2019
- Golang sync Pool is used whenever there is a lot of allocation and deallocation on a single Data Structure and you want to avoid gc overhead. link
- A Pool is a set of temporary objects that may be individually saved and retrieved
/etc/hostscontains domain resolution for your boxc.
Dec 13, 2019
- Gitlab can be a pain in the 🍑 sometimes.
- Use HTTPS url for remote. And then run this:
git config --global credential.helper store
Dec 12, 2019
- Launch Intellij Applications from command line by
Tools > Create command-line launcher.- Open a project by
$ idea . - Diff between two files by
$ idea diff file1 file2
- Open a project by
- SSH tunnels on a remote machine without actually opening that port using ssh config trickery:
- Add this to
~/.ssh/configwill forward remote's 3306 port to local's 9906:
Host tunnel
HostName database.example.com
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/coolio.example.key
LocalForward 9906 127.0.0.1:3306
User coolio
ssh -f -N tunnelto start the tunnel in background.
Dec 11, 2019
- Docker multistage builds for GoLang like use-cases. Final image is tiny.
- Maven - Possible to give command line flags and conditional dependencies options using
<profiles>at the top-level. Example:
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>prof1</id>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
<property>
<name>type</name>
<value>prof1</value>
</property>
</activation>
<dependencies>
<dependency> ...
</profile>
<profile> ..
- Maven -
<packaging>can also be of typepomand not justjar. That usually means the pom contains some modules like:
<modules>
<module>m1</module>
<module>m2</module>
<module>m3</module>
</modules>
- Each of these modules is a subfolder in the project and their poms contain the
<parent>tag pointing to the top level pom.
<parent>
<artifactId>papa</artifactId>
<groupId>com.company.papa</groupId>
<version>0.0.1</version>
</parent>
Dec 4, 2019
DigitalOceandoctl kubernetes cluster kubeconfig save <cluster-name>for downloading kubeconfig and putting it in./kube/config- Need to set
contextto see which cluster you're connecting tokubectl config current-contextkubectl config get-contextskubectl config use-context <context-name>
- Nodes are workers(machines). Each node can have multiple pods (each of which is a bunch of tightly knit containers (docker-compose like)).
- Service is an abstraction which defines a logical set of Pods and a policy by which to access them.
- Useful for decoupling backends and frontends
- For proxying or relaying network related things
- For load balancing etc.
- Get Everything(default namespace):
kubectl get allkubectl get all -n <namespace>
- Get:
kubectl get podskubectl get svckubectl get deployments- Get all deployments from a namespace yaml
kubectl get -n emojivoto deploy -o yaml
- Delete:
kubectl delete deploy/<name>- Deletes all pods and replicasetskubectl delete svc/<service>-
- Enter a container inside a pod?
kubectl exec -it my-pod --container main-app -- /bin/bash
- ServiceAccounts are for access restrictions and having the pod interact with API server. (kubectl works on the API server).
selectorin Service usually maps pods to servicesnodeSelectorin pod yaml can be used to map pods to nodePools etc by assigning labels to nodes. link- Setting up Linkerd for advanced monitoring. link
linkerd -n namespace tap deploy/web
- PersistentVolumeClaim to persist data. Deleting deployments will not delete pvc.
Dec 2, 2019
- Java make sure to run with flag
-Xmx2gfor 2gb heap memory or better (since Java8),-XX:MaxRAMPercentage=75.0for running with Heap memory = 75% of available ram!. - Unix pipe:
- Run the piped command with the output of the first command!
- Example
$ cat something | boxify
- Unix cut:
$ cut -d "delimiter" -f (field number) file.txt- can also be piped.
Nov 14, 2019
Cmd + tab= for switching between apps. But we already know that.Cmd + tab + qkill an open app 😍Cmd + tab + 1for opening all open windows for the app 😍 (just like swipe down with 3 fingers).ITERMwith ZSH: useful linkCmd + rightend of lineCmd + leftbegining of lineOption + rightnext wordOption + leftprevious word
- Copy from ssh vim to local clipboard:
set mouse=ihelps copy stuff easilyset numberandset number!for turning line numbers on or off.
Nov 14, 2019
- Mostly used for find and replace in files.
$ sed 's/unix/linux/g' geekfile.txtreplaces all occurances because ofg.$ sed -n '2 p' filenamePrints the second line from filename. (p is for print)sed OPTIONS FILENAME
Nov 13, 2019
- Gops for diagnosing go processes running on the system.
gops treefor looking at<pid>of your processgops pidfor basic details and network connections.gops stats pidfor goroutines etc.gops memstats pidfor memory usage statistics.gops gc pidfor triggering garbage collection.
Oct 31, 2019
CompletableFuture: Nice link
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = new CompletableFuture<String>();
completableFuture.get()blocks till future is complete to return the result.completableFuture.complete("YOLO")to manually complete a future..supplyAsync(()->{})will be non blocking.- Use
.thenApply(()->{})orthenApplyAsyncfor transformations. - Use
.thenAccept(()->{})orthenRun(()->{})for finshing the promise. - Final result of this chain can be accessed by
.get()
- Use
- The Async methods also have a variant with an argument that expects Executors (for more fine grained parallelism control).
Executor executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
- If your functions return a
CompletableFutureyou can combine the results usingthenCompose(). It is different fromthenApply()like flatMap is different from map.thenCompose()is used to combine two Futures where one future is dependent on the other,thenCombine()is used when you want two Futures to run independently and do something after both are complete.
- Handling Exceptions:
.handle((res, ex) -> {}or.exceptionally(ex -> {. - Java Functional: Interfaces with only one implementable methods. Lambda expressions can be used for these.
- Lambda functions can be declared as
// Functional interface example
class Hey {
public static double square(double num){
return Math.pow(num, 2);
}
}
Function<Double, Double> square = (Double x) -> x * x;
<IS THE SAME AS>
Function<Double, Double> square = hey::square;
- This can now be passed around as regular functions.
- For referring static methods, the syntax is:
ClassName :: methodName - For referring non-static methods, the syntax is
objRef :: methodName - Map and Filter in Java using
stream():List<String> collect = alpha.stream().map(String::toUpperCase).collect(Collectors.toList());Notice the collection at the end just like Python needs to convert it to list.
Oct 31, 2019
- Data race is not the same as a race condition.
- Compiler reorders some lines to optimize hardware usage and make the code faster. May result in weird results.
- Solutions:
synchronizemethods that modify shared variables (shared by multiple threads).volatilekeyword with shared variables ensures the instructions before/after it are actually run before/after it even after compiler optimization.
- Locks avoidance:
- Enforce a strict order on lock acquisition. (A after B etc.)
- Lock detection: Watchdog.
- Concurrent collections in Java:
java.util.concurrent - Lock free programming:
java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicIntegerAtomicInteger- useful methods: (incrementAndGet), (getAndIncrement) return new and old values respectively. No need for locks and synchronization.AtomicReference<T>- Use this to reference any object. Like the head of a stack data structureatomicReference.compareAndSet(oldExpectedValue, NewValue)
- Lock free thread safe data structure: (without synchronized) and using
AtomicReference and compareAndSet, Performance increase is mindblowing. Loop and retry till you were able to modify what you expected to modify.
public static class LockFreeStack<T> {
private AtomicReference<StackNode<T>> head = new AtomicReference<>();
private AtomicInteger counter = new AtomicInteger(0);
public void push(T value) {
StackNode<T> newHeadNode = new StackNode<>(value);
while (true) {
StackNode<T> currentHeadNode = head.get();
newHeadNode.next = currentHeadNode;
if (head.compareAndSet(currentHeadNode, newHeadNode)) {
break;
} else {
LockSupport.parkNanos(1);
}
}
counter.incrementAndGet();
}
public T pop() {
StackNode<T> currentHeadNode = head.get();
StackNode<T> newHeadNode;
while (currentHeadNode != null) {
newHeadNode = currentHeadNode.next;
if (head.compareAndSet(currentHeadNode, newHeadNode)) {
break;
} else {
LockSupport.parkNanos(1);
currentHeadNode = head.get();
}
}
counter.incrementAndGet();
return currentHeadNode != null ? currentHeadNode.value : null;
}
public int getCounter() {
return counter.get();
}
}
Oct 30, 2019
- For thread creation:
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run(){
// Do Something in new thread
}
});
- Or have your class extend Thread class. In either case,
run()needs to be implemented. - Have a list of
java.lang.Runnables and execute them together using a wrapper class that calls a start on each thread that implements them. - Loop over List (say
List<Runnable> tasks;) like:
for (Runnable task : tasks) {}
- Thread termination:
.interrupt()Can be checked inside the thread withThread.currentThread().isInterrupted()- Other option is to
thread.setDaemon(true)so that this thread is not a blocker for the application or the main thread while exiting.
thread.join()only returns when that thread is terminated (finished therun()function). (Also takes time in millis for returning before execution terminates).- Memory Management
!important- Stack = every local variable is pushed here. Local primitive types and local references. Every methods frame is added here. (This is what overflows during recursion). Exclusive: Not shared among threads
- Heap = Anything created with the
newoperator. Objects, Members of classes, static variables. Managed by the Garbage collector. Shared among threads
- Resource sharing among threads: Shared object instances, if are operated upon by different threads, need to be
Atomic. (Atomic = No intermediate states)- Use
synchronizedkeyword with the function. - OR use
synchronized(lockingObject){...}for more flexibility. The first technique locks all the synchronized functions for an object and not just the one function. The second technique is more like locks in Golang ❤️ - Use
volatilekeyword with double and long to make single line operations on them atomic.
- Use
Oct 28, 2019
- Class inside another class has to be static.
- MultiThreading and concurrency in Java. Following a course by
Michael Pogrebinsky. - OS Process:
- Metadata: like PID, Mode, Priority etc.
- Files: Files it is working with etc.
- Data (Heap)
- Code.
- Thread: atleast one main thread
- Thread:
- Stack - Region in memory where variables are stored and passed to functions.
- Instruction Pointer - Address of next instruction to execute.
- Problems
- Too many threads = thrashing.
- Thread Scheduling such that no thread is starved. OS usually employs dynamic priority.
- Multiprocessing:
Microservicesarchitectures.- Security and stability are of higher importance.
- Unrelated tasks.
- Multithreading:
- Tasks share a lot of data.
- Switching is cheaper.
- Java Generics: Used by util classes like List, Iterator etc.
- If using for a function, use it like this:
public static <T> void minus(T a, T b) {
System.out.println(a + "," + b);
}
- Easier to use with a Class
class Test<T>
{
// An object of type T is declared
T obj;
Test(T obj) { this.obj = obj; } // constructor
public T getObject() { return this.obj; }
}
Oct 14, 2019
- Quick tutorial here.
- Split screen horizontal:
ctrl + band% - Split screen vertical:
ctrl + band" - Navigate between screens:
ctrl + bandarrow - Close a pane:
ctrl + d - Detach a session:
ctrl + bandd tmux new -s <sessionname>or justtmuxstarts a new tmux session.tmux lsto list all sessionstmux attach -t <session-number>to attach to a sessiontmux -CCis a nice tmux iTerm integration.
tmux -S /tmp/pairwill start a shared session. Now make this/tmp/pairaccessable to all by doing achmod 777 /tmp/pairso other users can join your sessiontmux -S /tmp/pair attachwill allow users to join this session and watch you code (in multiple split screens if need be).
ctrl + b + [. Then use PageUp PageDown to scroll. q to quit.- When in scrollback mode. Use
ctrl + sfor searching through the scrollback buffer. tmux set-option -g history-limit 5000to increase scrollback buffer.
Oct 11, 2019
- Cassandra vs BigTable - Columnar store war!
- Cassandra is not on HDFS so is nice that way.
- BigTable maintains history of records which is nice
Oct 9, 2019
runtime.GOMAXPROCS(runtime.NumCPU())- Mac often needs to run
ulimit -n 65536in each session to increase number of open files limit. - Goroutines can get stuck sometimes.
runtime.Gosched()for it to yield that processor and allow other routines to run. - Amazing go JSON libraries:
Oct 7, 2019
- Column-oriented non-relational database management system that runs on top of HDFS.
- For billions of rows and millions of columns.
- Has column-families. Each column family can have a ton of columns which don't need to be consistent across rows.
- Indexed on only one key. (called row-id)
- Each row-id maintains the changes that occured on it with a timestamp. So, older values(columns) for a key can be fetched.
Oct 3, 2019
- awk is used for processing text based data.
- Nicely tied up with linux. (can be used with pipes)
- Sample usages:
awk '<pattern> {<action>}' filenameawk '{print}' file.txtprints entire fileawk '$9 == 500 { print $0}' /var/log/httpd/access.logfor patterns you can see filenames.awk -F ':' '{print $1}' file.txtSplits line by:instead of a space and prints the first item from each row.whois google.com | awk '/Registry Expiry Date:/ { print $4 }'
- Grep is just for filteration! AWK is a powerful programming language especially useful for csv type files.
Sep 23, 2019
algorithm
- Get all permutations of a string
from itertools import permutations
- Run a script which accepts input from stdin
python script < input-fileaccepts input line by line.
- She-bang works for python too.
#!/Users/dbatheja/venv3/bin/pythonas the first line in the file.- Make sure the file is executable (
chmod). - Run the script like:
./script.py
Sep 18, 2019
VIM> 🌍- Jump to end of line
$ - Jump to beginning of line
0 ggfor beginning of file,Gend of filedddelete line.yycopy current lineppastes current line.:tabnew filenameOpens file in a new tab.:<line-number>Jump to line.uundo,Ctrl + r/searchwordNavigate through the results withnandN.- Find and replace in selection: like perl regexes
- select text >
:>s/toreplace/replacewith/gc-(gfor all occurances,cfor interactive one by one).
- select text >
- Jump to file in folder like an IDE:
:tabe <filepath>Tab etc. also work here.- switch between tabs:
gtforward,gTbackwards.
July 11, 2019
algorithm
- Do the given two rectangles overlap? (Given the diagonal points)
- Easiest approach is to see when they don't overlap! and return True otherwise.
- Minimum steps to distribute coins in the tree.
- Can't wrap my head around this.
June 17, 2019
msc
- Final version of accuracy would be:
what percentage of frames are correctly labeled ?. - Memory usage inspection:
- Sublime text is a python process
- Interactive
pexpectis obviously a python process.
June 8, 2019
algorithm
- Goog Brush up!
- Python BFS can be done without using extra space (2 queue approach is not the best.). Use nested loops
- Outer loop loops over the level
- Inner loop connects the children
- Beautiful. (Keep track of the first child at each level, so root can be set to that in the outer loop)
- Vertical traversal of a tree = simple. Use my favourite Recursive approach that fills in a variable outside the function.
- When creating a data structure, keep in mind, creating multiple lists instead of a list of tuples can be faster sometimes.
- Use DFS when you have a graph of jobs dependent on each other, to create a final order of jobs to execute.
- If a node is checked for dependencies once, it is done!
- All possible subsets of size K:
- Find all possible subsets of size 1
- Pop everything and subsequently find all possible subsets of size 2
- etc.
- Recursive approach:
- inner function should have big array, so_far and budget!
- Karnaugh Maps: Compress the storage of truth tables. (K-Map) - A function can be written that represents the truth table.
- Decoding string from numbered brackets. Use stack, always edit the top of the stack whenever you encounter alphabets.
- Probability in a new-21(K) game to have points less than N. DP problem like climbing stairs. Final output = sum of dps[K:N+1].
- Find index of element in a sorted array (which is also rotated.)
- Find index of smallest element by comparing it with the first item in the array. (logn)
- Binary search in either of these based on target (logn)
- Beautiful and simple.
- MD5 hash is a compact digital fingerprint of a file. (Not bullet-proof, but still not bad)
from functools import lru_cache- LRU cache decorator with a maxsize- decorate a function with it
@lru_cache(max_size=32) - The function then has these options available:
func.cache_info(),func.cache_clear()
- decorate a function with it
- Feedback:
- Bomb all the coding rounds at-least!
- Usually all the questions have a follow up! Don't forget that.
- Better team player in the cultural fit round.
- Practice system design.
- Bomb all the coding rounds at-least!
June 1, 2019
algorithm
- No need to setup a debugger.
- Use PySnooper instead of well crafted prints.
- Just slap a decorator on the function you want to debug.
- Install:
pip install pysnooper - Deorator:
@pysnooper.snoop() - More Features: here
May 31, 2019
msc
- Don't save any distances, but only the max distance so far per column! (Don't have any high hopes from this)
- Check out torch multiprocessing - torch.multiprocessing is a wrapper around Python multiprocessing module and its API is 100% compatible with original module. So you can use
Queue,Pipe,Arrayetc.- TODO: Look at all of them multiprocessing techniques in python.
May 25, 2019
msc
nn.Conv2dexpects input in NCHW (batch, channels, height, width) format.nn.LSTMexpects input in (seq_len, batch, input_size) format.- Use tensor.permute to switch these dimensions.
May 22, 2019
algorithm
- Whenever you want to do something sketchy
sshy, just use pexpect. - Easy ssh, scp series of commands.
- Can even interact with the process.
- Sample usage:
child = pexpect.spawn('ssh username@host')
child.expect('.* password:')
child.sendline(password)
child.expect('.*login.*')
child.sendline('ssh further-in')
child.expect('.* password:')
child.sendline(password)
child.interact()
May 19, 2019
msc
- There are NaNs while training the cnns
- Caused due to Wrong divisions or sqrts. Adding tiny epsilons should help.
- Pytorch also has anomaly detection.
May 6, 2019
algorithm
- Complexity of recursive fibbonaci?
- Search space is a tree growing downwards fib(n-1) fib(n-2)
- Number of nodes in the leaves = 2^n
- Boom!
- External merge sort: For sorting large files with limited RAM.
May 6, 2019
msc
- This technique uses triplets of training samples to train.
- Anchor, Positive and Negative.
- Minimize the distance between anchor, positive sample and maximize distance between anchor and negative sample.
- Usually an
$\alpha$ is used (margin like SVM). It is a hyperparameter. - Use hard combinations of A, P and N to make the network smarter! (therwise most training samples are too easy for the neural net).
algorithm
- Finding anagrams doesn't require always sorting the string and looking for the same in t he hashmap (O(nLog(n)))
- One cool approach is just O(n), create an array of all possible characters in the word. And iterate over it to increase counter for each character. Then the key in the hashmap can be a tuple of this array.
May 5, 2019
algorithm
- RDBMS scaling - Master(writes) slave(reads) architecture - with async replication.
- This can be inconsistent!
- Sharding - Split data based on some key.
- But there can be uneven split of data
- Solution: using consistent hashing
- CAP theorem - is for NoSQL databases.
- RDBMS supports ACID
- Availability
- Consistency
- Isolation
- Durability
- NoSql supports BASE - (AP systems)
- Basically
- Available
- Softstate
- Consistency
- Distributed datastore: No master slave, All nodes have some backup in other nodes
- Uses consistent hash ring to decide node to save data in.
- Use gossip protocol for inter-node communication.
- Who doesn't use NoSQL databases:
- Stackoverflow, Youtube, Instagram, WhatsApp
- ACID is not guaranteed, two nodes have different versions of the data (Too many updates!)
- Not read optimized! Get users of age > 30.
- No implicit relations: And address can only exist if there is atleast one user with that address.
- Joins are hard!
- When to use it ?
- Many writes and not too many joins/updates.
- For analytical applications on unstructured data.
- Multi-level sharding can be used when you expect a node to have too much traffic. That node forwards the load to another cluster which evenly distributes the load across that cluster.
May 4, 2019
algorithm
- Redundancy of services and of data! For reliability! Cost: Expensive!
- Partitions - The only way to scale a relational database. Partition it based on some key! Comes at a cost of merges across partitions!
- Caches -
- Local Cache
- Global cache
- Distributed Cache - Uses consistent hashing - each node has a small piece of the cache, and will then send a request to another node for the data before going to the origin. Therefore, one of the advantages of a distributed cache is the increased cache space that can be had just by adding nodes to the request pool.
Memcached
- Proxies -
- Club requests into one big request to reduce load on the database. Usually a cache is placed in front of the proxy.
- Load Balancer -
- Series of load balancers are also often used.
- Queues -
- To process requests on their own capacity.
- Test everything
- One thing at a time. (You won't know what helped otherwise)
- Data driven development.
- Consistency, Availability and Partition Tolerance! Chose any two. Can't have all 3 in a distributed database.
- Can we sacrifice Partition Tolerance ?
- Not really if there is more than one nodes.
- Garbage collections also can cause this.
- Firewall / bugs in software.
- Can't have a CA system
- Consistency - All writes should be synced with all nodes!
- It's not actually chosing between C, A or P. It means in the time of a network partition, you have to chose between C or A. Can't have both. And Partition is something that can't be avoided.
May 3, 2019
algorithm
- Binary search tree iteration (Get the next smallest element):
- Very fast: Maintain a stack. Keep pushing items and set node to node.left on each iteration.
- Stack would be of size O(h) h = height of the tree.
- Whenever you pop an element, see if that node has a right child, if yes, push that to stack just like before (setting node to node.left each time).
- O(1) fetching and small stack size.
- That's also how you calculate height of a tree.
- Generators for fetching would use very less memory! But slower as access is not O(1)!
- Python's generators (functions that
yieldsomething) can also use recursive return. Just useyield fromwith the recursive function call.
April 22, 2019
algorithm
- Usual tree traversals employ a stack! which uses some memory usually (log(n))!
- Morris traversal doesn't take up space O(1) and O(n) complexity (Finding precursor seems like a big task taking logN, but if you look at the edges, there are atmost two passes over each of (n-1) edges Hence O(n)). Link to the post.
- Steps:
- If the left child of the current node is empty, the current node is output and its right child is used as the current node.
- If the left child of the current node is not empty, find the precursor node of the current node in the middle order traversal in the left subtree of the current node.
- If the right child of the precursor node is empty, set its right child to the current node. The current node is updated to the left child of the current node.
- If the right child of the precursor node is the current node, reset its right child to null (restore the shape of the tree). Output the current node. The current node is updated to the right child of the current node.
April 29, 2019
algorithm
- Count number of 1s in bit representation:
- each number has 2 parts:
- last digit (n%2) which is = n&1
- remaining digits (n/2) which is already calculated in = ret[n>>1]
- Beautiful DP 😍
- each number has 2 parts:
- Can be done in O(n). Use a stack to solve this!
- Push indices on to the stack!
- Make sure the stack has histograms with increasing height! With each histo, store the first occurance for that value on its left! (Remove bigger items when a new small item appears)
- Empty the stack one by one
- NOTE: whenever you remove an item, calculate area by comparing with the new top of stack.
- Actually O(n^2) but can be optimized by storing only the indices in the stack! O(n)!
- Find maximum area rectangle is a version of this problem.
- NOTE TO SELF: Whenever you store something in stack, make sure to store a tuple instead of a single value! You tend to suck otherwise!
April 25, 2019
algorithm
- You have a list of words. See if given word can be formed by using words in the list. (repetitions allowed)
- Brute force approach= all possible words. O(2^n) BAD!
- DP
- Maintain an array which stores if s[:i] can be formed from the list of words.
- Return value is the last item in this array.
- 🤖
April 22, 2019
algorithm
- For each word check suffixes and prefixes.
- If a suffix is a palindrome on its own (make it the center of your new string) and search for the reverse of the corresponding prefix.
- Similarly check the prefixes.
- Done!
- Another approach using Trie:
- Save the reversed words in a Trie.
- Linux Tricks: wow video
- Suspend a running command using
[Ctrl+z]and then send it to background usingbg!- It runs it like it was run with an
&side appended to it.
- It runs it like it was run with an
- Fix a long command that you messed up ?
fc mkdir -p folder/{1..100}/{1..100}etc.- SSH Tunnels:
ssh -L <local-port>:<host-ip>:<host-port> username@domain -N- For managing cloud instances without exposing ports to the internet.
- Suspend a running command using
April 19, 2019
algorithm
- Arguably this requires consistency, durability which are not what redis is known for.
- This article is great!
- Consistent hashing - Used by distributed caches!
- Where(which machine) to send the object, depends on which machine was below that hash number (in a counter clockwise direction or clockwise).
- To distribute load unevenly, one can have x instances of one server and 2x instances of another servers in the hash-ring.
- Great Post on Consistent Hashing
April 19, 2019
algorithm
- Space efficient probabilistic data structures.
- Beautifully uses multiple hash functions when filling up the bloom-filter-bit-array.
- Says DOES NOT EXIST with 100% confidence.
- Says DOES EXIST with a little less confidence.
- This Links to play around with probabilities etc.
April 19, 2019
algorithm
Zipin python expects iterables as it's arguments. It returns an iterable of tuples which takes one from each iterable. (The length of the resulting iterable is = length of the smallest iterable passed to it).- Now that we know all of this:
matrix = [[1,2,3], [4,5,6], [7,8,9]]- Transpose:
[*zip(*matrix)] = [(1, 4, 7), (2, 5, 8), (3, 6, 9)]Beautiful! 😢
- Rotating a matrix now is easier than ever.
- Clockwise: Reverse matrix (rows). Then take it's transpose!
- Anticlockwise: Transpose and then reverse.
- Number of subarrays with sum=k:
- Brute force (eww) = O(n^2)
- HashMap approach (Mind blowing ✨) = O(n)
- 3 variables: counter, map, sumtillnow
for item in arr:sumtillnow += itemcounter += map[sumtillnow-k]map[sumtillnow] += 1
return counter- This approach checks how many k-sum-subarrays end at that point! (Hence it checks the mapper for existing sum-k values in it)
April 14, 2019
msc
- Used a modified LeNet, Pytorch MatrixProfile implementation and finally an LSTM to complete the pipeline.
- Used all subsets from annotations to create folders marked with number of repetitions to prepare the training set.
- Can see end to end deployed in the very near future.
- Only the weights with
requires_grad=Trueneed to be sent to cuda!
April 12, 2019
msc
- Decided to use
torchvision.models.densenet121() - It has 7 million parameters.
- As a toy CNN, using this
April 6, 2019
msc
- Gradients seem to flow! :party:
- Should I make the image pixels learnable ? Instead of using CNN features ? 💣
- How to decide the window size ?
Just in time normalization doubt:
- pdf. The step where I'm supposed to get a scalar between -1 and 1, I get a vector! Stuck there!
- The autograd brute force approach is implemented.
- Sending back gradients now!
April 5, 2019
msc
- Preparing training data for matrix profile training: subproblem:
- Your network is supposed to find the frame which had the minimum distance to your frame
- Maybe learning weights of a 3D convnet using the matrix profile makes more sense for end to end learning.
- With filters of depth = the length of the entire sequence.
- Or better, just convolutions to the frames! and feeding this to an LSTM for counting class assignment!
- Getting a better output from the matrix profile seems more tedious as that would mean you have high correlation frame occurance exactly at the right times. Which means the distance matrix will have to be learned! Which would mean less distance.
- I have reasons to believe, the current implementation of the Matrix Profile is wrong!
April 1,2019
algorithm
- It means find the number which has the same set of digits but is greater than the given number. Link
- Clever tricks: Start iterating from back see if you find a number less than the previous number. Number = 5234976 - Found = 523[4]976
- If you don't, it means the number is the greatest possible number.
- If you do, replace it with the smallest number on it's right. 523[6]97[4]
- And then, ascending sort the numbers on the right! 523[6]479
- You've found the your number 😄
- Python union and intersection: Can't be done with
andandor!set3 = set1.union(set2)is the same asset1 | set2set3 = set1.intersection(set2)
March 27, 2019
algorithm
-
The Dijkstra's algorithm:
-
The
$A^*$ algorithm:
March 26, 2019
algorithm
- One is keep a heap of the first elements from all arrays!
- Better solution:
- Look at the middle element(m) in the largest array, and binary search it's index(i) in all other arrays.
- All elements on the left of that index are less than m and on the right are greater than m.
- See if i1 + i2 + .. == k or < k and based on that update the lists (get rid of elements less than i1, i2 etc. in arrays 1, 2 etc.)!
- Also update k = k - (i1 + i2 + i3)
- Recurse!
- Crazy solution! 💣
- Square matrix ? Think in terms of quad trees! (Split the array in 4 parts!).
- Trap water: Keep track of the left max and right max
- Iterate from the direction whichever is smaller! And keep adding water based on current value - leftmax (if we iterated left)!
- Elegant as 🦆
- Can also use a stack! Less elegant, but works!
March 25, 2019
algorithm
- Common Ancestor: Bottom up! If both left and right subtrees have one of the children, return the current node! else return None!
- Path to a node: BackTracking! Keep appending items to a passed array (by reference) and remove them if result was not found!
- Reverse a linked list inplace: prev, curr, next
while(curr is not None):next = curr.next,curr.next = prev,prev = curr,curr = next- Recursive solutions:
- Head recursive: First and rest: First
reverse(next)then,first.next.next = first, first.next = None.
- Head recursive: First and rest: First
RECURSION TIP: When going bottom up: Store something in a global variable!- Don't always have to return something!
- Return something only when you need like minimums and maximums! like most DPs!
- Stack for building calculator!
- Building your own regex matcher: DP! Build a table with n number of rows and m columns:
- n = length of string + 1
- m = length of pattern + 1
- Didn't quite understand this one!
- Merge Overlapping intervals:
- sort by the starting index before iterating!
- On each iteration, check if the starting index is less than the end of last element in the return array!
- Brilliant! 💡
- Also solves if the person can attend all the meetings!
- When finding the pair (of times etc.) with minimum difference in an array, consider sorting the array first! Then check adjascent elements only ❤️
- Jump game - Maximum jump from a particular position is given. Minimum jumps required to reach end:
- Keep track of current max-reach and last max-reach!
- In each jump-increment-iteration, iterate from i till last max-reach to update the current max-reach!
- Like BFS!
March 24,2019
algorithm
- Bisect - Binary searching and maintaining an ordered list:
import bisectbisect.bisect_left(a,x)will give location where the current element can be inserted in the array! (Before previous occurances)bisect.bisect_right(a,x)will give location where the current element can be inserted in the array! (After previous occurances)bisect.insort_left(a,x)andbisect.insort_right(a,x)actually adds the element!
- Counter - Dictionary of counts of iterable:
- Usage:
c = collections.Counter("reggae") - other methods:
c.update("shark")orc.subtract("lolol")
- Usage:
- Deque - Stacks and Queues - Python Lists are not optimized to perform
pop(0)orinsert(0, x):- Usage:
d = collections.deque(lst, [maxlen]) - Has methods like:
append, appendleft, pop, popleft - Useful methods like
d.rotate(n)Rotate by n steps,d.count(x)count elements equal to x.
- Usage:
- OrderedDict - List of tuples!
- Supports all dictfunctions too!
- Usage:
od = collections.OrderedDict(d)or can submit a dict sorted on keys/vals - useful method:
od.popitem()removes a(k,v)from the end. Can remove from beginning if argumentFalseis passed to it.
- defaultdict - dictionary of lists/sets etc
- Usage
dd = collections.defaultdict(list) set/list/intcan be used for default initialization of the value for the key that is being accessed.
- Usage
- Python reduce has to be imported:
from functools import reduce - Regex:
import rere.searchwill search anywhere in string,re.matchat the beginning (Useless).re.findallwill try to find all occurances!
March 21,2019
algorithm
- Median from a running list ?
- Maintain two heaps! One for smaller elements and one for larger elements! Their tops will contribute to the median.
- Another approach ? Keep a sorted list! Insertion will be O(logn) and median will be the middle of the sorted list! Same complexity simple solution!
- In place array update ? Use an encoding for different cases! (like substitute 2,3,4 when array can actually have only 0s and 1s).
- 2D Matrix with sorted rows and cols. How to find an element in this ?
- O(m + n) soln: Start looking from top right corner: (row=0, col = m)
- If target is bigger -> discard row
- If target is smaller -> discard column
- 🍋
- O(m + n) soln: Start looking from top right corner: (row=0, col = m)
- Rotating an array in place (by k):
a[:k], a[k:] = a[-k:], a[:k]- Or reverse(reverse(
a[:n-k]), reverse(a[n-k:]))
March 21,2019
algorithm
- Is number(n) a power of 3 ? Without loops/recursions ?
- Find biggest power of 3 which is a valid int! (3^19) (call it
a) - Number is a power if
a%n == 0.
- Find biggest power of 3 which is a valid int! (3^19) (call it
- For power of 4, see if number has 1s at odd bit locations!
1, 100, 10000, ..and prepare a mask like10101010101. - Python
a[::2]will give all elements on even locations anda[1::2]will give all on odd locations.a[::-1]will return the reversed array! 🐯a[::2] = some_slice_of_same_sizeinplace! Isn't Python neat ? 🐍
- Dynamic programming: Always use loops to fill up stuff! Instead of recursion!
- Smaller numbers ahead of each number! Loop back from the end and maintain a BST with counts of how many smaller numbers were encountered at each node.
- Increasing subsequence! - DP again! Check sequences of sizes 1 and then 2 etc.
- Keep iterating, if new element is larger than everything, append! else replace/update an existing item in the list! That's it!
- NOTE: the elements will be incorrect, but the length is correct:
- Dry run the seq:
[8, 2, 5, 1, 6, 7, 9, 3]8 -> [8]2 -> [2]5 -> [2, 5]1 -> [1, 5]6 -> [1, 5, 6]7 -> [1, 5, 6, 7]9 -> [1, 5, 6, 7, 9]3 -> [1, 3, 6, 7, 9]Final answer is the length of this sequence found! (The elements in the sequence are incorrect though!)
- A poorer DP O(n^2) solution also exists:
for i in range(len(A))nestfor j in range(0,i), keep track of all the sequences that end atA[i]
March 20,2019
algorithm
- Maximum Length Subarray: (Kanade's algorithm O(n)) Keep track of global minimum subarray and of minLengthSubarray from the left. if sum is +ve of the subarray, it must be added to the right side!
- Best day to buy/sell stocks is also a version of this problem.
- Sharding : Split database by a key (say city ID). That's it, each shard is a different server. Easier to scale! Boom!
- Hash functions : Mod by the maximum number of positions available!
- Consistent Hash Ring : LoadBalancing/Caching/Cassandra uses it too. Instead of looking for the exact key from the hash function output, store the result in the next address-which is bigger than the key! If all locations are smaller, put it in the first element! Hence the ring 💍!
March 19,2019
algorithm
- When finding longest substring, split on problematic point and recurse!
- When having to use a quad loop, see if two double-loops and a dict can suffice!
- Data structure for O(1) insert delete and randomsample = list + dict with keys as items and values as index locations of those items in the list.
- In a 2D array, if rows and columns are sorted, find top n elements! Create the first row as a heap and keep adding the items from the last used column to it!
heapq.heappush and heapq.heappop - Bits! For a 32 bit integer max number = 0x7FFFFFFF (as if the first bit is 1, the number is negative).
- Why do we need this ? If the final result is greater than this max value, that means the number is negative. First, find the absolute value of this -ve number is found which is always: **IN PYTHON: **
-x = complement(x-1) - And then the pythonic complement is found!
~()which will be the actual negative number!
- Why do we need this ? If the final result is greater than this max value, that means the number is negative. First, find the absolute value of this -ve number is found which is always: **IN PYTHON: **
- Recursively reverse an array! =
rev(arr[l/2:]) + rev(arr[:l/2])
March 18, 2019
- Python since 3.6 has static type checking!
from typing import Dict, List, Tuple, Anya: List[Dict[str, int]] = [{"yellow":10}]- Complex types can also be assigned to other variables!
-
Awesome functions like
.nsmallest(n, iterable)/ .merge(*iterables) -
Use it as:
heapq.heapify(lst) #inplaceThen useheapq.heappush(heap, val)orheappop(heap) -
More python trickery:
print("xyz"*False or "yellow") will print yellow
March 15, 2019
algorithm
- Use 2 dicts to solve this!
- Great Problem
- How to find all possible triplets ?
- Recursively call the function that adds to a global array!
- Append only if the size of the triplet is 3.
- Call the function like merge_sort! without having to return anything!
- If the message exceeds the given max_size, all the messages will be prepended with some text of fixed length!
- Good Problem!
March 11, 2019
algorithm
- This is also known as common child problem. Two strings with deletion allowed, what is the longest list of characters common to both strings (in order ofcourse).
- NP hard problem.
- This has optimal substructure and overlapping subproblems! Enter Dynamic Programming! g4g
- Suppose substrings are lcs(A[:n-1], B[:m-1])
- If the last character is the same, subsequence length = 1 + lcs(A[:n-2], B[:m-2])
- Else it is = max(lcs(A[:n-2], B[:m-1]), lcs(A[:n-1], B[:m-2]))
- Weird Hackerrank bug - when your program times out in
Python3submit the same inPyPy3and see if it runs :|
March 11, 2019
algorithm
- Generators are just wrappers around closures internally.
- Use List comprehensions (
[x*2 for x in range(256)]) when you need to iterate over the sequence multiple times. - Use Generators (
(x*2 for x in range(256))) (same asyield) when you need to iterate over the sequence once! - xrange uses yielding(generator) and range creates the list. (Python3's range = Python2's xrange)
- Sorting a string in python:
''.join(sorted(a)) - Find all substrings in a string:
- use a nested loop. Inner loop iterating from i to length! (Keep yielding the results)
March 8, 2019
algorithm
- TIP: Don't always think recursively. Think if there is a optimized loop solution possible.
- TIP: Whenever you want parallel execution(inside recursion), think of a queue (like Breadth First Search)!
- Total possible moves by a knight are 8.
- Keep popping elements from this q in a loop.
- For each item popped, add to the q the next possible 8 moves.
- Pythonic: Init a 2D array using array comprehension
[[0]*n for i in range(n)]💣
- Dynamic, High-Level(like Python) JIT compiler and Fast(like C) for scientific computing.
brew cask install julia- GitHub Link
MiniZinc:- Parameters - (Constants that don't change)
int: budget = 1000; - Variables - (Variables that you want to compute)
var 0..1000: a; - Constraints - (Constraints on variables)
constraint a + b < budget; - Solver - (Solve the optimization problem)
solve maximize 3*a + 2*b;orsolve satisfy
- Parameters - (Constants that don't change)
- More MiniZinc Tricks:
enum COLOR = {RED, GREEN, BLUE}then vars can be of typeCOLORlikevar COLOR: a;- To get all solutions run with flag
minizinc --all-solutions test.mzn - Parameters can be given a value later on using a file with extension
.dznlikeminizinc test.mzn values.dzn(The model MUST be provided with the values of the parameters from a single / multiple dzn files) - Array declarations for parameters:
array[range/enum] of int: arr1- 2D
array[enum1, enum2] of float: consumption - Generator operations on arrays:
constraint forall(i in enum)(arr1[i] >= 0)solve maximize sum(i in enum)(arr1[i]*2) < 10
- Array Comprehensions:
[expression | generator, generator2 where condition]- example:
[i+j | i,j in 1..4 where i < j]
- example:
- TLDR:
- enums to name objects
- arrays to capture information about objects
- comprehensions for building constraints
If elsecan be used inside forall blocks and outside the nested forall blocks.if condition then <blah> else <blah2> endif
March 7, 2019
- Use Pyglet for making graphics in Python.
- Use Q-Learning! It's great!
- This code-bullet video is great!
- Pythonic way to do it:
reversed(list(enumerate(lst)))
March 6, 2019
algorithm
- Transpose first -
- You transpose only on one side of the diagonal. (Inner loop should be
for j in range(i,n)- OR -for j in range(0,i))
- You transpose only on one side of the diagonal. (Inner loop should be
- Then reverse column order
- Easy Peasy!
- Pythonic array init
a = [0]*10 - Pythonic
for i in range(a,b)Remember that b in this is not inclusive! - Suppose, in an array, something(x) is added from range p to q for each test-row. Find maximum element in the final array:
- Store x in arr[p] and -x in arr[q], so while iterating from left to right, the items will be +x only in the range p to q. 😮
March 4, 2019
msc
- This paper for Visual Rhythm Prediction with Feature-Aligning Network seems useful.
- Various features could be used like:
- Original Frames
- Frame Residuals
- Optical Flow Detection
- Scene change detection
- Body Pose detection
- The features could be misaligned as some features just depend on one frame while others depend on multiple frames.
- Solution: Feature Alignment Layer
- Employs Attention mechanism which is a hit in NLP
- Solution: Feature Alignment Layer
- Finally sequence labelling with BiLSTM
- Also a [Conditional Random Field] layer to make prediction aware of consecutive predictions. (Instead of my existing Linear layer ?)
Feb 27, 2019
- Make a function in your server callable through the clients.
- Makes use of Google's protocol buffers instead of (JSON in REST etc.)
- Serve SDKs instead of APIs.
- Nice gRPC python example.
Feb 26, 2019
- Completed video capture and matrix profile generation. (NON REAL TIME)
- Next task is count-classes for sure.
- Batching windows into fixed size regions (100 frames).
- Thinking of using classes 0-10 in this region.
Feb 12, 2019
msc
- Should I keep a fixed window and have classes for respective counts ?
- Should I let the window size be variable and have a moving class count ?
algorithm
- Quicksort - remember
return quicksort(arr[:pivotPosition]) + [pivot] + quicksort(arr[pivotPosition+1:]) - Mergesort - remember
return arr- Calls
mergesort(left)andmergesort(right)internally.
- Calls
Feb 9, 2019
- Google Docs:
Tools > Voice Typing🐙 - Gonna start typing 😉 tonight!
msc
- Decided to use some numpy Gaussian Noise with a decided mean and std to generate noise.
- Applied noise on normalized waves (values between 0 - 1) so, if we decide on a mu/sigma (say 0, 0.1), we'll know that for 60% of the waves a maximum of 10% distortion will be added to the signal.
Feb 3, 2019
- New connections in Cloudera, Goldman.
- Gooogleeee
- GoLang Delve Debugging.
Jan 30, 2019
msc
- Submitted in 2019. Next task = Read this paper.
- "Wavelets in a wave are like words in a sentence" - Jan Van Gemert
- Try adding noise to my sine waves.
- Have counting classes at the end instead of peaks and valleys.
- Read papers Visual Rhythm Prediction and Video CNN
- Maybe also try:
- Training an LSTM from scratch
- Use a stacked LSTM with the first one being my peak detector.
Jan 29, 2019
- It can replace a
try-finallyblock - It is used as a context manager.
- Can be implemented by implementing
__enter__and__exit__methods in a class!
- LSTMs trained just on sine waves showed some good signs on the Matrix Profile ❤️
- Waiting for the meeting to decide how to make it and end to end model!
Jan 22, 2019
- Came across this nice short tutorial for creating my first tiny sublime text plugin.
- I have decided to call it
meow - 🐱
- Finished it. Find it here
msc
- I was expecting LSTMs to be better, (They were probably overfitting). TCNs show a better understanding of the curves (judging by the learned probabilities).
Jan 22, 2019
msc
- Nice blog post
- Given a sequence of occurences, what is the probability that the dice rolled was biassed or unbiassed ? (Could this be used for our scenario ?) Given a sequence of matrix profile inputs, what is the prob that there were 2 peaks, 4 peaks etc. ?
- A Conditional Random Field* (CRF) is a standard model for predicting the most likely sequence of labels that correspond to a sequence of inputs.
Jan 22, 2019
- Poisson ~ counting process.
- Probability of Number of occurences (k) in a small time interval (h).
$P[X(h + s) - X(s) = k]$ =$\frac{(\lambda h)^k e^{-\lambda.h}}{k !}$ - These interval probabilities are conditionally independent!
- Expected Number of occurences in interval (h) =
$\lambda. h$ - Sum of two poisson processes is also a poisson with
$\lambda s$ added. - Uniform distribution: If an event of a Poisson Process occurs during interval [0, t], the time of occurance of this event is uniformly distributed over [0, t].
-
PROBLEMS TAKEAWAY:- Don't forget the law of total probabilities (Summation) for calculating PDFs with a variable input etc. There can be questions with a mixture of Poisson (Probability that Count of something is k) and Bernoulli (Probability that number of successes is k) distributions.
- From a combination of poissons, Given an arrival: prob that arrival was from p1 =
$\frac{\lambda_1}{\lambda_1 + \lambda_2}$ - This will be just a product if not given an arrival. (Bayes! Duh!)
-
A joint flow can also be decomposed with rates
$\lambda.p$ and$\lambda.(1-p)$ (Instead of mixing it up with a binomial).
- Maximising winning probability = equate first derivative to 0 and solve!
- For calculating the prob from x to infinity, don't forget you can always compute it as [ 1 - P(0 to x)].
Jan 17, 2019
- Found an issue to work on in Spotify's Luigi. Working on creating a pull request for the same.
- Currently, a dictionary {bool, worker} is returned along with the worker details.
- an object of type
LuigiRunResultshould be returned
- Got responses from
BeatsandLuigion the PRs. 😍
Jan 15, 2019
msc
- Should I use the (n x n) distance profile for my training ?
- IDEA: Make use of the fact that a repetition means it has a peak and the part after the peak is a mirror of the part before the peak.
- Video by Siraj
- New neural networks for time series datasets. (Uses integral calculus)
- Remember residual nets
$x_{k+1} = x_{k} + F(x_k)$ can be written as$x_{k+1} = x_{k} + h.F(x_k)$ - Find original function by taking integral of the derivative.
- Frame your net as an ODE!
- Use ODE solvers after that like Euler's method or better (Adjoint Method)
- Tutorial
sudo apt-get install build-essential
target: dependency1 dependency2 ...
[TAB] action1
[TAB] action2
- Target can be all, clean etc.
- all/First target is executed if make is run without arguments. Otherwise
make target - Target can also be filenames. If targets and filenames clash, avoid these targets to be treated as files :
.PHONY: all clean - Dry run =
make -n @echo $(shell ls)to print output of ls command- Running make inside subdirectories:
subtargets:
cd subdirectory && $(MAKE)
include 2ndmakefileto halt current makefile execution and execute the other makefile.- Use prefix
-with actions/include to ignore errors.
Jan 13, 2019
- Created a pull request with my new beat 💃
- Following these MIT Lectures for Applied probability
- Poisson is just Bernoulli trials with n (number of trials) (Granularity) approaching infinity.
- Success = Arrival
- Memoryless
- Causal = Based on what has happened before.
Jan 10, 2019
msc
- Golang has tags which are just backticks. These add meta information to struct fields and can be accessed by using the reflect package
import "reflect"type Name struct { VariableName int mytag:"variableName" }obj = Name{12};r = reflect.TypeOf(obj);field, found := r.FieldByName(VariableName)field.Tag.Get("mytag")
- These tags make having a config like .yaml easier!
- Your beat implements ** Run, Stop and New ** methods.
- If you add new configs to .yaml, add them to
_meta/beat.yamland also to the code inconfig/config.go - If you add more fields in the published message, add them to Run method and also in
_meta/fields.yml- Use make update after any of the above changes!
Jan 9, 2019
- I have decided to contribute to Elastic Beats! Cz go go go!
- Following these setup instructions.
- Use EditorConfig file for your open-source projects fellas! Installed the sublime plugin.
magefile= Make like tool for converting go-functions to make-target like executables.- Installed govendor for dependency management.
- Beats contain
- Data collection logic aka The Beater!
- Publisher - (Implemented already by
libbeatwhich is a utility for creating custom beats)
- Bare minimum message requirements:
- Message should be of type
map[string]interface{}(like JSON) - should contain fields
@timestampandtype
- Message should be of type
- Virtual environment python2
go get github.com/magefile/mage- After breaking my head for hours!
- Update in Makefile in
$GOPATH/src/github.com/elastic/beats/libbeat/scripts/Makefile: change this key to:ES_BEATS?=./vendor/github.com/elastic/beats(It has a comment next to it, but this was not mentioned in the docs for some reason) - Install a fresh Python2.7 from conda (I used the bash setup for my Mac)
- Create a virtualenvironment in folder
yourbeat/build/with the namepython-env
- Update in Makefile in
- Run
make setupinside your beat folder - Need to play around with Make!
- Next episode = Writing the Beater!
- Just print the model to see what the architecture looks like.
model.state_dict()contains all the weights (layer-wise)- Use
torchvision.utils.make_gridto plot them all.
Jan 7, 2019
msc
Idea to make it end to end trainable. Can I use policy gradients to make it end to end trainable ? Reward the states which end up in the correct count ? Woah! Can I ?- Policy gradient on top of the matrix profile output ?
- Good Toy task - make the Net remember a sequence of numbers pattern!
- Peak counter presentation link
Jan 6, 2019
Following the Go Tour now!
- Workspace =
~/go/src/( Typically a single workspace is used for all go-programs) (All repositories inside this workspace ) (Usually create a folder structure like~/go/src/github.com/live-wire/project/to avoid clashes in the future)-
$ go env GOPATH(Set the environment variable GOPATH to change the workspace)
-
-
$ go filename.gogenerates an executable binary! -
$ go installin this folder adds that binary to~/go/bin/(Make sure it is added to PATH so you can run the installed packages right away) - Go discourages use of Symlinks in the workspace
- Workspace contains
srcandbin - Use
go buildto see if your program compiles - First line in a Go program must be
package blahwhere the files belonging to this package must all have this. This package name must not always be unique, just the path where it resides should be! Usepackage mainfor executables. - Importing packages
"fmt"
"github.com/live-wire/util" )
fmt.Println(util.something)
- Testing. A file blah_test.go will have the tests:
import "testing" - Looping over variableName which could be an array, slice, string, or map (use range):
for key,value := range variableName {}
- Capitalize the stuff in the file that you want to export to other packages!
- Named return. Name the return values and assign them inside the function
ret1 = a + b
ret2 = a - b
return
}
var a,b = true, "lol"Usevarover:=everywhere!- If in go can have a small declaration before the condition (whose scope ends with if)
defercalls function after the surrounding function returns! (All defers are pushed to a stack)- Pointers var p *int
- i = 24; p = &i (*p = i)
- Structs = collections of fields
A int
B int
}
- Pointers to structs can access the fields without using the star!
p = *lol; p.A = 12instead of(*p).A = 12 - Slices are just references to the underlying arrays
cats = [3]string{"peppy", "potat", "blackie"}; potat := cats[0:2]Anything can be appended to these slices but not to the arrays.potat = append(potat, "tom") - Maps:
map[keytype]valuetypemake sure to surround it all withmake(..)when initializing - Function pointers:
func (v *Vertex) fun(arg int) {}can be called asv.fun(10)(The star makes it in-place)- define a
String()function for a struct like python's__str__and__repr__functions.
- define a
- Interfaces:
type I interface { M()}Now all variables of type I will have to implement this function. Likefunc (t *T) M() {}now all variables of type T will have a function available called M and can be casted to type I.- Each variable is of type
interface{}
- Each variable is of type
- Errors: cast the erroneous variable with the error class.
- define
type ErrType float64 func (e ErrType) Error()string { return fmt.Sprintf("%f",e) }- Use it as
ErrType(12.23) - It will also be of type error!
- define
- Go Routines:
- Usage
go functionName()
- Usage
- Channels (For communication among go-routines): (Like maps and slices, channels must be created before use)
ch := make(chan int)- Channels need to close themselves by calling when
close(c)when reading in a loop (to exit a range)for i := range c {}
- To select a channel to run:
case res := <-resc:
fmt.Println(res)
case err := <-errc:
fmt.Println(err)
}
}
- This is important as `select` makes the current routine wait for communication on the respective channels! Can be used to make the main thread wait!
- Mutex (Mutual exclusion): Thread safety, sharing resources by locking/unclocking them (Counters)
import "sync"- Create a struct with a field say
muxof typesync.Mutex - This field has functions Lock() and Unlock() attached to it.
- Example:
st.mux.Lock() // Your object Locked
defer st.mux.Unlock() // called after this function ends
st.counter ++
// NEAT!
}
Jan 2, 2019
- [Blog post] by Karpathy on Reinforcement Learning!
- Good video by Xander.
- Deep Q Learning with function approximation (which can be a CNN etc.)
- "Whenever there is a disconnect between how magical something seems and how simple it is under the hood I get all antsy and really want to write a blog post" - Karpathy You Go Boy!
- Policy Gradients are end to end trainable and favourites for attacking Reinforcement Learning problems.
- Needs billions of samples for training as the rewarding set of moves will occur not-so-frequently. And it needs a lot of them to be able to make a policy that leads to rewards.
- Nice take-away = Policy gradients help incorporate stochastic, non-differentiable flows which can be backpropagated through. Stochastic computation paths. These work best if there are a few discrete choices.
- Trust Region Policy is generally used in practice. (Monotonically improves)
- Keyboard/mouse input programatically = Pyautogui
- Applying for AI jobs! In amazing teams? Be useful to them! Read what they must be reading right now!
Jan 1, 2019
- Could TCNs replace LSTMs for Sequence Tasks ?
- TCNs have a longer memory and have Convolutions (faster to train, fewer parameters)
- TCNs employs residual modules instead of simple conv layers with dilations.
- It employs
Weight Normalization- For each layer, before applying the activations, normalize! ((x - mean) / std)
- Recap:
Batch Normalizationnormalizes values out of the activation function.
- It employs
- I could also try to implement a bi-directional TCN as I did with CNN 😏
- Looking at Copy Memory task from the TCN implementation.
Applying TCN was not learning that well. I used ELU instead of RELU in the TemporalBlock of the TCN implementationIt significantly improved the learning results.- Also implemented the bidirectional variant of TCN and as expected, it does better than the unidirectional one!
- Pretty happy with these TCN results and planning to use this as the peak detection model if not LSTM/GRU!
Align the existing labels of repetitions by dragging them along the time axis such that it minimizes the loss- Think of ways to auto-label the dataset.
Dec 31, 2018
- Need to play around with the deepdream notebook of google and generate some art!
- Implemented the loss-plotter for plotting the moving average of my bidirectional CNN experiment. My implementation of the bidirectional CNN has more learnable parameters, so not a fair competition!
- See you next year. 🍻
Dec 29, 2018
msc
- Convolutions Visualizer
- Output size after convolutions: discuss.pytorch post
o = [i + 2*p - k - (k-1)*(d-1)]/s + 1(o = output, p = padding, k = kernel_size, s = stride, d = dilation)
- A dilated kernel is a a huge sparse kernel!
- Got a simple CNN with dilations to learn like an LSTM learns a sequence. It is okay but not great! But look at the number of parameters it needs 😮 only 18 compared to over 1000 in LSTMs.
- Reading this paper now and planning to implement TCNs for my sequence modelling task. It should give me a better feel about how to use convolutions with dilations instead of LSTMs. (Bi-directional LSTMs already look promising for the task)
How about a new Convolutional architecture that mimics the bi-directional nature of LSTMs ?- Use
torch.flipto reverse a tensor. link
- Use
- Finished first draft of my own Bidirectional CNN with dilations! It clearly works better than a (conventional) unidirectional CNN without dilations!
- Next experiment = trying TCN
Dec 28, 2018
- Serialization and Deserialization wrapper for several languages!
- Tutorial
- Ideology:
- Low level features are local! (Kernels and Convolutions)
- What's useful in one place will also be useful in another place in the image. (Weight sharing in kernels)
- Smaller kernel = more information = more confusion
- Larger kernel = More information = Less attention to detail
- Output of a convolution layer:
- Depth = Number of filters applied
- Width, Height =
$W=\frac{W−F+2P}{S} + 1$ (where W is current width, F is filter width (receptive field, P = padding, S = Stride)) - Recommended settings for keeping same dimensions = (S = 1) and (P = (F-1)/2)
Dec 23, 2018
- Chat with Juergen Schmidhuber
- Self-Improving computer program that solves problems in an optimal way. Adds a constant overhead (which seems huge/infeasible to us right now for the problems at hand but it is constant.) But if you think of all-problems (Googol problems), this is a big-big thing. Right ?
- LSTMs and RNNs are just looking for local minimums by descending down them gradients. Imbecile! lol!
- Look for a shortest program that can create a universe! Only the random points create problems and big lines of code (not compressible - more bits to be described). The most fundamental things of nature can be described in a few lines of code.
- Seemingly random = Not understood as of now! = UGLY!
msc
- There are other activations like ELU, SELU etc.
- They make RELU differentiable at x=0! (RELU =
$max(0,x)$ , ELU = $max(0,x) + min(0, \alpha*(exp(x)-1))$)
- They make RELU differentiable at x=0! (RELU =
- Learnable parameters in 1D-CNNs = For each kernel: kernel_params + 1 (bias)
- 1D CNN Pytorch:
- Input/Output = (N (Batch size), C(input/output channels), L(length of sequence))
- 1D CNN Pytorch:
Try to make a bidirectional CNN with dilations model!- Looks like I wasn't employing the dilations before. Was just using the FCN. 🙈
Dec 22, 2018
Bidirectional=Truewith same number of hidden parameters (actually multiplied by 2 for both directions), performs much better for peak detection.- Make sure to double the input params of the linear layer that follows it when you make it bidirectional.
- A fair competition would be competing against a regular(unidirectional) LSTM with double the hidden units.
- Calculating parameters in a bidirectional LSTM/GRU/RNN:
- First Layer: 2 * (inp * hidden + hidden) (Multiplied by 2 as bidirectional)
- Output of first/upcoming hidden layers: 2 * (hidden*hidden + hidden)
- Input of second/upcoming hidden layers: 2 * ((hidden+hidden)*hidden + hidden)
- Output same as before.
- 💣
- Model trained on sequence length 50 does alright on sequences of length 100 as well.
- Need to try Convolutions with dilations now.
Dec 17, 2018
- Set up docker for my project community
- Docker networking
ports: [host:container](Compose creates a network in which all the containers reside) docker psshows all containersdocker exec -it <containerid> /bin/bashto open a containerdocker system pruneremove dangling images- Docker volumes = shared storage for containers on the host!
- Docker networking
- TODO: Play around with container networking! (Crucial before setting up some Nginxes)
msc
- Number of parameters in an RNN (LSTM)
torch.nn.Modulemodel is NOT DEPENDENT on the sequence length- Longer the sequence, the harder it will be to understand for a simple model.
- Number of parameters explained:
- Weights multiplied by 4 for all the 4 sets of Weights and Biases
Wlink. Number of weights and biases is multiplied by 3 for GRUs and 1 for regular RNNs. - Into an LSTM layer:
- input --> hidden_dim (input*hidden_dim + hidden_dim) * 4
- Coming out from an LSTM layer:
- It should output something with dimensions = hidden_dim because it also needs to be fed back to possibly more layers!
- hidden_dim --> hidden_dim (hidden_dim*hidden_dim + hidden_dim) * 4
- ⚡️
- Weights multiplied by 4 for all the 4 sets of Weights and Biases
- Since the sequence length doesn't account for a change in parameters, the same model can be trained over several sequence lengths to make it more robust!
How to make the final model end to end trainable?
Dec 14, 2018
msc
Idea: Should I one hot encode X values(by categorizing them into range categories) as well ?- ^ ^ Not required I guess! LSTM does well (for small sequences of length 20 or so) using Cross-Entropy-Loss. (Negative log of Softmax! as the loss).
- Followed the following steps:
- Generate class-wise scores using the output of a NN (RNN-LSTM-2 Layers and 10 hidden units for today's experiments)
- Use
torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()as thecriterionto get the loss by comparing output and target! - Call
loss.backward()to backpropagate the loss andoptimizer.step()to actually update the weights. - Now your model will output the class scores!
- Use
torch.nn.functional.softmax(torch.squeeze(output), 1)to get an interpretable probabilistic output per class. ❤️
- Rock on 🤘
Dec 11, 2018
algorithm
- Create functions like
__eq__(self, other),__le__(self, other)inside the class to overload the corresponding operators. Compare the objects of your classes like a boss! - Use the decorator
@staticmethodwith a function in a class to mark it as a static method. This will be callable by ClassName.method or classObject.method! - Override methods
__str__to make the object printable when printed directly and__repr__to make the object printable even when a part of an array etc.
Heapify RECAP
- Heapify! = log(n) = (Trickle down! ALWAYS TRICKLE DOWN)
- Insert element at the top and call heapify once.
- Pop element by first swapping the first with the last and removing the last! Then call heapify once.
- BuildHeap = n/2 * log(n) = (Start from bottom) check children for heap property (trickle up)
- loop from items n/2 to 1 and call heapify on all of them! (Called once initially!)
Dec 6, 2018
msc
- combining multiple generators -
from itertools import chaingenerator3 = chain(generator1(), generator2())
- Sine waves - Manual Peak detection can look at the local minimas and maximas! What about the global characteristics ? How to tackle them ? :sad:
- Wrote
sine_generator.pyto generate X, Y from the sine waves generated. -
IDEA: Maybe merge the wavelet peaks that are too close to each other based on a threshold- Or prune based on amplitude/stretch_factor on both sides of the peak.
-
Fourier transform: Get the original bunch of waves from the combination wave
- It will show spikes where the actual components occur.
- Wind the wave into a circle, the center of mass shifts(on changing the wind frequency) only when it finds a component frequency.
- How ?
Integral of -$g(t)e^{2\pi i f t}$ (Depicts the center of mass (scaled)).
Dec 4, 2018
- Amazing project by NVIDIA. It renders the world after training on real videos.
- Want a setup whenever you open python console ?
- Set an environment variable
PYTHONSTARTUPwith the path to a python file that imports stuff! 💣
- Set an environment variable
msc
- Generating sine-wavelets is taking some shape. The variables when generating a combination of sine-wavelets are:
- begin = 0 # Can have values 0 or pi/2 (growing or decreasing function)
- wavelength_factor = 0.5 # chop the wave (values between 0 and 1)
- stretch_factor = 3 # Stretch the wave to span more/less than 2pi
- amplitude_factor = 0.5 # Increase/decrease the height of each curve
- ground = 2 # base line for the wave
Dec 3, 2018
msc
-Yield in Python If a function yields something instead of return, it is a generator function which can be iterated upon. try calling next(f) on f where f = gen_function(). It will return the next value from the generator. - It reduces the memory footprint! and is coool!
- Generating a bunch of sine-waves today.
np.linspace(start, end, num)gives num values between start and end.tensor.view()is like reshape of numpy (-1 means calculate its value based on the other parameters specified)Prophet: Forecasting procedure implemented by Facebook. link. It's nice for periodic data with a trend. (It assumes there is yearly, monthly, weekly data available). post- Experimenting with sine-wavelets! Trying to create complex randomized sine-waves with varying [amplitude, wavelength (cropping the wave), stretch factor (making the wave span less or more than 2pi) and ground (the base of the wave which is 0 by default)].
Idea: Will it be possible to model the matrix-profile as sine-wavelets using regression ?Idea for RealTime: Learn a wavelet-like-sequence-of-frames from the given video that represents a repetitionIdea: more than one frame at a time to the matrix profile
Dec 2, 2018
msc
- Link to my summary of the paper
- Use softmax to discretize the output and model conditional distributions. If there are way too many output values, use the
$\mu$ -law. (Try Mu-law or some alternative) - Look at LS-SVR Lest square support vector regression.
- Also try the Gated-activation-units (tanh, sigmoid approach like pixelCNN, Wavenet) instead of regular RELUs.
- Seems like WaveNets are cheaper than LSTMs. So my experiments shoule be in this order.
- Skip-Connections: If some future layers(like the fully connected ones) need some information from the initial layers (like edges etc.) that might be otherwise lost/made too abstract.
- Residual Learning: Like skip connections, allow the gradients to flow back freely. Force the networks to learn something new with every new layer added. (Also handle the vanishing gradient problem)
-
Cool Convolutions:
- Kernel for box-blur = np.ones((3,3)) / 9 (Note that sum of all values in the kernel = 1)
- Edge detection: all -1s, center = 8
- Sobel Edge (less affected by noise)= [[-1, -2, -1],[0,0,0],[1, 2, 1]]
Nov 28, 2018
msc
- Link to my summary of the paper
- Reading the paper Conditional Image generation using PixelCNN Decoders. Link
- PixelCNN employs the Conditional Gated PixelCNN on portraits. It uses Flicker Images and crops them using a face detector!
- Face Embeddings are generated using a triplet loss function which ensures that embeddings for one person are further away from embeddings for other people. (FaceNet link)
- Use Linear Interpolation (between a pair of embeddings) to generate a smooth output from one to the next generation. Looks beautiful! DeepMind's generations.
Nov 28, 2018
msc
- Idea - find the sequence of images in the video that show the maximum similarity when super-imposed on the upcoming frames.
- Activation functions and derivatives:
-
LSTM: link
Notations:$h_t$ = output at each time step,$C_t$ = Cell State,$x_t$ = Input at a time step.- Forget Gate: I consumes the previous time step, merges it with current input, passes it through a sigmoid gate output(0 to 1) and pointwise multiplies the result with the cell state. (It specifies how much needs to be passed to the next state).
$f_t = \sigma (W_f[h_{t-1}, x_t] + b_f)$ (This square brackets means the h and x are concatenated and more weights for W_f to learn) - Cell state: It decides what needs to be saved in the current state. It takes the output from pointwise multiplication of forget gate and old cell-state and then adds (the tanh of current input and sigmoid of current input(for making it range from 0 to 1))
$i_t = \sigma (W_i[h_{t-1}, x_t] + b_i)$
$C_t^{-} =tanh(W_c[h_{t-1}, x_t] + b_c)$
$C_t = C_t^{-} * i_t + f_t * C_{t-1}$ (Here * is pointwise multiplication) (This is the state stored for this cell that is forwarded to the next time-step) - Output: We still haven't figured out what to output (
$h_t$ ). Now take this computed cell state, tanh it to make it span from -1 to 1 and pointwise multiply it with the sigmoid of current input.
$h_t = tanh(C_t) * \sigma (W_o[h_{t-1}, x_t] + b_o)$ This output is then sent upward (out) and also to the next time step. - Easy peasy 🍋 squeezy!
- Forget Gate: I consumes the previous time step, merges it with current input, passes it through a sigmoid gate output(0 to 1) and pointwise multiplies the result with the cell state. (It specifies how much needs to be passed to the next state).
-
LSTM Variants:
- There is a variant which uses coupled forget and input gates: merges sigmoids for
$f_t$ and$i_t$ and uses$1 - f_t$ instead of$i_t$ . - There is a variant which uses peep-hole connections everywhere (Adds State value C_t everywhere in all W[]s)
-
GRU:
- No Cell state variable to be forwarded through timesteps.
- Only output is generated which is propagated up and to the next timestep.
- Lesser parameters to train.
- Uses the coupled forget and input gates idea.
-
$f_t = \sigma (W_f[h_{t-1}, x_t] + b_f)$
$c_t = \sigma (W_c[h_{t-1}, x_t] + b_c)$
$h_t^{-} = tanh (W_o[c_t * h_{t-1}, x_t] + b_o)$
$h_t = (1 - f_t)*h_{t-1} + f_t * h_t^{-}$ -> This is the output that is forwarded upwards and into the next time step.
- Probably experiment with this as well, as it has lesser parameters to train for the small dataset we have.
- There is a variant which uses coupled forget and input gates: merges sigmoids for
Nov 27, 2018
algorithm
- Making your implementation of (say a LinkedList) iterable in Python:
- Declare a member variable which contains the current (
__current) element (for iterations) - Declare function
__iter__which inits the first element in__currentand returns self! - Declare function
__next__which callsStopIteration()or updates the__currentand returns the actual item(node)! - 💣 You can now do a
for node in LinkedList:(elegant af)
- Declare a member variable which contains the current (
-
Self-balancing trees : (AVL Trees, Red-Black Trees, B-trees)
-
B-Trees link: Generalization of a 2-3 tree (Inorder traversal = sorted list. Node can have 1 (and 2 children) or 2 keys (and 3 children))
- All leaves must be at the same level
- Number of children = x is
$B<= x < 2B$ (Note the < sign in upper bound) - If B = 2, It is a 2-3 tree (2 Keys, 3 children)
- Insertion is okay, when overflows (more elements in a node than the allowed number of keys), move the middle element up. If keeps overflowing, keep going up till you reach the root.
- Deletion - Trickier! Delete the node, Rotation!
- Why? - Large datasets - On-disk data structure (not in-memory). It makes fewer larger accesses to the disk! - they are basically like maps with sorted keys (that can enable range operations)!
- Databases nowadays usually implement B+ trees (store data in leaves and don't waste space) and not B-trees.
-
B-Trees link: Generalization of a 2-3 tree (Inorder traversal = sorted list. Node can have 1 (and 2 children) or 2 keys (and 3 children))
Nov 26, 2018
- Autoencoders: Lower dimensional latent space link
- Variational Autoencoders: Instead of bottleneck neurons, a distribution is learned (mean and variance) (Backpropagation Reparamatrized trick is used where the stochastic part is kept separate from mean and std. so gradients can flow back)
- New Type: Disentangled Variational Autoencoder - Changing the latent variables leads to interpretable things in the input space (few causal features from a high dimensional space - latent variables (and understandable)).
Nov 25, 2018
msc
- Link to my summary of the paper
- Going through the PixelRNN paper as it is kind of a prerequisite for WaveNet.
- Latent Variables: link
- Latent variable is not directly observable by the machine (potentially observable - hypothesis - using features and examples)
- In most interesting datasets, there are no/missing labels!
- Principal Component Analysis / Maximum Likelihood estimation / Variational AutoEncoders. We use it when some data is missing! Who else uses this ? - Auto Encoders.
- Latent variables capture, in some way, an underlying phenomenon in the system being investigated
- After calculating the latent variables in a system, we can use these fewer number of variables, instead of the K columns of raw data. This is because the actual measurements are correlated with the latent variable
- Two Dimensional RNNs link used for generating patterns in images.
- Autoregressive - A value is a function of itself (in a previous timestep). AR(1) means the process includes instance of t-1.
- Uber's pyro - Probabilistic programming (Bayesian statistics) with PyTorch. Build Bayessian Deep learning models.
- Traditional ML models like XGBoost and RandomForests don't work well with small data. source
- Used for Semi-supervised learning.
- Variational inference models for time-series forecasting ? SVI ? (IDEA ?
msc?)
Nov 14, 2018
algorithm
- Decision Trees:
Baggingmight not necessarily give better results but the results will have lower variance and will be more reliable / reproducible. - Checking if a tree is a BST: Keep track of the min and max value in the subtree! That's all!
Nov 12, 2018
msc
- Crazy reddit post
- Papers to read series: PixelRNN/PixelCNN/WaveNet/ByteNet
- ConvNets haven't been able to beat RNNs in question answering (Can't keep running hidden state of the past like RNNs)
IDEA: Try to generate a sine wave based on the number of repetitions in the duration specified! Minimize Loss somehow! How to deal with repetitions of varying lengths though ?IDEA: Think of a minimum repetition wave, try to minimize loss by varying the wavelength. The entire signal could be a combination of such wave-lets(scaled)
Nov 9, 2018
Maths Numbers Primes
- The
$\zeta(s) = \frac{1}{1^s} + \frac{1}{2^s} + \frac{1}{3^s} + \frac{1}{4^s} ...$ - This is undefined for real numbers <=1 and is convergent for any values greater.
- Great video.
- Where is this function zero apart from the trivial(-2, -4, -6 etc.) ones. (On the strip between zero and 1 somewhere)
- Rieman's hypothesis = they lie on the line where the real-component = 1/2. This tells us something about the distribution of primes.
- Take away: How many primes are less than x ?
$\frac{x}{ln(x)}$ 💣 and the prime density is$\frac{1}{ln(x)}$
msc
- How can I use the repeating properties of a sine wave for repetition counting ? Generate some features ?
October 26, 2018
Algorithm Puzzle
- The Graph needs to have all nodes with even degree and only zero or 2 nodes with odd degree for the Eulerian Walk to be possible. (Same as being able to draw a figure without lifting the pencil or drawing on the same line again)
October 25, 2018
- Tinkercad by Autodesk - Awesome for prototyping 3D models for 3Dprinting
- Ostagram Style transfer on images.
- Distances (Minimize both of these during optimization):
-
$D_s$ - Style Distance -
$D_c$ - Content Distance
-
- It is amazing how easy it was to run this :O (Loving PyTorch 🔥)
msc
torchvision.transformscontains a bunch of image transformation options- Chain them up using
transforms.Composelike this:
loader = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize(imsize), # scale imported image
transforms.CenterCrop(imsize), # Center crop the image
transforms.ToTensor()]) # transform it into a torch tensor
unloader = transforms.ToPILImage()
and use it like:
def image_loader(image_name):
image = Image.open(image_name)
# fake batch dimension required to fit network's input dimensions
image = loader(image).unsqueeze(0)
return image.to(device, torch.float)
- Import a pre-trained model like: (link)
cnn = torchvision.models.vgg19(pretrained=True).features.to(device).eval()
# In Pytorch, vgg is implemented with sequential modules containing _features_ and _classifier_(fully connected layers) hence the use of ".features"
These models expect some normalizations in the input
- Finished a wrapper around the neural style transfer tutorial code. ❤️
October 24, 2018
msc
- Preprocessing:
- Using Bresenhem's Line algorithm to sample representative elements from a list.
- Sample m items from n:
lambda m,n: [i*n//m + n//(2*m) for i in range(m)] - Finally sampling 10fps for all videos using this technique
- Sample m items from n:
- Making images Black&White
- Resizing images to 64x64 for now (Toy Dataset)
- Using Bresenhem's Line algorithm to sample representative elements from a list.
October 23, 2018
- DCM files(from both MRI and CT scans) contain pixel_array for each slice.
- A different file contains information about the contours of tumour - corresponding to the slices.
- Learnings:
- Fail Fast, Move on, Don't try to protect your code
- Spend time on MLH challenges, win cool stuff like the Google home mini 😉
- Check out Algolia (Hosted search API) for quick prototyping
Link to the problem.
- Solution:
- No one can move more than two positions backwards (2 bribes each) (Break if someone does)
- Start from the back: See how many bribes the small number took to reach there. If the number at the end is 4, see from 4-2= 2 to end-1 if there are numbers bigger than 4 and keep a count :happy:
October 14, 2018
- Two types of TTS(text to speech):
- Concatenative TTS: Basically needs a human sound database (from a single human) (Ewww)
- Parametric TTS: Model stores the parameters
- PixelRNN, PixelCNN - Show that it is possible to generate synthetic images one pixel at a time or one color channel at a time. (Involving thousands of predictions per image)
- Dilated convolutions support exponential expansion of the receptive field instead of linear
- Saves memory, but also preserves resolution.
- Parametrising convolution kernels as Kronecker-products is a cool idea. (It is a nice approximation technique - very natural)
- Reduces number of parameters by over 3x with accuracy loss of not over 1%.
- Convolutions arithmetic. Link
October 12, 2018
msc
- Things to try:
October 11, 2018
msc
- When you have bias in the number of classes in your training data:
- Oversample smaller classes
- Use
WeightedRandomSampler
- Transfer Learning is the way to go most of the times. Don't always freeze the pretrained convnet when you have a lot of training data
- Always try to overfit a small dataset before scaling up. 💥
October 10, 2018
msc
- Discuss about IndRNN (Long sequence problems for Recurrent neural network)
- Plot activations in layers(one by one) over timesteps. Activation vs Timestep.
- NEWMA - online change point detection
- Logistic classifier vs LDA: LDA assumes
$p(x/w)$ (class densities) is assumed to be Gaussian. It involves the use of marginal density$p(x)$ for the calculation of unknown parameters but for Logistic,$p(x)$ is a part of the Constant term. LDA is the better approach if Gaussian Assumption is valid. - L1-distance =
$\sum_p (V_1^p - V_2^p)$ , L2-distance =$\sqrt{(\sum_p (V_1^p - V_2^p)^2)}$ - Square-root is a monotonic function (Can be avoided when using L2)
- KNN is okay in low dimensional datasets. Usually not okay with images.
- Linear Classifier:
- Better than KNN because
- parameters need to be checked instead of all existing images.
- Template is learned and negative-dot-product is used as distance with the template instead of L1, L2 distances like in KNN
- The class score function has the form
$Wx_i + b$ . You get scores for each class. - If you plot a row of W, it will be a template vector for a class. Loss is a different thing be it SVM(hinge loss) or softmax (cross-entropy).
- And once you have the loss, you can perform optimization over the loss.
- Better than KNN because
- Lagrange Multipliers - awesome MIT video.
- BOTTOM LINE - Helps find points where Gradient(first partial derivatives) of a function are parallel to the gradients of the constraints and also the constraints are satisfied. post
October 5, 2018
- Brute-Force -
$2^n$ (For each item, decide take/no-take) - Greedy approach - Sort based on a criteria (weight, value or value/weight) - complexity = nlogn for sorting
- You could get stuck @ a local optimum
- these approaches often provide adequate/often not optimal solutions.
- Build a tree - Dynamic Programming - (Finds the optimal solution)
- Left means take element and right means no-take
-
Dynamic programming:
- Optimal Substructure
- Overlapping subproblems
- At each node, given the remaining weight, just maximize the value by chosing among the remaining items.
- Variants:
subset sum,scuba divlink etc.
October 3, 2018
msc
-
Even the
nn.LSTMimplementation gives bad results. I suspect this could be because the sequence length is too huge? Trying to generate a sequence with a smaller length. -
Maybe look at some other representation of the 1D signal ? (Like HOG ?)
-
PvsNP - What can be computed in a given amount of space and time ? (Polynomial vs Non Deterministic Polynomial)
- P = Polynomial, NP = Non Polynomial but the answer can be checked in polynomial time.
- NP-complete = Hardest problem in NP
- Can prove a problem is np-complete if it is in NP and is NP-hard
- NP complete problems can be used to solve any problems in NP 👑
- If A can be converted to B in Poly, A >= B
"If P = NP, then there would be no special value in creative leaps, no fundamental gap between solving a problem and recognising a solution once its found. Everyone who could appreciate a symphony would be Mozart and everyone who could follow a step by step argument would be Gauss!" - Scott Aronson
October 2, 2018
- Python style guide
- MIT Algorithm assignments page.
- Example coding interview
- Interview prep blog post
- Topics importante:
- Complexity
- Sorting (nlogn)
- Hashtables, Hashsets
- Trees - binary trees, n-ary trees, and trie-trees
- Red/black tree
- Splay tree
- AVL tree
- Graphs - objects and pointers, matrix, and adjacency list
- breadth-first search
- depth-first search.
- computational complexity
- tradeoffs
- implement them in real code.
- Dijkstras
- A*
- Make absolutely sure you can't think of a way to solve it using graphs before moving on to other solution types.
- NP-completeness
- traveling salesman
- knapsack problem
- Greedy approaches
- Math
- Combinatorics
- Probability link
- Operating System
- Threads, Processes
- Locks, mutexes, semaphores and monitors
- deadlock, livelock
- context-switching
- Scheduling
- Algo books
September 26, 2018
msc
- If you share the weights across time, then your input time sequences can be a variable length. Because each time before backpropagating loss, you go over atleast a sequence.
- Shared weights means fewer parameters to train.
- IDEA! - For longer sequences, maybe share less weights across time.
- nn.LSTM: Suppose we have 2 layers.
- Input to L1 = input, (h1, c1)
- Output from L1 = (h1_, c1_)
- Input to L2 = h1_, (h2, c2)
- Output from L2 = (h2_, c2_) ==> final output = h2_
tensor.size()=np.shape||tensor.view(_)=np.reshape- From what I've found out, batching in pytorch gives a speedup when running on GPU. Not very critical while prototyping on toy-datasets.
September 25, 2018
msc
- Recursive network that is going to be trained with very long sequences, you could run into memory problems when training because of that excessive length. Look at truncated-BPTT. Pytorch discussion link.
- Ways of dealing with looooong sequences in LSTM: link
- TBPTT (in the point above)
- Truncate sequence
- Summarize sequence
- Random sampling
- Use encoder decoder architecture
September 24, 2018
- Tried to generate a sine wave and make a Neural Net predict the number of valleys in the wave (Could be a useful step while calculating the final count from the 1D signal in the matrix profile)
- I assumed a signal of a fixed length (100). I trained a simple MLP on it assuming 100 features in the input. (Overfits and fails to generalize -- as expected)
- I want to train an LSTM/GRU on it now. Since it learns to generate a sine wave (as some of the online examples show). I am hoping it will be able to learn counting.
os.cpu_count()gives the number of cores.- threading.Thread vs multiprocessing.Process nice video
- Use Threading for IO tasks and Process for CPU intensive tasks.
- Threading makes use of one core and switches context between the threads on the same core.
- Processing makes use of all the cores (Like a badass)
September 23, 2018
msc
- This video by Andrej Karpathy.
- Idea about the thesis project:
- Karpathy uses a feature vector (one-hot vecotor for all characters possible)-->(feature vector from a CNN) for each timestep.
- In the output layer, would it be better to have a one-hot vector representing the count instead of a single cell which will calculate the count ?
- Should I pad the input sequence with 0s based on the video with the maximum number of points in the matrix profile ? (For a fixed
seq_length) ? - To make the learning process for blade-counting online, need an RNN with 3 outputs, clockwise-anticlockwise-repetition
-
seq_lengthin the RNN is the region where it can memorize.(size of input sequence (batch size of broken input)) - Gradient clipping for exploding gradients (because while backpropagating, same matrix(
$W_h$ ) is multiplied to the gradient several times ((largest eigenvalue is > 1))) - LSTM for vanishing gradients (same reason as above (largest eigenvalue is < 1))
- LSTMs are super highways for gradient flow
- GRU has similar performance as LSTM but has a single hidden state vector to remember instead of LSTM's (hidden-state-vector and c vector)
- During training, feed it not the true input but its generated output with a certain probability p. Start out training with p=0 and gradually increase it so that it learns to general longer and longer sequences, independently. This is called schedualed sampling. paper
September 19, 2018
- When someone says random variable, it is a single dimension!
- Central limit theorem: If any random variable is sampled infinitely, it ends up being normally distributed
- Expectation values:
-
Discrete
$E[x] = \mu = \frac {1}{n}\sum_{i=0}^n x_i$ $E[(x-\mu)^2] = \sigma^2 = \frac{1}{n}\sum_{i=0}^{n}(x-\mu)^2$
-
Continuous:
$E[x] = \mu = \int_{-\infty}^{+\infty} x.p(x)dx$ $E[(x-\mu)^2] = \sigma^2 = \int_{-\infty}^{+\infty} (x-\mu)^2.p(x)dx$
-
Discrete
- Multivariate Gaussian:
$p(x) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi\Sigma}}\exp\big{(}-\frac{1}{2}(x-\mu)^T\Sigma(x-\mu))\big{)}$ - Covariance Matrix:
$\Sigma$ - $\Sigma = E[(x-\mu)(x-\mu)^T] = E\big{[}\begin{bmatrix} x_1 -\mu_1\ x_2 - \mu_2 \end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix} x_1 - \mu_1 & x_2 - \mu_2 \end{bmatrix}^T\big{]} = \begin{bmatrix}\sigma_1^2 & \sigma_{12}\ \sigma_{21} & \sigma_2^2 \end{bmatrix}$
- Always symetric and positive-semidefinite (Hermitian) (All the eigen values are non-negative).
- For a diagonal matrix, the elements on the diagonal are the eigen values.
- You can imagine the distribution (for 2D features) as a hill by looking at the covariance matrix.
- Normally distributed classes:
- Use formula
$(x-\mu)^T\Sigma^{-1}(x-\mu) = C$ to get the equation of an ellipse(the iso curve thatseaborn.jointplotplots). - The orientation and axes of this ellipse depend on the eigen vectors and eigen values respectively of the covariance matrix.
- Use formula
September 17, 2018
- Different parts of the image are masked separately
- Image segmentation
- Multi class classification inside a single image
- Data is value - Andrew Trask (OpenMind) video
This Recurrent net is a classifier and classifies names of people to its origins
- First pytorch RNN implementation using this tutorial
- Only used linear (fully connected layers in this)
self.i2h = nn.Linear(input_size + hidden_size, hidden_size)
self.i2o = nn.Linear(input_size + hidden_size, output_size)
self.softmax = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1)
def forward(self, input, hidden):
combined = torch.cat((input, hidden), 1)
hidden = self.i2h(combined)
output = self.i2o(combined)
output = self.softmax(output)
return output, hidden
- The hidden component obtained after each output-calculation is fed back to the next input
- For this sequence of words, at each epoch, hidden layer is re-initialized to zeros (
hidden = model.initHidden()) and model's gradients are reset (model.zero_grad()) - Training examples are also randomly fed to it
- Negative Log Likelihood loss (
nn.NLLLoss) is employed as it goes nicely with a LogSoftmax output (last layer). - Torch
.unsqueeze(0)adds a dimension with 1 in 0th location. (tensor(a,b) -> tensor(1,a,b))
- Use
read_only_fieldsin theMetaclass inside a serializer to make it non-updatable - Views should contain all access-control logic
September 12, 2018
- Link to MathJax's landing page.
- Download the chrome extension from here.
- Bayes
$P(w/x) = \frac{P(x/w). P(w)}{P(x)}$ - Normal (Univariate)
$N(\mu, \sigma) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2 \pi \sigma^2}} \exp{-\frac{(x - \mu)^2}{2\sigma^2}}$ -
Decision theory:
- An element(x) belongs to class1 if
$P(w_1 | x) > P(w_2 | x)$ (posterior probability comparison) - i.e.
$P( x | w_1) P(w_1) > P( x | w_2) P(w_2)$ - where
$P(x | w_1) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2 \pi \sigma^2}} \exp{-\frac{(x - \mu)^2}{2\sigma^2}}$ - Boom!
- An element(x) belongs to class1 if
- Use
np.random.normal(self.mean, self.cov, self.n)for univariate andnumpy.random.multivariate_normalfor multivariate data generation
- Multivariate contours:
sns.jointplot(x="x", y="y",kind="kde", data=df); - Visualizing distributions 1D:
sns.distplot(np.random.normal(0, 0.5, 100), color="blue", hist=False, rug=True);
September 9, 2018
Karpathy's talk and ofcourse his unreasonable blog post.
- RNNs are freaking flexible:
- one to many -> Image Captioning (image to sequence of words)
- many to one -> Sentiment Classification (seq of words to positive or negative sentiment)
- many to many -> Machine Translation (seq of words to seq of words)
- many to many -> Video classification (using frame level CNNs)
- These carry state unlike regular NNs. Might not produce the same output for the same input
- Rules of thumb:
- Use RMSProp, Adam (sometimes SGD)
- Initialize forget gates with high bias (WHAT ?)
- Avoid L2 Regularization
- Use dropout along depth
- Use clip gradients (to avoid exploding gradients) (LSTMs take care of vanishing gradients)
- You can look for interpretable cells (Like one of the cell fires when there is a quote sequence going on)
- When using RNN with CNN, plug extra information(CNN's output) directly to a RNN's (green - recurrent layer)
- Use Mixture Density Networks especially when generating something.
September 8, 2018
msc
- Earned basic badge in pytorch forum.
- Finished plotting utility of train, test accuracy vs epochs and train vs test accuracy
- Finished plotting utility of loss vs epochs
- Finished plotting of Learning rate vs epochs
- To get reproducible results with torch:
torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True torch.manual_seed(1973) - Call
model.train()before training andmodel.eval()after training to set the mode. (It matters when you have layers like Batchnorm or Dropout) - Use
torch.nn.functional.<methods>for non linear activations etc. where the model parameters like (training=True/False) doesn't matter. If using it with dropout make sure to pass arguments training=False or use the corresponding torch.nn. (Layers).
September 2, 2018
- Finished Routing
- Permissions / Groups
- TODO
September 1, 2018
- Django Rest Framework tutorials are amazing.
- TokenAuthentication is needed for multipurpose API (But this doesn't support browsable APIs). Solution: Use SessionAuthentication as well (But this needs CSRF cookie set) Solution: Extend SessionAuthentication class and override enforce_csrf function and just return it. Boom! Browsable API with TokenAuthentication.
- Views can be Class based or function based. ViewSets are even a further abstraction over class based views (Class based views can make use of generics and mixins).
- URLs are defined separately in a file usually called
urls.py. (Use Routers if you're using ViewSets). - Model is defined by extending django.db.models.Model. All the field types are defined here:
code = models.TextField() - Serializer has to be defined for the model by extending rest_framework.serializers.HyperlinkedModelSerializer / ModelSerializer . Primary key relations etc are defined here. Serializer and Views are where the API is brewed.
- project/project/settings.py contains all the project settings and resides in
django.conf.settings.
Useful commands: - django-admin.py startproject projectname - django-admin.py startapp appname - python manage.py makemigrations - python manage.py migrate - python manage.py runserver
August 28, 2018
msc
Amazing video by Karpathy. (Timing: 1:21:47)
- Convolutional net on the frame and the low-level representation is an input to the RNN
- Make neurons in the ConvNet recurrent. Usually neurons in convnets represent a function of a local neighbourhood, but now this could also incorporate the dotproduct of it's own or neighbours previous activations making it a function of previous activations of the neighbourhood for each neuron. Each neuron in the convnet - Recurrent!
** An idea for repetition estimation: Maybe look for activation spikes in the deepvis toolbox by Jason Yosinski and train a simple classifier on them. **
- Used the
LeNetarchitecture. - Got
95%test and99%train accuracy. Is it still an overfit ?
- Coordconv layers - for sharper object generation (GANs), Convolutional Neural Networks too and definitely Reinforcement learning. Paper here
- Intrinsic Dimension - Lower Dimension representation of neural networks (Reduces Dimensions). Paper here
August 24, 2018
msc
- Implemented a Dynamic Neural Network using Pytorch's amazing dynamic Computation graphs and
torch.nn. - Fully Connected layers using
torch.nn.Linear(input_dimension, output_dimension) - Autograd is epic.
- Implemented a reusable save_model_epochs function to save model training state
- Cool Findings:
- A fairly simple Dynamic net crushes the Spiral Dataset!
- Tried the Dynamic Net (Fully connected) on Sign Language Digits Dataset and it seems to overfit (Train: 99%, Test: 85%) as expected.
- Will try to build a new net(
TenNet) to crush this set now.
- Tried Spotify's Luigi for workflow development
- Tried Threading module and decorators and ArgumentParser.
August 15, 2018
- A ConvNet architecture is in the simplest case a list of Layers that transform the image volume into an output volume (e.g. holding the class scores)
- There are a few distinct types of Layers (e.g. CONV/FC/RELU/POOL are by far the most popular)
- Each Layer accepts an input 3D volume and transforms it to an output 3D volume through a differentiable function
- Each Layer may or may not have parameters (e.g. CONV/FC do, RELU/POOL don’t)
- Each Layer may or may not have additional hyperparameters (e.g. CONV/FC/POOL do, RELU doesn’t)
- Filter = Receptive Field
- In general, setting zero padding to be P=(F−1)/2 when the stride is S=1 ensures that the input volume and output volume will have the same size spatially.
- We can compute the spatial size of the output volume as a function of the input volume size (W), the receptive field size of the Conv Layer neurons (F), the stride with which they are applied (S), and the amount of zero padding used (P) on the border. How many neurons “fit” is given by (W−F+2P)/S+1
- Parameter sharing scheme is used in Convolutional Layers to control the number of parameters. It turns out that we can dramatically reduce the number of parameters by making one reasonable assumption: That if one feature is useful to compute at some spatial position (x,y), then it should also be useful to compute at a different position (x2,y2). Only D unique set of weights (one for each depth slice)
- It is worth noting that there are only two commonly seen variations of the max pooling layer found in practice: A pooling layer with F=3,S=2 (also called overlapping pooling), and more commonly F=2,S=2. Pooling sizes with larger receptive fields are too destructive.
- Rules of thumb CNN architecture:
- The input layer (that contains the image) should be divisible by 2 many times.
- The conv layers should be using small filters (e.g. 3x3 or at most 5x5), using a stride of S=1, and crucially, padding the input volume with zeros in such way that the conv layer does not alter the spatial dimensions of the input.
- The pool layers are in charge of downsampling the spatial dimensions of the input. The most common setting is to use max-pooling with 2x2 receptive fields (i.e. F=2), and with a stride of 2 (i.e. S=2). Note that this discards exactly 75% of the activations in an input volume
- Keep in mind that ConvNet features are more generic in early layers and more original-dataset-specific in later layers.
- Transfer learning rules of thumb:
- New dataset is small and similar to original dataset. Use CNN codes (CNN as a feature descriptor)
- New dataset is large and similar to the original dataset. We can fine-tune through the full network.
- New dataset is small but very different from the original dataset. It might work better to train the SVM classifier from activations somewhere earlier in the network.
- New dataset is large and very different from the original dataset. We can fine-tune through the full network with initialized weights from a pretrained network.
- It’s common to use a smaller learning rate for ConvNet weights that are being fine-tuned, in comparison to the (randomly-initialized) weights for the new linear classifier that computes the class scores of your new dataset.
August 13, 2018
- The Bayes error defines the minimum error rate that you can hope toachieve, even if you have infinite training data and can recover the true probability distribution.
- Stochastic Gradient Descent approximates the gradient from a small number of samples.
- RMSprop is an adaptive learning rate method that reduces the learning rate using exponentially decaying average of squared gradients. Uses second moment. It smoothens the variance of the noisy gradients.
- Momentum smoothens the average. to gain faster convergence and reduced oscillation.
- Exponential weighted moving average used by RMSProp, Momentum and Adam
- Data augmentation consists in expanding the training set, for example adding noise to the training data, and it is applied before training the network.
- Early stopping, Dropout and L2 & L1 regularization are all regularization tricks applied during training.
- To deal with exploding or vanishing gradients, when we compute long-term dependencies in a RNN, use LSTM.
- In LSTMs, The memory cells contain an element to forget previous states and one to create ‘new’ memory states.
- In LSTMs Input layer and forget layer update the value of the state variable.
- Autoencoders need an encoder layer that is of different size
than the input and output layers so it doesn't learn a one on one representation
- Denoising Autoencoder: The size of the input is smaller than the size of the hidden layer (overcomplete).(use regularization!)
- Split-brain auto encoders are composed of concatenated cross-channel encoders. are able to transfer well to other, unseen tasks.
- GANs
- Unsupervised Learning:
- It can learn compression to store large datasets
- Density estimation
- Capable of generating new data samples
- "Inverse Compositional Spatial Transformer Networks." ICSTN stores the geometric warp (p) and outputs the original image, while STN only returns the warped image (Pixel information outside the cropped region is discarded).
- Fully convolutional indicates that the neural network is composed of convolutional layers without any fully-connected layers or MLP usually found at the end of the network. The main difference with CNN is that the fully convolutional net is learning filters every where. Even the decision-making layers at the end of the network are filters.
- Residual Nets - Two recent papers have shown (1) Residual Nets being equivalent to RNN and (2) Residuals Nets acting more like ensembles across several layers. The performance of an network depends on the number of short paths in the unravelled view. 1.The path lengths in residual networks follow a binomial distribution.
- Capsule - A group of neurons whose activity vector represents the instantiation parameters of a specific type of entity.
- Receptive field networks treat images as functions in Scale-Space
- Pointnets PointNets is trained to do 3D shape classification, shape part segmentation and scene semantic parsing tasks. PointNets are able to capture local structures from nearby point and the combinatorial interactions among local structures. PointNets directly consumes unordered point sets as inputs.
- Hard attention focus on multiple sharp points in the image, while soft attention focusses on smooth areas in the image
- YOLO limitations: Inappropriate treatment of error, Generalizing errors, Prediction of objects
- Curriculum Learning - Easier samples come at the beginning of the training.
July 23, 2018
Nice Numpy tricks.
- A * B in numpy is element wise and so is +, -, /, np.sqrt(A) (It will broadcast if shape not same)
- np.dot(A,B) = A.dot(B) --> Matrix Multiplication
- Use Broadcasting wherever possible (faster)
- If the arrays do not have the same rank, prepend the shape of the lower rank array with 1s until both shapes have the same length.
- In any dimension where one array had size 1 and the other array had size greater than 1, the first array behaves as if it were copied along that dimension
- One Hidden Layer NN is a universal approximator
- Always good to have more layers. (Prevent overfitting by using Regularization etc.)
-
Initialization:
- For Activation tanh =
np.random.randn(N)/sqrt(N) - For RELU =
np.random.randn(n)*sqrt(2/n) - Batch Norm makes model robust to bad initialization
- For Activation tanh =
-
Regularization: (ADDED TO LOSS at the end)
- L2 - Prefers diffused weight vectors over peaky weights = 1/2 (Lambda.W^2)
- L1 - Makes weight vectors sparse (invariant to noisy inputs) (Only a subset of neurons actually matters)
- Dropout(p=0.5) with L2(lambda cross validated) => In Practice
-
Loss = Average of losses over individual runs(training points)
$L = 1/N \sum{L_i}$ - Hinge Loss - (SVM) =>
$L_i = \sum_{j \ne y}{max(0, f_j - f_y + \delta)}$ . (Squared hinge loss also possible) ($\delta = margin$ ) - Cross Entropy - (Softmax) =>
$L_i = -log(e^{f_y} / \sum{e^{f_j}})$ - Large number of classes (Imagenet etc.) use Hierarchial Softmax.