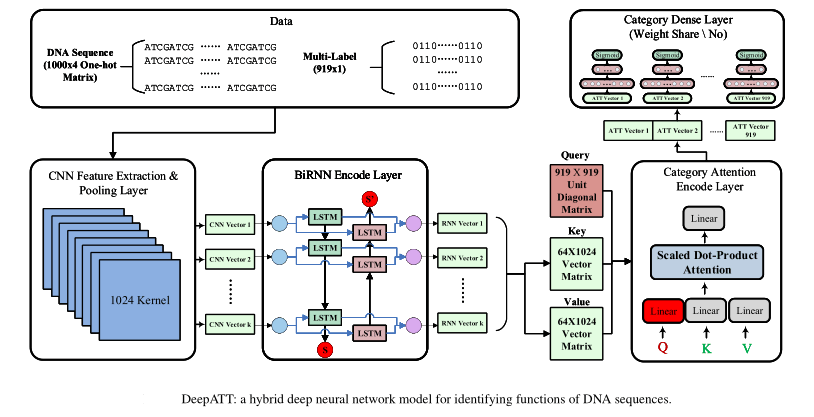
DeepATT is a model for identifying functional effects of DNA sequences. This is implemented by tensorflow-2.0. Our model has four built-in neural network constructions: convolution layer captures regulatory motifs, recurrent layer captures a regulatory grammar, category attention layer (improved from self-attention layer) selects corresponding valid features for different functions, and category dense layer (improved from local-connected dense layer) classifies the labels with feature vectors selected by the query vectors of the regulatory functions. We compare DeepATT with DeepSEA and DanQ, which are all implemented or replicated on our own platform. Comparison results demonstrate that DeepATT achieves state-of-the-art performance of 0.94519 AV-AUROC and 0.39522 AV-AUPR, which is far better than other non-coding DNA regulatory function prediction methods. The performances of all the models that were described in the original paper are shown in the below Table.
| Model | DeepSEA | DanQ | DanQ_JASPAR | DeepATT | DeepATT_Plus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AV-AUPR | 0.34163 | 0.37089 | 0.37936 | 0.39522 | 0.39324 |
| AV-AUROC | 0.93260 | 0.93837 | 0.94174 | 0.94519 | 0.94432 |
| Parameter number | 61,723,119 | 46,926,479 | 67,892,175 | 7,808,057 | 7,900,775 |
Key Points:
- We propose a hybrid deep neural network method with four built-in neural network layers, DeepATT, for identifying 919 regulatory functions on nearly 5 million DNA sequences. We firstly design a category attention layer and category dense layer in order to distinguish specific representations of different DNA functions.
- We replicate two state-of-the-art models, DeepSEA and DanQ, in order to compare different model architectures with our novel model construction. DeepATT performs significantly better than other prediction tools for identifying DNA functions.
- Our novel model mine important correlation among different DNA functions according to the category attention module. The attention mechanism calculates scores of feature vectors to estimate all functional targets for different DNA regulatory functions.
- Our novel model reduce the number of hyper-parameters by attention mechanism and local full-connected, on the basis of ensuring prediction accuracy. The attention mechanism determines relevant characteristics for each binary target, and the local connection eliminates all unnecessary features for specific connections
@article{Li2020DeepATT,
title={DeepATT: a hybrid category attention neural network for identifying functional effects of DNA sequences},
author={Li, Jiawei and Pu, Yuqian and Tang, Jijun and Zou, Quan and Guo, Fei},
journal={Briefings in Bioinformatics},
year={2020},
}
My Manuscript: [PDF]
My Homepage: https://www.ljwstruggle.com/
-
DeepSEA
CNN + Pool + CNN + Pool + CNN + Pool + Dense + Dense
-
DanQ
CNN(320 kernels) + Pool + BidLSTM + Dense + Dense
-
DanQ_JASPAR
CNN(1024 kernels) + Pool + BidLSTM + Dense + Dense
-
DeepATT
CNN + Pool + BidLSTM + Category Multi-Head-Attention + Category-Dense(relu)(weight-share) + Category-Dense(sigmoid)(weight-share)
-
DeepATT-Plus
CNN + Pool + BidLSTM + Category Multi-Head-Attention + Category-Dense(relu)(weight-share) + Category-Dense(sigmoid)(no weight-share)
There we use NLLLoss or FocalLoss. (You can change the config file to use these loss functions.)
We have implemented four optimization methods that include SGD, Adadelta, Adagrad, Adam and RMSprop. (You can change the config file to use these methods.)
We run the code on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS with a GTX 1080ti GPU. It takes 1 or 2 hours to train one model for one epoch. And it takes 1 or 2 days to get one trained model. And we have trained 28 models to do comparision.
Python (3.7.3) | Tensorflow (2.0.0) | CUDA (10.0) | cuDNN (7.6.0)
You need to first download the training, validation, and testing sets from DeepSEA. You can download the datasets from
here. After you have extracted the
contents of the tar.gz file, move the 3 .mat files into the ./data/ folder.
None
Because of my RAM limited, I firstly transform the train.mat file to .tfrecord files.
python process/preprocess.py
Then you can train the model initially.
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python main.py -e train -c ./config/config_0.json
When you have trained successfully, you can evaluate the model.
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python main.py -e test -c ./config/config_0.json
You can get my result in the ./result/ directory.
We use two metrics to evaluate the model. (AUROC, AUPR)
| Model | Optimizer | Loss | Learning Rate | Scheduler | Batch Size | AVG AUPR | AVG AUROC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DeepSEA* | Adam | NLL | 0.001 | None | 64 | 0.26140 | 0.89225 |
| DeepSEA* | Adam | NLL | 0.0005 | None | 64 | 0.29214 | 0.90847 |
| DeepSEA* | Adam | Focal | 0.001 | None | 64 | 0.24434 | 0.87009 |
| DeepSEA* | Adam | Focal | 0.0005 | None | 64 | 0.25994 | 0.88411 |
| DanQ* | Adam | NLL | 0.001 | None | 64 | 0.33254 | 0.92363 |
| DanQ* | Adam | NLL | 0.0005 | None | 64 | 0.35921 | 0.93399 |
| DanQ* | Adam | Focal | 0.001 | None | 64 | 0.34454 | 0.92875 |
| DanQ* | Adam | Focal | 0.0005 | None | 64 | 0.34962 | 0.93160 |
| DanQ_JASPAR* | Adam | NLL | 0.001 | None | 64 | 0.37443 | 0.93827 |
| DanQ_JASPAR* | Adam | NLL | 0.0005 | None | 64 | 0.37872 | 0.94001 |
| DanQ_JASPAR* | Adam | Focal | 0.001 | None | 64 | 0.37692 | 0.93954 |
| DanQ_JASPAR* | Adam | Focal | 0.0005 | None | 64 | 0.38441 | 0.94171 |
| DeepATT | Adam | NLL | 0.001 | StepLR | 64 | 0.39304 | 0.94422 |
| DeepATT | Adam | NLL | 0.001 | None | 64 | 0.38519 | 0.94232 |
| DeepATT | Adam | NLL | 0.0005 | StepLR | 64 | 0.39619 | 0.94486 |
| DeepATT | Adam | NLL | 0.0005 | None | 64 | 0.39267 | 0.94436 |
| DeepATT | Adam | Focal | 0.001 | StepLR | 64 | 0.39246 | 0.94432 |
| DeepATT | Adam | Focal | 0.001 | None | 64 | 0.39303 | 0.94332 |
| DeepATT | Adam | Focal | 0.0005 | StepLR | 64 | 0.39522 |
0.94519 |
| DeepATT | Adam | Focal | 0.0005 | None | 64 | 0.39488 | 0.94491 |
| DeepATT_Plus | Adam | NLL | 0.001 | StepLR | 64 | 0.38595 | 0.94271 |
| DeepATT_Plus | Adam | NLL | 0.001 | None | 64 | 0.37768 | 0.93932 |
| DeepATT_Plus | Adam | NLL | 0.0005 | StepLR | 64 | 0.38125 | 0.94196 |
| DeepATT_Plus | Adam | NLL | 0.0005 | None | 64 | 0.38406 | 0.94293 |
| DeepATT_Plus | Adam | Focal | 0.001 | StepLR | 64 | 0.38772 | 0.94266 |
| DeepATT_Plus | Adam | Focal | 0.001 | None | 64 | 0.38711 | 0.94274 |
| DeepATT_Plus | Adam | Focal | 0.0005 | StepLR | 64 | 0.39324 |
0.94432 |
| DeepATT_Plus | Adam | Focal | 0.0005 | None | 64 | 0.38797 | 0.94308 |
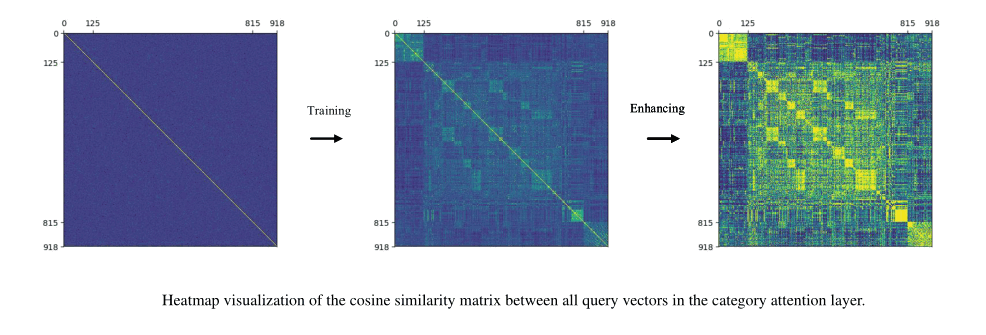
We analyze all trained query vectors in the category attention layer, in order to mine the correlation among 919 DNA non-coding regulatory functions. In the category attention module, we generate a 919 x 919 diagonal matrix as input to the attention layer. First, we randomly generate 919 independent query vectors within 100-length. We calculate the cosine similarity matrix of these randomly query vectors, however, we obtain no valid correlation information. Then, we effectively train query vectors in the category attention layer and calculate the cosine similarity matrix for 919 chromatin features (125 DNase features, 690 TF features, 104 Histone features). Basically, we can find out some subtle correlations among the same function category. Moreover, we enhance the cosine similarity matrix by the sigmoid function. Some obvious small blocks indicate a lot of learned correlation information between 919 DNA non-coding regulatory functions. It need to be stated that three major categories of various non-coding functions are quantified as DNase I sensitivity for 0-124 items, Transcription factor (TF) binding for 125-814 items and Histone-mark profile for 815-918 items. It's worth noting that the cosine similarity matrix reveals some sub-categories in the TF binding functions. We visualize the cosine similarity matrix by using heatmap, as shown in below figure.
If you encounter any issue or have a feedback, please don't hesitate to raise an issue.
Predicting effects of noncoding variants with deep learning-based sequence model | Github
DanQ: a hybrid convolutional and recurrent deep neural network for quantifying the function of DNA sequences | Github