This software implements a routing (i.e. driving instructions) software based on the Raspberry Pi Zero. Driving instructions will be given in real-time while you're on the road using two kinds of signals: Audio messages and vibrations (generated by vibration motors to be put onto your helmet).
The installation is based on Raspbian Stretch 2017-11-29.
Change keyboard layout:
sudo dpkg-reconfigure keyboard-configuration # reboot afterwardsSet timezone:
sudo raspi-config # -> Localisation Options -> Change Timezone -> Europe -> ZurichEnable SSH:
sudo raspi-config # -> 5 Interfacing Options -> P2 SSH -> YesDo not forget to change the password
passwd
Block the kernel module responsible for the internal soundcard to improve
chances that a Bluetooth speaker will be reconnected to after a reboot: Create a file /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist.conf with the following content:
blacklist snd_bcm2835
Allow flask to use port 5000 (without root privileges) and at the same time users to connect on http default port 80, by redirecting traffic directed to port 80 onto port 5000:
sudo iptables -A PREROUTING -t nat -p tcp --dport 80 -j REDIRECT --to-ports 5000 # port redirection for outsiders
sudo iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT -o lo -p tcp --dport 80 -j REDIRECT --to-port 5000 # port redirection for localhost, see https://askubuntu.com/a/579540
sudo mkdir /etc/iptables
sudo sh -c 'sudo iptables-save > /etc/iptables/rules.v4' # iptables rules are ephemeral, save them into a file, from https://stackoverflow.com/a/82278Load iptables rules at network startup by creating the file /etc/network/if-pre-up.d/iptablesload with the following content:
#!/bin/sh
iptables-restore < /etc/iptables/rules.v4
exit 0make it executable by issuing:
sudo chmod +x /etc/network/if-pre-up.d/iptablesload(Sources: https://askubuntu.com/q/444729 , https://serverfault.com/q/246829, https://www.thomas-krenn.com/de/wiki/Iptables_Firewall_Regeln_dauerhaft_speichern , https://help.ubuntu.com/community/IptablesHowTo#Saving_iptables )
Enable serial interface:
sudo raspi-config # -> 5 Interfacing Options -> P6 Serial -> login shell: no -> serial port hardware: yesConnect to WiFi (ideally an Android Hotspot) using GUI (see top-right corner)
Install necessary software:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt install vim gpsbabel python-espeak libgeos-dev gpsd gpsd-clients python-gps colordiff tcpdump # install OS packages
pip3 install gpsd-py3 tenacity openrouteservice Flask gpiozero shapely pyproj pyttsx3 # install python packagesConfigure gpsd, by ensuring that the following settings are present in /etc/default/gpsd:
USBAUTO="false"
GPSD_OPTIONS="/dev/serial0"
GPSD_SOCKET="/var/run/gpsd.sock"
Enable and start gpsd daemon:
sudo systemctl enable gpsd.socket
sudo systemctl start gpsd.socketClone git repo:
cd ~; git clone https://github.com/htwchur/wearables-and-navigation.gitSetup autostart:
sudo cp ~/wearables-and-navigation/src/init/wan-router /etc/init.d/wan-router
sudo chmod +x /etc/init.d/wan-router
sudo update-rc.d wan-router defaultsStart software for the first time (this will happen automatically with future boots):
sudo /etc/init.d/wan-router startA restart may be necessary in order to make everything work smoothly (especially gpsd).
Point your browser at the IP address of the Raspberry Pi to reach the GUI.
If you're using an Android Hotspot, you can get the IP addresses of connected clients
using the app Termux and issuing the command ip neigh.
The GUI will allow you to route yourself to predefined locations or to stop the currently running routing.
In src/config.py you'll find some configurable values, among these are:
routing: When and how exactly to make routing announcementsvibration: Timings for vibrationannouncers: What types of announcers to be usedgpsd: Where to read GPS information (ip and port of a gpsd daemon, may be on localhost)
Issue the following command to make configuration changes work:
sudo /etc/init.d/wan-router restartSummary: /etc/init.d/wan-router start --> start-flask-dev.sh --> flask-app.py --> main.py
The application will be installed and used as a daemon. The daemon control script is at /etc/init.d/wan-router. It expects the code to be at /home/pi/wearables-and-navigation/src/. Specifically, it will launch start-flask-dev.sh which then starts the Flask application flask-app.py including a webserver, which in turn starts a new process of main.py for every newly requested destination. The setup is a bit atypically for a web application because the calculations (routing) will only just have started when Flask returns an HTTP response. The routing (main.py) will be started asynchronously as a new process. If a new routing request or the ressource /kill is called, the old routing process will be terminated and a new process will be started.
cd src/; export GPIOZERO_PIN_FACTORY=mock; ./main.py --lat 46.85449 --lon 9.52864
Explanation:
- Setting
GPIOZERO_PIN_FACTORYis necessary (only) on a system that is not a Raspberry Pi --latand--lonare the destination coordinates (these are necessary)
In order for signal handling in the Flask application to work, unfortunately one needs to disable auto-reloading of files by setting FLASK_DEBUG=1 in start-flask-dev.sh. When changing a file, one needs to stop Flask by pressing Ctrl-c or calling sudo /etc/init.d/wan-router stop and then restart it.
The HTML code for the GUI can be found in src/templates/, which uses Jinja2 templates. Use the follwing code to add destinations:
<div><button lat="46.85286" lon="9.51322" class="coord-submitter" type="button">HTW Hauptgebäude</button></div>Instead of using a hardware GPS, we can also inject faked GPS data. For this we need either a .nmea file or a .gpx file that will be converted to NMEA format. You can find a converter in utils/. Usage:
./gpx2nmea.sh infile.gpx outfile.nmeaNote that the GPX file name must not contain umlauts.
To inject the faked position call:
gpsfake -c 1 -P 55555 feldis-brambrueesch-2011-09-03-161919.nmeaTo test gpsd, call:
cgps localhost:55555 # for fake gps
or
cgps localhost:2947 # for hardware gps
To increase the processing speed, decrement both
gpsfakeparamenter-cconfig.py-->routing['main_poll_interval']
to a value of 0.1 (seconds).
Logs are written to /var/log/wan-router.log and /var/log/wan-router.err. These paths are defined in /etc/init.d/wan-router.
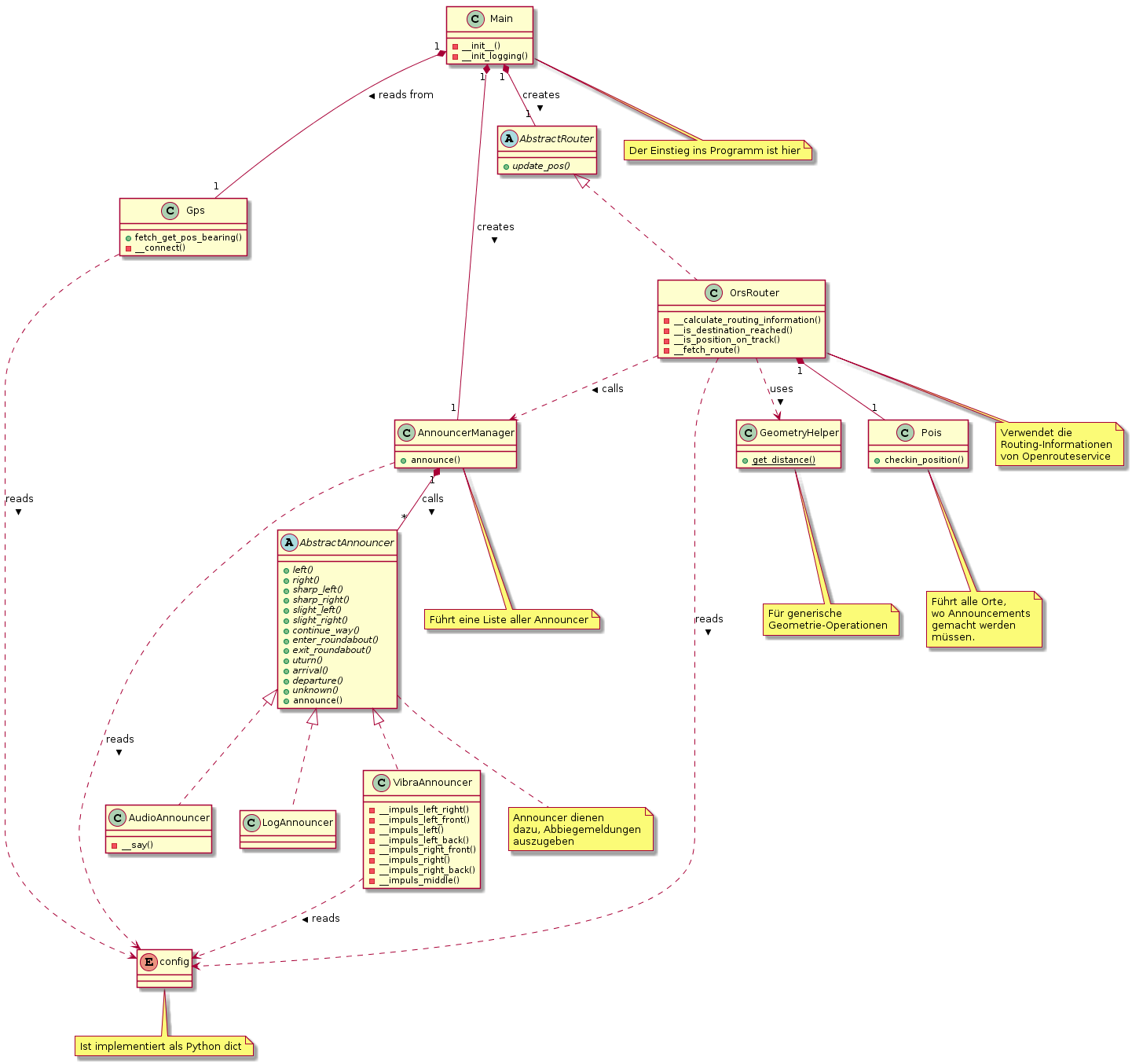
The class diagram was rendered using http://plantuml.com/ .
Routing requests in orsrouter.py contain the current bearing (driving direction, also known as track) in order to get a higher quality driving instruction. A bearing plus tolerance can be submitted as described in https://openrouteservice-py.readthedocs.io/en/latest/#module-openrouteservice.directions (parameter bearings). There are two issues:
- A test (by walking) indicated that the bearing read through gpsd is sometimes zero, about every tenth read. This probably indicates invalid values.
- When routing to a certain destination is chosen, this would normally happen when not driving. The direction read from gpsd will then be nonsensical.
We should check if the usability will be better if we make the exact point of time of an announcement depending on the current speed of the driver.
Since user-chosen destination coordinates may not exactly be reached using a routing engine such as Openrouteservice, it might be better to look at the destination coordinates according to the routing engine and not those specified by the user to compare if the destination has been reached.
- Website: https://haptic-navigation.ch
- Openrouteservice: 4.7
- Python: 2.7.13
- changed in src/config.py in routing ors_routing_profile from cycling-safe to cycling-regular
- added testing routes in src/templates/index.html
- changed in src/audioannouncer.py, vibraannouncer.py, logannouncer.py, abstractannouncer.py due to changed commands
- added testing routes in src/templates/index.html
- changed in src/audioannouncer.py, vibraannouncer.py, added straight command
- added testing routes in src/templates/index.html
- changed arrival signal in src/vibraannouncer.py. Changed length of signal (impulsdauer) to 1s. Minor changes in control_haptic_with_keyboard_0620.py
- changed testing routes in src/templates/index.html