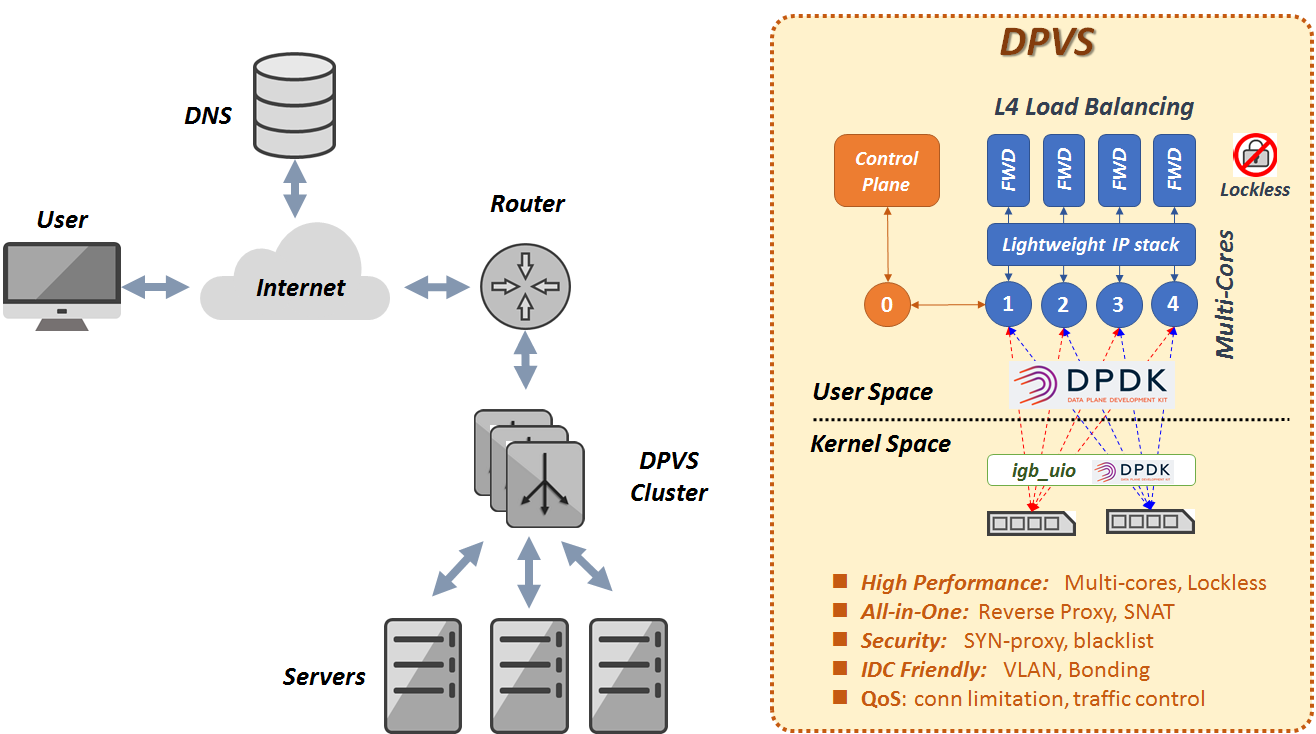
DPVS is a high performance Layer-4 load balancer based on DPDK. It's derived from Linux Virtual Server LVS and its modification alibaba/LVS.
Notes: The name
DPVScomes from "DPDK-LVS".
Several techniques are applied for high performance:
- Kernel by-pass (user space implementation).
- Share-nothing, per-CPU for key data (lockless).
- RX Steering and CPU affinity (avoid context switch).
- Batching TX/RX.
- Zero Copy (avoid packet copy and syscalls).
- Polling instead of interrupt.
- Lockless message for high performance IPC.
- Other techs enhanced by DPDK.
Major features of DPVS including:
- L4 Load Balancer, including FNAT, DR, Tunnel, DNAT modes, etc.
- SNAT mode for Internet access from internal network.
- NAT64 forwarding in FNAT mode for quick IPv6 adaptation without application changes.
- Different schedule algorithms like RR, WLC, WRR, MH(Maglev Hashing), Conhash(Consistent Hashing) etc.
- User-space Lite IP stack (IPv4/IPv6, Routing, ARP, Neighbor, ICMP ...).
- Support KNI, VLAN, Bonding, Tunneling for different IDC environment.
- Security aspect, support TCP syn-proxy, Conn-Limit, black-list, white-list.
- QoS: Traffic Control.
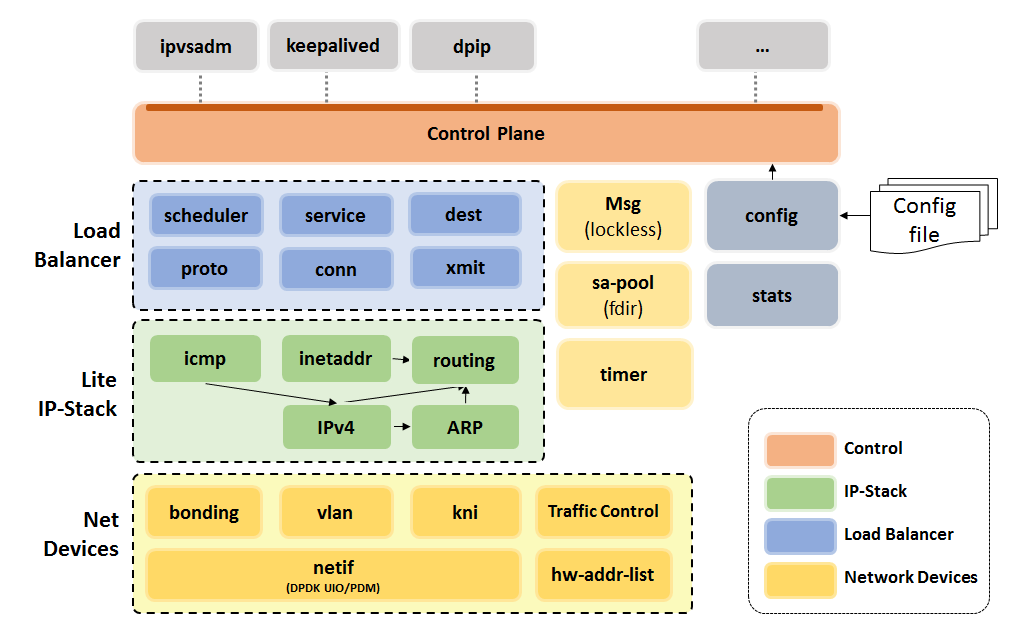
DPVS feature modules are illustrated as following picture.
This quick start is tested with the environment below.
- Linux Distribution: CentOS 7.2
- Kernel: 3.10.0-327.el7.x86_64
- CPU: Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2650 v3 @ 2.30GHz
- NIC: Intel Corporation Ethernet Controller 10-Gigabit X540-AT2 (rev 03)
- Memory: 64G with two NUMA node.
- GCC: gcc version 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-4)
Other environments should also be OK if DPDK works, please check dpdk.org for more info.
- Please check this link for NICs supported by DPDK: http://dpdk.org/doc/nics.
- Note
flow control(rte_flow) is needed forFNATandSNATmode with multi-cores.
Notes: To let dpvs work properly with multi-cores, rte_flow items must support "ipv4, ipv6, tcp, udp" four items, and rte_flow actions must support "drop, queue" at least.
$ git clone https://github.com/iqiyi/dpvs.git
$ cd dpvsWell, let's start from DPDK then.
Currently, dpdk-stable-20.11.1 is recommended for DPVS, and we will not support dpdk version earlier than dpdk-20.11 any more. If you are still using earlier dpdk versions, such as dpdk-stable-17.11.2, dpdk-stable-17.11.6 and dpdk-stable-18.11.2, please use earlier dpvs releases, such as v1.8.10.
Notes: You can skip this section if experienced with DPDK, and refer the link for details.
$ wget https://fast.dpdk.org/rel/dpdk-20.11.1.tar.xz # download from dpdk.org if link failed.
$ tar xf dpdk-20.11.1.tar.xzThere are some patches for DPDK to support extra features needed by DPVS. Apply them if needed. For example, there's a patch for DPDK kni driver for hardware multicast, apply it if you are to launch ospfd on kni device.
Notes: Assuming we are in DPVS root directory and dpdk-stable-20.11.1 is under it, please note it's not mandatory, just for convenience.
$ cd <path-of-dpvs>
$ cp patch/dpdk-stable-20.11.1/*.patch dpdk-stable-20.11.1/
$ cd dpdk-stable-20.11.1/
$ patch -p1 < 0001-kni-use-netlink-event-for-multicast-driver-part.patch
$ patch -p1 < 0002-pdump-change-dpdk-pdump-tool-for-dpvs.patch
$ ...
Tips: It's advised to patch all if your are not sure about what they are meant for.
Use meson-ninja to build DPDK libraries, and export environment variable PKG_CONFIG_PATH for DPDK app (DPVS). The dpdk.mk in DPVS checks the presence of libdpdk.
$ cd dpdk-stable-20.11.1
$ mkdir dpdklib # user desired install folder
$ mkdir dpdkbuild # user desired build folder
$ meson -Denable_kmods=true -Dprefix=dpdklib dpdkbuild
$ ninja -C dpdkbuild
$ cd dpdkbuild; ninja install
$ export PKG_CONFIG_PATH=$(pwd)/../dpdklib/lib64/pkgconfig/libdpdk.pcTips: You can use script dpdk-build.sh to facilitate dpdk build. Run
dpdk-build.sh -hfor the usage of the script.
Next is to set up DPDK hugepage. Our test environment is NUMA system. For single-node system please refer to the link.
$ # for NUMA machine
$ echo 8192 > /sys/devices/system/node/node0/hugepages/hugepages-2048kB/nr_hugepages
$ echo 8192 > /sys/devices/system/node/node1/hugepages/hugepages-2048kB/nr_hugepages
$ mkdir /mnt/huge
$ mount -t hugetlbfs nodev /mnt/hugeInstall kernel modules and bind NIC with uio_pci_generic driver. Quick start uses only one NIC, normally we use two for FNAT cluster, even four for bonding mode. For example, suppose the NIC we would use to run DPVS is eth0, in the meantime, we still keep another standalone NIC eth1 for debugging.
$ modprobe uio_pci_generic
$ cd dpdk-stable-20.11.1
$ insmod dpdkbuild/kernel/linux/kni/rte_kni.ko carrier=on
$ ./usertools/dpdk-devbind.py --status
$ ifconfig eth0 down # assuming eth0 is 0000:06:00.0
$ ./usertools/dpdk-devbind.py -b uio_pci_generic 0000:06:00.0Notes:
- An alternative to the
uio_pci_genericisigb_uio, which is moved to a separated repository dpdk-kmods.- A kernel module parameter
carrieris added torte_kni.kosince DPDK v18.11, and the default value for it is "off". We need to loadrte_kni.kowith the extra parametercarrier=onto make KNI devices work properly.
dpdk-devbind.py -u can be used to unbind driver and switch it back to Linux driver like ixgbe. You can also use lspci or ethtool -i eth0 to check the NIC PCI bus-id. Please refer to DPDK site for more details.
Notes: PMD of Mellanox NIC is built on top of libibverbs using the Raw Ethernet Accelerated Verbs AP. It doesn't rely on UIO/VFIO driver. Thus, Mellanox NICs should not bind the
igb_uiodriver. Refer to Mellanox DPDK for details.
It's simple, just set PKG_CONFIG_PATH and build it.
$ export PKG_CONFIG_PATH=<path-of-libdpdk.pc> # normally located at dpdklib/lib64/pkgconfig/libdpdk.pc
$ cd <path-of-dpvs>
$ make # or "make -j" to speed up
$ make installNotes:
- Build dependencies may be needed, such as
pkg-config(version 0.29.2+),automake,libnl3,libnl-genl-3.0,openssl,poptandnumactl. You can install the missing dependencies by using the package manager of the system, e.g.,yum install popt-devel(CentOS).- Early
pkg-configversions (v0.29.2 before) may cause dpvs build failure. If so, please upgrade this tool.
Output files are installed to dpvs/bin.
$ ls bin/
dpip dpvs ipvsadm keepaliveddpvsis the main program.dpipis the tool to set IP address, route, vlan, neigh, etc.ipvsadmandkeepalivedcome from LVS, both are modified.
Now, dpvs.conf must locate at /etc/dpvs.conf, just copy it from conf/dpvs.conf.single-nic.sample.
$ cp conf/dpvs.conf.single-nic.sample /etc/dpvs.confand start DPVS,
$ cd <path-of-dpvs>/bin
$ ./dpvs &Check if it's get started ?
$ ./dpip link show
1: dpdk0: socket 0 mtu 1500 rx-queue 8 tx-queue 8
UP 10000 Mbps full-duplex fixed-nego promisc-off
addr A0:36:9F:9D:61:F4 OF_RX_IP_CSUM OF_TX_IP_CSUM OF_TX_TCP_CSUM OF_TX_UDP_CSUMIf you see this message. Well done, DPVS is working with NIC dpdk0!
Don't worry if you see this error:
EAL: Error - exiting with code: 1
Cause: ports in DPDK RTE (2) != ports in dpvs.conf(1)
It means the NIC count of DPVS does not match
/etc/dpvs.conf. Please usedpdk-devbindto adjust the NIC number or modifydpvs.conf. We'll improve this part to make DPVS more "clever" to avoid modify config file when NIC count does not match.
What config items does dpvs.conf support? How to configure them? Well, DPVS maintains a config item file conf/dpvs.conf.items which lists all supported config entries and corresponding feasible values. Besides, some config sample files maintained as ./conf/dpvs.*.sample show the configurations of dpvs in some specified cases.
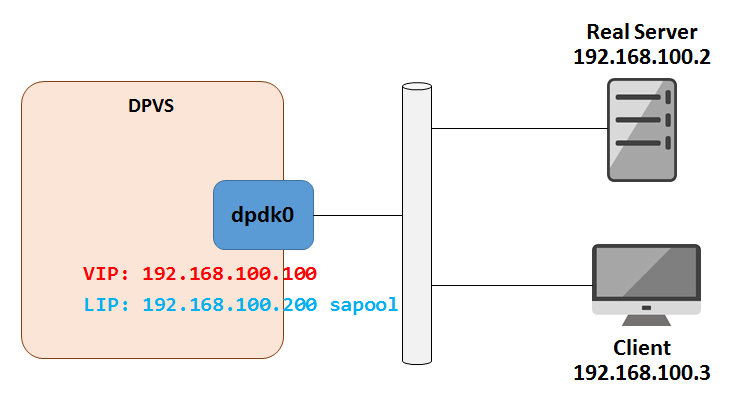
The test topology looks like the following diagram.
Set VIP and Local IP (LIP, needed by FNAT mode) on DPVS. Let's put commands into setup.sh. You do some check by ./ipvsadm -ln, ./dpip addr show.
$ cat setup.sh
VIP=192.168.100.100
LIP=192.168.100.200
RS=192.168.100.2
./dpip addr add ${VIP}/24 dev dpdk0
./ipvsadm -A -t ${VIP}:80 -s rr
./ipvsadm -a -t ${VIP}:80 -r ${RS} -b
./ipvsadm --add-laddr -z ${LIP} -t ${VIP}:80 -F dpdk0
$
$ ./setup.shAccess VIP from Client, it looks good!
client $ curl 192.168.100.100
Your ip:port : 192.168.100.3:56890More configure examples can be found in the Tutorial Document. Including,
- WAN-to-LAN
FNATreverse proxy. - Direct Route (
DR) mode setup. - Master/Backup model (
keepalived) setup. - OSPF/ECMP cluster model setup.
SNATmode for Internet access from internal network.- Virtual Devices (
Bonding,VLAN,kni,ipip/GRE). UOAmodule to get real UDP client IP/port inFNAT.- ... and more ...
We also listed some frequently asked questions in the FAQ Document. It may help when you run into problems with DPVS.
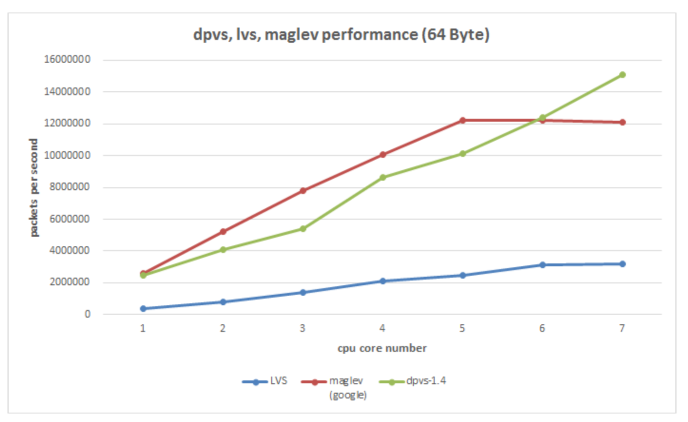
Our test shows the forwarding speed (pps) of DPVS is several times than LVS and as good as Google's Maglev.
Please refer to the License file for details.
Please refer to the CONTRIBUTING file for details.
Currently, DPVS has been widely accepted by dozens of community cooperators, who have successfully used and contributed a lot to DPVS. We just list some of them alphabetically as below.
| CMSoft |  |
|---|---|
| IQiYi |  |
| NetEase |  |
| Shopee |  |
| Xiaomi |  |
DPVS is developed by iQiYi QLB team since April 2016. It's widely used in iQiYi IDC for L4 load balancer and SNAT clusters, and we have already replaced nearly all our LVS clusters with DPVS. We open-sourced DPVS at October 2017, and are excited to see that more people can get involved in this project. Welcome to try, report issues and submit pull requests. And please feel free to contact us through Github or Email.
- github:
https://github.com/iqiyi/dpvs - email:
iig_cloud_qlb # qiyi.com(Please remove the white-spaces and replace#with@).