artomator (aka Artifact Registry Automator) automates the creation of Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) with Binary Authorization attestation for container images in Artifact Registry (AR). artomator will automatically add SBOM attestations to any image pushed to registry with the artomator-sbom label.
docker build -t $TAG --label artomator-sbom=spdx .The value of the label dictates SBOM format. The two supported formats are cyclonedx and spdx). artomator also creates Binary Authorization attestation to support project or cluster levels policies.
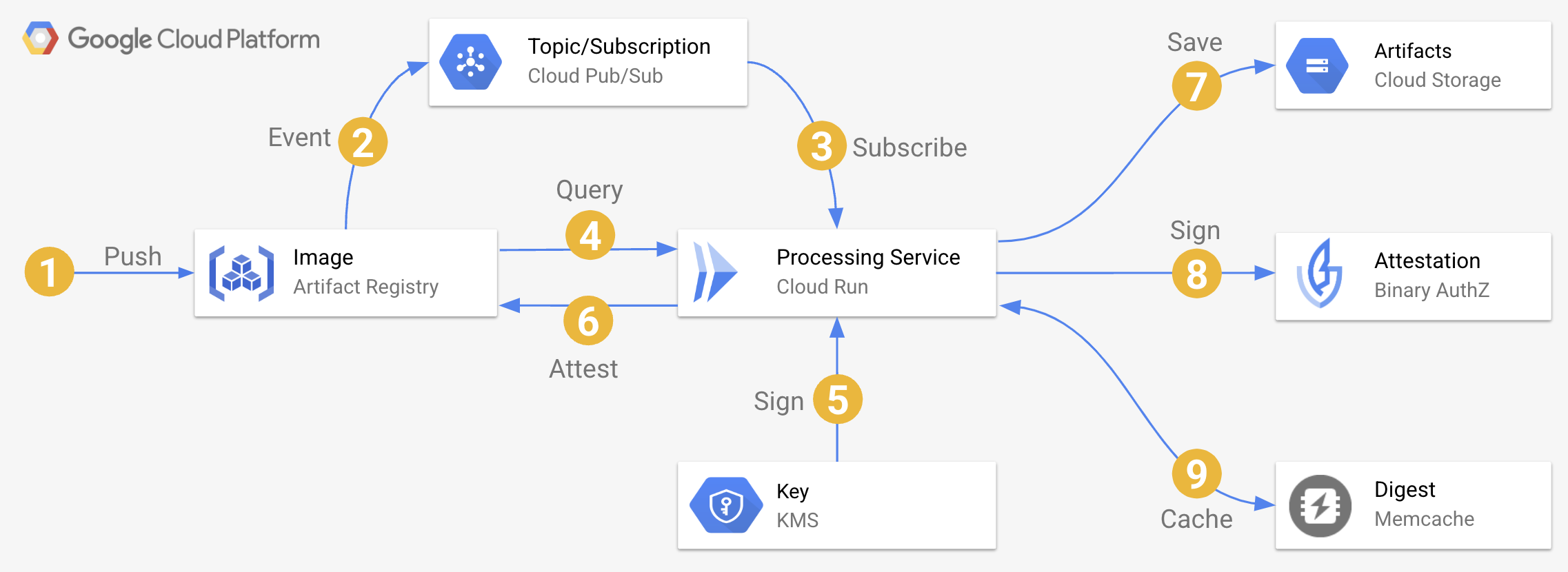
- Whenever an image is published to the Artifact Registry
- A registry event is automatically published onto PubSub topic named
gcr - PubSub subscription pushes that event to
artomatorservice in Cloud Run with operation type and the image digest - If the operation type is
INSERT, theartomatorservice retrieves metadata for that image from registry and check its labels - If the image includes
artomator-sbomlabel, the service signs that image using KMS key - And creates new attestation based on the type of the label to the image in the registry (e.g.
spdx) - If GCS bucket is configured,
artomatorwill also save the generated artifacts to that bucket - On successful completion,
artomatoralso creates Binary Authorization attestation usingartomator-attestorwith associated KMS key - Finally
artomatoralso stores the processed image digests in a Redis store to avoid re-processing the same image again
Technically, adding attestation to an image creates yet another event, and could cause recursion. To prevent this and to allow
artomatorto scale to multiple instances the Redis-based cache is used which caches the processed digests for 72 hrs.
To processes images, artomator uses a few open source projects:
- cosign for image signing and verification
- syft for SBOM generation
- trivy for vulnerability scans
- jq for JSON operations
In addition to attaching attestations to image in Artifact Registry and the Binary Authorization note, artomator also saves all the generated reports in GCS bucket (for example sbom.json). To make these names predictable, artomator prefixes them with the image SHA. For example, if the image digest is:
us-west1-docker.pkg.dev/s3cme1/artomator/tester@sha256:acaccb6c8f975ee7df7f46468fae28fb5014cf02c2835d2dc37bf6961e648838then the list of artifacts in the registry for that image will be:
- acaccb6c8f975ee7df7f46468fae28fb5014cf02c2835d2dc37bf6961e648838-sbom.json
- acaccb6c8f975ee7df7f46468fae28fb5014cf02c2835d2dc37bf6961e648838-meta.json
where:
-sbom.jsonis SPDX 2.3 formatted SBOM file-meta.jsonis the image metadata in the registry as it was when the image was processed
The prerequisites to deploy artomator include:
To deploy the prebuilt artomator, first clone this repo:
git clone git@github.com:mchmarny/artomator.gitThen navigate to the deployment directory inside of that cloned repo:
cd artomator/deploymentNext, authenticate to GCP:
gcloud auth application-default loginInitialize Terraform:
terraform initNote, this flow uses the default, local terraform state. Make sure you do not check the state files into your source control (see
.gitignore), or consider using persistent state provider like GCS.
When done, apply the Terraform configuration:
terraform applyWhen promoted, provide requested variables:
project_idis the GCP project ID (not the name)locationis GCP region to deploy to
When completed, this will output the configured resource information.
To test the deployed artomator, use any valid Dockerfile you already have:
docker build -t $TEST_IMAGE_TAG --label artomator-sbom=spdx .
docker push $TEST_IMAGE_TAGTo clean all the resources provisioned by this setup run:
terraform destroyNote, this does not remove the created KMS resources.
This is my personal project and it does not represent my employer. While I do my best to ensure that everything works, I take no responsibility for issues caused by this code.