Authors: Andrea Piras, Shi Chenghao, Michael Sebek, Gordana Ispirova, Giulia Menichetti (giulia.menichetti@channing.harvard.edu)
The binding interactions between small molecules and proteins are the basis of cellular functions. Yet, experimental data available regarding compound-protein interaction (CPI) is not harmonized into a single entity but rather scattered across multiple institutions, each maintaining databases with different formats. Extracting information from these multiple sources remains challenging due to data heterogeneity.
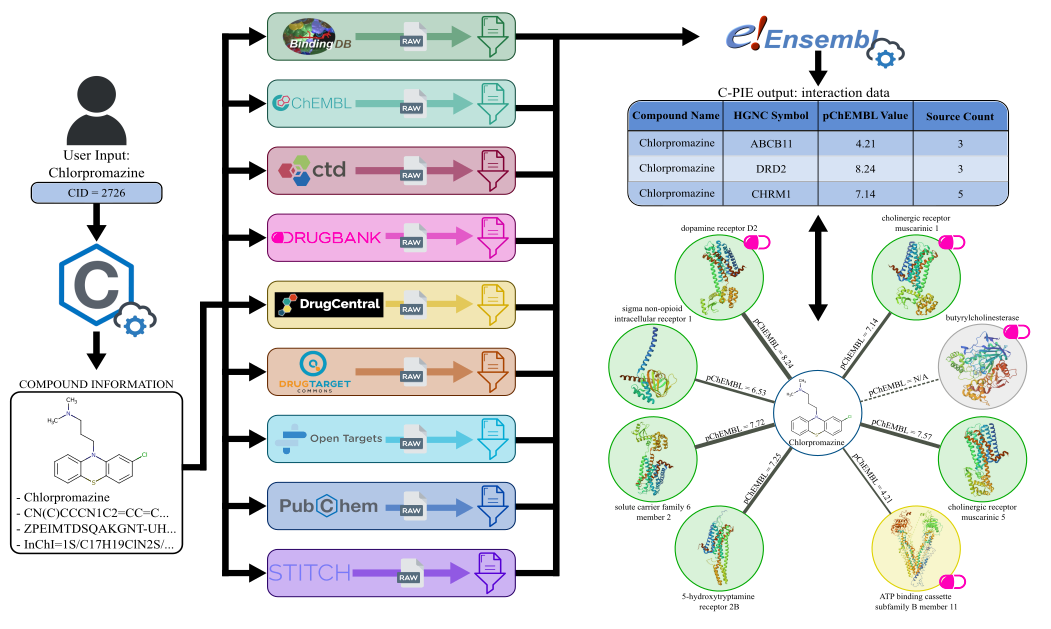
CPIExtract interactively extracts, filters and harmonizes CPI data from 9 databases, providing the output in tabular format (csv).
The package provides two separate pipelines:
- Comp2Prot: Extract protein target interactions for compounds provided as input
- Prot2Comp: Extract compound interactions for proteins provided as input
The pipeline extracts compound information from an input identifier using the PubChem REST API, accessed with the PubChemPy Python package. Then, it uses the information to perform compound matching for each database, extracting raw interaction data. This data is then filtered for each database with a custom filter, ensuring only high-quality interactions are returned in the output. Finally, protein data are extracted using the Biomart Python package, harmonizing the information from the 9 databases. The collected output is finally returned to the user in a .csv file.
An exemplary pipeline workflow is depicted in the figure below. An equivalent output network is also shown.
The pipeline follows a workflow similar to the other pipeline. It extracts protein information from an input identifier using the Biomart Python package. It performs the same database matching and filtering and then harmonizes the interaction data extracting compounds information with the PubChemPy Python package. The output is finally returned to the user in a .csv file.
- Installing the necessary dependencies:
Working with Conda is recommended, but it is not essential. If you choose to work with Conda, these are the steps you need to take:
-
Ensure you have Conda installed.
-
Download the
environment.ymland navigate to the directory of your local/remote machine where the file is located. -
Create a new conda environment with the
environment.ymlfile:conda env create -f environment.yml
-
Activate your new conda environment:
conda activate CPIExtract
-
Ensure the following dependencies are installed before proceeding:
pip install numpy pandas mysql-connector-python biomart pubchempy chembl-webresource-client tqdm
- Install the package:
pip install cpiextract-
Ensure you have Python installed.
-
Copy the project to your local or remote machine:
git clone https://github.com/menicgiulia/CPIExtract.git- Navigate to the project directory:
cd CPIExtract-main- Installing the necessary dependencies:
Working with Conda is recommended, but it is not essential. If you choose to work with Conda, these are the steps you need to take:
-
Ensure you have Conda installed.
-
Create a new conda environment with the
environment.ymlfile:conda env create -f environment.yml
-
Activate your new conda environment:
conda activate CPIExtract
-
Ensure the following dependencies are installed before proceeding:
pip install numpy pandas mysql-connector-python biomart pubchempy chembl-webresource-client
-
Set up your PYTHONPATH (Replace
/user_path_to/CPIExtract-main/cpiextractwith the appropriate path of the package in your local/remote machine.):On Linux/Mac:
export PYTHONPATH="/user_path_to/CPIExtract-main/cpiextract":$PYTHONPATH
On Windows shell:
set PYTHONPATH="C:\\user_path_to\\CPIExtract-main\\cpiextract";%PYTHONPATH%
On Powershell:
$env:PYTHONPATH = "C:\\user_path_to\\CPIExtract-main\\cpiextract;" + $env:PYTHONPATH
We provide several Jupyer Notebooks to simplify the databases' download and maintenance. To use these notebooks, follow these steps:
-
Make sure you have the
jupyterpackage installed.pip install jupyter
-
Start the Jupyter Kernel
a) If you are working on a local machine:
jupyter notebook --browser="browser_of_choice"Or:
jupyter lab --browser="browser_of_choice"Replace browser_of_choice with your preferred browser (e.g., chrome, firefox). The browser window should pop up automatically. If it doesn't, copy and paste the link provided in the terminal into your browser. The link should look something like this:
b) If you are working on a remote machine:
jupyter notebook --no-browser
Then copy and paste the link provided in the terminal in your local browser of choice, it should look something like this:
-
Navigate to the selected notebook in the Jupyter Notebook interface and start executing the cells.
To operate the package, and try the examples it is necessary to have downloaded databases .csv and .tsv files either in a local directory or stored in a mySQL server as tables. The compressed preprocessed data necessary to reproduce the results in the manuscript are provided in subdirectory data - Databases.zip. This data is intended for use with the Local Execution mode. Please make sure to download the .zip file separately and not with the whole GitHub directory.
Create a local folder, name it data and extract the files with the following code, which will save the databases in data/Databases subdirectory(Replace /user_path_to/data/ with the appropriate path of the package in your local/remote machine):
On Linux/Mac:
cd /user_path_to/data/
mkdir -p Databases
unzip Databases.zip -d Databases/On Windows shell/Powershell:
cd user_path_to\\data
mkdir Databases
tar -xf Databases.zip -C Databases\\Although the data used is up to date, each database periodically releases updated versions that will make the zipped data obsolete.
For this reason, we suggest periodically redownloading the databases to have the latest CPI information available.
We also strongly recommend preprocessing the databases to obtain significantly faster execution times.
To ease this process, we provide two notebooks to download (db_download.ipynb) and preprocess (db_preprocessing.ipynb) the databases.
Users can also load the databases into a mySQL server.
- We suggest using mySQL Workbench CE. Once set up, create a database schema named
cpie. - (If the package has been installed with pip)
Download thedbs_config.jsonand save it into the data folder. - Load the downloaded and preprocessed databases as tables into the SQL database, which can be done using the provided SQL_load.ipynb notebook.
The package allows the user to execute two pipelines, Compound-Proteins-Extraction (Comp2Prot) and the Protein-Compounds-Extraction (Prot2Comp). The Comp2Prot pipeline retrieves proteins interacting with the small molecule passed as input, while Prot2Comp returns compounds interacting with the input protein. Both pipelines comprise three phases: input data extraction, data filtering, and harmonization. The package is designed to support multiple user scenarios based on different storage and software availability.
When running the pipeline locally, it is essential to load the databases first. To do this, please refer to the example jupyter notebook Comp2Prot_example.ipynb and follow the instructions in cell [2]: Load in Required Datasets.
Before loading the data make sure you are in the parent directory of data or adjust data_path according to your setup.
from cpiextract import Comp2Prot, Prot2Comp
import pandas as pd
import os
# Root data path
data_path = 'data/Databases/'
#Downloaded from BindingDB on 3/30/2023
file_path=os.path.join(data_path, 'BindingDB.csv')
BDB_data=pd.read_csv(file_path,sep=',',usecols=['CID', 'Ligand SMILES','Ligand InChI','BindingDB MonomerID','Ligand InChI Key','BindingDB Ligand Name','Target Name Assigned by Curator or DataSource','Target Source Organism According to Curator or DataSource','Ki (nM)','IC50 (nM)','Kd (nM)','EC50 (nM)','pH','Temp (C)','Curation/DataSource','UniProt (SwissProt) Entry Name of Target Chain','UniProt (SwissProt) Primary ID of Target Chain'],on_bad_lines='skip')
#Downloaded from STITCH on 2/22/2023
file_path=os.path.join(data_path, 'STITCH.tsv')
sttch_data=pd.read_csv(file_path,sep='\t')
#Downloaded from ChEMBL on 2/01/2024
file_path=os.path.join(data_path, 'ChEMBL.csv')
chembl_data=pd.read_csv(file_path,sep=',')
file_path=os.path.join(data_path, 'CTD.csv')
CTD_data=pd.read_csv(file_path,sep=',')
#Downloaded from DTC on 2/24/2023
file_path=os.path.join(data_path, 'DTC.csv')
DTC_data=pd.read_csv(file_path,sep=',',usecols=['CID', 'compound_id','standard_inchi_key','target_id','gene_names','wildtype_or_mutant','mutation_info','standard_type','standard_relation','standard_value','standard_units','activity_comment','pubmed_id','doc_type'])
#Downloaded from DrugBank on 3/2/2022
file_path=os.path.join(data_path, 'DB.csv')
DB_data=pd.read_csv(file_path, sep=',')
#Downloaded from DrugCentral on 2/25/2024
file_path=os.path.join(data_path, 'DrugCentral.csv')
DC_data=pd.read_csv(file_path, sep=',')
# Data stored in pandas dataframes
data = {
'chembl': chembl_data,
'bdb': BDB_data,
'stitch': sttch_data,
'ctd': CTD_data,
'dtc': DTC_data,
'db': DB_data,
'dc': DC_data
}
C2P = Comp2Prot(execution_mode='local', dbs=data)
P2C = Prot2Comp(execution_mode='local', dbs=data)The databases are stored on the mySQL server.
from cpiextract import Comp2Prot, Prot2Comp
# Exmeplative dictionary containing the configuration info to connect to the mySQL server
info = {
"host": "XXX.XX.XX.XXX",
"user": "user",
"password": "password",
"database": "cpie",
}
C2P = Comp2Prot(execution_mode='server', server_info=info)
P2C = Prot2Comp(execution_mode='server', server_info=info)Once instantiated, the user can choose between the functions comp_interactions or comp_interactions_select for Comp2Prot, and the functions prot_interactions or prot_interactions_select for Prot2Comp.
The function comp_interactions from Comp2Prot accepts the following parameters:
input_id- the compound idpChEMBL_thresh- the minimum interaction pChEMBL value required to be added to the output filestitch_stereo- to select whether to consider the specific compound stereochemistry or group all stereoisomers interactions from STITCHotp_biblio- to select whether to include the bibliography data from OTP. This parameter is only available for Comp2Prot as OTP provides only known drug interactions for proteinsdtc_mutated- to select whether also to consider interactions with mutated target proteins from DTCdc_extra- to select whether to include possibly non-Homo sapiens interactions
The output will include all the interactions found and a data frame containing the statements for all the datasets for the specific input compound.
# Chlorpromazine InChIKey
comp_id = 'ZPEIMTDSQAKGNT-UHFFFAOYSA-N'
interactions, db_states = C2P.comp_interactions(input_id=comp_id, pChEMBL_thres=0, stitch_stereo=True, otp_biblio=False, dtc_mutated=False, dc_extra=False)To extract interactions only from selected databases, use the alternate function specifying which databases to use in an underscore-separated string (to include all databases, which equates to using the previous function, use 'pc_chembl_bdb_stitch_ctd_dtc_otp_dc_db'). In the following example, only four databases are used to limit the output size.
# Chlorpromazine InChIKey
comp_id = 'ZPEIMTDSQAKGNT-UHFFFAOYSA-N'
# Interactions extracted from PubChem, ChEMBL, DB and DTC only.
interactions, db_states = C2P.comp_interactions_select(input_id=comp_id, selected_dbs='pc_chembl_db_dtc', pChEMBL_thres=0, stitch_stereo=True, otp_biblio=False, dtc_mutated=False, dc_extra=False)Prot2Comp works similarly, with the exception that both functions only have the following additional parameters, as OTP will retrieve only known compounds interacting with the input protein:
pChEMBL_thresh- the minimum interaction pChEMBL value required to be added to the output filestitch_stereo- to select whether to consider the specific compound stereochemistry or group all stereoisomers interactions from STITCHdtc_mutated- to select whether also to consider interactions with mutated target proteins from DTCdc_extra- to select whether to include possibly non-Homo sapiens interactions
Here are two examples demonstrating the use of the two functions from Prot2Comp:
# HGNC symbol for Kallikrein-1
prot_id = 'KLK1'
interactions, db_states = P2C.prot_interactions(input_id=prot_id, pChEMBL_thres=0, stitch_stereo=True, dtc_mutated=False, dc_extra=False)
# Interactions extracted from PubChem, ChEMBL, DB and DTC only.
interactions, db_states = P2C.prot_interactions_select(input_id=prot_id, selected_dbs='pc_chembl_db_dtc', pChEMBL_thres=0, stitch_stereo=True, dtc_mutated=False, dc_extra=False)Root folder organization (__init__.py files removed for simplicity):
│ .gitignore
│ environment.yml // current conda env settings used
│ README.md
│ Comp2Prot_example.ipynb // Comp2Prot pipeline testing notebook
│ Prot2Comp_example.ipynb // Prot2Comp pipeline testing notebook
│
├───data // data storage location
│ ├───dbs_config.json // file with databases configuration for the mySQL server
│ ├───input // pipeline input data location
│ │ ├───db_compounds.csv // DrugBank compounds example dataset
│ │ ├───db_proteins.csv // DrugBank protein example dataset
│ │ └───foodb_compounds.csv // FooDB compound example dataset
│ └───output // pipeline output data location
│ ├───C2P.csv // Comp2Prot output file for db_compounds.csv
│ ├───foodb.csv // Comp2Prot output file for foodb_compounds.csv
│ └───P2C.csv // Prot2Comp output file for db_proteins.csv
│
└───cpiextract
│
├───data_manager
│ ├───APIManager.py // to extract raw data from databases' APIs
│ ├───DataManager.py // Abstract data manager class
│ ├───LocalManager.py // to extract raw data from downloaded databases
│ └───SQLManager.py // to extract raw data from SQL server
│
├───databases
│ ├───BindingDB.py // BDB database class
│ ├───ChEMBL.py // ChEMBLB database class
│ ├───CTD.py // CTD database class
│ ├───Database.py // Abstract database class
│ ├───DrugBank.py // DB database class
│ ├───DrugCentral.py // DC database class
│ ├───DTC.py // DTC database class
│ ├───OTP.py // OTP database class
│ ├───PubChem.py // PubChem database class
│ └───Stitch.py // STITCH database class
│
├───pipelines
│ ├───Comp2Prot.py // Comp2Prot pipeline class
│ ├───Pipeline // Abstract pipeline class
│ └───Prot2Comp.py // Prot2Comp pipeline class
│
├───servers
│ ├───BiomartServer.py // to connect to Biomart API
│ ├───ChEMBLServer.py // to connect to ChEMBL API
│ └───PubChemServer.py // to connect to PubChem API
│
├───sql_server
│ └───sql_connection.py // to connect to the SQL server
│
└───utils
├───helper.py // helper functions and classes
└───identifiers.py // functions to extract identifiers for compounds and proteins
- Details about each function (what is it used for, what are the input parameters, the possible values of the input parameters, what is the output) from the pipeline are available in the
cpiextractfolder, in the comments before each class function. - An example of the use of the implemented functions is available in the jupyter notebooks Comp2Prot_example.ipynb and Prot2Comp_example.ipynb, which can be executed to test the proper installation of the package and it's functionalities.
This project is licensed under the terms of the MIT license.