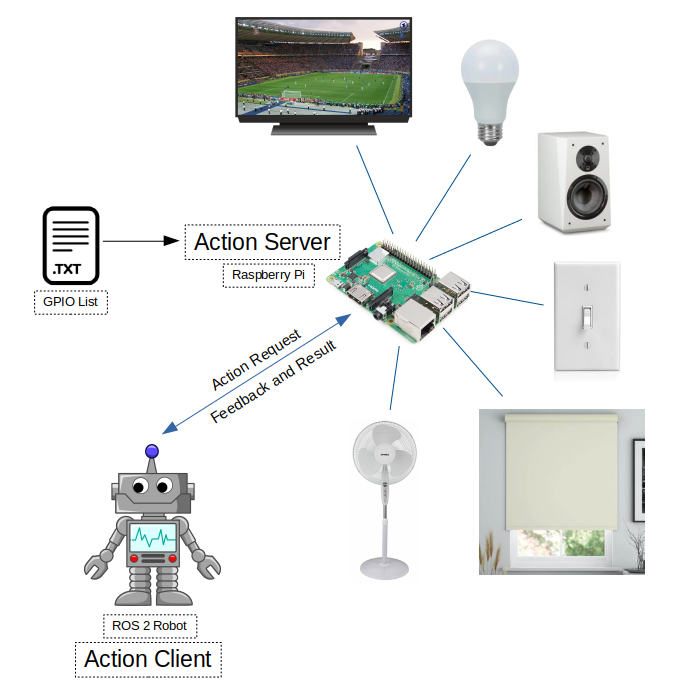
ROS 2 package to control Raspberry Pi GPIO pins
This packages allows you set and read Raspberry Pi GPIO pins via ROS 2 action calls.
Tested with Raspberry Pi3, ROS2 Eloquent, and Ubuntu 18.04 Server
Link to the project video: https://www.linkedin.com/embed/feed/update/urn:li:ugcPost:6654600397346484224
source /opt/ros/<ros2_distro>/setup.bash
mkdir <your_ros2_ws_name>
cd your_ros2_ws_name
mkdir src
cd src
git clone https://github.com/mlherd/ros2_pi_gpio.git
cd ..
colcon build --sysmlink-install
source install/setup.bash
-
- Download Ubuntu Server 64-bit
- Flash the image file on your MicroSD card. I use Etcher on Ubuntu and Rufus on Windows.
- Etcher: https://www.balena.io/etcher/
- Rufus: https://rufus.ie/
- Default user name is ubuntu and password is ubuntu.
- Set up WiFi connection. You can skip this step if you want use the eternet port.
-
sudo nano /etc/netplan/50-cloud-init.yaml
-
network: ethernets: eth0: dhcp4: true optional: true version: 2 wifis: wlan0: optional: true dhcp4: true access-points: "<Your WiFi Name>": password: "<Your WiFi Password>"- Save the file and apply the changes
sudo netplan --debug trysudo netplan --debug generatesudo netplan --debug apply
- Save the file and apply the changes
-
Generate SSH Keys
sudo ssh-keygen -A
-
Install ROS 2 Eloquent
https://index.ros.org/doc/ros2/Installation/Eloquent/Linux-Install-Debians/- Make sure you install ROS-Base Install (Bare Bones)
-
Install development tools and ROS tools
https://index.ros.org/doc/ros2/Installation/Eloquent/Linux-Development-Setup/
-
-
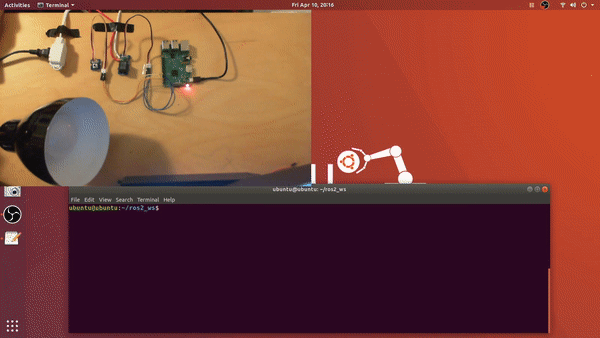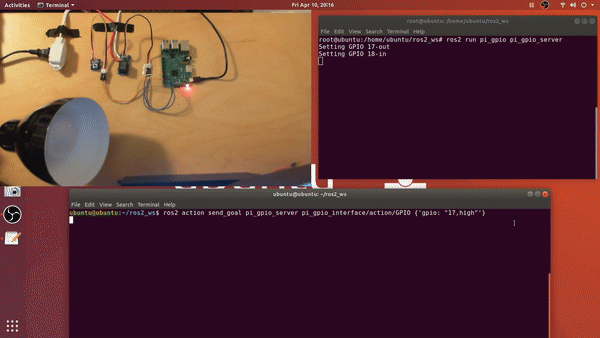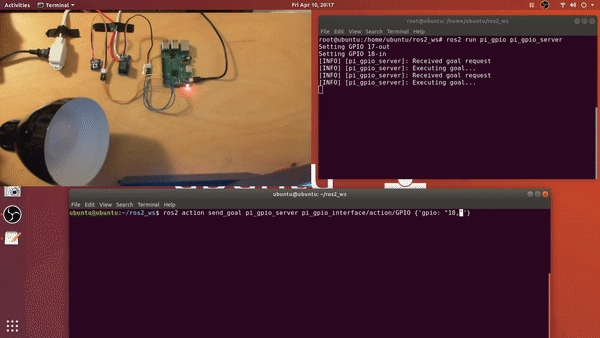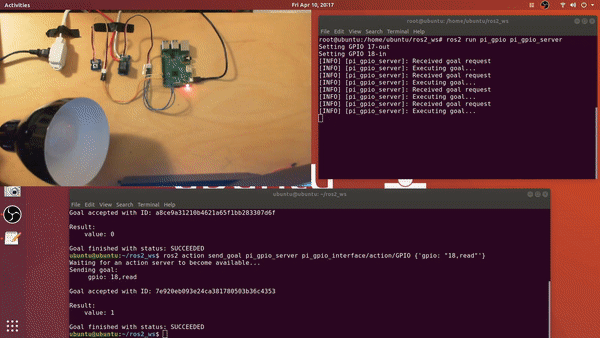
- <pin_id>,<input_output>
- example:
- 17,out
- 18,in
-
- You may need to have super user permissions to access GPIO pins
sudo suros2 run pi_gpio pi_gpio_server
-
- example via command line interface:
- ros2 action send_goal <action_name> <action_message_type> <action_goal>
ros2 action send_goal pi_gpio_server pi_gpio_interface/action/GPIO {'gpio: "17,high"'}ros2 action send_goal pi_gpio_server pi_gpio_interface/action/GPIO {'gpio: "18,low"'}ros2 action send_goal pi_gpio_server pi_gpio_interface/action/GPIO {'gpio: "18,read"'}
- example via command line interface:
-
- ROS 2 action server node
-
- Action name: pi_gpio
- Action type: pi_gpio_interface/action/GPIO
- pi_gpio (pi_gpio_interface/action/GPIO)
- Goal
- string gpio
- Result
- int32 value
- Feedback
- int32 feedback
- Goal