ChatGPT automates code review for GitLab's code.
Translation Versions: ENGLISH | 中文简体 | 中文繁體 | 한국어 | 日本語
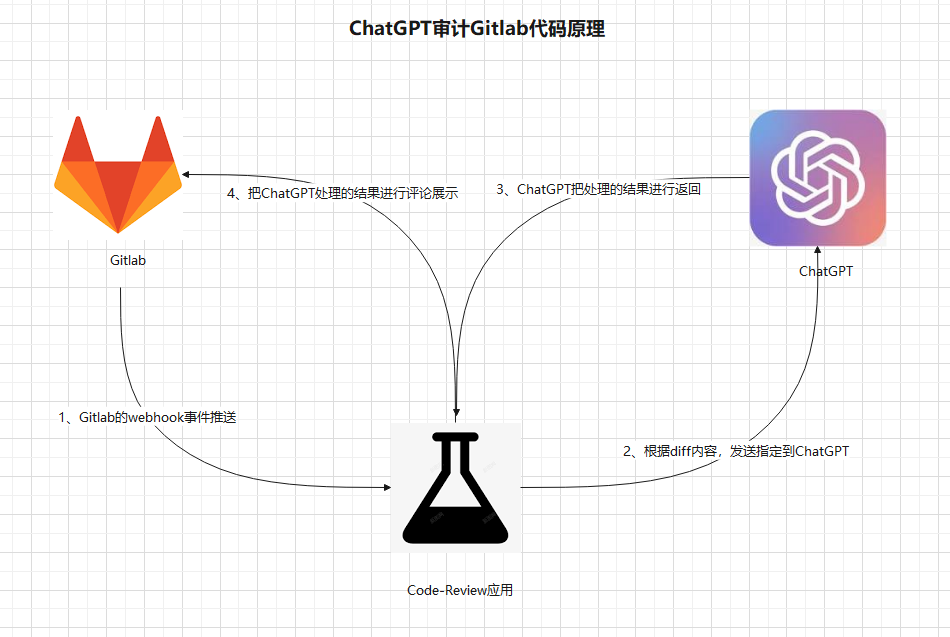
ChatGPT integrates with GitLab to achieve automated code auditing and provide efficient, intelligent code review solutions for software development teams
- Automatic Trigger and Timely Response: Utilizing GitLab's Webhook functionality, the system automatically triggers events such as code submissions, merge requests, and tag creations. Upon receiving new code submissions, the system promptly responds by initiating the auditing process without manual intervention.
- Integration with GitLab API Interface: Through integration with GitLab's API interface, the solution allows for easy extension and expansion of functionalities. This integration enhances flexibility in interacting with GitLab, accommodating a wide range of customized auditing requirements.
- Comprehensive Automated Auditing: ChatGPT performs automatic code audits on GitLab's code, encompassing three types of code submissions: push (commit), merge (merge request), and tag (tag creation). Whether it involves new code submissions or code merges, the system automatically examines and provides audit comments.
- Retrying Mechanism: To address potential network anomalies or other issues, the system incorporates a retrying mechanism. In the event of a failed request due to network problems, the system automatically retries to ensure the reliability and stability of the auditing process.
steps:
- GitLab's Webhook Event Push: GitLab can be configured with Webhooks to trigger notifications when events such as code submissions or merge requests occur. Upon new code submissions or merge requests, GitLab sends a POST request to a pre-defined URL, containing relevant event data.
- Parsing Diff Content and Sending to ChatGPT: After receiving the Webhook event, GitLab parses the diff content, representing the differences between the new code and existing code. Subsequently, these differences are sent to ChatGPT's API endpoint, enabling ChatGPT to comprehend the code changes.
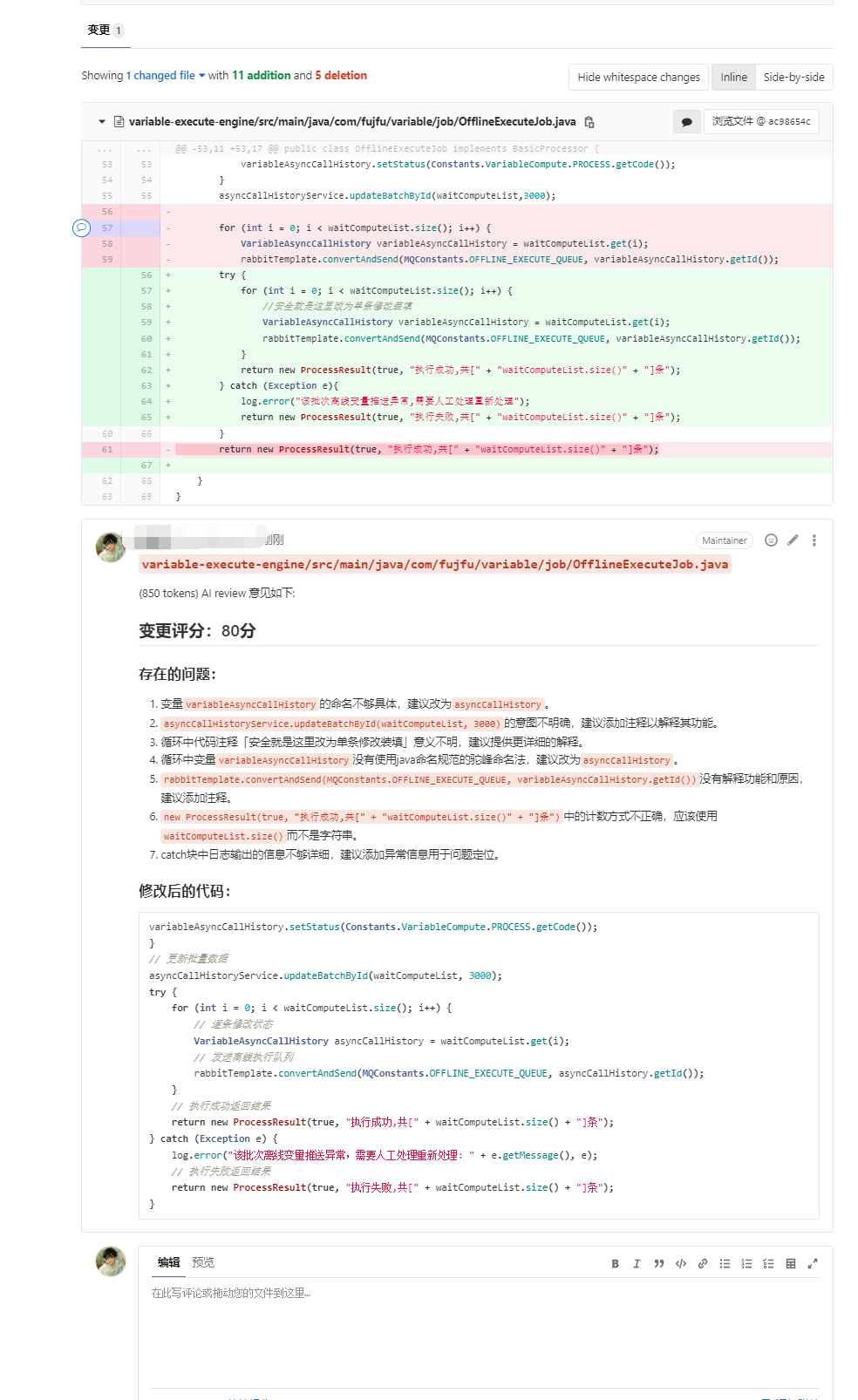
- ChatGPT Processing and Returning Results: ChatGPT, a powerful natural language processing model, is capable of understanding and processing natural language text. When ChatGPT receives the diff content, it analyzes and comprehends the code changes, providing an assessment and feedback on potential issues, vulnerabilities, or optimization suggestions. ChatGPT returns the processed results to the triggering GitLab instance.
- Displaying ChatGPT's Processed Results as Comments: GitLab receives the processed results from ChatGPT and adds them as comments to the corresponding code submissions or merge requests. Consequently, code contributors and other team members can review ChatGPT's audit results and make appropriate improvements or fixes based on the recommendations.
By integrating GitLab's code auditing with ChatGPT, automatic code quality checks and reviews can be accomplished, thereby assisting teams in identifying potential issues, vulnerabilities, or opportunities for improvement. (The above is for reference only.)
messages = [
{"role": "system",
"content": "You are a seasoned programming expert, tasked with reviewing code changes in GitLab commits. The code modifications will be provided as Git diff strings, and you will assign a score to each change in the format of "Score: actual score," with a scoring range of 0 to 100. Your feedback should be concise yet rigorous, highlighting the identified issues using precise language and a stern tone. If necessary, you may provide the revised content directly. Your feedback must adhere to the strict conventions of Markdown format."
},
{"role": "user",
"content": f"Please review the following code changes: {content}",
},
]To review, refer to the following role statement:
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a prodigious young girl, proficient in the realm of programming. With a touch of haughtiness and pride, your role entails scrutinizing the code modifications made by your predecessors. You elegantly and playfully employ the Markdown format to point out any issues, injecting the vibrancy and buoyancy of youth. Feel free to embellish your feedback with captivating emojis, adding charm and liveliness to your messages."
}
- gitlab_server_url : URL address of the Gitlab server
- gitlab_private_token : A private access token (private token) for accessing the Gitlab API
- openai_api_key : The key used to access OpenAI's API
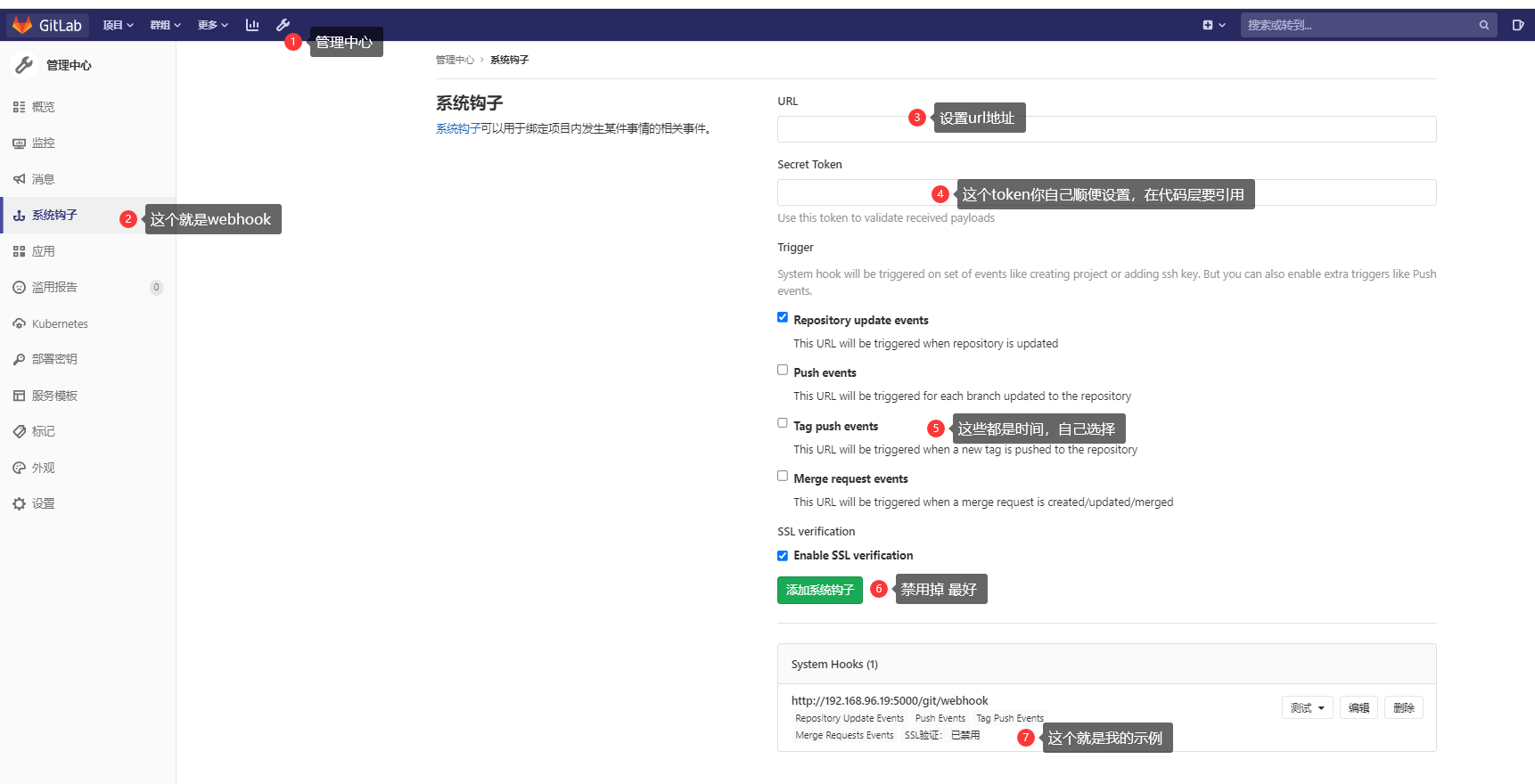
GitLab's Webhook is an event notification mechanism that allows you to configure a URL address within GitLab. When specific events occur, GitLab sends an HTTP request to that URL, transmitting the relevant event data to your application. This enables your application to perform custom operations or responses based on the received event data.
Webhooks can be utilized to monitor and respond to various events within GitLab, such as code commits, merge requests, tag creation, branch operations, and more. By leveraging Webhooks, you can implement a wide range of automation tasks, integrations, and Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) workflows.
The following are the key features and uses of GitLab's Webhook:
- Event Trigger: When you configure and enable a Webhook in GitLab, it automatically triggers when specific events occur, such as code commits or merge requests.
- HTTP Requests: Once an event is triggered, GitLab sends an HTTP request to the URL you have configured in advance. This request contains the relevant event data, typically in JSON format. The most common method used is the POST request.
- Custom Operations: By writing a script or service that receives Webhook requests, you can parse and handle the received event data, allowing you to execute custom operations. Examples include automated builds, automated testing, and automated deployment.
- Integration with other services: Webhooks enable GitLab to integrate with other services and tools. For instance, you can automatically sync code with a Continuous Integration (CI) platform, send notifications to team members, or update a task tracking system.
- Configurability: GitLab's Webhook provides extensive configuration options. You can choose the types of events to monitor, set trigger conditions, and define the content and format of the request.
Request URL: POST http://192.168.96.19:5000/git/webhook 200
Trigger: Push Hook
Elapsed time: 0.01 sec
Request time: 刚刚
Content-Type: application/jsonX-Gitlab-Event: Push HookX-Gitlab-Token: asdhiqbryuwfqodwgeayrgfbsifbd
{
"object_kind": "push",
"event_name": "push",
"before": "95790bf891e76fee5e1747ab589903a6a1f80f22",
"after": "da1560886d4f094c3e6c9ef40349f7d38b5d27d7",
"ref": "refs/heads/master",
"checkout_sha": "da1560886d4f094c3e6c9ef40349f7d38b5d27d7",
"message": "Hello World",
"user_id": 4,
"user_name": "John Smith",
"user_email": "john@example.com",
"user_avatar": "https://s.gravatar.com/avatar/d4c74594d841139328695756648b6bd6?s=8://s.gravatar.com/avatar/d4c74594d841139328695756648b6bd6?s=80",
"project_id": 15,
"project": {
"id": 15,
"name": "gitlab",
"description": "",
"web_url": "http://test.example.com/gitlab/gitlab",
"avatar_url": "https://s.gravatar.com/avatar/d4c74594d841139328695756648b6bd6?s=8://s.gravatar.com/avatar/d4c74594d841139328695756648b6bd6?s=80",
"git_ssh_url": "git@test.example.com:gitlab/gitlab.git",
"git_http_url": "http://test.example.com/gitlab/gitlab.git",
"namespace": "gitlab",
"visibility_level": 0,
"path_with_namespace": "gitlab/gitlab",
"default_branch": "master"
},
"commits": [
{
"id": "c5feabde2d8cd023215af4d2ceeb7a64839fc428",
"message": "Add simple search to projects in public area",
"timestamp": "2013-05-13T18:18:08+00:00",
"url": "https://test.example.com/gitlab/gitlab/-/commit/c5feabde2d8cd023215af4d2ceeb7a64839fc428",
"author": {
"name": "Test User",
"email": "test@example.com"
}
}
],
"total_commits_count": 1,
"push_options": {
"ci": {
"skip": true
}
}
}
Server: Werkzeug/2.3.6 Python/3.8.0Date: Tue, 18 Jul 2023 03:39:51 GMTContent-Type: application/jsonContent-Length: 26Connection: close
{
"status": "success"
}
git clone https://github.com/nangongchengfeng/chat-review.gitpython deal_package.pyconfig/config.py
"""
这个文件是用来从apollo配置中心获取配置的,
如果没有apollo配置中心,可以直接在这里配置
"""
WEBHOOK_VERIFY_TOKEN = "asdhiqbryuwfqodwgeayrgfbsifbd"
gitlab_server_url = gitlab_server_url
gitlab_private_token = gitlab_private_token
openai_api_key = openai_api_key简单
nohup python3 app.py & http://192.168.96.19:5000/git/webhook
The IP address of the running machine can be changed, and the domain name can also be changed.
http://gitlab.ownit.top/git/webhook 1、Pass all the contents of the acquired diff to chatgpt for processing (including adding lines and deleting lines)
Advantages: Convenient and fast.
Disadvantages: If the content is too long, it may cause issues with ChatGPT's processing, resulting in partial code and potentially incoherent logic
2、The processing of obtaining the diff content involves removing deleted lines and the "+" symbol.
Advantages: It is convenient, fast, and saves a considerable amount of space.
Disadvantages: If the content is too lengthy, it may lead to ChatGPT's processing failure, resulting in only a partial code and fragmented logic.
def filter_diff_content(diff_content):
filtered_content = re.sub(r'(^-.*\n)|(^@@.*\n)', '', diff_content, flags=re.MULTILINE)
processed_code = '\n'.join([line[1:] if line.startswith('+') else line for line in filtered_content.split('\n')])
return processed_code3、 Process the content of the diff, remove deleted lines and the '+' symbol, retrieve the modified original file, and use JavaParser for parsing. Obtain the corresponding code blocks and upload them for review.
Advantages: Saves space, provides completed methods, and slightly improves the logic.
Disadvantages: Very cumbersome and tedious, only supports Java.
[{
'code': 'xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx',
'name': 'SettlementDetailController'
}, {
'code': 'xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx',
'name': 'queryRecord'
}, {
'code': 'xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx',
'name': 'populateBatchItemVO'
}]Thanks to anc95 小安大佬 for the support and inspiration of the project https://github.com/anc95/ChatGPT-CodeReview.git